Abstract
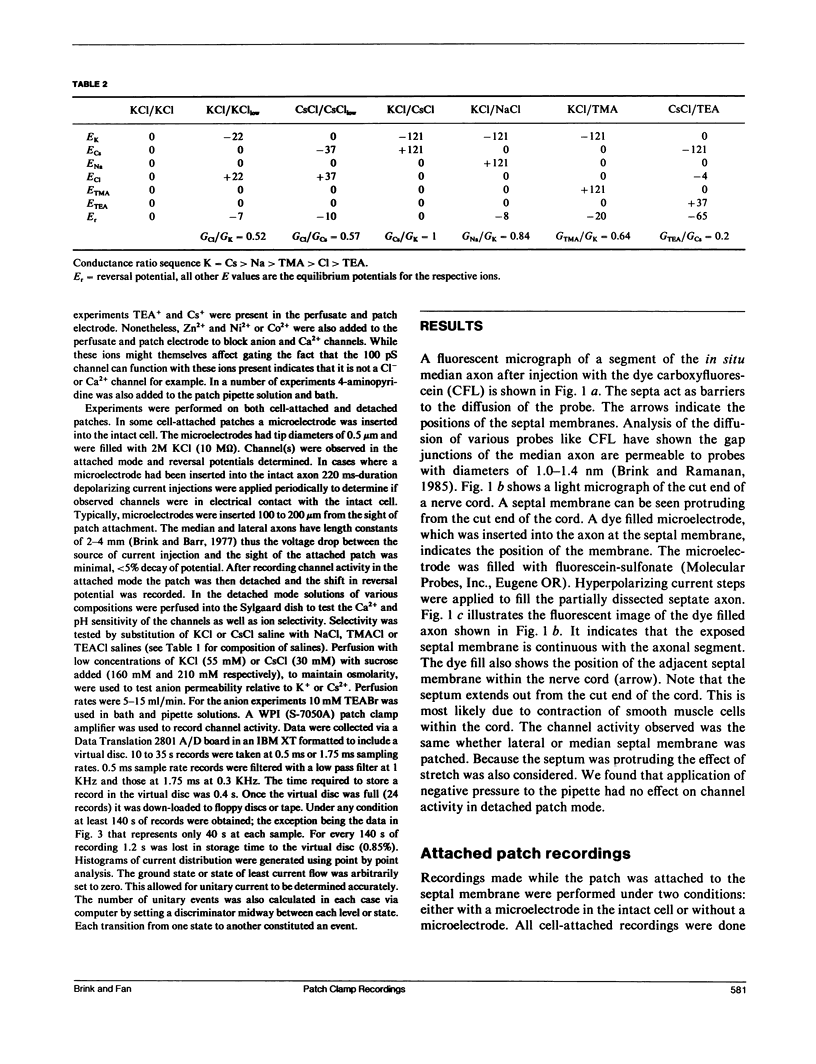
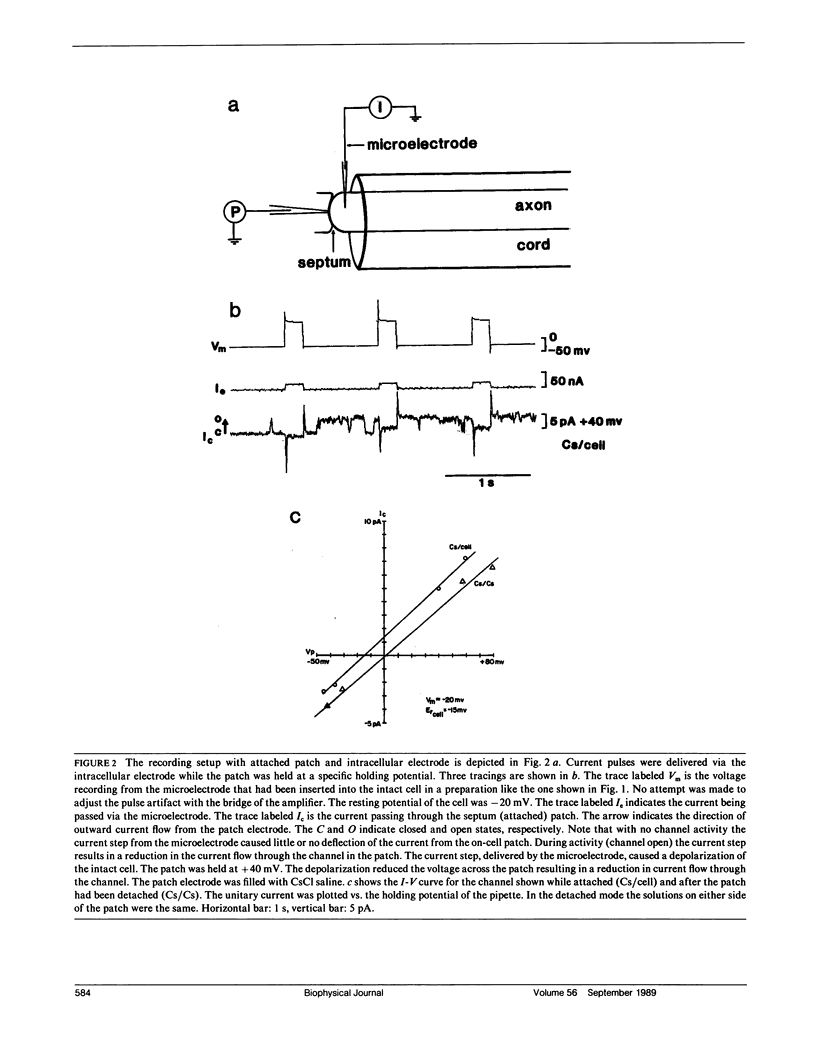
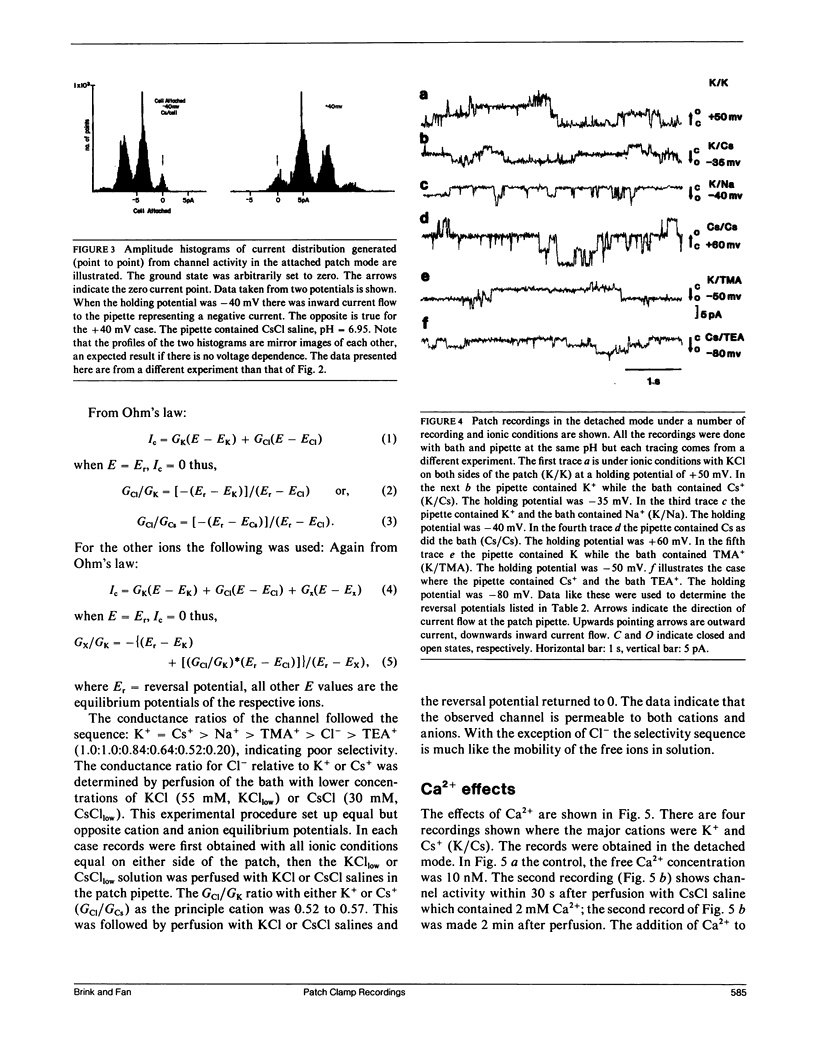
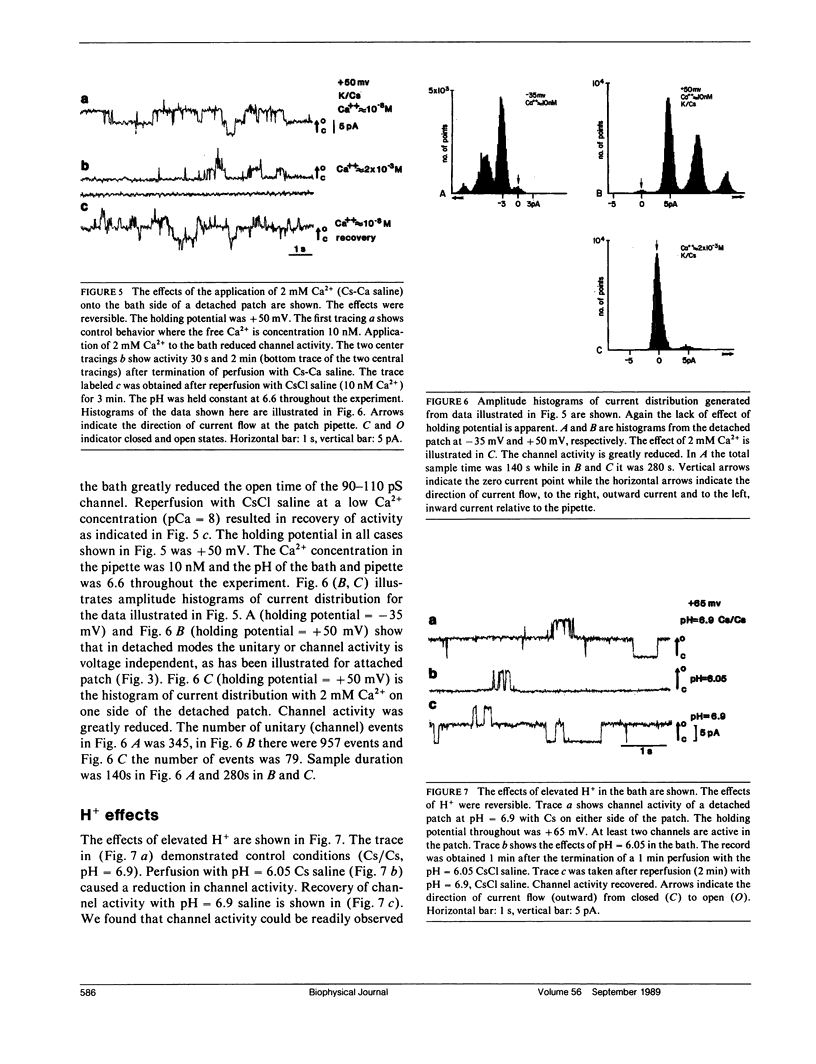
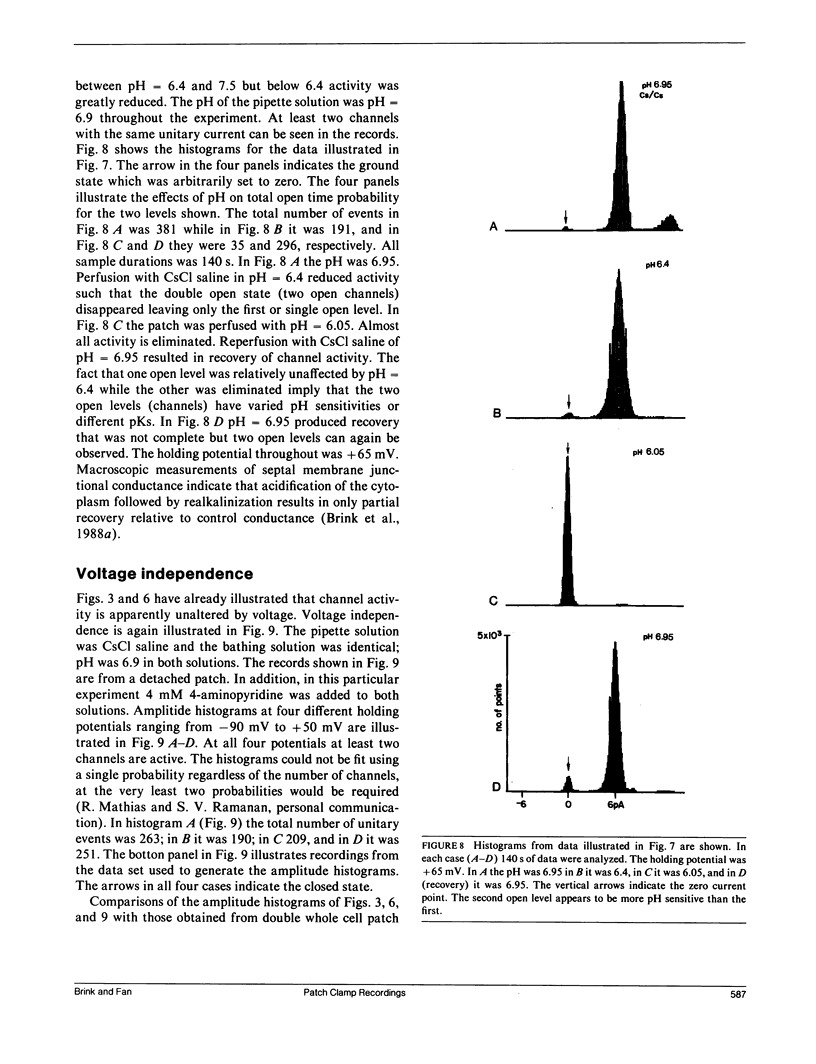
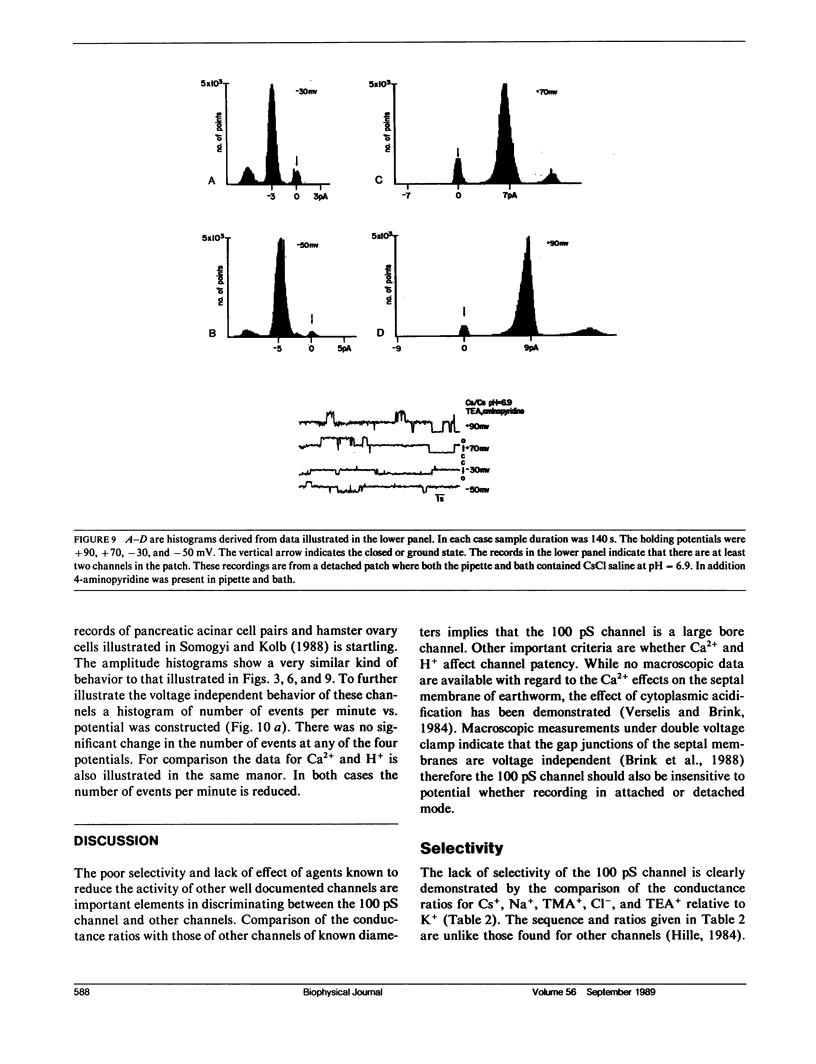
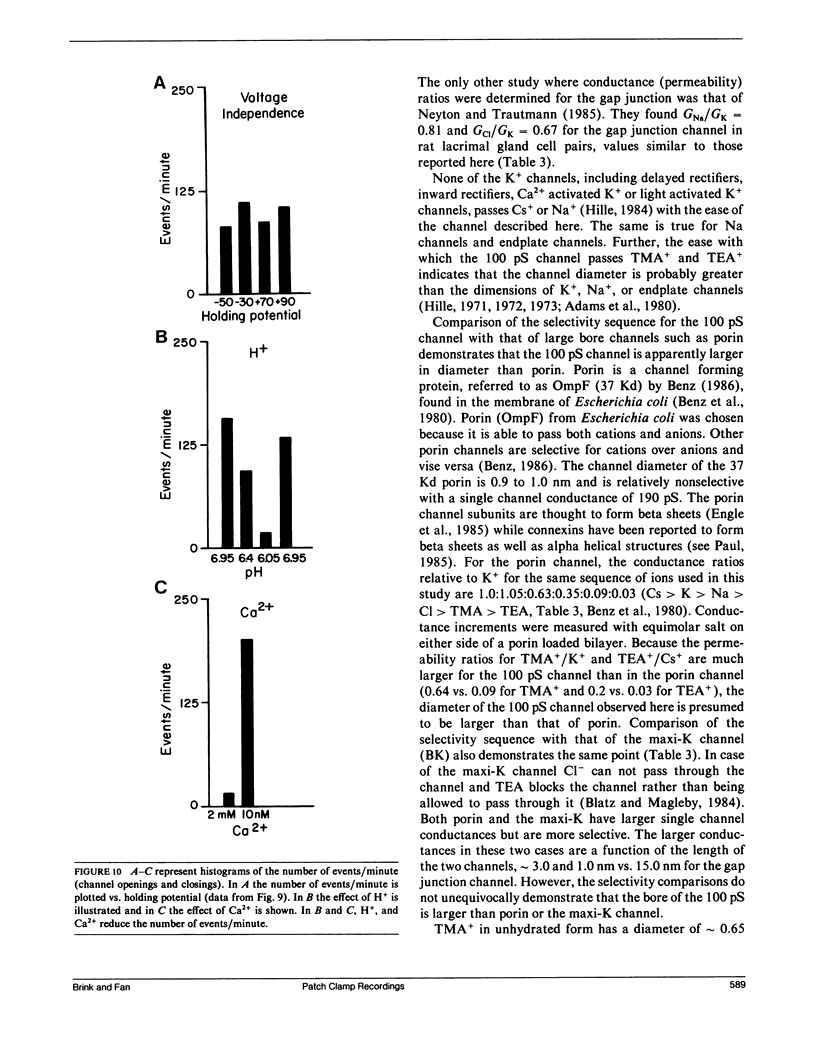
The septal membranes of the median and lateral giant axons of earthworm, which contain gap junctions, were exposed by cutting one segment of the cord. Patch recordings were obtained from the exposed cytoplasmic side of the septum. Seal resistances ranged from 2 to 15 G omega. The patch could be excised (detached) or left attached to the whole cell. Two types of channels were observed. One type was blocked by tetraethylammonium (TEA) or Cs+ and had a unitary conductance of 30-40 pS. It appears to be a K+ channel. The other channel type had a unitary conductance of 90-110 pS and was unaffected by TEA+ or Cs+. In the detached configuration the channel was shown to conduct Cs+, K+, Na+, TMA+, Cl- and TEA+ even in the presence of 2 mM Zn2+, 1 mM Ni2+, 1 mM Co2+, and 4 mM 4-aminopyridine. The conductance ratios relative to K+ were 1.0 for Cs+, 0.84 for Na+, 0.64 for TMA+, 0.52 for Cl- and 0.2 for TEA+. The channel appears to be voltage insensitive whether monitored in detached or attached recording mode. Both H+ and Ca2+ reduce the probability of opening. Thus, the 100 pS channel has many of the properties expected of a gap junction channel.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams D. J., Dwyer T. M., Hille B. The permeability of endplate channels to monovalent and divalent metal cations. J Gen Physiol. 1980 May;75(5):493–510. doi: 10.1085/jgp.75.5.493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benz R., Janko K., Läuger P. Pore formation by the matrix protein (porin) of Escherichia coli in planar bilayer membranes. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1980;358:13–24. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1980.tb15382.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bezanilla F. Single sodium channels from the squid giant axon. Biophys J. 1987 Dec;52(6):1087–1090. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(87)83304-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blatz A. L., Magleby K. L. Ion conductance and selectivity of single calcium-activated potassium channels in cultured rat muscle. J Gen Physiol. 1984 Jul;84(1):1–23. doi: 10.1085/jgp.84.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brink P. R., Dewey M. M. Evidence for fixed charge in the nexus. Nature. 1980 May 8;285(5760):101–102. doi: 10.1038/285101a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brink P. R., Mathias R. T., Jaslove S. W., Baldo G. J. Steady-state current flow through gap junctions. Effects on intracellular ion concentrations and fluid movement. Biophys J. 1988 May;53(5):795–807. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(88)83159-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brink P. R., Ramanan S. V. A model for the diffusion of fluorescent probes in the septate giant axon of earthworm. Axoplasmic diffusion and junctional membrane permeability. Biophys J. 1985 Aug;48(2):299–309. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(85)83783-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brink P., Barr L. The resistance of the septum of the median giant axon of the earthworm. J Gen Physiol. 1977 May;69(5):517–536. doi: 10.1085/jgp.69.5.517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burt J. M., Spray D. C. Single-channel events and gating behavior of the cardiac gap junction channel. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(10):3431–3434. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.10.3431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flagg-Newton J., Simpson I., Loewenstein W. R. Permeability of the cell-to-cell membrane channels in mammalian cell juncton. Science. 1979 Jul 27;205(4404):404–407. doi: 10.1126/science.377490. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girsch S. J., Peracchia C. Lens cell-to-cell channel protein: I. Self-assembly into liposomes and permeability regulation by calmodulin. J Membr Biol. 1985;83(3):217–225. doi: 10.1007/BF01868696. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodenough D. A. The structure and permeability of isolated hepatocyte gap junctions. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1976;40:37–43. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1976.040.01.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hille B. Potassium channels in myelinated nerve. Selective permeability to small cations. J Gen Physiol. 1973 Jun;61(6):669–686. doi: 10.1085/jgp.61.6.669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hille B. The permeability of the sodium channel to metal cations in myelinated nerve. J Gen Physiol. 1972 Jun;59(6):637–658. doi: 10.1085/jgp.59.6.637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hille B. The permeability of the sodium channel to organic cations in myelinated nerve. J Gen Physiol. 1971 Dec;58(6):599–619. doi: 10.1085/jgp.58.6.599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kensler R. W., Brink P. R., Dewey M. M. The septum of the lateral axon of the earthworm: a thin section and freeze-fracture study. J Neurocytol. 1979 Oct;8(5):565–590. doi: 10.1007/BF01208510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loewenstein W. R. Junctional intercellular communication: the cell-to-cell membrane channel. Physiol Rev. 1981 Oct;61(4):829–913. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1981.61.4.829. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowenstein W. R. Regulation of cell-to-cell communication by phosphorylation. Biochem Soc Symp. 1985;50:43–58. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makowski L., Caspar D. L., Phillips W. C., Baker T. S., Goodenough D. A. Gap junction structures. VI. Variation and conservation in connexon conformation and packing. Biophys J. 1984 Jan;45(1):208–218. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84149-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neyton J., Trautmann A. Single-channel currents of an intercellular junction. 1985 Sep 26-Oct 2Nature. 317(6035):331–335. doi: 10.1038/317331a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noma A., Tsuboi N. Dependence of junctional conductance on proton, calcium and magnesium ions in cardiac paired cells of guinea-pig. J Physiol. 1987 Jan;382:193–211. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obaid A. L., Socolar S. J., Rose B. Cell-to-cell channels with two independently regulated gates in series: analysis of junctional conductance modulation by membrane potential, calcium, and pH. J Membr Biol. 1983;73(1):69–89. doi: 10.1007/BF01870342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peracchia C. Calmodulin-like proteins and communicating junctions. Electrical uncoupling of crayfish septate axons is inhibited by the calmodulin inhibitor W7 and is not affected by cyclic nucleotides. Pflugers Arch. 1987 Apr;408(4):379–385. doi: 10.1007/BF00581132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peracchia C., Dulhunty A. F. Low resistance junctions in crayfish. Structural changes with functional uncoupling. J Cell Biol. 1976 Aug;70(2 Pt 1):419–439. doi: 10.1083/jcb.70.2.419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Politoff A., Pappas G. D., Bennett M. V. Cobalt ions cross an electrotonic synapse if cytoplasmic concentration is low. Brain Res. 1974 Aug 16;76(2):343–346. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(74)90466-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saez J. C., Spray D. C., Nairn A. C., Hertzberg E., Greengard P., Bennett M. V. cAMP increases junctional conductance and stimulates phosphorylation of the 27-kDa principal gap junction polypeptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2473–2477. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somogyi R., Kolb H. A. Cell-to-cell channel conductance during loss of gap junctional coupling in pairs of pancreatic acinar and Chinese hamster ovary cells. Pflugers Arch. 1988 Jul;412(1-2):54–65. doi: 10.1007/BF00583731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spray D. C., Bennett M. V. Physiology and pharmacology of gap junctions. Annu Rev Physiol. 1985;47:281–303. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.47.030185.001433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spray D. C., Saez J. C., Brosius D., Bennett M. V., Hertzberg E. L. Isolated liver gap junctions: gating of transjunctional currents is similar to that in intact pairs of rat hepatocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(15):5494–5497. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.15.5494. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spray D. C., White R. L., de Carvalho A. C., Harris A. L., Bennett M. V. Gating of gap junction channels. Biophys J. 1984 Jan;45(1):219–230. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84150-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turin L., Warner A. E. Intracellular pH in early Xenopus embryos: its effect on current flow between blastomeres. J Physiol. 1980 Mar;300:489–504. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veenstra R. D., DeHaan R. L. Measurement of single channel currents from cardiac gap junctions. Science. 1986 Aug 29;233(4767):972–974. doi: 10.1126/science.2426781. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verselis V., Brink P. R. Voltage clamp of the earthworm septum. Biophys J. 1984 Jan;45(1):147–150. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84143-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weingart R. Electrical properties of the nexal membrane studied in rat ventricular cell pairs. J Physiol. 1986 Jan;370:267–284. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp015934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weingart R. The permeability to tetraethylammonium ions of the surface membrane and the intercalated disks of sheep and calf myocardium. J Physiol. 1974 Aug;240(3):741–762. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young J. D., Cohn Z. A., Gilula N. B. Functional assembly of gap junction conductance in lipid bilayers: demonstration that the major 27 kd protein forms the junctional channel. Cell. 1987 Mar 13;48(5):733–743. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90071-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



