Abstract
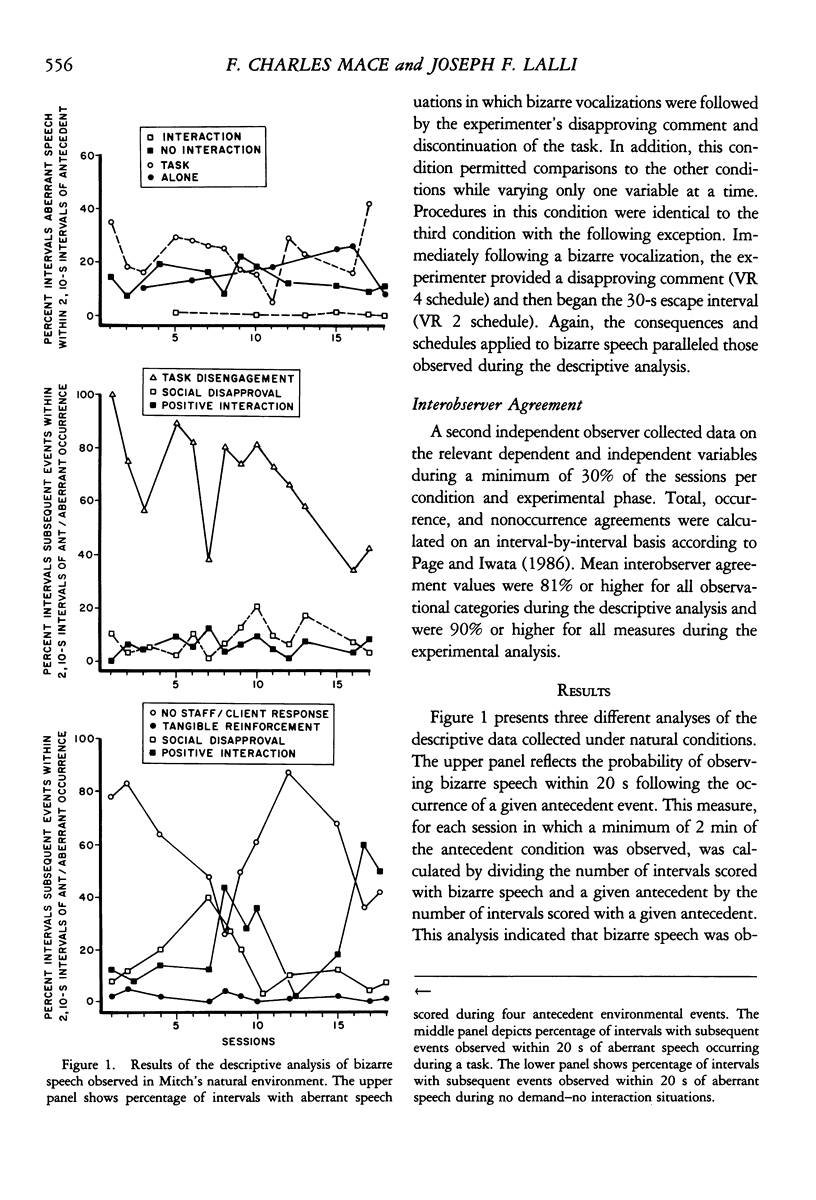
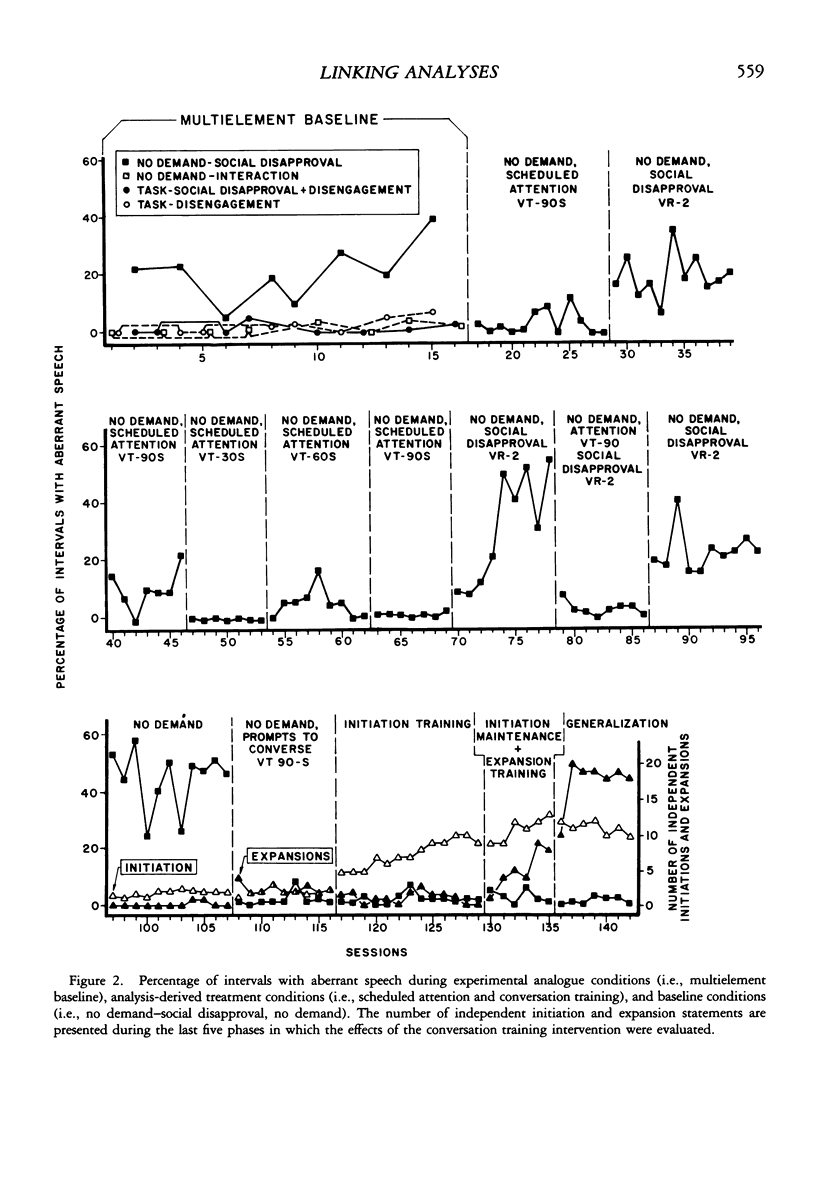
Descriptive and experimental methods were used to analyze the environmental determinants of an adult's bizarre speech. A descriptive analysis of behavior under natural conditions indicated that bizarre vocalizations occurred most often in the presence of task-related demands and in the absence of adult attention. Further, bizarre speech occurring during tasks was followed frequently by the cessation of task demands by staff or the subject's voluntary disengagement from task-related activities; bizarre speech observed during noninteractional periods (i.e., in the absence of adult attention) was frequently followed by staff attention. The escape and attention hypotheses were tested under analogue conditions. Results of the experimental analysis supported only the attention hypothesis; that is, bizarre speech appeared to function as an attention-producing behavior. The functional analysis data were used to select two different yet functionally equivalent treatments. The first treatment provided the subject with noncontingent scheduled attention. The second intervention taught the subject social language skills in the form of initiation and expansion statements. Both interventions were effective in suppressing maladapted speech. Advantages of linking descriptive and experimental analyses are discussed.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Carr E. G., Durand V. M. Reducing behavior problems through functional communication training. J Appl Behav Anal. 1985 Summer;18(2):111–126. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1985.18-111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carr E. G., Newsom C. D., Binkoff J. A. Escape as a factor in the aggressive behavior of two retarded children. J Appl Behav Anal. 1980 Spring;13(1):101–117. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1980.13-101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carr E. G., Newsom C. Demand-related tantrums. Conceptualization and treatment. Behav Modif. 1985 Oct;9(4):403–426. doi: 10.1177/01454455850094001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper L. J., Wacker D. P., Sasso G. M., Reimers T. M., Donn L. K. Using parents as therapists to evaluate appropriate behavior of their children: application to a tertiary diagnostic clinic. J Appl Behav Anal. 1990 Fall;23(3):285–296. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1990.23-285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durand V. M., Crimmins D. B. Assessment and treatment of psychotic speech in an autistic child. J Autism Dev Disord. 1987 Mar;17(1):17–28. doi: 10.1007/BF01487257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durand V. M., Crimmins D. B. Identifying the variables maintaining self-injurious behavior. J Autism Dev Disord. 1988 Mar;18(1):99–117. doi: 10.1007/BF02211821. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haring T. G., Roger B., Lee M., Breen C., Gaylord-Ross R. Teaching social language to moderately handicapped students. J Appl Behav Anal. 1986 Summer;19(2):159–171. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1986.19-159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mace F. C., Belfiore P. Behavioral momentum in the treatment of escape-motivated stereotypy. J Appl Behav Anal. 1990 Winter;23(4):507–514. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1990.23-507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mace F. C., Lalli J. S., Lalli E. P. Functional analysis and treatment of aberrant behavior. Res Dev Disabil. 1991;12(2):155–180. doi: 10.1016/0891-4222(91)90004-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


