Abstract
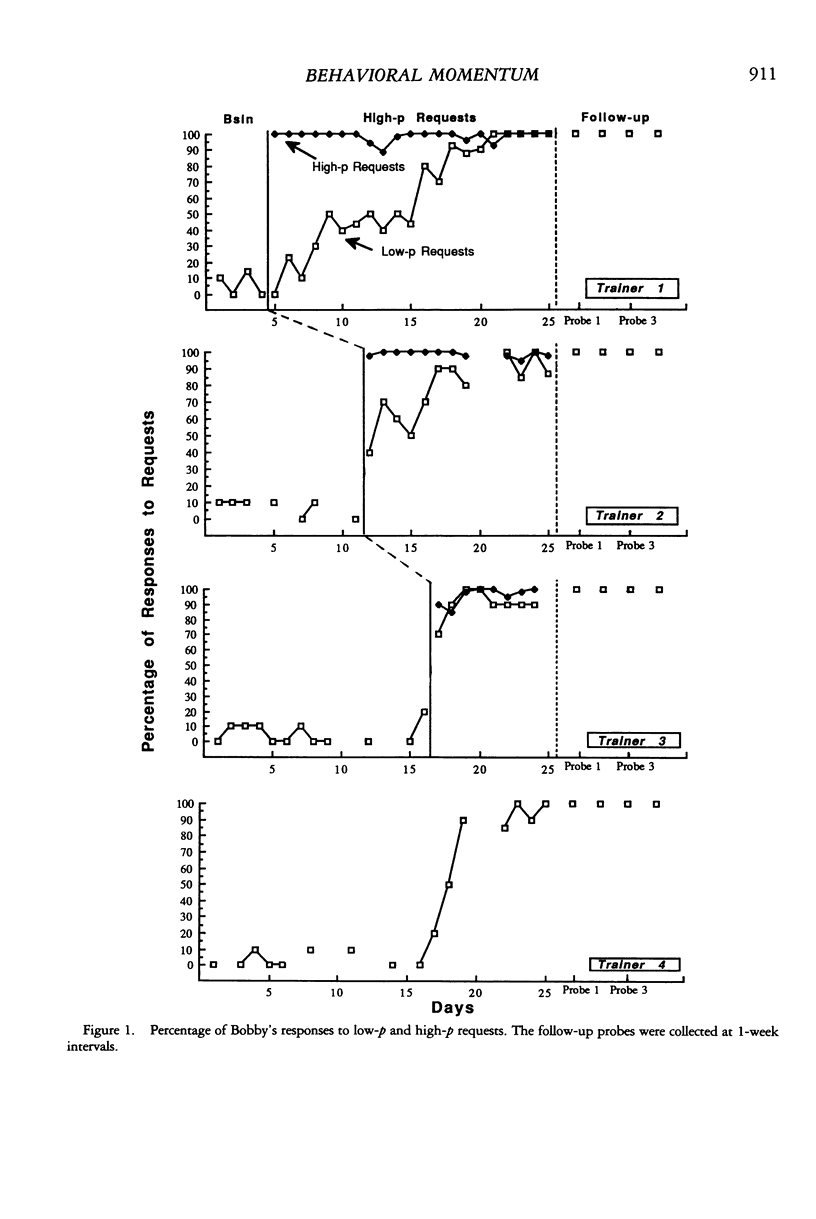
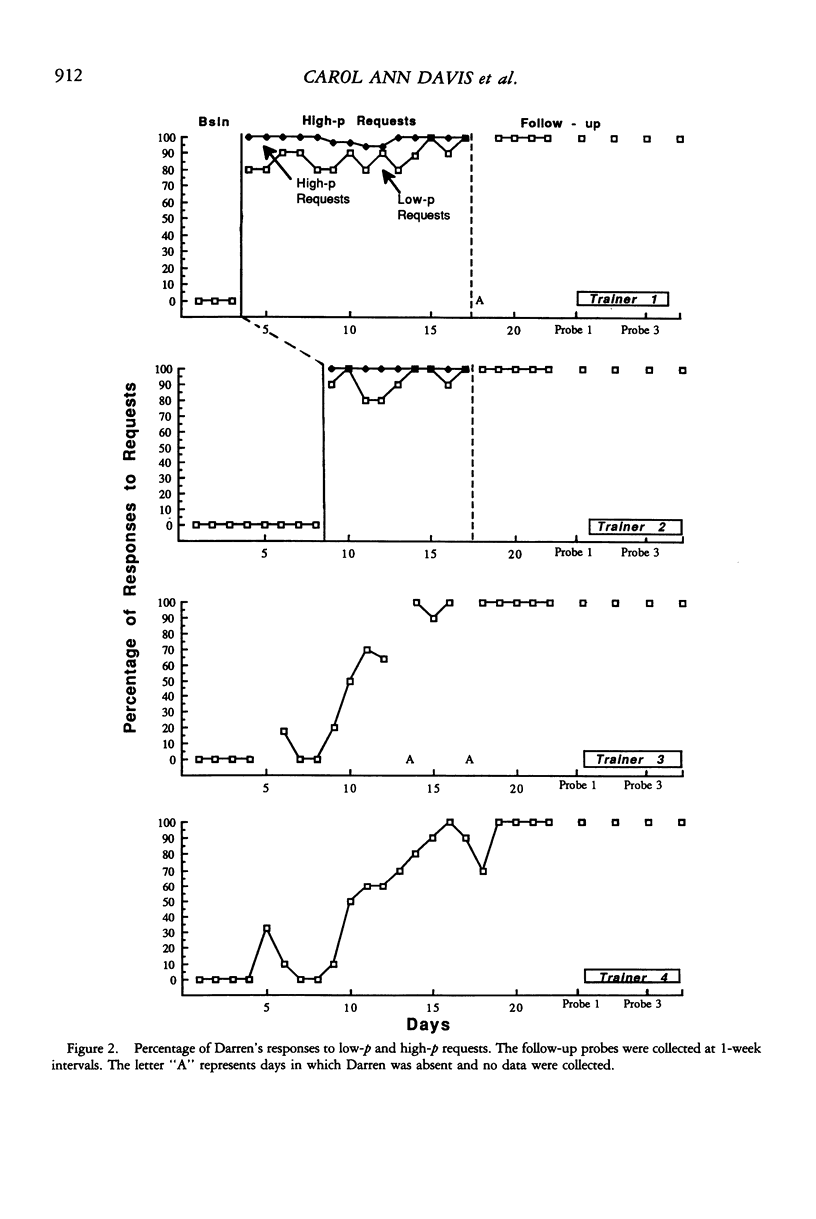
The failure to respond to requests in young children often is maintained by the reactions of the adults that encounter this behavior. This failure to respond to requests has been identified as a primary reason for the children's exclusion from community, social, and instructional opportunities. Numerous interventions that target the failure to respond have consisted of punishment and reinforcement procedures. More recently, antecedent interventions have focused on changing the context in which a request is delivered. In the current study, high-probability requests were provided as an antecedent to delivering a low-probability request. The requests were delivered by multiple trainers in an attempt to produce generalized appropriate responding to adults who did not use the high-probability sequence. Results showed an immediate increase in appropriate responding in 2 children when the intervention was delivered. In addition, when the intervention was implemented by more than one adult, spontaneous increases in responding also were observed toward adults who had never implemented the request sequence. Improvements in responding to requests were maintained after the intervention was discontinued.
Full text
PDF









Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brady M. P., Shores R. E., McEvoy M. A., Ellis D., Fox J. J. Increasing social interactions of severely handicapped autistic children. J Autism Dev Disord. 1987 Sep;17(3):375–390. doi: 10.1007/BF01487067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell B. J., Brady M. P., Linehan S. Effects of peer-mediated instruction on the acquisition and generalization of written capitalization skills. J Learn Disabil. 1991 Jan;24(1):6–14. doi: 10.1177/002221949102400103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carr E. G., Durand V. M. Reducing behavior problems through functional communication training. J Appl Behav Anal. 1985 Summer;18(2):111–126. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1985.18-111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carr E. G., Newsom C. D., Binkoff J. A. Stimulus control of self-destructive behavior in a psychotic child. J Abnorm Child Psychol. 1976;4(2):139–153. doi: 10.1007/BF00916518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carr E. G., Taylor J. C., Robinson S. The effects of severe behavior problems in children on the teaching behavior of adults. J Appl Behav Anal. 1991 Fall;24(3):523–535. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1991.24-523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doleys D. M., Wells K. C., Hobbs S. A., Roberts M. W., Cartelli L. M. The effects of social punishment on noncompliance: a comparison with timeout and positive practice. J Appl Behav Anal. 1976 WINTER;9(4):471–482. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1976.9-471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haring T. G., Kennedy C. H. Contextual control of problem behavior in students with severe disabilities. J Appl Behav Anal. 1990 Summer;23(2):235–243. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1990.23-235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horner R. H., Day H. M., Sprague J. R., O'Brien M., Heathfield L. T. Interspersed requests: a nonaversive procedure for reducing aggression and self-injury during instruction. J Appl Behav Anal. 1991 Summer;24(2):265–278. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1991.24-265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mace F. C., Belfiore P. Behavioral momentum in the treatment of escape-motivated stereotypy. J Appl Behav Anal. 1990 Winter;23(4):507–514. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1990.23-507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mace F. C., Hock M. L., Lalli J. S., West B. J., Belfiore P., Pinter E., Brown D. K. Behavioral momentum in the treatment of noncompliance. J Appl Behav Anal. 1988 Summer;21(2):123–141. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1988.21-123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevin J. A., Mandell C., Atak J. R. The analysis of behavioral momentum. J Exp Anal Behav. 1983 Jan;39(1):49–59. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1983.39-49. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parrish J. M., Cataldo M. F., Kolko D. J., Neef N. A., Egel A. L. Experimental analysis of response covariation among compliant and inappropriate behaviors. J Appl Behav Anal. 1986 Fall;19(3):241–254. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1986.19-241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stokes T. F., Baer D. M., Jackson R. L. Programming the generalization of a greeting response in four retarded children. J Appl Behav Anal. 1974 Winter;7(4):599–610. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1974.7-599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volkmar F. R., Siegel A. E. Young children's responses to discrepant social communications. J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 1979 Apr;20(2):139–149. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7610.1979.tb00494.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahler R. G., Dumas J. E. Maintenance factors in coercive mother-child interactions: the compliance and predictability hypotheses. J Appl Behav Anal. 1986 Spring;19(1):13–22. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1986.19-13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfensberger W. Social role valorization: a proposed new term for the principle of normalization. Ment Retard. 1983 Dec;21(6):234–239. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


