Abstract
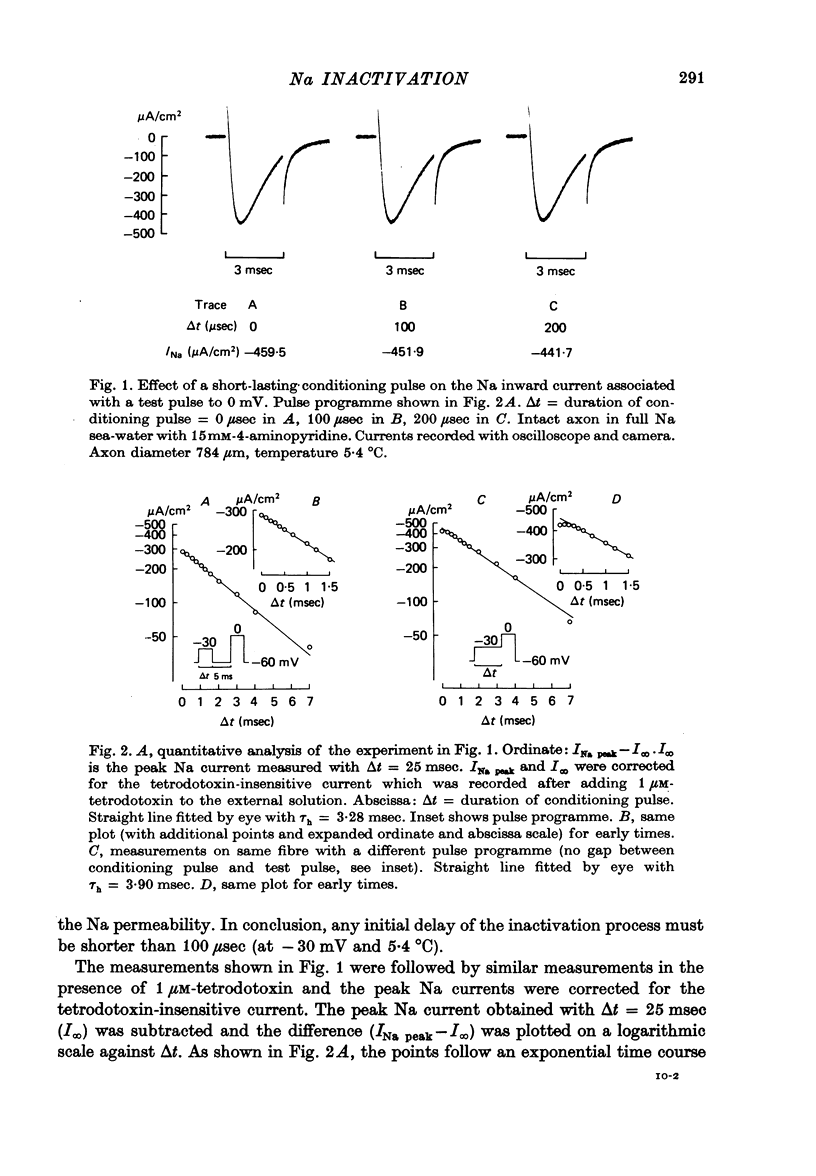
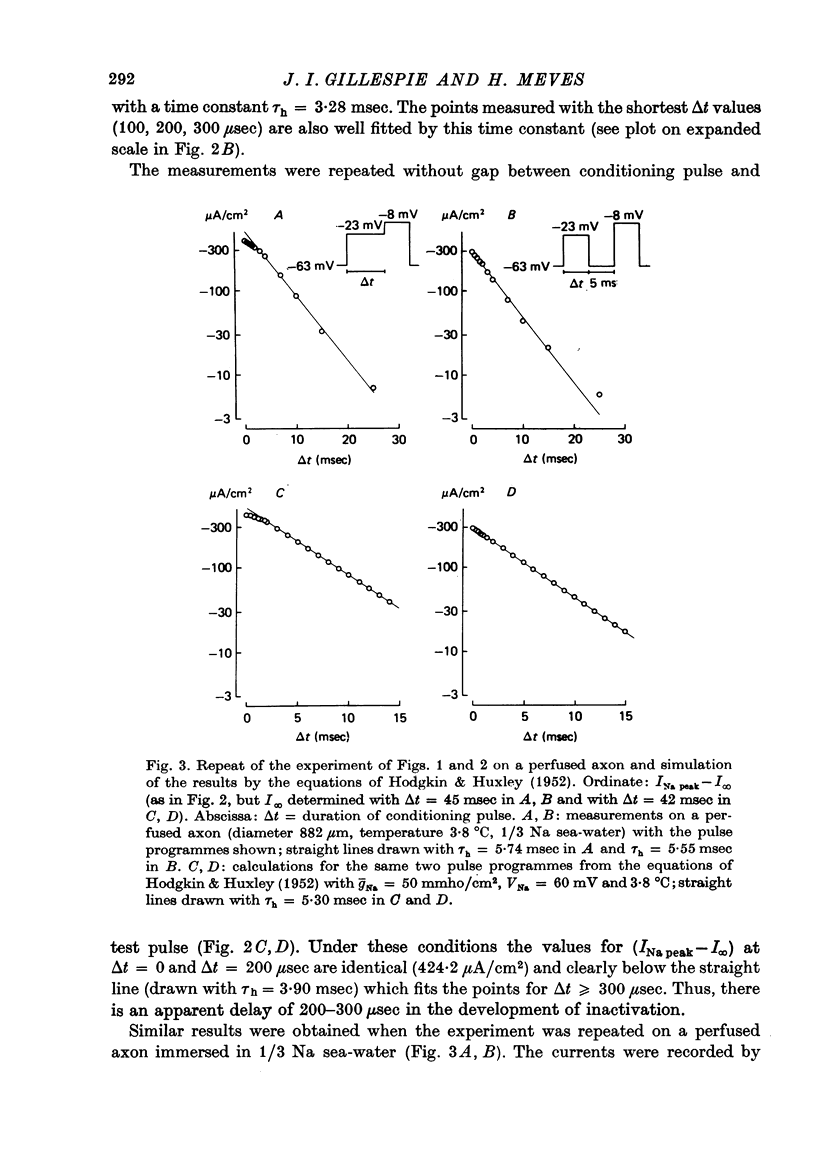
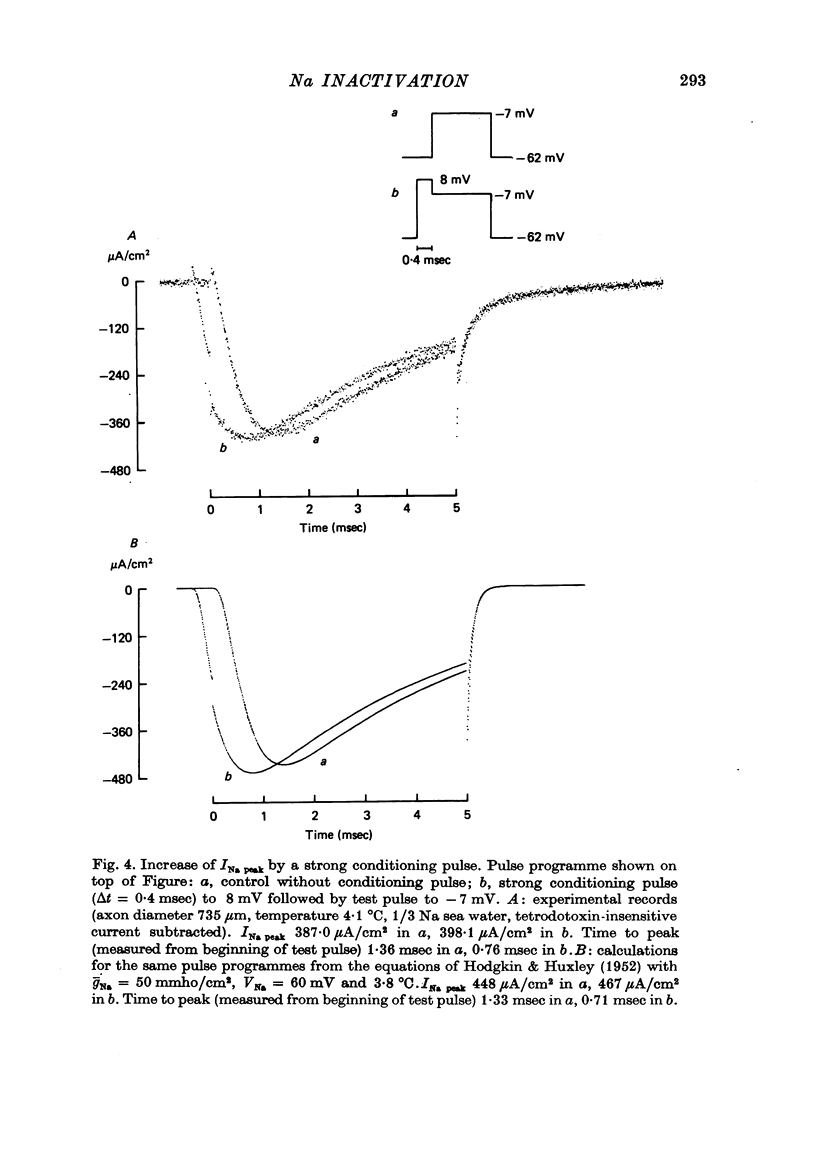
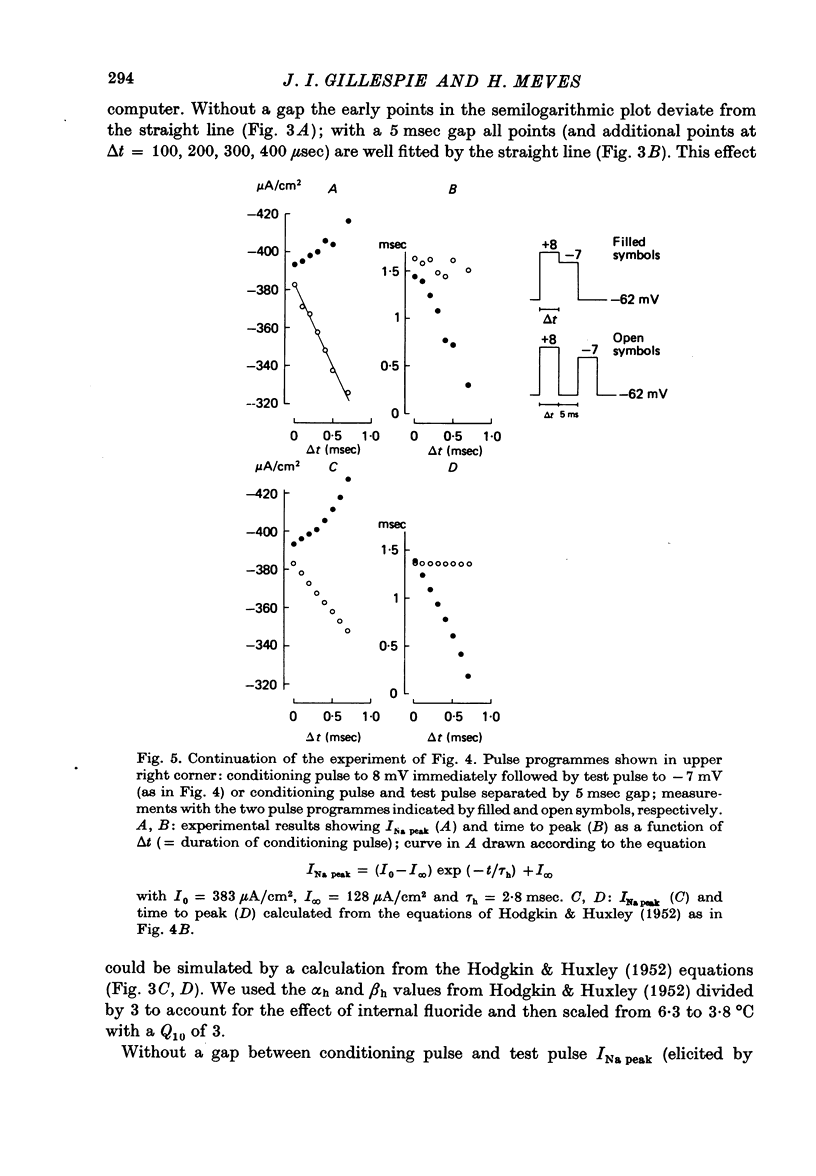
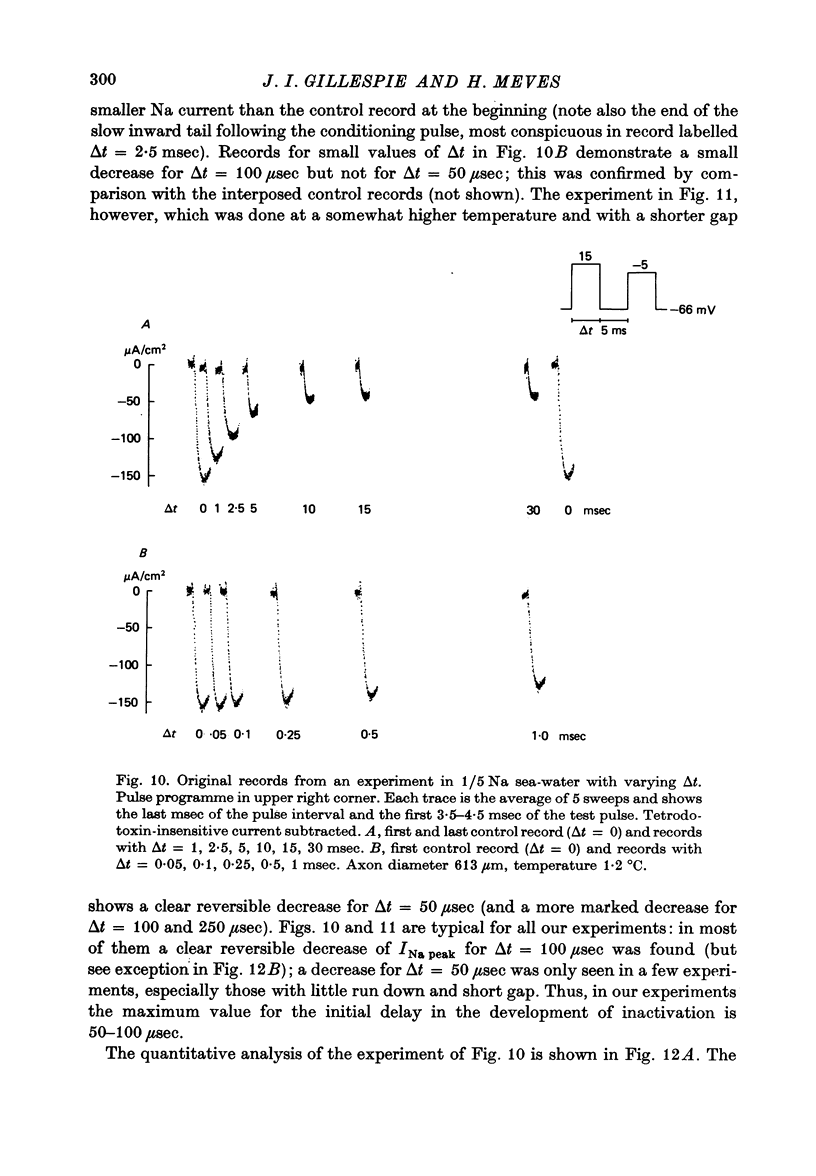
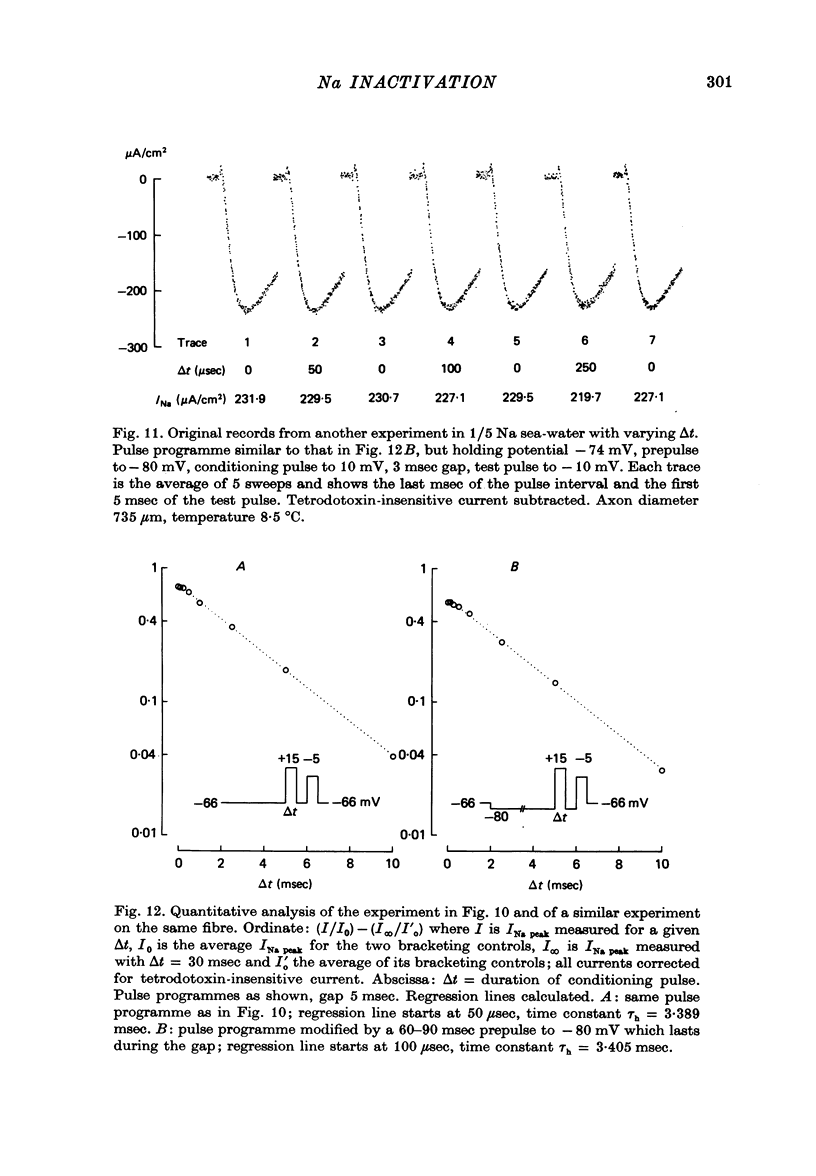
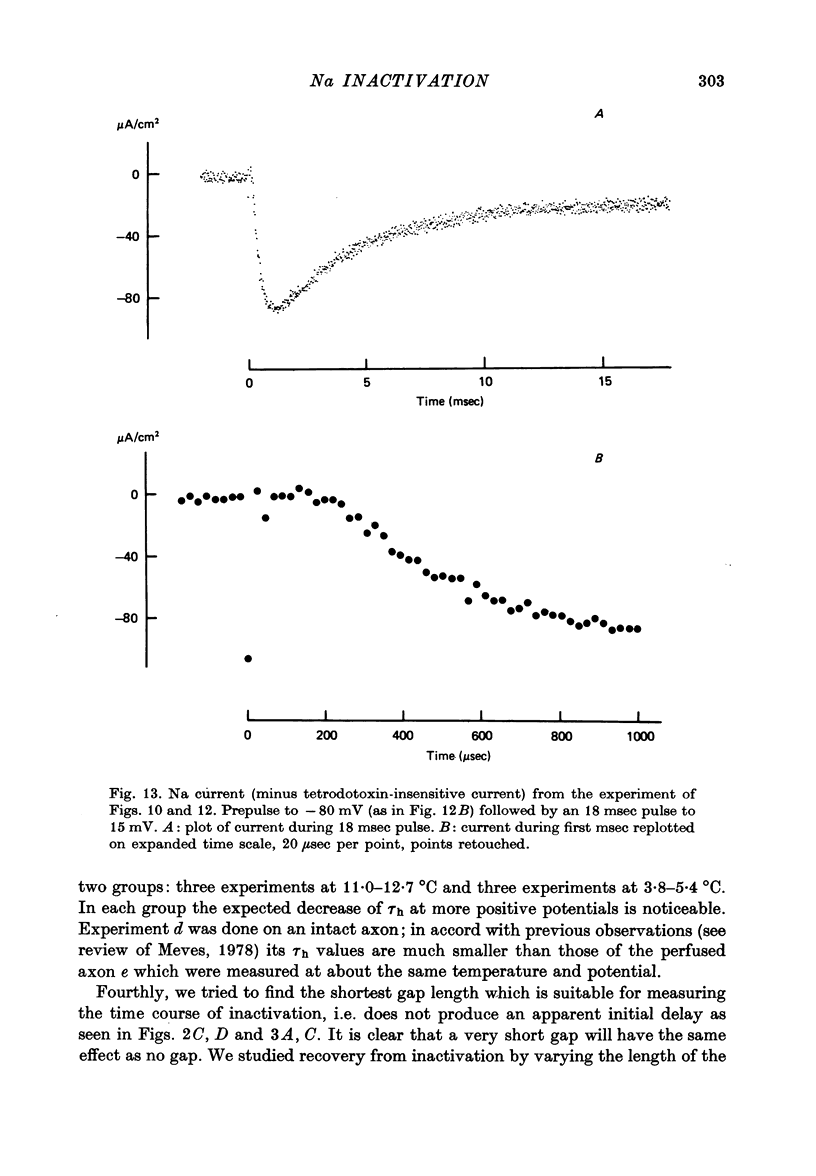
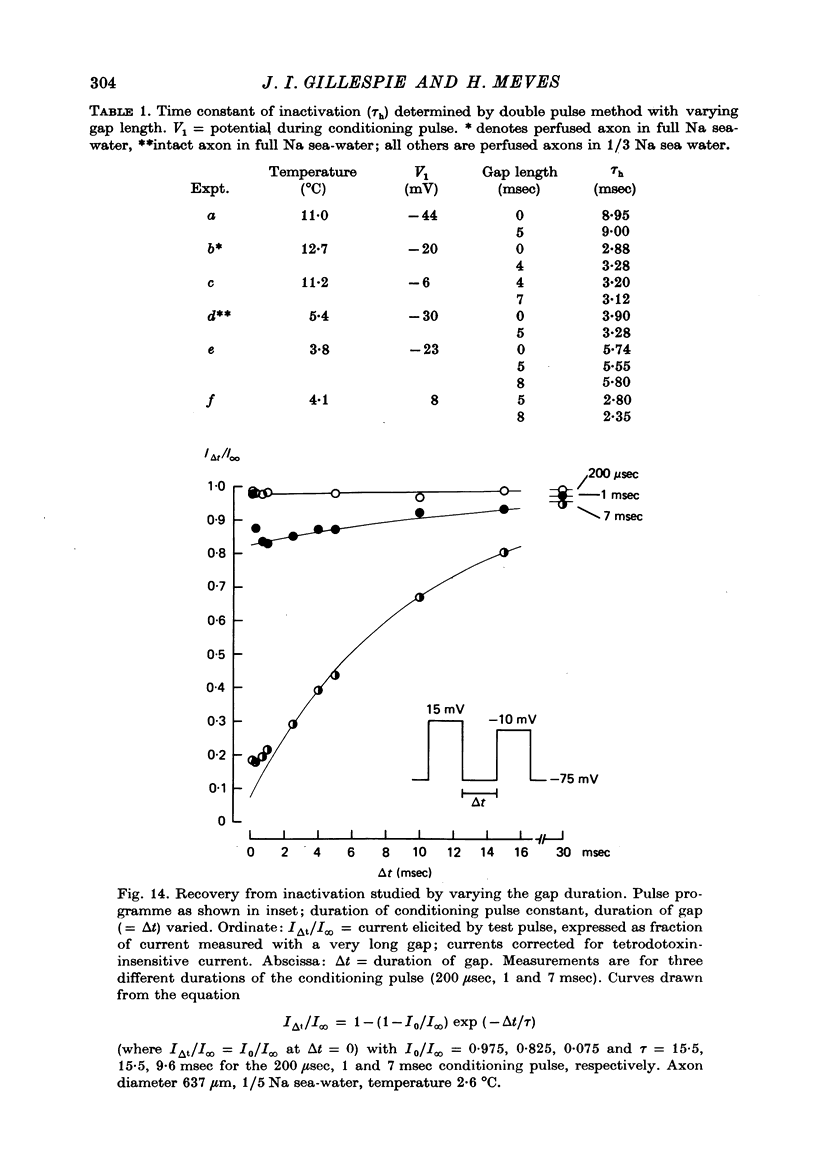
1. The time course of Na inactivation was studied in intact and perfused squid giant axons under voltage-clamp conditions. 2. The pulse programme consisted of a conditioning pulse of varying duration, followed after an interval of 3-8 msec by test pulse. The measurements were done in sea water with 1/3 or 1/5 of the normal Na concentration. In most experiments a 100 microseconds conditioning pulse was sufficient to reduce INa peak elicited by the test pulse. In some experiments even a 50 microseconds conditioning pulse produced a clear reversible decrease of INa peak. We conclude that the upper limit for an initial delay in the development of inactivation is 50-100 microseconds; this applies to temperatures between 0 and 13 degrees C and membrane potentials between -40 and 15 mV. The decrease of INa peak with increasing duration of the conditioning pulse was consistent with an exponential decay starting at 50 or 100 microseconds. 3. With large Na currents in full Na sea water the time course of inactivation became sigmoid. This is attributed to a long-lasting tail of inward current which follows the conditioning pulse and produces a voltage drop across the series resistance. 4. If the conditioning pulse and the test pulse were not separated by an interval, INa peak showed a sigmoid dependence on the duration of the conditioning pulse. This phenomenon is predicted by the equations of Hodgkin & Huxley (1952) as first pointed out by Kniffki, Siemen & Vogel (1978). With sufficiently strong conditioning pulses INa peak could even increase in size.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armstrong C. M. Currents associated with the ionic gating structures in nerve membrane. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1975 Dec 30;264:265–277. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1975.tb31488.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BAKER P. F., HODGKIN A. L., SHAW T. I. Replacement of the axoplasm of giant nerve fibres with artificial solutions. J Physiol. 1962 Nov;164:330–354. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1962.sp007025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bezanilla F., Armstrong C. M. Inactivation of the sodium channel. I. Sodium current experiments. J Gen Physiol. 1977 Nov;70(5):549–566. doi: 10.1085/jgp.70.5.549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bezanilla F., Rojas E., Taylor R. E. Sodium and potassium conductance changes during a membrane action potential. J Physiol. 1970 Dec;211(3):729–751. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler W. K., Hodgkin A. L., Meves H. The effect of changing the internal solution on sodium inactivation and related phenomena in giant axons. J Physiol. 1965 Oct;180(4):821–836. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler W. K., Meves H. Evidence for two types of sodium conductance in axons perfused with sodium fluoride solution. J Physiol. 1970 Dec;211(3):653–678. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler W. K., Meves H. Rate constants associated with changes in sodium conductance in axons perfused with sodium fluoride. J Physiol. 1970 Dec;211(3):679–705. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman L., Hahin R. Initial conditions and the kinetics of the sodium conductance in Myxicola giant axons. II. Relaxation experiments. J Gen Physiol. 1978 Dec;72(6):879–898. doi: 10.1085/jgp.72.6.879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman L., Schauf C. L. Inactivation of the sodium current in Myxicola giant axons. Evidence for coupling to the activation process. J Gen Physiol. 1972 Jun;59(6):659–675. doi: 10.1085/jgp.59.6.659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HUXLEY A. F. A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. J Physiol. 1952 Aug;117(4):500–544. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HUXLEY A. F., KATZ B. Measurement of current-voltage relations in the membrane of the giant axon of Loligo. J Physiol. 1952 Apr;116(4):424–448. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura J. E., Meves H. The effect of temperature on the asymmetrical charge movement in squid giant axons. J Physiol. 1979 Apr;289:479–500. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012748. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kniffki K. D., Siemen D., Vogel W. Delayed development of sodium permeability inactivation in the nodal membrane [proceedings]. J Physiol. 1978 Nov;284:92P–93P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meves H. Inactivation of the sodium permeability in squid giant nerve fibres. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1978;33(2):207–230. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(79)90029-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meves H., Pichon Y. The effect of internal and external 4-aminopyridine on the potassium currents in intracellularly perfused squid giant axons. J Physiol. 1977 Jun;268(2):511–532. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meves H. The effect of zinc on the late displacement current in squid giant axons. J Physiol. 1976 Jan;254(3):787–801. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramón F., Anderson N., Joyner R. W., Moore J. W. Axon voltage-clamp simulations. A multicellular preparation. Biophys J. 1975 Jan;15(1):55–69. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(75)85791-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAYLOR R. E., MOORE J. W., COLE K. S. Analysis of certain errors in squid axon voltage clamp measurements. Biophys J. 1960 Nov;1:161–202. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3495(60)86882-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeh J. Z., Oxford G. S., Wu C. H., Narahashi T. Dynamics of aminopyridine block of potassium channels in squid axon membrane. J Gen Physiol. 1976 Nov;68(5):519–535. doi: 10.1085/jgp.68.5.519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


