Abstract
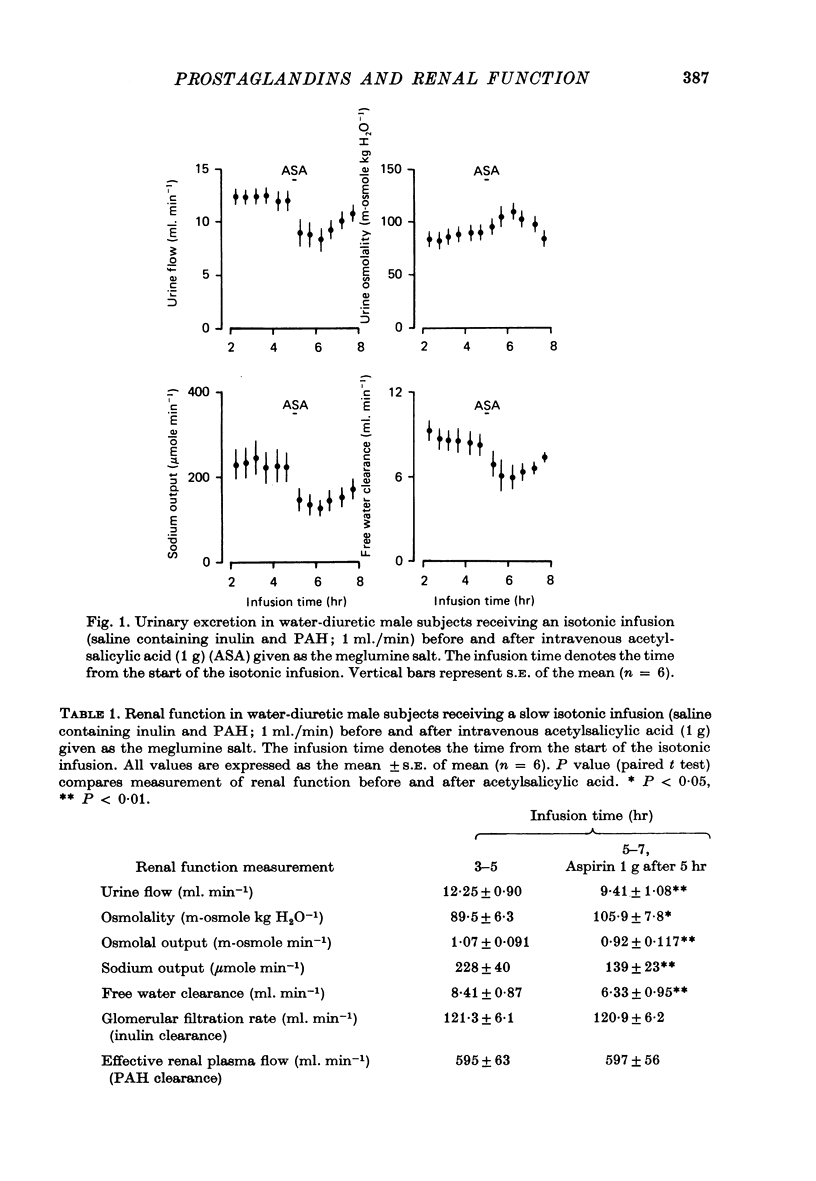
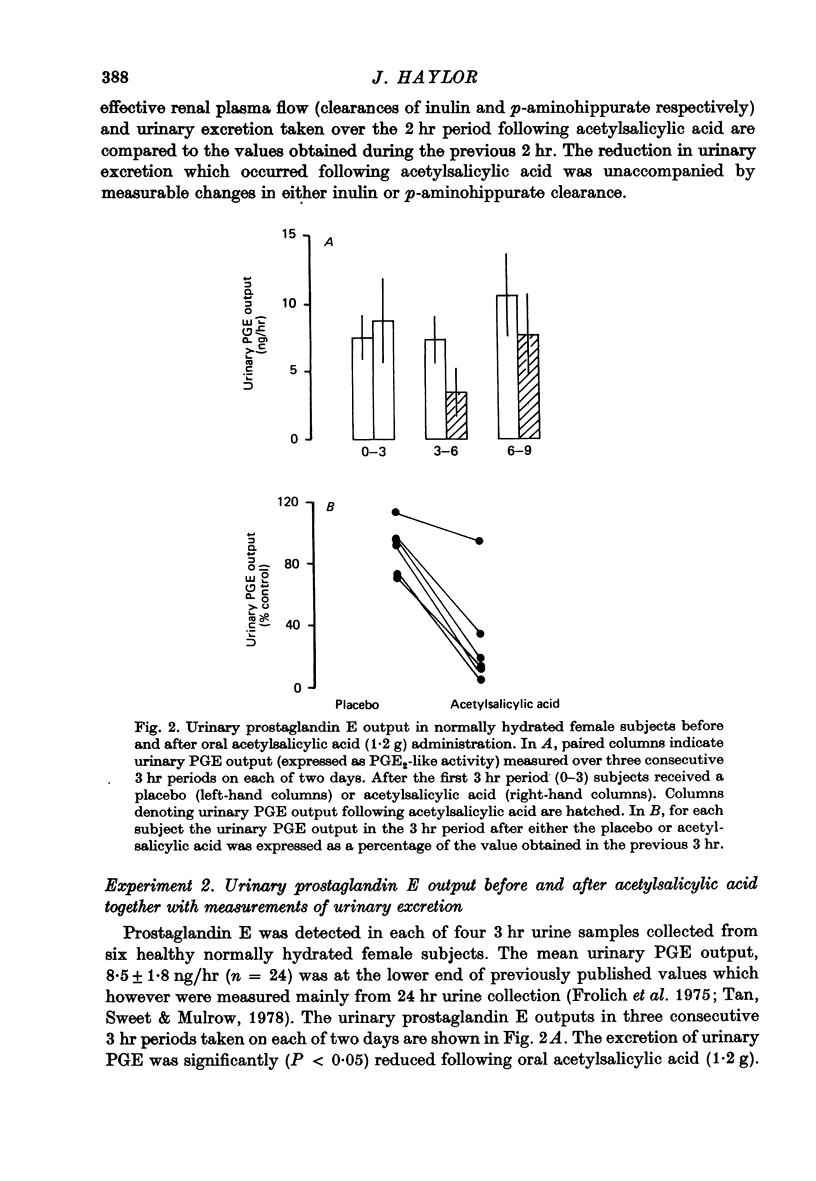
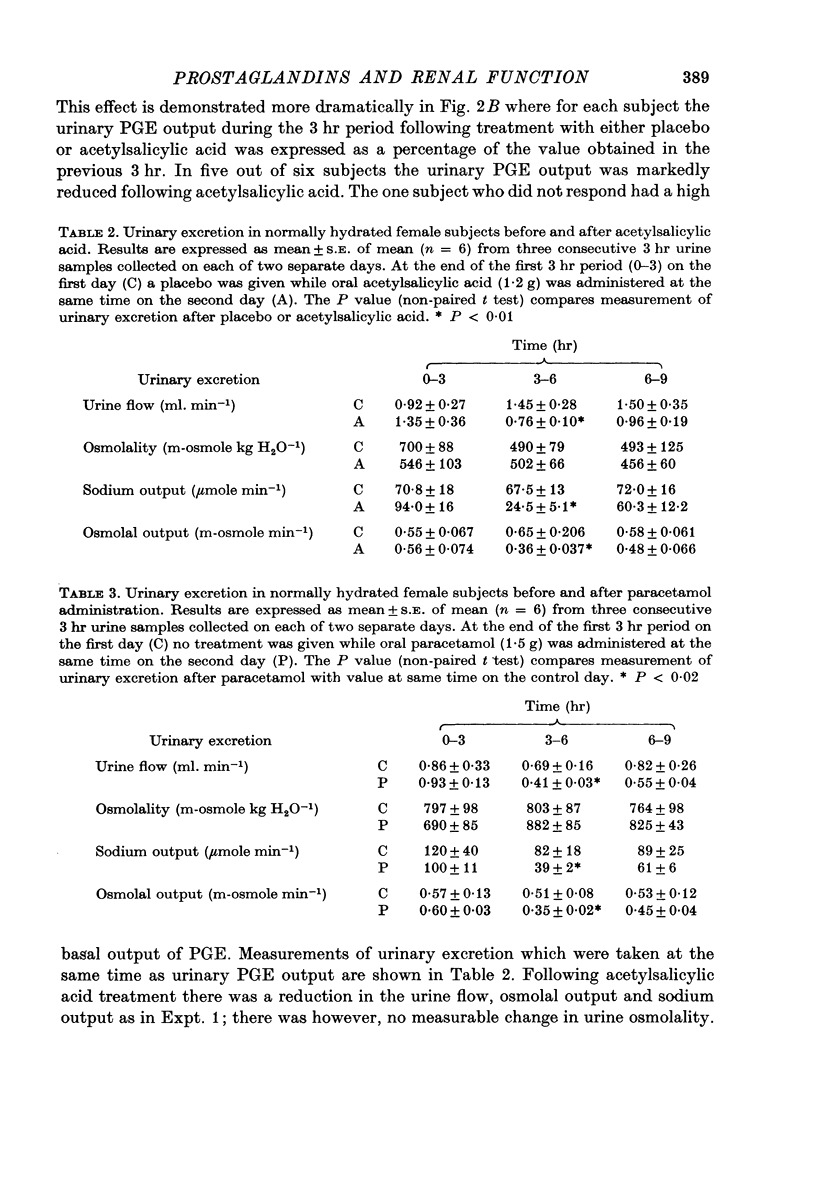
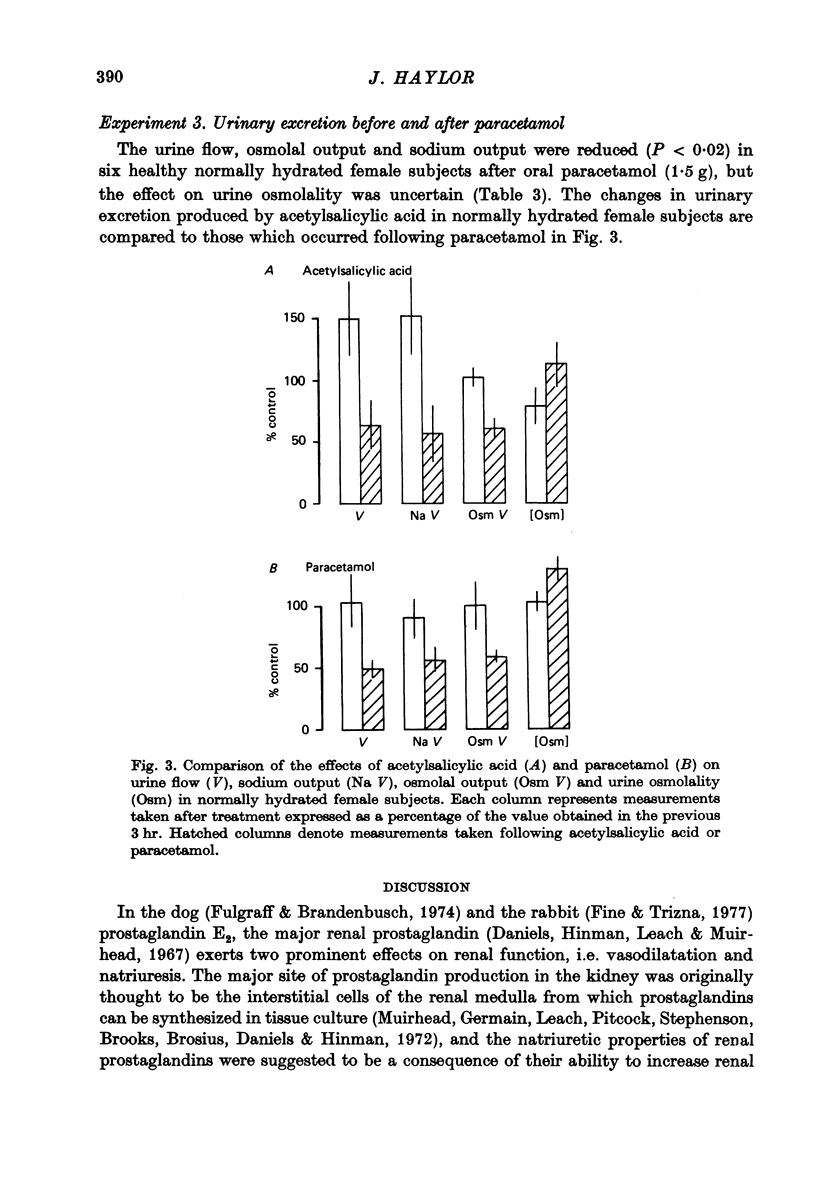
1. Experiments were performed to determine the changes in renal function which occur following prostaglandin synthetase inhibition in healthy conscious humans. It was hoped that such experiments could provide information on the mechanism by which renal prostaglandin synthesis influences urinary excretion. 2. In water-diuretic male subjects (receiving a slow saline infusion) the renal excretion of sodium and water was reduced following I.V. acetylsalicylic acid (1 g) administration, while the effective renal plasma flow (p-aminohippurate clearance), and glomerular filtration rate (inulin clearance) remained unaltered. 3. In normally hydrated female subjects on an unrestricted diet, the mean urinary prostaglandin E output was 8.5 ng/hr. The renal excretion of sodium, water and urinary prostaglandin E were significantly reduced (P less than 0.05) following oral acetylsalicylic acid (1.2 g) administration. 4. In normally hydrated female subjects on an unrestricted diet the renal excretion of sodium and water was reduced following oral paracetamol (1.5 g) administration. 5. It is concluded that following renal prostaglandin synthetase inhibition in conscious humans, the excretion of sodium and water can be reduced without measurable changes in the glomerular filtration rate or effective renal plasma flow. It is suggested that in conscious healthy humans, the kidney may continually synthesize prostaglandin which might help to maintain sodium and water excretion by a direct action on the renal tubule without influencing renal blood flow. The relevance of this hypothesis to the intrarenal location of prostaglandin synthetase is discussed.
Full text
PDF









Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson R. J., Berl T., McDonald K. M., Schrier R. W. Prostaglandins: effects on blood pressure, renal blood flow, sodium and water excretion. Kidney Int. 1976 Sep;10(3):205–215. doi: 10.1038/ki.1976.99. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOJESEN E. A method for determination of inulin in plasma and urine. Acta Med Scand Suppl. 1952;266:275–282. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1952.tb13376.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beeley L., Kendall M. J. Effect of aspirin on renal clearance of 125I-diatrizoate. Br Med J. 1971 Mar 27;1(5751):707–708. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5751.707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg K. J. Acute effects of acetylsalicylic acid on renal function in normal man. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1977 Jan 3;11(2):117–123. doi: 10.1007/BF00562902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg K. J., Bergan A. Effects of different doses of acetylsalicylic acid on renal oxygen consumption. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1977 May;37(3):235–241. doi: 10.3109/00365517709091488. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berl T., Raz A., Wald H., Horowitz J., Czaczkes W. Prostaglandin synthesis inhibition and the action of vasopressin: studies in man and rat. Am J Physiol. 1977 Jun;232(6):F529–F537. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1977.232.6.F529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwell G. J., Flower R. J., Vane J. R. Some characteristics of the prostaglandin synthesizing system in rabbit kidney microsomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Jul 22;398(1):178–190. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(75)90181-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohman S. O. Demonstration of prostaglandin synthesis in collecting duct cells and other cell types of the rabbit renal medulla. Prostaglandins. 1977 Oct;14(4):729–744. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(77)90201-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burry H. C., Dieppe P. A. Apparent reduction of endogenous creatinine clearance by salicylate treatment. Br Med J. 1976 Jul 3;2(6026):16–17. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6026.16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bygdeman M., Samuelsson B. Analyses of prostaglandins in human semen. Prostaglandins and related factors 44. Clin Chim Acta. 1966 Apr;13(4):465–474. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(66)90238-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carr A. A. Hemodynamic and renal effects of a prostaglandin, PGA 1, in subjects with essential hypertension. Am J Med Sci. 1970 Jan;259(1):21–26. doi: 10.1097/00000441-197001000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavallo T. Cytochemical localization of endogenous peroxidase activity in renal medullary collecting tubules and papillary mucosa of the rat. Lab Invest. 1976 Mar;34(3):223–228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniels E. G., Hinman J. W., Leach B. E., Muirhead E. E. Identification of prostaglandin E2 as the principal vasodepressor lipid of rabbit renal medulla. Nature. 1967 Sep 16;215(5107):1298–1299. doi: 10.1038/2151298a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donker A. J., Arisz L., Brentjens J. R., van der Hem G. K., Hollemans H. J. The effect of indomethacin on kidney function and plasma renin activity in man. Nephron. 1976;17(4):288–296. doi: 10.1159/000180733. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Düsing R., Melder B., Kramer H. J. Prostaglandins and renal function in acute extracellular volume expansion. Prostaglandins. 1976 Jul;12(1):3–10. doi: 10.1016/s0090-6980(76)80002-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELLIOTT H. C., Jr, MURDAUGH H. V., Jr Effects of acetylsalicylic acid on excretion of endogenous metabolites by man. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1962 Feb;109:333–335. doi: 10.3181/00379727-109-27193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fine L. G., Trizna W. Influence of prostaglandins on sodium transport of isolated medullary nephron segments. Am J Physiol. 1977 Apr;232(4):F383–F390. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1977.232.4.F383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flower R. J. Drugs which inhibit prostaglandin biosynthesis. Pharmacol Rev. 1974 Mar;26(1):33–67. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frölich J. C., Wilson T. W., Sweetman B. J., Smigel M., Nies A. S., Carr K., Watson J. T., Oates J. A. Urinary prostaglandins. Identification and origin. J Clin Invest. 1975 Apr;55(4):763–770. doi: 10.1172/JCI107987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fülgraff G., Brandenbusch G. Comparison of the effects of the prostaglandins A1, E2, and F2alpha on kidney function in dogs. Pflugers Arch. 1974 May 24;349(1):9–17. doi: 10.1007/BF00587912. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill J. R., Jr, Frölich J. C., Bowden R. E., Taylor A. A., Keiser H. R., Seyberth H. W., Oates J. A., Bartter F. C. Bartter's syndrome: a disorder characterized by high urinary prostaglandins and a dependence of hyperreninemia on prostaglandin synthesis. Am J Med. 1976 Jul;61(1):43–51. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(76)90029-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grantham J. J., Orloff J. Effect of prostaglandin E1 on the permeability response of the isolated collecting tubule to vasopressin, adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate, and theophylline. J Clin Invest. 1968 May;47(5):1154–1161. doi: 10.1172/JCI105804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haylor J., Lote C. J. Further evidence for a physiological role of endogenous prostaglandin biosynthesis in the regulation of frog skin permeability [proceedings]. J Physiol. 1977 Mar;266(1):41P–42P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haylor J., Lote C. J. Proceedings: The role of endogenous prostaglandin synthesis in the maintenance of frog skin permeability. J Physiol. 1976 May;257(1):50P–51P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haylor J., Lote C. J. Renal function in conscious rats after indomethacin. Evidence for a tubular action of endogenous prostaglandins. J Physiol. 1980 Jan;298:371–381. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janszen F. H., Nugteren D. H. Histochemical localisation of prostaglandin synthetase. Histochemie. 1971;27(2):159–164. doi: 10.1007/BF00284957. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimberly R. P., Gill J. R., Jr, Bowden R. E., Keiser H. R., Plotz P. H. Elevated urinary prostaglandins and the effects of aspirin on renal function in lupus erythematosus. Ann Intern Med. 1978 Sep;89(3):336–341. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-89-3-336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsson C., Anggård E. Mass spectrometric determination of prostaglandin E2, F2alpha and A2 in the cortex and medulla of the rabbit kidney. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1976 Apr;28(4):326–328. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1976.tb04169.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsson C., Anggård E. Regional differences in the formation and metabolism of prostaglandins in the rabbit kidney. Eur J Pharmacol. 1973 Jan;21(1):30–36. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(73)90202-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MEIERS H. G., WETZELS E. PHENYLBUTAZON UND NIERENFUNKTIONEN. Arzneimittelforschung. 1964 Apr;14:252–258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGiff J. C., Itskovitz H. D. Prostaglandins and the kidney. Circ Res. 1973 Nov;33(5):479–488. doi: 10.1161/01.res.33.5.479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison A. R., Nishikawa K., Needleman P. Unmasking of thromboxane A2 synthesis by ureteral obstruction in the rabbit kidney. Nature. 1977 May 19;267(5608):259–260. doi: 10.1038/267259a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mountokalakis T., Karambasis T. Aspirin and renal function. Lancet. 1977 Jul 9;2(8028):88–88. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)90091-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muirhead E. E., Germain G., Leach B. E., Pitcock J. A., Stephenson P., Brooks B., Brosius W. L., Daniels E. G., Hinman J. W. Production of renomedullary prostaglandins by renomedullary interstitial cells grown in tissue culture. Circ Res. 1972 Sep;31(9 Suppl):161–172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papanicolaou N., Safar M., Hornych A., Fontaliran F., Weiss Y., Bariety J., Milliez P. The release of renal prostaglandins during saline infusion in normal and hypertensive subjects. Clin Sci Mol Med. 1975 Nov;49(5):459–463. doi: 10.1042/cs0490459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patak R. V., Mookerjee B. K., Bentzel C. J., Hysert P. E., Babej M., Lee J. B. Antagonism of the effects of furosemide by indomethacin in normal and hypertensive man. Prostaglandins. 1975 Oct;10(4):649–659. doi: 10.1016/s0090-6980(75)80012-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramsay A. G., Elliott H. C. Effect of acetylsalicylic acid on ionic reabsorption in the renal tubule. Am J Physiol. 1967 Aug;213(2):323–327. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1967.213.2.323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remuzzi G., Cavenaghi A. E., Mecca G., Donati M. B., de Gaetano G. Human renal cortex generates prostacyclin-like activity. Thromb Res. 1978 Feb;12(2):363–366. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(78)90307-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roman R. J., Kauker M. L. Renal effect of prostaglandin synthetase inhibition in rats: micropuncture studies. Am J Physiol. 1978 Aug;235(2):F111–F118. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1978.235.2.F111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sirois P., Gagnon D. J. Release of prostaglandins from the rabbit renal medulla. Eur J Pharmacol. 1974 Sep;28(1):18–24. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(74)90107-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. W., Finkelstein N., Aliminosa L., Crawford B., Graber M. THE RENAL CLEARANCES OF SUBSTITUTED HIPPURIC ACID DERIVATIVES AND OTHER AROMATIC ACIDS IN DOG AND MAN. J Clin Invest. 1945 May;24(3):388–404. doi: 10.1172/JCI101618. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith W. L., Bell T. G. Immunohistochemical localization of the prostaglandin-forming cyclooxygenase in renal cortex. Am J Physiol. 1978 Nov;235(5):F451–F457. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1978.235.5.F451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith W. L., Wilkin G. P. Immunochemistry of prostaglandin endoperoxide-forming cyclooxygenases: the detection of the cyclooxygenases in rat, rabbit, and guinea pig kidneys by immunofluorescence. Prostaglandins. 1977 May;13(5):873–892. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(77)90217-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector D., Zusman R. M., Caldwell B. V., Speroff L. The distribution of prostaglandins A, E, and F in the human kidney. Prostaglandins. 1974 May 10;6(3):263–270. doi: 10.1016/s0090-6980(74)80053-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swain J. A., Heyndrickx G. R., Boettcher D. H., Vatner S. F. Prostaglandin control of renal circulation in the unanesthetized dog and baboon. Am J Physiol. 1975 Sep;229(3):826–830. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1975.229.3.826. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan S. Y., Sweet P., Mulrow P. J. Impaired renal production of prostaglandin E2: a newly identified lesion in human essential hypertension. Prostaglandins. 1978 Jan;15(1):139–150. doi: 10.1016/s0090-6980(78)80012-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tweeddale M. G., Ogilvie R. I. Antagonism of spironolactone-induced natriuresis by aspirin in man. N Engl J Med. 1973 Jul 26;289(4):198–200. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197307262890408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VANE J. R. A sensitive method for the assay of 5-hydroxytryptamine. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1957 Sep;12(3):344–349. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1957.tb00146.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whorton A. R., Smigel M., Oates J. A., Frölich J. C. Regional differences in prostacyclin formation by the kidney. Prostacyclin is a major prostaglandin of renal cortex. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Apr 28;529(1):176–180. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(78)90116-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zusman R. M., Keiser H. R. Prostaglandin biosynthesis by rabbit renomedullary interstitial cells in tissue culture. Stimulation by angiotensin II, bradykinin, and arginine vasopressin. J Clin Invest. 1977 Jul;60(1):215–223. doi: 10.1172/JCI108758. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


