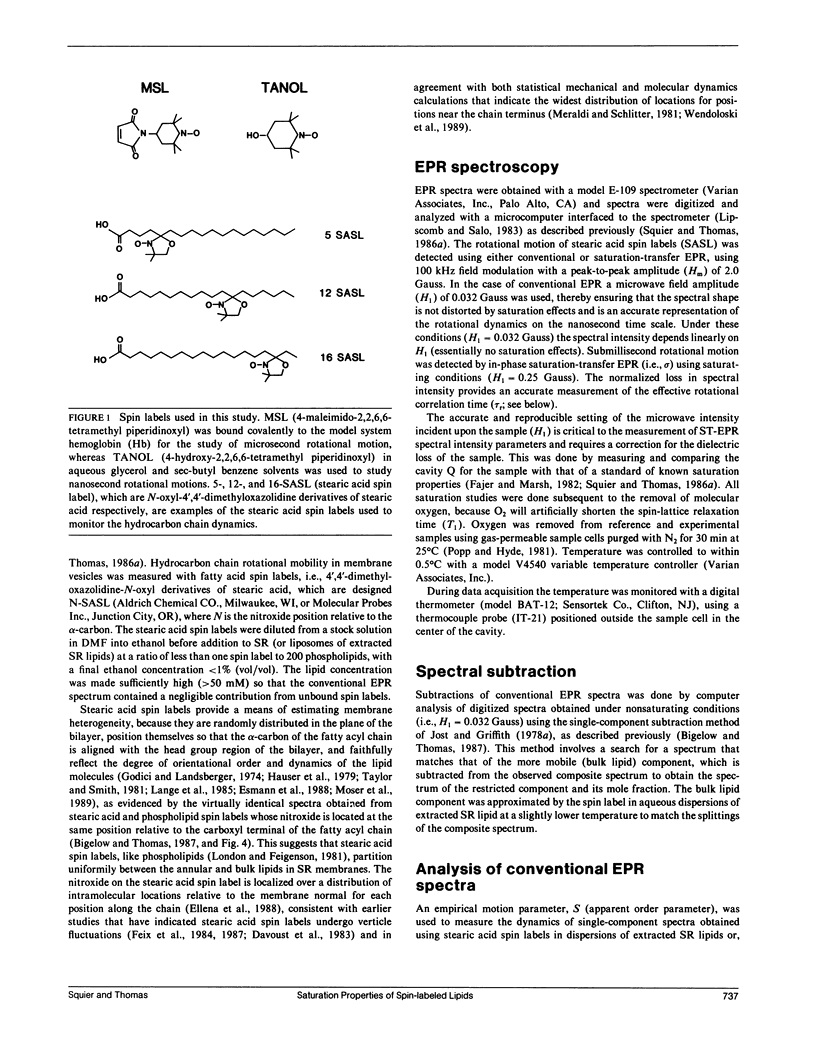
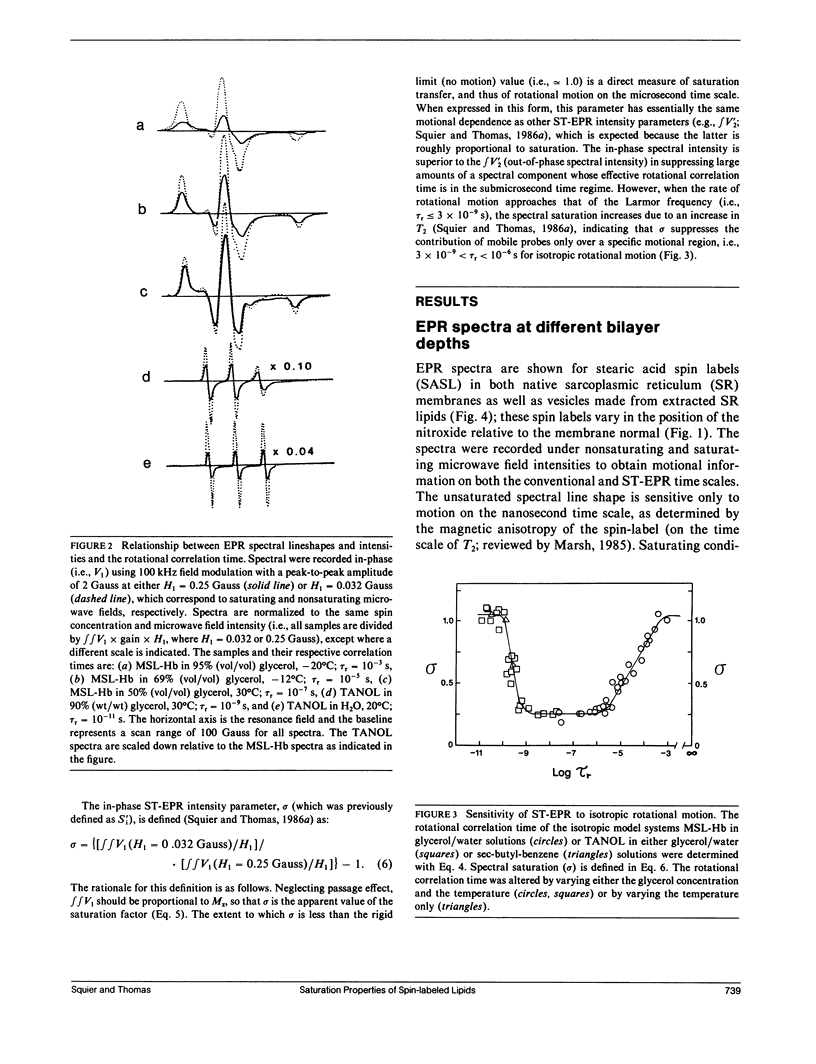
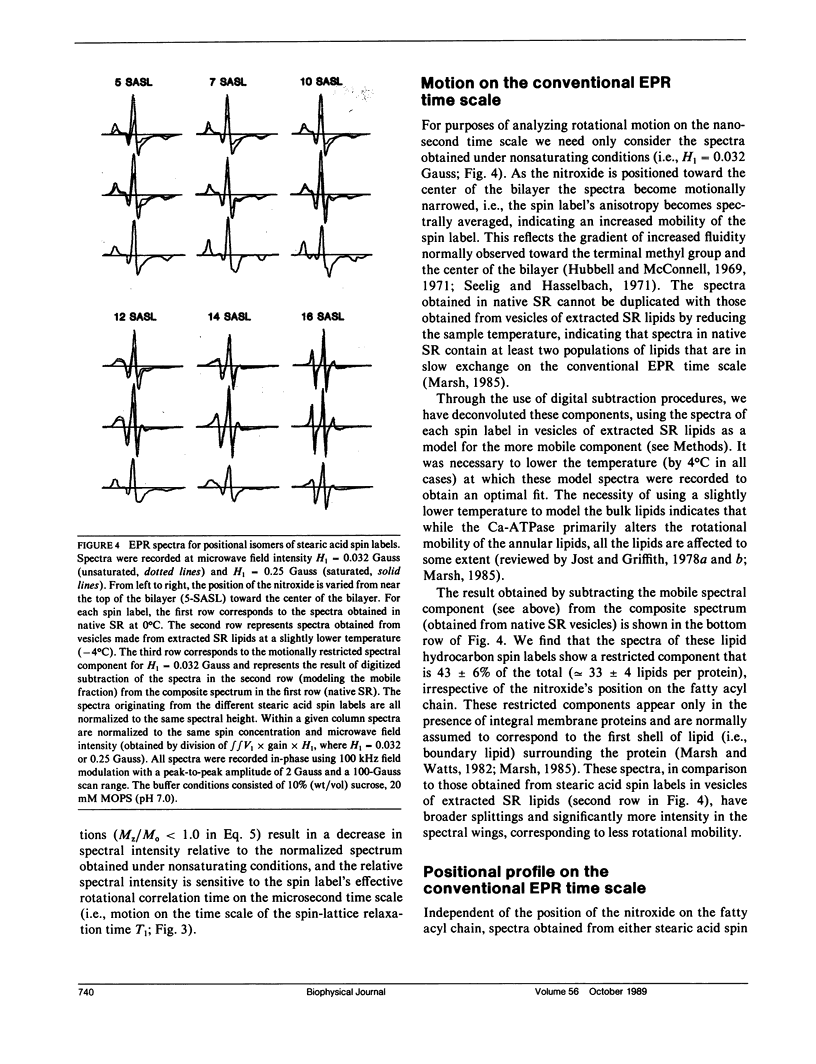
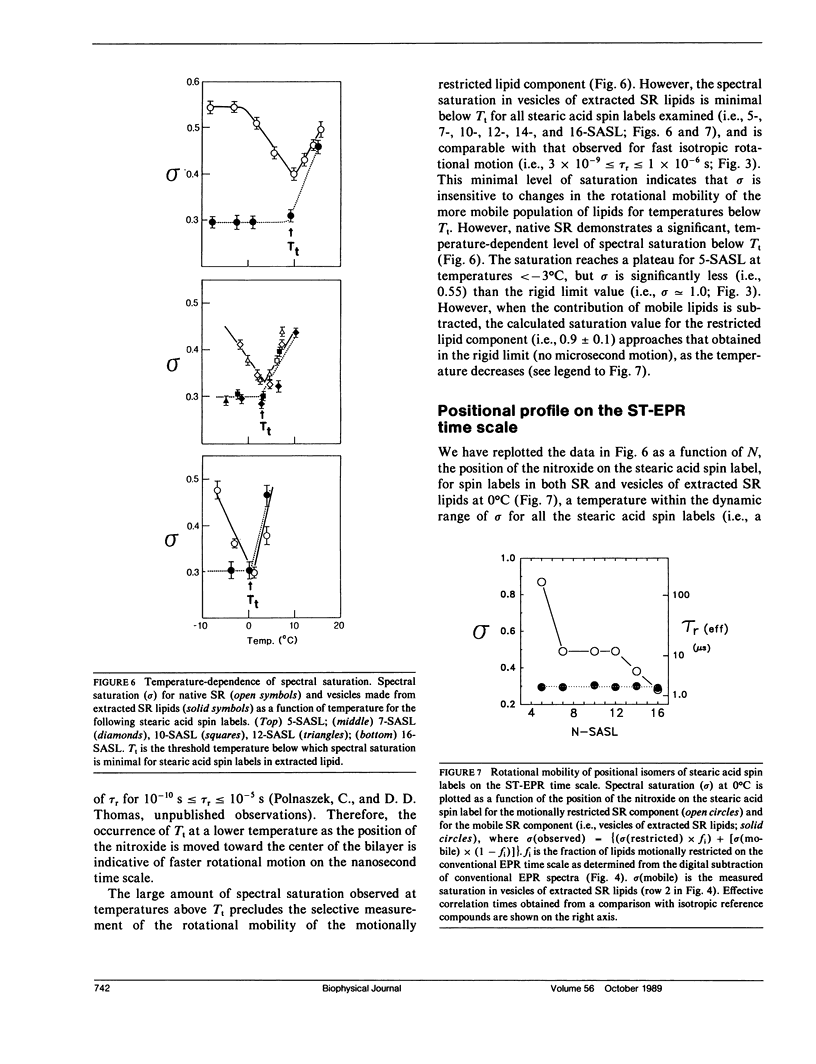
Abstract
We have developed a saturation transfer EPR (ST-EPR) method to measure selectively the rotational dynamics of those lipids that are motionally restricted by integral membrane proteins and have applied this methodology to measure lipid-protein interactions in native sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) membranes. This analysis involves the measurement of spectral saturation using a series of six stearic acid spin labels that are labeled with a nitroxide at different carbon atom positions. A large amount of spectral saturation is observed for spin labels in native SR membranes, but not for spin labels in dispersions of extracted SR lipids, implying that the motional properties of those lipids interacting with the Ca-ATPase, i.e., the boundary or annular lipid, can be directly measured without the need for spectral subtraction procedures. A comparison of the motional properties of the restricted lipid, measured by ST-EPR, with those measured by digital subtraction of conventional EPR spectra qualitatively agree, for in both cases the Ca-ATPase restricts the rotational mobility of a population of lipids, whose rotational mobility increases as the nitroxide is positioned toward the center of the bilayer. However, the ability of ST-EPR to directly measure the motionally restricted lipid in a model-independent means provides the greater precision necessary to measure small changes in the rotational dynamics of the lipid at the protein-lipid interface, providing a valuable tool in clarifying the relationship between the physical nature of the protein-lipid interface and membrane function.
Full text
PDF









Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Almeida L. M., Vaz W. L., Zachariasse K. A., Madeira V. M. Fluidity of sarcoplasmic reticulum membranes investigated with dipyrenylpropane, an intramolecular excimer probe. Biochemistry. 1982 Nov 9;21(23):5972–5977. doi: 10.1021/bi00266a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bigelow D. J., Squier T. C., Thomas D. D. Temperature dependence of rotational dynamics of protein and lipid in sarcoplasmic reticulum membranes. Biochemistry. 1986 Jan 14;25(1):194–202. doi: 10.1021/bi00349a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bigelow D. J., Thomas D. D. Rotational dynamics of lipid and the Ca-ATPase in sarcoplasmic reticulum. The molecular basis of activation by diethyl ether. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 5;262(28):13449–13456. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carruthers A., Melchior D. L. Effects of lipid environment on membrane transport: the human erythrocyte sugar transport protein/lipid bilayer system. Annu Rev Physiol. 1988;50:257–271. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.50.030188.001353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis D. G., Inesi G., Gulik-Krzywicki T. Lipid molecular motion and enzyme activity in sarcoplasmic reticulum membrane. Biochemistry. 1976 Mar 23;15(6):1271–1276. doi: 10.1021/bi00651a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davoust J., Seigneuret M., Hervé P., Devaux P. F. Collisions between nitrogen-14 and nitrogen-15 spin-labels. 2. Investigations on the specificity of the lipid environment of rhodopsin. Biochemistry. 1983 Jun 21;22(13):3146–3151. doi: 10.1021/bi00282a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delmelle M., Butler K. W., Smith I. C. Saturation transfer electron spin resonance spectroscopy as a probe of anisotropic motion in model membrane systems. Biochemistry. 1980 Feb 19;19(4):698–704. doi: 10.1021/bi00545a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deuticke B., Haest C. W. Lipid modulation of transport proteins in vertebrate cell membranes. Annu Rev Physiol. 1987;49:221–235. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.49.030187.001253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- East J. M., Melville D., Lee A. G. Exchange rates and numbers of annular lipids for the calcium and magnesium ion dependent adenosinetriphosphatase. Biochemistry. 1985 May 21;24(11):2615–2623. doi: 10.1021/bi00332a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellena J. F., Archer S. J., Dominey R. N., Hill B. D., Cafiso D. S. Localizing the nitroxide group of fatty acid and voltage-sensitive spin-labels in phospholipid bilayers. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 May 9;940(1):63–70. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(88)90008-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellena J. F., Pates R. D., Brown M. F. 31P NMR spectra of rod outer segment and sarcoplasmic reticulum membranes show no evidence of immobilized components due to lipid-protein interactions. Biochemistry. 1986 Jul 1;25(13):3742–3748. doi: 10.1021/bi00361a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esmann M., Hideg K., Marsh D. Novel spin-labels for the study of lipid-protein interactions. Application to (Na+, K+)-ATPase membranes. Biochemistry. 1988 May 31;27(11):3913–3917. doi: 10.1021/bi00411a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evers A. S., Berkowitz B. A., d'Avignon D. A. Correlation between the anaesthetic effect of halothane and saturable binding in brain. Nature. 1987 Jul 9;328(6126):157–160. doi: 10.1038/328157a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLCH J., LEES M., SLOANE STANLEY G. H. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J Biol Chem. 1957 May;226(1):497–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fajer P., Thomas D. D., Feix J. B., Hyde J. S. Measurement of rotational molecular motion by time-resolved saturation transfer electron paramagnetic resonance. Biophys J. 1986 Dec;50(6):1195–1202. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(86)83562-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feix J. B., Popp C. A., Venkataramu S. D., Beth A. H., Park J. H., Hyde J. S. An electron-electron double-resonance study of interactions between [14N]- and [15N]stearic acid spin-label pairs: lateral diffusion and vertical fluctuations in dimyristoylphosphatidylcholine. Biochemistry. 1984 May 8;23(10):2293–2299. doi: 10.1021/bi00305a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feix J. B., Yin J. J., Hyde J. S. Interactions of 14N:15N stearic acid spin-label pairs: effects of host lipid alkyl chain length and unsaturation. Biochemistry. 1987 Jun 30;26(13):3850–3855. doi: 10.1021/bi00387a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez J. L., Rosemblatt M., Hidalgo C. Highly purified sarcoplasmic reticulum vesicles are devoid of Ca2+-independent ('basal') ATPase activity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Jul;599(2):552–568. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90199-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fong T. M., McNamee M. G. Stabilization of acetylcholine receptor secondary structure by cholesterol and negatively charged phospholipids in membranes. Biochemistry. 1987 Jun 30;26(13):3871–3880. doi: 10.1021/bi00387a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franks N. P., Lieb W. R. Neuron membranes: anaesthetics on the mind. Nature. 1987 Jul 9;328(6126):113–114. doi: 10.1038/328113a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godici P. E., Landsberger F. R. The dynamic structure of lipid membranes. A 13C nuclear magnetic resonance study using spin labels. Biochemistry. 1974 Jan 15;13(2):362–368. doi: 10.1021/bi00699a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauser H., Guyer W., Howell K. Lateral distribution of negatively charged lipids in lecithin membranes. Clustering of fatty acids. Biochemistry. 1979 Jul 24;18(15):3285–3291. doi: 10.1021/bi00582a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hidalgo C., Ikemoto N., Gergely J. Role of phospholipids in the calcium-dependent ATPase of the sarcoplasmic reticulum. Enzymatic and ESR studies with phospholipid-replaced membranes. J Biol Chem. 1976 Jul 25;251(14):4224–4232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hidalgo C. Lipid-protein interactions and the function of the Ca2+-ATPase of sarcoplasmic reticulum. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1987;21(4):319–347. doi: 10.3109/10409238609113615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horváth L. I., Brophy P. J., Marsh D. Exchange rates at the lipid-protein interface of myelin proteolipid protein studied by spin-label electron spin resonance. Biochemistry. 1988 Jan 12;27(1):46–52. doi: 10.1021/bi00401a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horváth L. I., Brophy P. J., Marsh D. Influence of lipid headgroup on the specificity and exchange dynamics in lipid-protein interactions. A spin-label study of myelin proteolipid apoprotein-phospholipid complexes. Biochemistry. 1988 Jul 12;27(14):5296–5304. doi: 10.1021/bi00414a052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbell W. L., McConnell H. M. Molecular motion in spin-labeled phospholipids and membranes. J Am Chem Soc. 1971 Jan 27;93(2):314–326. doi: 10.1021/ja00731a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbell W. L., McConnell H. M. Orientation and motion of amphiphilic spin labels in membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Sep;64(1):20–27. doi: 10.1073/pnas.64.1.20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyde J. S. Saturation-transfer spectroscopy. Methods Enzymol. 1978;49:480–511. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(78)49021-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyde J. S., Thomas D. D. New EPR methods for the study of very slow motion: application to spin-labeled hemoglobin. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1973 Dec 31;222:680–692. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1973.tb15295.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson M. E., Lee L., Fung L. W. Models for slow anisotropic rotational diffusion in saturation transfer electron paramagnetic resonance at 9 and 35 GHz. Biochemistry. 1982 Aug 31;21(18):4459–4467. doi: 10.1021/bi00261a041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jost P. C., Griffith O. H., Capaldi R. A., Vanderkooi G. Evidence for boundary lipid in membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Feb;70(2):480–484. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.2.480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jost P. C., Griffith O. H. The spin-labeling technique. Methods Enzymol. 1978;49:369–418. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(78)49019-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jost P., Griffith O. H., Capaldi R. A., Vanderkooi G. Identification and extent of fluid bilayer regions in membranous cytochrome oxidase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Jun 22;311(2):141–152. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90261-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jähnig F. Structural order of lipids and proteins in membranes: evaluation of fluorescence anisotropy data. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6361–6365. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jähnig F., Vogel H., Best L. Unifying description of the effect of membrane proteins on lipid order. Verification for the melittin/dimyristoylphosphatidylcholine system. Biochemistry. 1982 Dec 21;21(26):6790–6798. doi: 10.1021/bi00269a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles P. F., Watts A., Marsh D. Spin-label studies of lipid immobilization in dimyristoylphosphatidylcholine-substituted cytochrome oxidase. Biochemistry. 1979 Oct 16;18(21):4480–4487. doi: 10.1021/bi00588a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lange A., Marsh D., Wassmer K. H., Meier P., Kothe G. Electron spin resonance study of phospholipid membranes employing a comprehensive line-shape model. Biochemistry. 1985 Jul 30;24(16):4383–4392. doi: 10.1021/bi00337a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanzetta P. A., Alvarez L. J., Reinach P. S., Candia O. A. An improved assay for nanomole amounts of inorganic phosphate. Anal Biochem. 1979 Nov 15;100(1):95–97. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90115-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- London E., Feigenson G. W. Fluorescence quenching in model membranes. 2. Determination of local lipid environment of the calcium adenosinetriphosphatase from sarcoplasmic reticulum. Biochemistry. 1981 Mar 31;20(7):1939–1948. doi: 10.1021/bi00510a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh D. Electron spin resonance: spin labels. Mol Biol Biochem Biophys. 1981;31:51–142. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-81537-9_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh D. Molecular motion in phospholipid bilayers in the gel phase: long axis rotation. Biochemistry. 1980 Apr 15;19(8):1632–1637. doi: 10.1021/bi00549a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh D. Selectivity of lipid-protein interactions. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 1987 Dec;19(6):677–689. doi: 10.1007/BF00762302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh D., Watts A., Barrantes F. J. Phospholipid chain immobilization and steroid rotational immobilization in acetylcholine receptor-rich membranes from Torpedo marmorata. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Jul 6;645(1):97–101. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(81)90516-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh D., Watts A. Molecular motion in phospholipid bilayers in the gel phase: spin label saturation transfer ESR studies. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 May 14;94(1):130–137. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(80)80197-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martonosi M. A. Thermal analysis of sarcoplasmic reticulum membranes. FEBS Lett. 1974 Oct 15;47(2):327–329. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)81040-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meraldi J. P., Schlitter J. A statistical mechanical treatment of fatty acyl chain order in phospholipid bilayers and correlation with experimental data. B. Dipalmitoyl-3-sn-phosphatidylcholine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Jul 20;645(2):193–210. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(81)90190-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore B. M., Lentz B. R., Meissner G. Effects of sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase on phospholipid bilayer fluidity: boundary lipid. Biochemistry. 1978 Nov 28;17(24):5248–5255. doi: 10.1021/bi00617a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moser M., Marsh D., Meier P., Wassmer K. H., Kothe G. Chain configuration and flexibility gradient in phospholipid membranes. Comparison between spin-label electron spin resonance and deuteron nuclear magnetic resonance, and identification of new conformations. Biophys J. 1989 Jan;55(1):111–123. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(89)82784-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owicki J. C., McConnell H. M. Theory of protein-lipid and protein-protein interactions in bilayer membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):4750–4754. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.4750. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owicki J. C., Springgate M. W., McConnell H. M. Theoretical study of protein--lipid interactions in bilayer membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Apr;75(4):1616–1619. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.4.1616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paddy M. R., Dahlquist F. W., Davis J. H., Bloom M. Dynamical and temperature-dependent effects of lipid-protein interactions. Application of deuterium nuclear magnetic resonance and electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy to the same reconstitutions of cytochrome c oxidase. Biochemistry. 1981 May 26;20(11):3152–3162. doi: 10.1021/bi00514a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pates R. D., Marsh D. Lipid mobility and order in bovine rod outer segment disk membranes. A spin-label study of lipid-protein interactions. Biochemistry. 1987 Jan 13;26(1):29–39. doi: 10.1021/bi00375a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pates R. D., Watts A., Uhl R., Marsh D. Lipid-protein interactions in frog rod outer segment disc membranes. Characterization by spin labels. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Apr 11;814(2):389–397. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(85)90460-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson L. T., Edelman J., Chan S. I. Statistical mechanics of lipid membranes. Protein correlation functions and lipid ordering. Biophys J. 1984 May;45(5):863–871. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84232-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice D. M., Meadows M. D., Scheinman A. O., Goñi F. M., Gómez-Fernández J. C., Moscarello M. A., Chapman D., Oldfield E. Protein-lipid interactions. A nuclear magnetic resonance study of sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2,Mg2+-ATPase, lipophilin, and proteolipid apoprotein-lecithin systems and a comparison with the effects of cholesterol. Biochemistry. 1979 Dec 25;18(26):5893–5903. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seelig A., Seelig J. The dynamic structure of fatty acyl chains in a phospholipid bilayer measured by deuterium magnetic resonance. Biochemistry. 1974 Nov 5;13(23):4839–4845. doi: 10.1021/bi00720a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seelig J., Hasselbach W. A spin label study of sarcoplasmic vesicles. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Jul 15;21(1):17–21. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01434.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seelig J., Tamm L., Hymel L., Fleischer S. Deuterium and phosphorus nuclear magnetic resonance and fluorescence depolarization studies of functional reconstituted sarcoplasmic reticulum membrane vesicles. Biochemistry. 1981 Jun 23;20(13):3922–3932. doi: 10.1021/bi00516a040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selinsky B. S., Yeagle P. L. Two populations of phospholipids exist in sarcoplasmic reticulum and in recombined membranes containing Ca-ATPase. Biochemistry. 1984 May 8;23(10):2281–2288. doi: 10.1021/bi00305a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silvius J. R., McMillen D. A., Saley N. D., Jost P. C., Griffith O. H. Competition between cholesterol and phosphatidylcholine for the hydrophobic surface of sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase. Biochemistry. 1984 Jan 31;23(3):538–547. doi: 10.1021/bi00298a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinensky M., Pinkerton F., Sutherland E., Simon F. R. Rate limitation of (Na+ + K+)-stimulated adenosinetriphosphatase by membrane acyl chain ordering. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):4893–4897. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.4893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Squier T. C., Bigelow D. J., Thomas D. D. Lipid fluidity directly modulates the overall protein rotational mobility of the Ca-ATPase in sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 5;263(19):9178–9186. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Squier T. C., Hughes S. E., Thomas D. D. Rotational dynamics and protein-protein interactions in the Ca-ATPase mechanism. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 5;263(19):9162–9170. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Squier T. C., Thomas D. D. Applications of new saturation transfer electron paramagnetic resonance methodology to the rotational dynamics of the Ca-ATPase in sarcoplasmic reticulum membranes. Biophys J. 1986 Apr;49(4):937–942. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(86)83721-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Squier T. C., Thomas D. D. Methodology for increased precision in saturation transfer electron paramagnetic resonance studies of rotational dynamics. Biophys J. 1986 Apr;49(4):921–935. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(86)83720-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Squier T. C., Thomas D. D. Relationship between protein rotational dynamics and phosphoenzyme decomposition in the sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca-ATPase. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 5;263(19):9171–9177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor M. G., Smith I. C. Reliability of nitroxide spin probes in reporting membrane properties: a comparison of nitroxide- and deuterium-labeled steroids. Biochemistry. 1981 Sep 1;20(18):5252–5255. doi: 10.1021/bi00521a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas D. D., Bigelow D. J., Squier T. C., Hidalgo C. Rotational dynamics of protein and boundary lipid in sarcoplasmic reticulum membrane. Biophys J. 1982 Jan;37(1):217–225. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(82)84671-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas D. D., Hidalgo C. Rotational motion of the sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5488–5492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watts A., Marsh D. Saturation transfer ESR studies of molecular motion in phosphatidylglycerol bilayers in the gel phase: effects of pretransitions and pH titration. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Apr 6;642(2):231–241. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(81)90442-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watts A. Protein-lipid interactions: do the spectroscopists now agree? Nature. 1981 Dec 10;294(5841):512–513. doi: 10.1038/294512a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wendoloski J. J., Kimatian S. J., Schutt C. E., Salemme F. R. Molecular dynamics simulation of a phospholipid micelle. Science. 1989 Feb 3;243(4891):636–638. doi: 10.1126/science.2916118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeagle P. L., Selinsky B. S., Albert A. D. Perturbations of phospholipid head groups by membrane proteins in biological membranes and recombinants. Biophys J. 1984 Jun;45(6):1085–1089. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84256-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


