Abstract
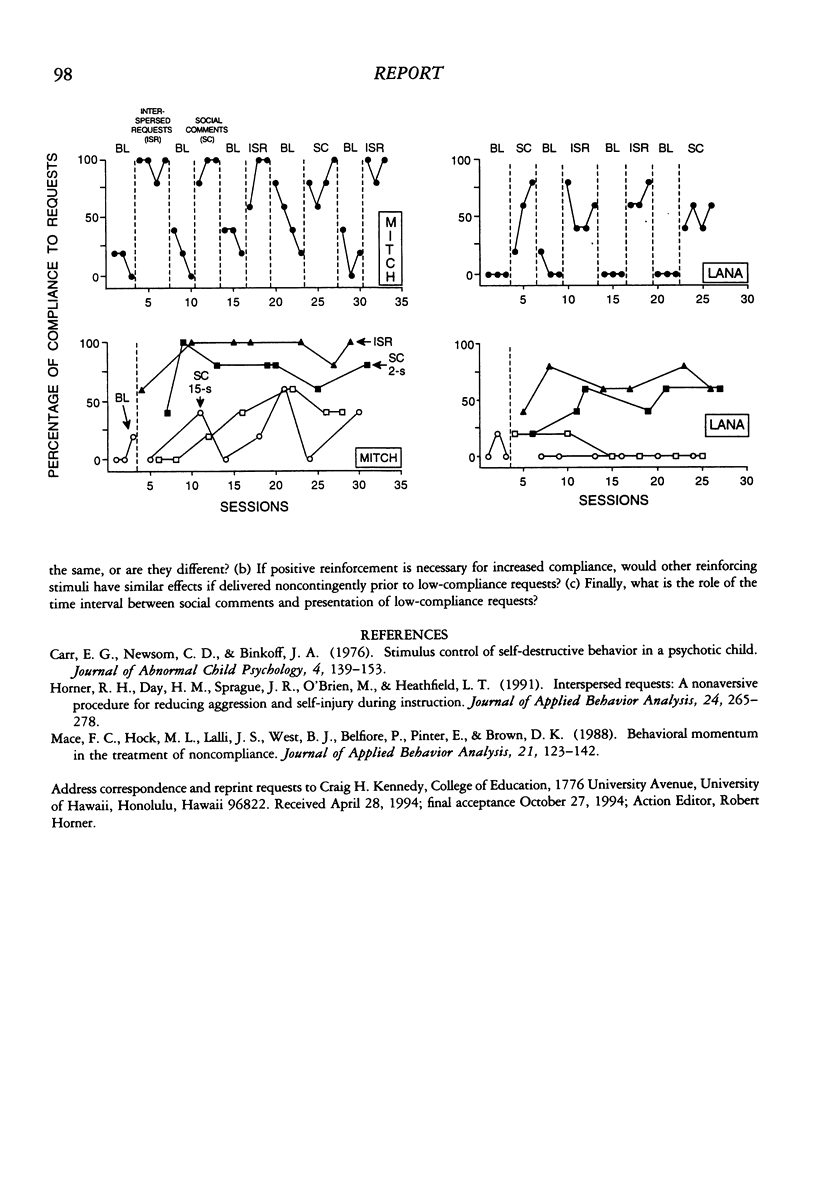
Two students were alternately presented with interspersed high-compliance requests and social comments as antecedents to low-compliance requests. An initial comparison demonstrated similar positive effects on compliance for interspersed requests and social comments. A second analysis indicated that the effectiveness of social comments for increasing compliance was related to the time interval between social comments and low-compliance requests.
Keywords: compliance, interspersed requests, social comments, reinforcement, students with severe disabilities
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Carr E. G., Newsom C. D., Binkoff J. A. Stimulus control of self-destructive behavior in a psychotic child. J Abnorm Child Psychol. 1976;4(2):139–153. doi: 10.1007/BF00916518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horner R. H., Day H. M., Sprague J. R., O'Brien M., Heathfield L. T. Interspersed requests: a nonaversive procedure for reducing aggression and self-injury during instruction. J Appl Behav Anal. 1991 Summer;24(2):265–278. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1991.24-265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mace F. C., Hock M. L., Lalli J. S., West B. J., Belfiore P., Pinter E., Brown D. K. Behavioral momentum in the treatment of noncompliance. J Appl Behav Anal. 1988 Summer;21(2):123–141. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1988.21-123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


