Abstract
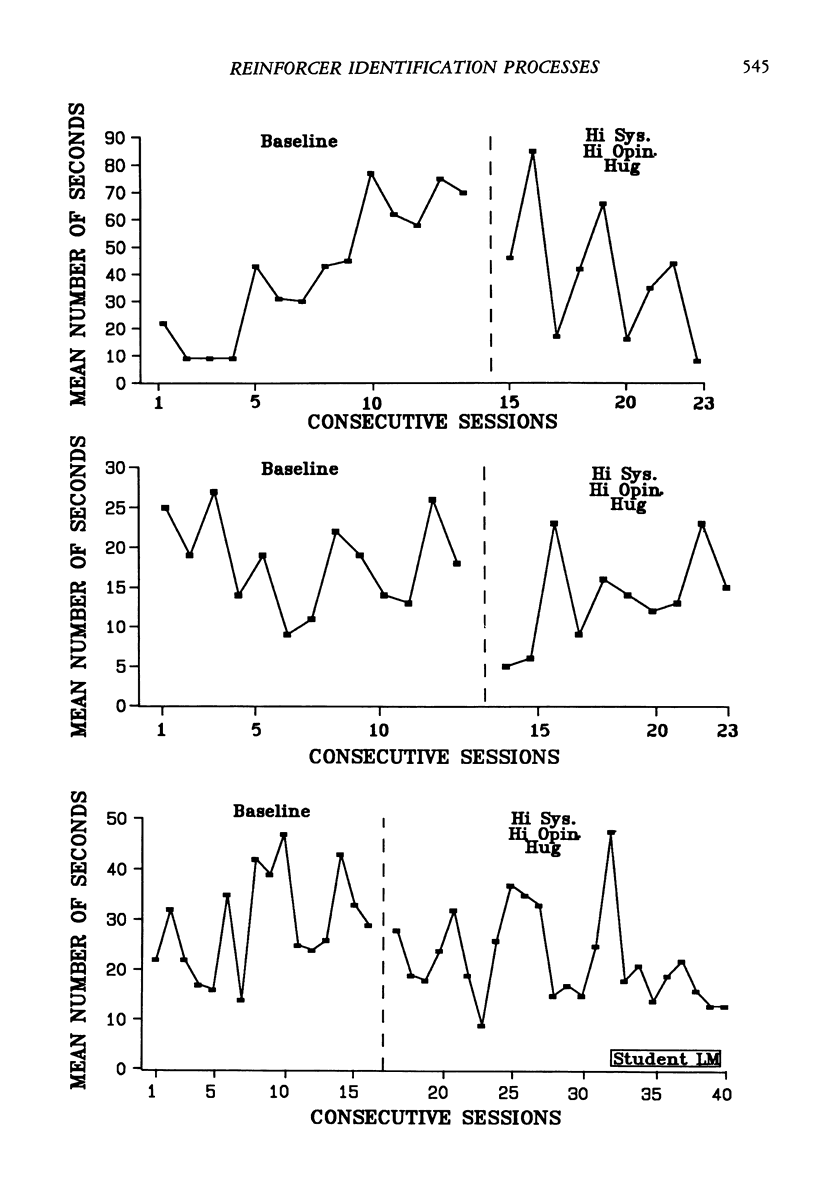
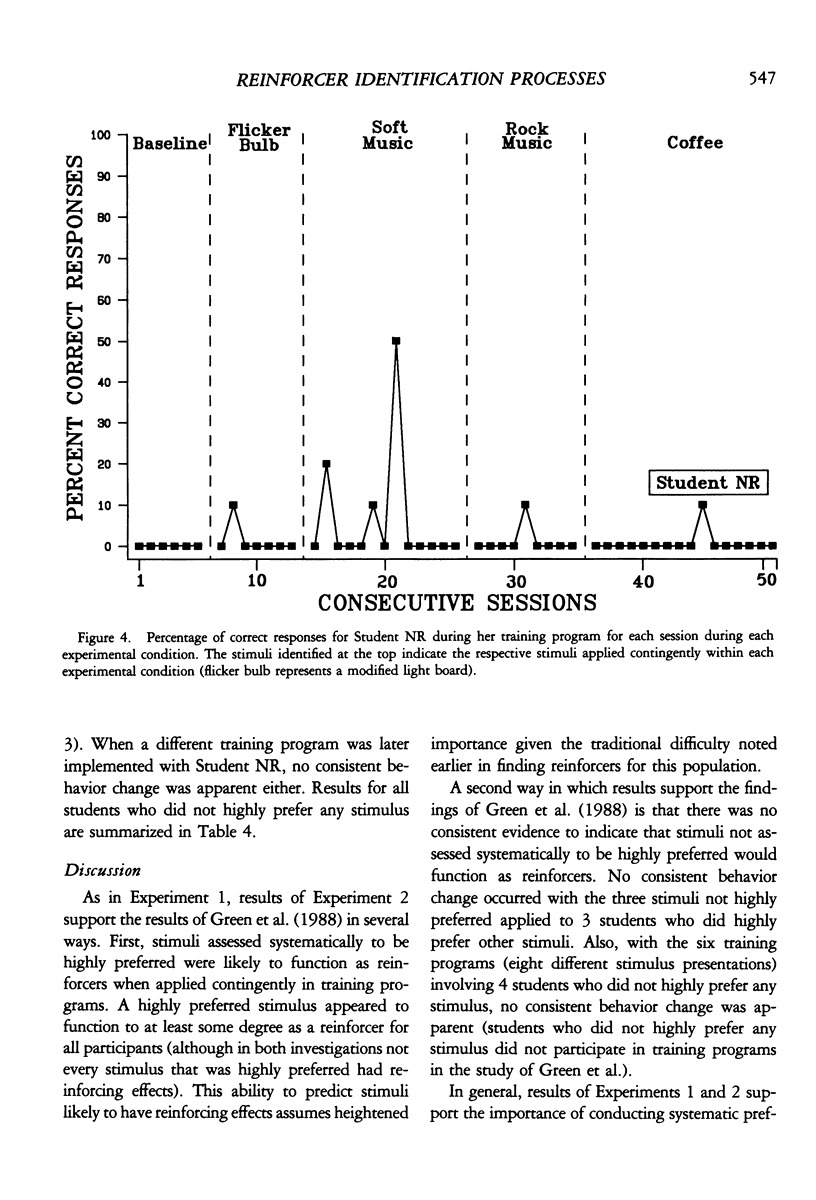
We evaluated comprehensively a preference assessment for identifying reinforcers for persons with profound multiple handicaps. Four experiments were conducted involving 18 individuals. Results of Experiment 1 replicated previous findings in that the assessment identified student preferences for respective stimuli, and caregiver opinion of preferences did not coincide with the systematic assessment. Results of Experiment 2 indicated highly preferred stimuli were likely to function as reinforcers in training programs, whereas stimuli not highly preferred did not function as reinforcers. Results of Experiment 3 suggested the 12 stimuli used in the assessment represented a comprehensive stimulus set for identifying preferences, although the utility of the set sometimes could be enhanced by caregiver opinion. Results of Experiment 4 indicated the assessment identified preferences likely to be maintained over time. Overall, results are discussed in terms of identifying limits and alternatives to a behavioral teaching technology when applied to persons with profound multiple handicaps.
Full text
PDF









Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bailey J., Meyerson L. Vibration as a reinforcer with a profoundly retarded child. J Appl Behav Anal. 1969 Summer;2(2):135–137. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1969.2-135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green C. W., Reid D. H., White L. K., Halford R. C., Brittain D. P., Gardner S. M. Identifying reinforcers for persons with profound handicaps: staff opinion versus systematic assessment of preferences. J Appl Behav Anal. 1988 Spring;21(1):31–43. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1988.21-31. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwata B. A. Negative reinforcement in applied behavior analysis: an emerging technology. J Appl Behav Anal. 1987 Winter;20(4):361–378. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1987.20-361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konarski E. A., Johnson M. R., Crowell C. R., Whitman T. L. Response deprivation and reinforcement in applied settings: A preliminary analysis. J Appl Behav Anal. 1980 Winter;13(4):595–609. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1980.13-595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landesman-Dwyer S., Sackett G. P. Behavioral changes in nonambulatory, profoundly mentally retarded individuals. Monogr Am Assoc Ment Defic. 1978;(3):55–144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason S. A., McGee G. G., Farmer-Dougan V., Risley T. R. A practical strategy for ongoing reinforcer assessment. J Appl Behav Anal. 1989 Summer;22(2):171–179. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1989.22-171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'brien F., Bugle C., Azrin N. H. Training and maintaining a retarded child's proper eating. J Appl Behav Anal. 1972 Spring;5(1):67–72. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1972.5-67. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pace G. M., Ivancic M. T., Edwards G. L., Iwata B. A., Page T. J. Assessment of stimulus preference and reinforcer value with profoundly retarded individuals. J Appl Behav Anal. 1985 Fall;18(3):249–255. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1985.18-249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsons M. B., Reid D. H. Assessing food preferences among persons with profound mental retardation: providing opportunities to make choices. J Appl Behav Anal. 1990 Summer;23(2):183–195. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1990.23-183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid D. H., Phillips J. F., Green C. W. Teaching persons with profound multiple handicaps: a review of the effects of behavioral research. J Appl Behav Anal. 1991 Summer;24(2):319–336. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1991.24-319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wacker D. P., Berg W. K., Wiggins B., Muldoon M., Cavanaugh J. Evaluation of reinforcer preferences for profoundly handicapped students. J Appl Behav Anal. 1985 Summer;18(2):173–178. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1985.18-173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


