Abstract
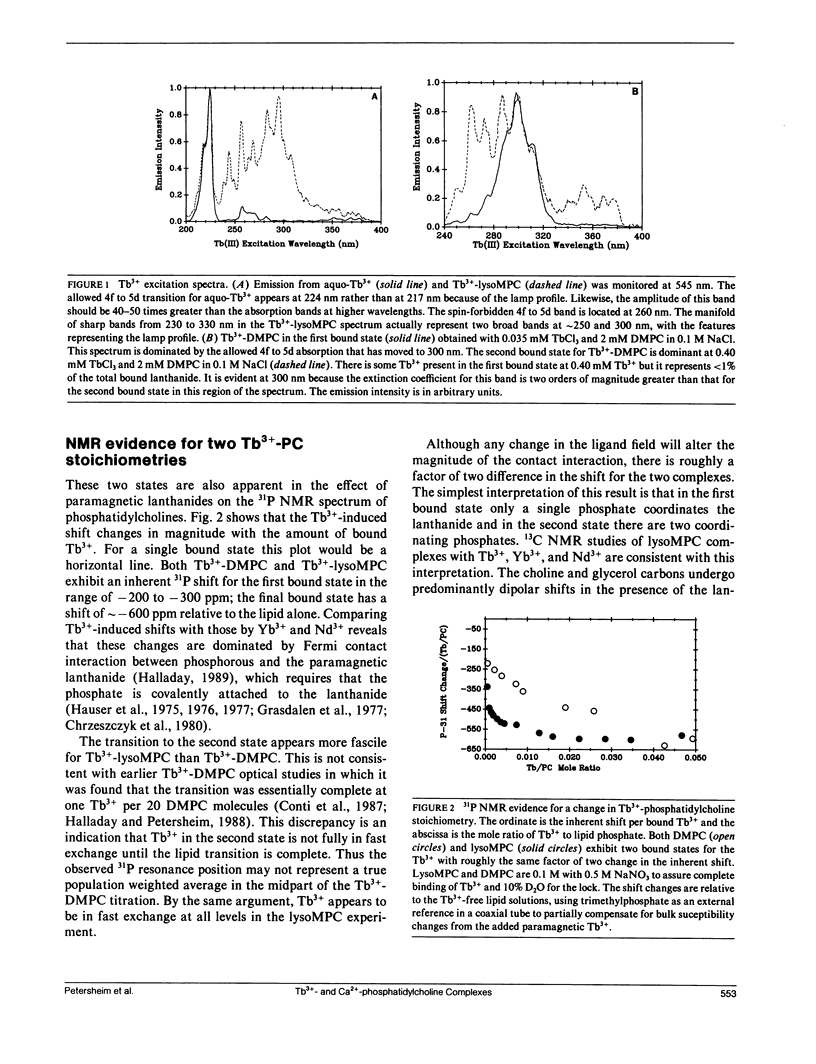
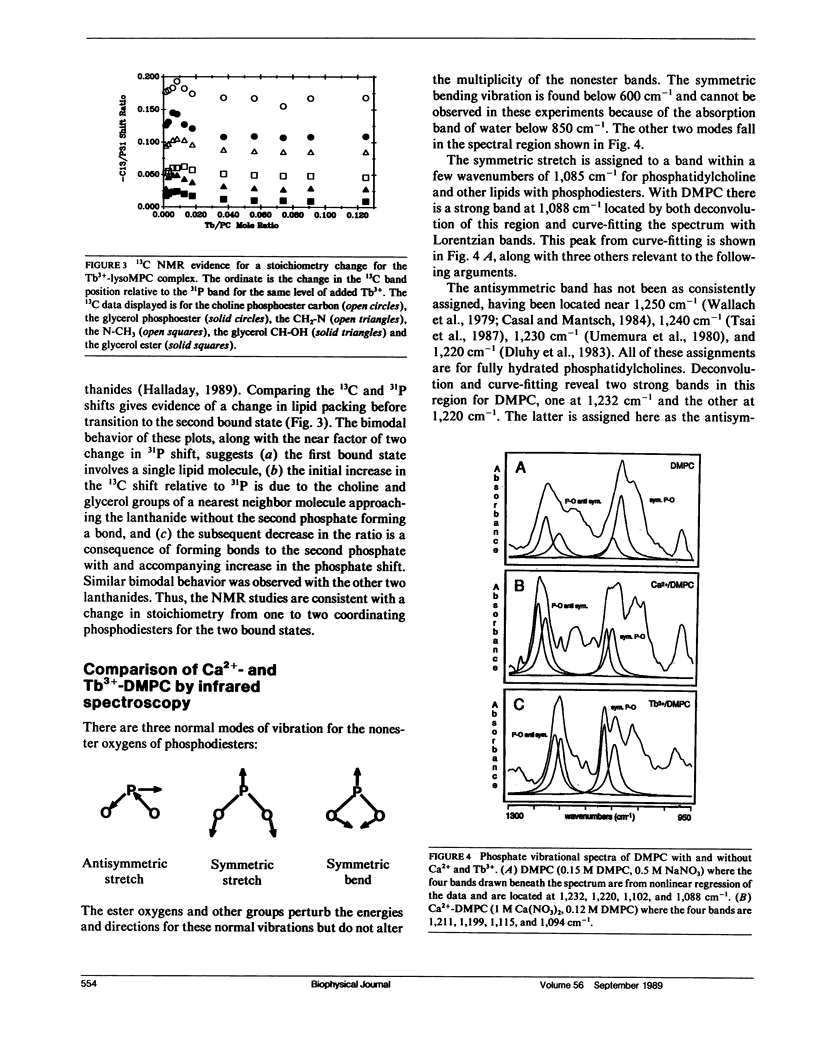
The paramagnetic and luminescent lanthanides are unique probes of cation-phospholipid interactions. Their spectroscopic properties provide the means to characterize and monitor complexes formed with lipids in ways not possible with biochemically more interesting cations, such as Ca2+. In this work, Tb3+-phosphatidylcholine complexes are described using the luminescence properties of Tb3+, the effect of its paramagnetism on the 31P NMR and 13C NMR spectra of the lipid, and changes in the infrared spectrum of the lipid induced by the cation. There are two Tb3+-phosphatidylcholine complexes with very different coordination environments, as evidenced by changes in the optical excitation spectrum of the lanthanide. The NMR experiments indicate that the two complexes differ in the number of phosphate groups directly coordinating Tb3+. Tb3+ binding induces changes in the phosphodiester infrared bands that are most consistent with bidentate chelation of Tb3+ by each phosphate, whereas Ca2+-induced changes are more consistent with monodentate coordination. The significance of this discrepancy is discussed.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akutsu H., Seelig J. Interaction of metal ions with phosphatidylcholine bilayer membranes. Biochemistry. 1981 Dec 22;20(26):7366–7373. doi: 10.1021/bi00529a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altenbach C., Seelig J. Ca2+ binding to phosphatidylcholine bilayers as studied by deuterium magnetic resonance. Evidence for the formation of a Ca2+ complex with two phospholipid molecules. Biochemistry. 1984 Aug 14;23(17):3913–3920. doi: 10.1021/bi00312a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bentz J., Alford D., Cohen J., Düzgüneş N. La3+-induced fusion of phosphatidylserine liposomes. Close approach, intermembrane intermediates, and the electrostatic surface potential. Biophys J. 1988 Apr;53(4):593–607. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(88)83138-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casal H. L., Mantsch H. H. Polymorphic phase behaviour of phospholipid membranes studied by infrared spectroscopy. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Dec 4;779(4):381–401. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(84)90017-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chrzeszczyk A., Wishnia A., Springer C. S., Jr Evidence for cooperative effects in the bind of polyvalent metal ions to pure phosphatidylcholine bilayer vesicle surfaces. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Oct 20;648(1):28–48. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(81)90121-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conti J., Halladay H. N., Petersheim M. An ionotropic phase transition in phosphatidylcholine: cation and anion cooperativity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Aug 7;902(1):53–64. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(87)90135-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grasdalen H., Göran Eriksson L. E., Westman J., Ehrenberg A. Surface potential effects on metal ion binding to phosphatidylcholine membranes 31P NMR study of lanthanide and calcium ion binding to egg-yolk lecithin vesicles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Sep 5;469(2):151–162. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90177-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn J. F., Collins J. M., Lis L. J. Anion influence on the binding of divalent cations to phosphatidylcholine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Dec 21;736(2):235–240. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(83)90289-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauser H., Hinckley C. C., Krebs J., Levine B. A., Phillips M. C., Williams R. J. The interaction of ions with phosphatidylcholine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Aug 1;468(3):364–377. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90288-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauser H., Phillips M. C. Conformation of the lecithin polar group in charged vesicles. Nature. 1976 Jun 3;261(5559):390–394. doi: 10.1038/261390a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauser H., Phillips M. C., Levine B. A., Williams R. J. Ion-binding to phospholipids. Interaction of calcium and lanthanide ions with phosphatidylcholine (lecithin). Eur J Biochem. 1975 Oct 1;58(1):133–144. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02357.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrmann T. R., Jayaweera A. R., Shamoo A. E. Interaction of europium(III) with phospholipid vesicles as monitored by laser-excited europium(III) luminescence. Biochemistry. 1986 Sep 23;25(19):5834–5838. doi: 10.1021/bi00367a074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liao M. J., Prestegard J. H. Ion specificity in fusion of phosphatidic acid-phosphatidylcholine mixed lipid vesicles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Oct 2;601(3):453–461. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90549-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntosh T. J. Differences in hydrocarbon chain tilt between hydrated phosphatidylethanolamine and phosphatidylcholine bilayers. A molecular packing model. Biophys J. 1980 Feb;29(2):237–245. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(80)85128-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersheim M., Blodnieks J., Halladay H. N. Optical, infrared and NMR studies of cation-phospholipid interactions. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1989;292:87–96. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersheim M., Sun J. On the coordination of La3+ by phosphatidylserine. Biophys J. 1989 Apr;55(4):631–636. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(89)82860-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott H. L., Pearce P. A. Calculation of intermolecular interaction strengths in the P beta' phase in lipid bilayers. Implications for theoretical models. Biophys J. 1989 Feb;55(2):339–345. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(89)82810-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sears B., Hutton W. C., Thompson T. E. Effects of paramagnetic shift reagents on the 13C nuclear magnetic resonance spectra of egg phosphatidylcholine enriched with 13C in the N-methyl carbons. Biochemistry. 1976 Apr 20;15(8):1635–1639. doi: 10.1021/bi00653a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seelig J., Macdonald P. M., Scherer P. G. Phospholipid head groups as sensors of electric charge in membranes. Biochemistry. 1987 Dec 1;26(24):7535–7541. doi: 10.1021/bi00398a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tatulian S. A. Effect of lipid phase transition on the binding of anions to dimyristoylphosphatidylcholine liposomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Dec 21;736(2):189–195. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(83)90283-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai Y. S., Ma S. M., Kamaya H., Ueda I. Fourier transform infrared studies on phospholipid hydration: phosphate-oriented hydrogen bonding and its attenuation by volatile anesthetics. Mol Pharmacol. 1987 Jun;31(6):623–630. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umemura J., Cameron D. G., Mantsch H. H. A Fourier transform infrared spectroscopic study of the molecular interaction of cholesterol with 1,2-dipalmitoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Oct 16;602(1):32–44. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90287-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallach D. F., Verma S. P., Fookson J. Application of laser Raman and infrared spectroscopy to the analysis of membrane structure. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Aug 20;559(2-3):153–208. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(79)90001-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wendoloski J. J., Kimatian S. J., Schutt C. E., Salemme F. R. Molecular dynamics simulation of a phospholipid micelle. Science. 1989 Feb 3;243(4891):636–638. doi: 10.1126/science.2916118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


