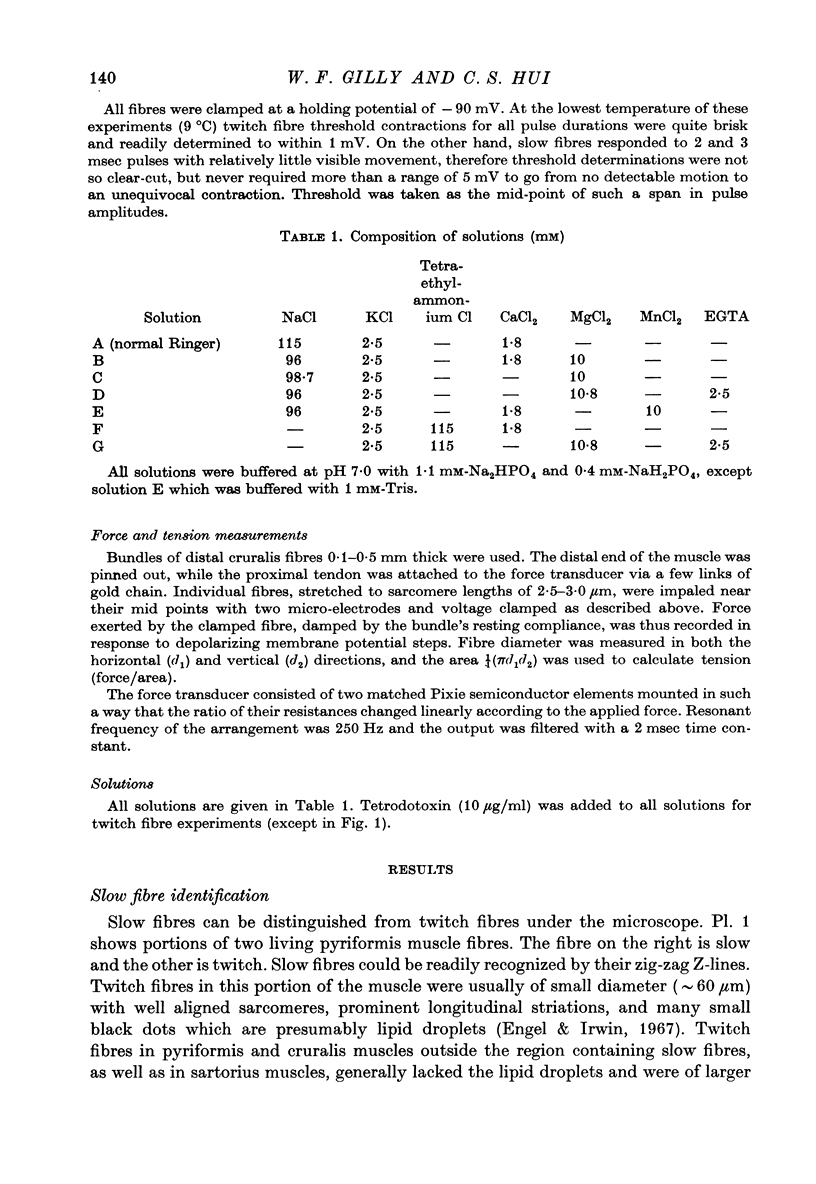
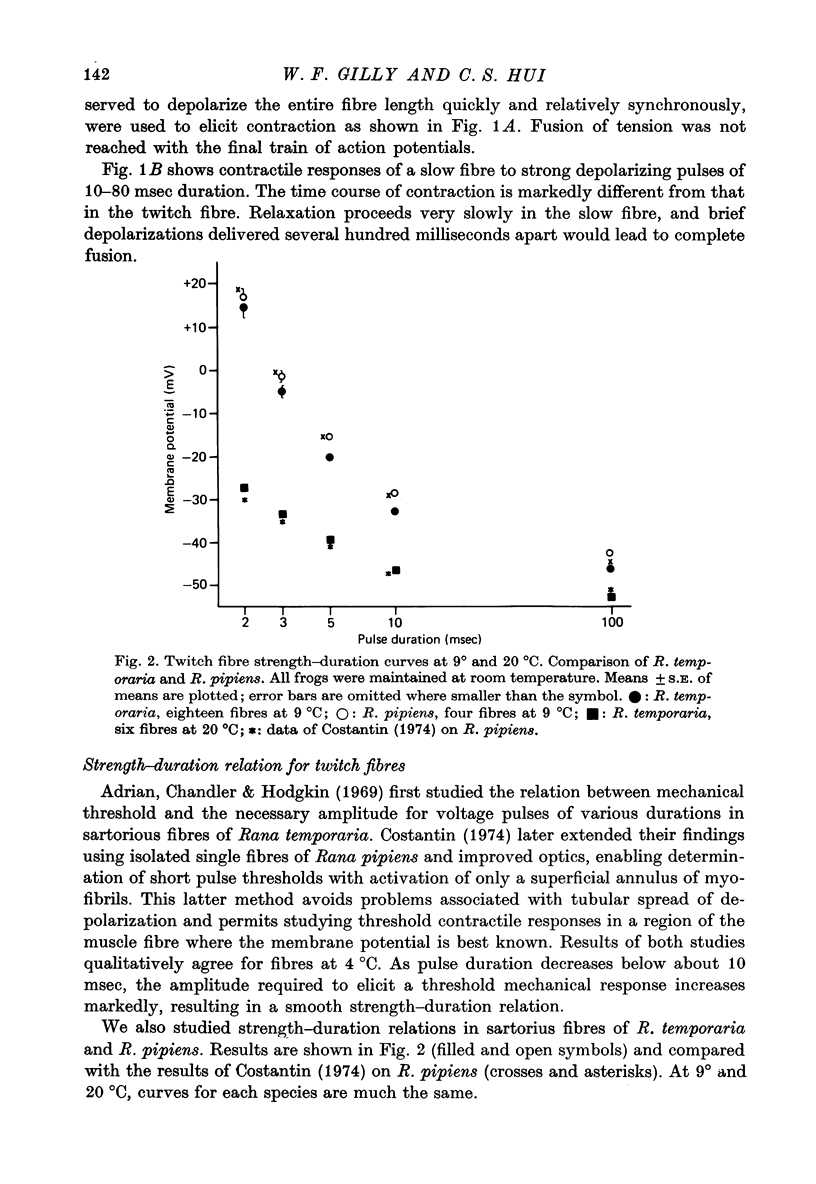
Abstract
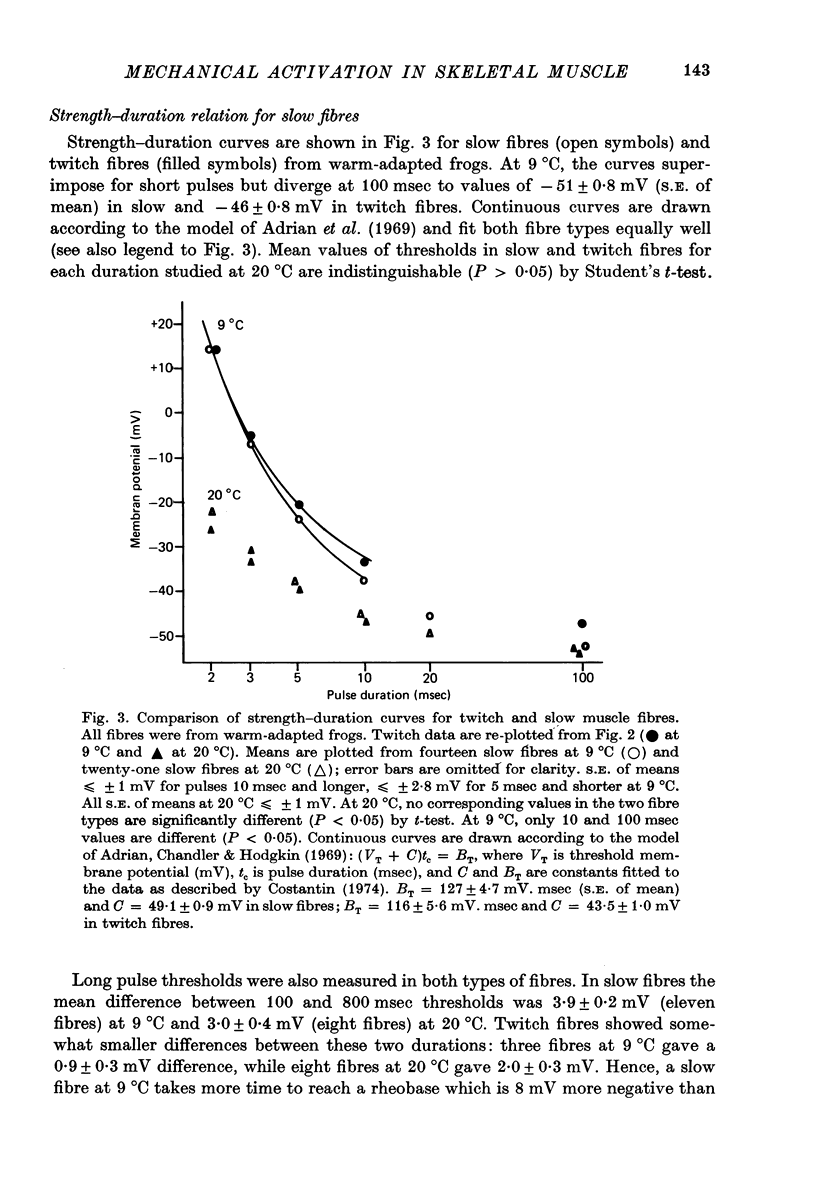
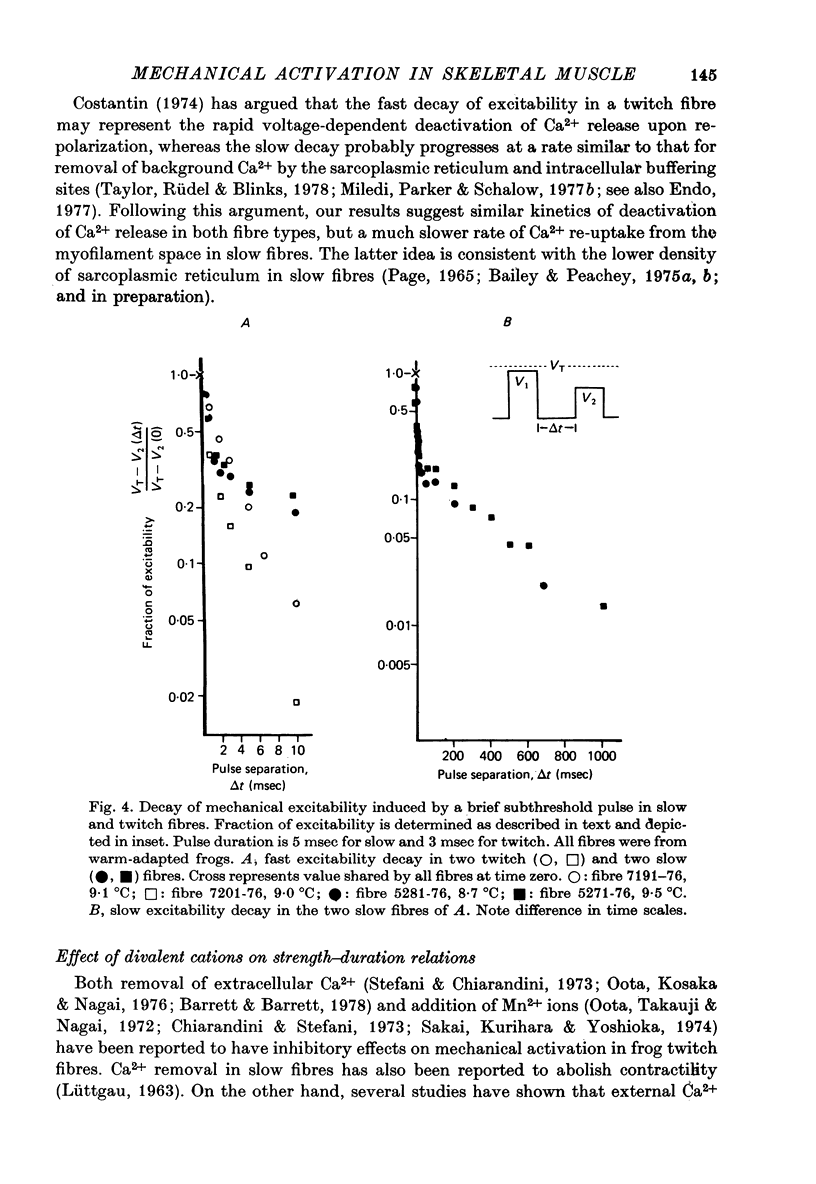
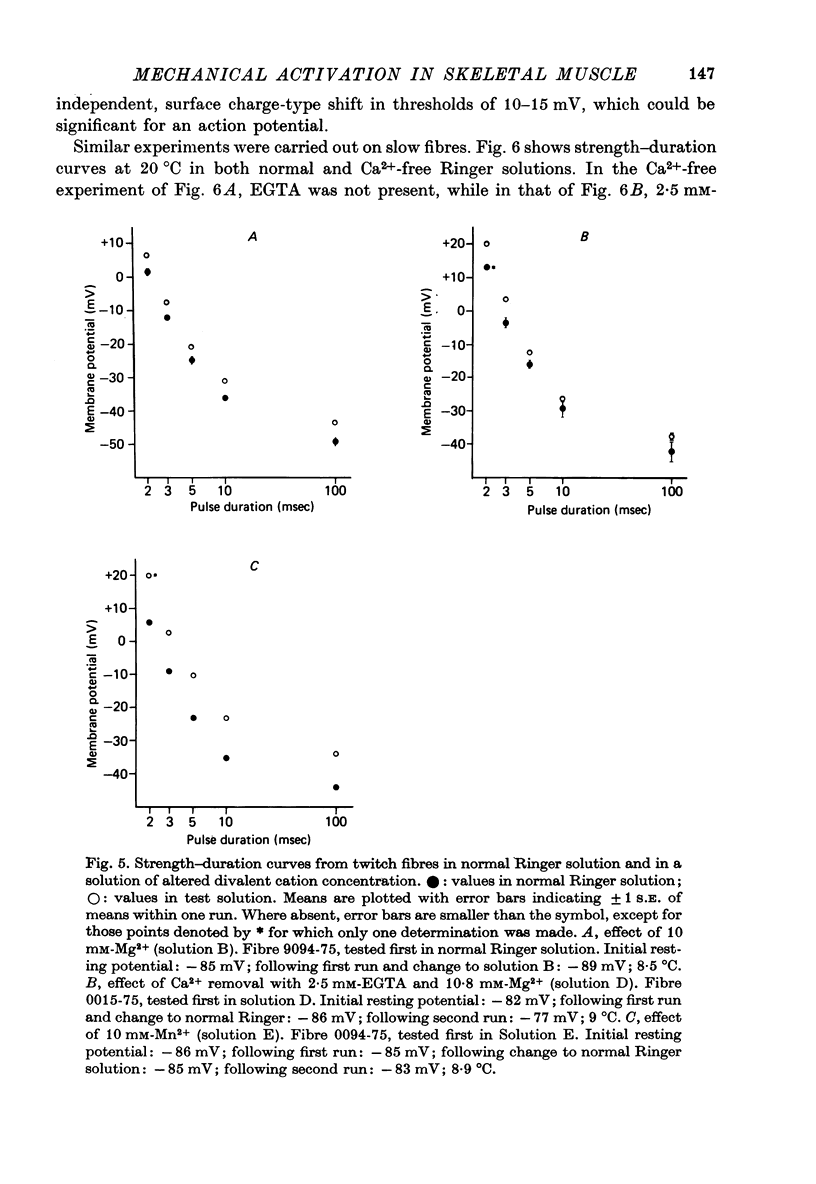
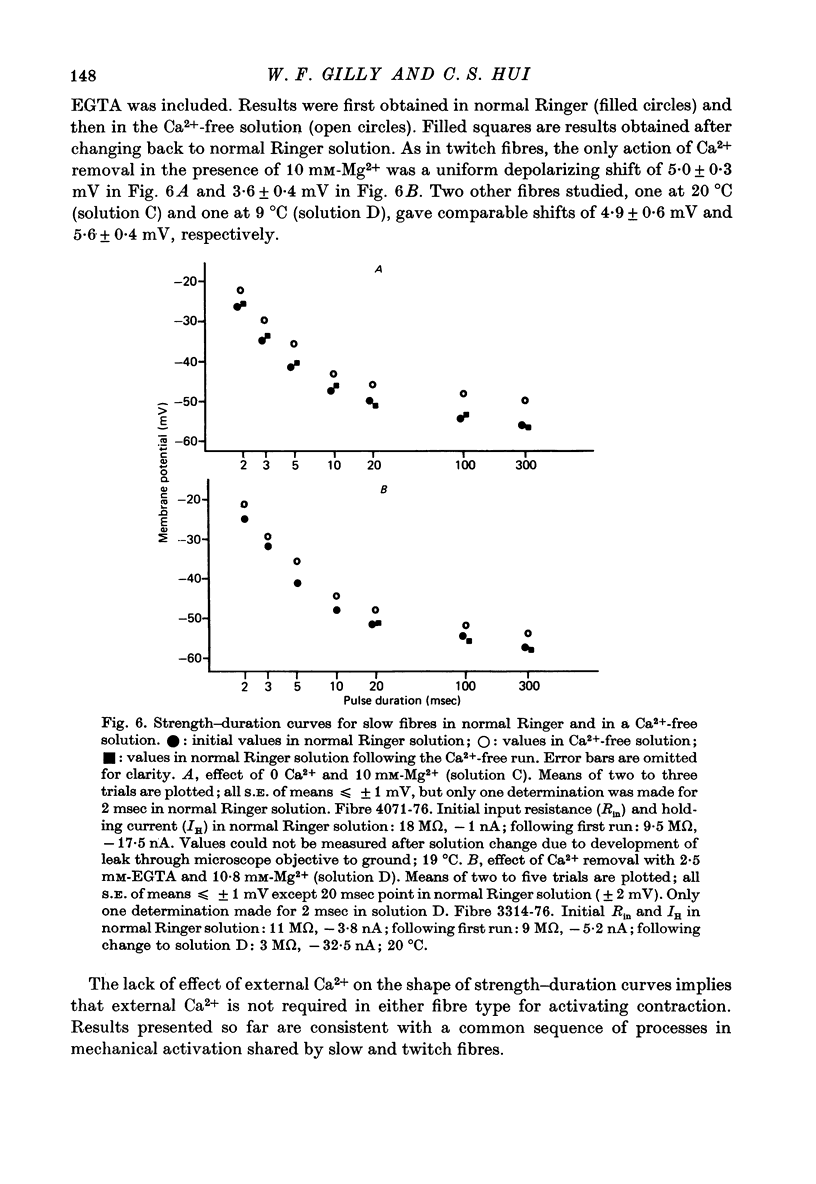
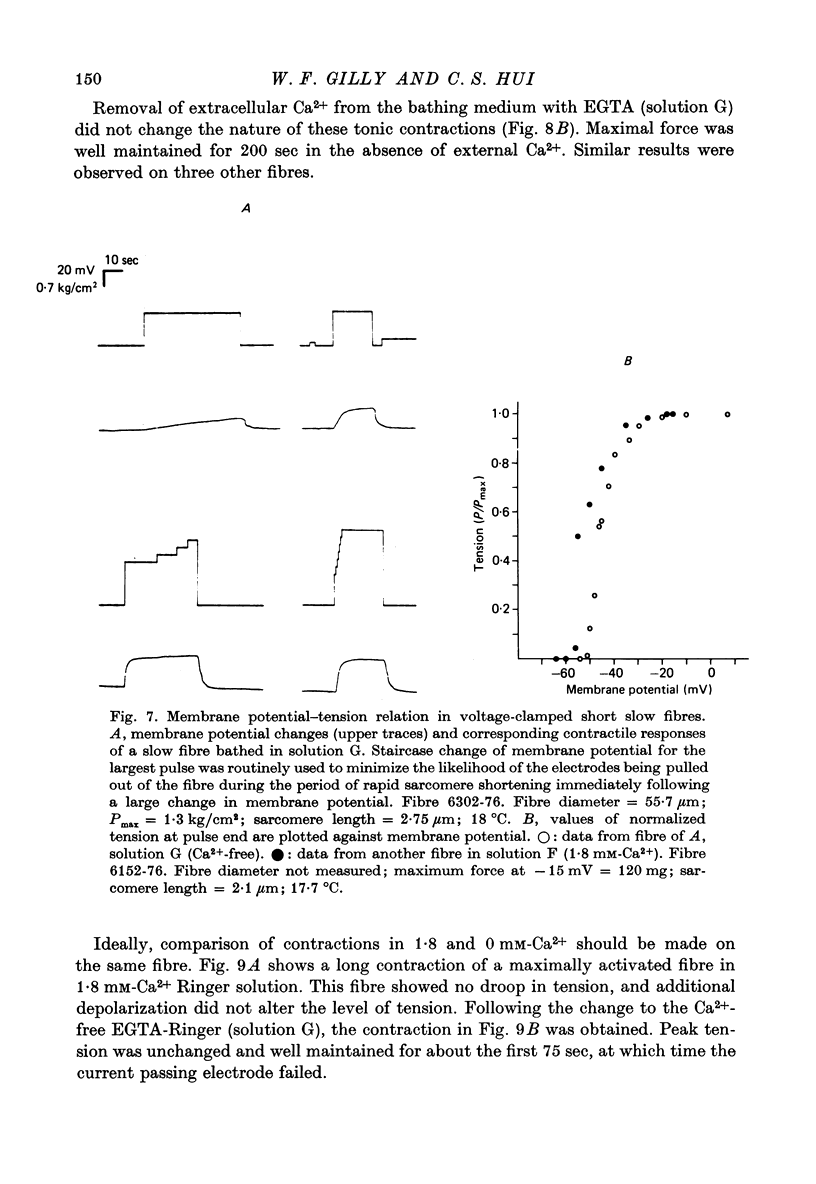
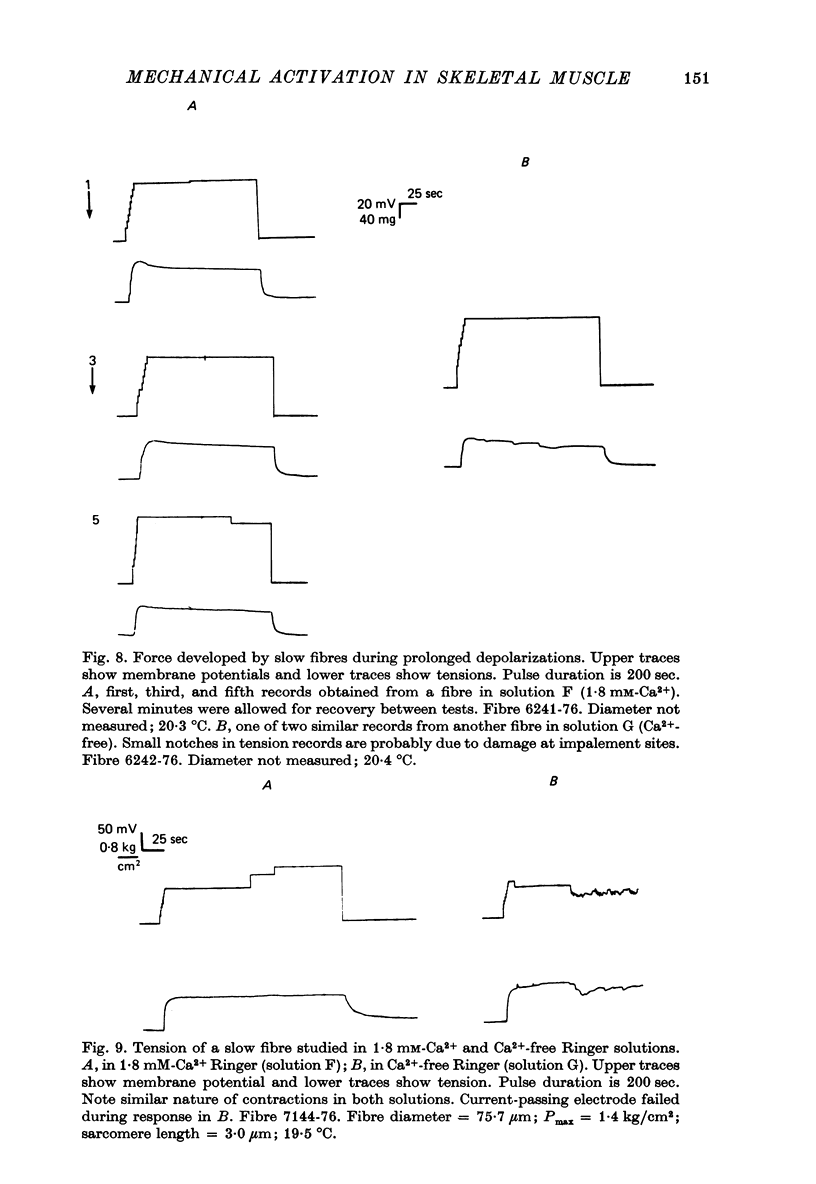
1. Slow and twitch muscle fibres of the frog were studied with a two-micro-electrode point voltage-clamp method. Slow fibres were identified in pyriformis and cruralis muscles by their appearance in the light microscope, electrical characteristics, and rate of sarcomere shortening or of tension development. 2. The relation between the amplitude and duration of threshold depolarizing pulses was determined in sartorius twitch and pyriformis slow fibres. Strength-duration relations for contractile activation are very similar in the two fibre types. 3. The effect of a brief subthreshold pulse on the threshold voltage level decays with a half-time of 1-2 msec at 9 degrees C in both slow and twitch fibres. This fast decay, thought to reflect voltage-dependent deactivation of Ca2+ release following repolarization, is followed by a slower decay of greatly different rates in the two fibre types. the slower components of decay might reflect the rate of background Ca2+ removal by the sarcoplasmic reticulum. 4. Reducing external Ca2+ levels to about about 0.1 microM with 2.5 mM-EGTA has no effect on the shapes of strength-duration curves for both slow and twitch fibres, suggesting that activator Ca2+ in both fibre types originates entirely from intracellular stores. 5. "Tonic' contractions were studied using voltage-clamped short cruralis slow fibres at 20 degrees C. Reducing external Ca2+ to about 0.1 microM had no effect on the steepness of the steady-state tension-voltage relation or on the ability of slow fibres to maintain maximal tension during long (200 sec) depolarizations to membrane potentials of up to +50 mV. 6. Functional similarities in activation kinetics of slow and twitch fibres are discussed in relation to the sensing of tubular membrane potential by the sarcoplasmic reticulum, to Ca2+ release from it, and to possible mechanisms involved in these processes. Processes leading to the rapid turning on and off of Ca2+ release in response to changes in tubular membrane potential are probably similar in slow and twitch fibres. However, the apparent lack of voltage-and time-dependent inactivation of Ca2+ release in slow fibre points to a major difference in the two types of muscle.
Full text
PDF











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adrian R. H., Chandler W. K., Hodgkin A. L. The kinetics of mechanical activation in frog muscle. J Physiol. 1969 Sep;204(1):207–230. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adrian R. H., Costantin L. L., Peachey L. D. Radial spread of contraction in frog muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1969 Sep;204(1):231–257. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adrian R. H., Peachey L. D. The membrane capacity of frog twitch and slow muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1965 Nov;181(2):324–336. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aidley D. J. Transient changes in isotonic shortening velocity of frog rectus abdominis muscles in potassium contracture. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1965 Oct 12;163(991):215–223. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1965.0068. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong C. M., Bezanilla F. M., Horowicz P. Twitches in the presence of ethylene glycol bis( -aminoethyl ether)-N,N'-tetracetic acid. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jun 23;267(3):605–608. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(72)90194-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett N., Barrett E. F. Excitation-contraction coupling in skeletal muscle: blockade by high extracellular concentrations of calcium buffers. Science. 1978 Jun 16;200(4347):1270–1272. doi: 10.1126/science.96524. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blinks J. R., Rüdel R., Taylor S. R. Calcium transients in isolated amphibian skeletal muscle fibres: detection with aequorin. J Physiol. 1978 Apr;277:291–323. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bárány M. ATPase activity of myosin correlated with speed of muscle shortening. J Gen Physiol. 1967 Jul;50(6 Suppl):197–218. doi: 10.1085/jgp.50.6.197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caputo C., Fernandez de Bolaños P. Membrane potential, contractile activation and relaxation rates in voltage clamped short muscle fibres of the frog. J Physiol. 1979 Apr;289:175–189. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiarandini D. J., Stefani E. Effects of manganese on the electrical and mechanical properties of frog skeletal muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1973 Jul;232(1):129–147. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costantin L. L. Contractile activation in frog skeletal muscle. J Gen Physiol. 1974 Jun;63(6):657–674. doi: 10.1085/jgp.63.6.657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costantin L. L. Contractile activation in skeletal muscle. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1975;29(2):197–224. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(76)90023-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costantin L. L., Podolsky R. J., Tice L. W. Calcium activation of frog slow muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1967 Jan;188(2):261–271. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costantin L. L. The effect o f calcium on contraction and conductance thresholds in frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1968 Mar;195(1):119–132. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dörrscheidt-Käfer M. The action of Ca2+ , Mg2+ and H+ on the contraction threshold of frog skeletal muscle: Evidence for surface charges controlling electro-mechanical coupling. Pflugers Arch. 1976 Mar 11;362(1):33–41. doi: 10.1007/BF00588678. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo M. Calcium release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum. Physiol Rev. 1977 Jan;57(1):71–108. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1977.57.1.71. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel W. K., Irwin R. L. A histochemical-physiological correlation of frog skeletal muscle fibers. Am J Physiol. 1967 Aug;213(2):511–518. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1967.213.2.511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Floyd K., Smith I. C. The mechanical and thermal properties of frog slow muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1971 Mar;213(3):617–631. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franzini-Armstrong C. Membrane particles and transmission at the triad. Fed Proc. 1975 Apr;34(5):1382–1389. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franzini-Armstrong C. Studies of the triad. IV. Structure of the junction in frog slow fibers. J Cell Biol. 1973 Jan;56(1):120–128. doi: 10.1083/jcb.56.1.120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilly W. F., Hui C. S. Contractile activation in slow and twitch muscle fibres of the frog. Nature. 1977 Mar 10;266(5598):186–188. doi: 10.1038/266186a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilly W. F., Hui C. S. Membrane electrical properties of frog slow muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1980 Apr;301:157–173. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013196. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilly W. F., Hui C. S. Voltage-dependent charge movement in frog slow muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1980 Apr;301:175–190. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilly W. F. Slow fibers in the frog cruralis muscle. Tissue Cell. 1975;7(1):203–210. doi: 10.1016/s0040-8166(75)80017-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godt R. E. Calcium-activated tension of skinned muscle fibers of the frog. Dependence on magnesium adenosine triphosphate concentration. J Gen Physiol. 1974 Jun;63(6):722–739. doi: 10.1085/jgp.63.6.722. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HOROWICZ P. Potassium contractures in single muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1960 Sep;153:386–403. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heistracher P., Hunt C. C. The relation of membrane changes ot contraction in twitch muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1969 May;201(3):589–611. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008774. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess A. Vertebrate slow muscle fibers. Physiol Rev. 1970 Jan;50(1):40–62. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1970.50.1.40. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUFFLER S. W., VAUGHAN WILLIAMS E. M. Properties of the 'slow' skeletal muscles fibres of the frog. J Physiol. 1953 Aug;121(2):318–340. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1953.sp004949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUFFLER S. W., VAUGHAN WILLIAMS E. M. Small-nerve junctional potentials; the distribution of small motor nerves to frog skeletal muscle, and the membrane characteristics of the fibres they innervate. J Physiol. 1953 Aug;121(2):289–317. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1953.sp004948. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovács L., Schneider M. F. Contractile activation by voltage clamp depolarization of cut skeletal muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1978 Apr;277:483–506. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUETTGAU H. C. THE ACTION OF CALCIUM IONS ON POTASSIUM CONTRACTURES OF SINGLE MUSCLE FIBRES. J Physiol. 1963 Oct;168:679–697. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miledi R., Parker I., Schalow G. Calcium transients in frog slow muscle fibres. Nature. 1977 Aug 25;268(5622):750–752. doi: 10.1038/268750a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miledi R., Parker I., Schalow G. Measurement of calcium transients in frog muscle by the use of arsenazo III. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1977 Aug 22;198(1131):201–210. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1977.0094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miledi R., Stefani E., Steinbach A. B. Induction of the action potential mechanism in slow muscle fibres of the frog. J Physiol. 1971 Sep;217(3):737–754. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nasledov G. A. Correlative study of certain morphological and functional features of muscle fibers. Fed Proc Transl Suppl. 1965 Nov-Dec;24(6):1091–1095. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nasledov G. A., Mandelstam J. E., Radzjukewich T. L. A study of excitation-contraction coupling in frog tonic muscle fibers of Rana temporaria. Experientia. 1972 Nov 15;28(11):1305–1306. doi: 10.1007/BF01965310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nasledov G. A. Sootnoshenie mezhdu velichinoi membrannogo potentsiala i sokrashcheniem v tonicheskom myshechnom volokne. Fiziol Zh SSSR Im I M Sechenova. 1969 May;55(5):569–575. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nasledov G. A., Thesleff S. Denervation changes in frog skeletal muscle. Acta Physiol Scand. 1974 Feb;90(2):370–380. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1974.tb05598.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nasledov G. A., Zachar J., Zacharová D. The ionic requirements for the development of contracture in isolated slow muscle fibres of the frog. Physiol Bohemoslov. 1966;15(4):293–306. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oota I., Kosaka I., Nagai T. Role of superficially membrane-bound calcium on excitation-contraction coupling in frog skeletal muscle. Jpn J Physiol. 1976;26(2):117–126. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.26.117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oota I., Takauji M., Nagai T. Effect of manganese ions on excitation-contraction coupling in frog sartorius muscle. Jpn J Physiol. 1972 Aug;22(4):379–392. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.22.379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PODOLSKY R. J., COSTANTIN L. L. REGULATION BY CALCIUM OF THE CONTRACTION AND RELAXATION OF MUSCLE FIBERS. Fed Proc. 1964 Sep-Oct;23:933–939. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PORTZEHL H., CALDWELL P. C., RUEEGG J. C. THE DEPENDENCE OF CONTRACTION AND RELAXATION OF MUSCLE FIBRES FROM THE CRAB MAIA SQUINADO ON THE INTERNAL CONCENTRATION OF FREE CALCIUM IONS. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 May 25;79:581–591. doi: 10.1016/0926-6577(64)90224-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Page S. G. A comparison of the fine structures of frog slow and twitch muscle fibers. J Cell Biol. 1965 Aug;26(2):477–497. doi: 10.1083/jcb.26.2.477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peachey L. D. Muscle. Annu Rev Physiol. 1968;30:401–440. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.30.030168.002153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHANES A. M. Calcium influx in frog rectus abdominus muscle at rest and during potassium contracture. J Cell Comp Physiol. 1961 Jun;57:193–202. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1030570308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakai T., Kurihara S., Yoshioka T. Action of manganese ions on excitation-contractions coupling of frog skeletal muscle fibres. Jpn J Physiol. 1974 Oct;24(5):513–530. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.24.513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandow A., Krishna M., Pagala D., Sphicas E. C. Excitation-contraction coupling: effects of "zero"-Ca2+ medium. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Sep 8;404(1):157–163. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(75)90157-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. S., Ovalle W. K., Jr Varieties of fast and slow extrafusal muscle fibres in amphibian hind limb muscles. J Anat. 1973 Oct;116(Pt 1):1–24. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stefani E., Chiarandini D. J. Skeletal muscle: dependence of potassium contractures on extracellular calcium. Pflugers Arch. 1973 Oct 17;343(2):143–150. doi: 10.1007/BF00585709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stefani E., Steinbach A. B. Resting potential and electrical properties of frog slow muscle fibres. Effect of different external solutions. J Physiol. 1969 Aug;203(2):383–401. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stefani E., Uchitel O. D. Potassium and calcium conductance in slow muscle fibres of the toad. J Physiol. 1976 Feb;255(2):435–448. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhukov E. K. Tri protsessa, opredeliaiushchie soderzhanie kal'tsiia v apparate sokrashcheniia skeletnoi myshtsy. Fiziol Zh SSSR Im I M Sechenova. 1967 Nov;53(11):1393–1399. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]