Abstract
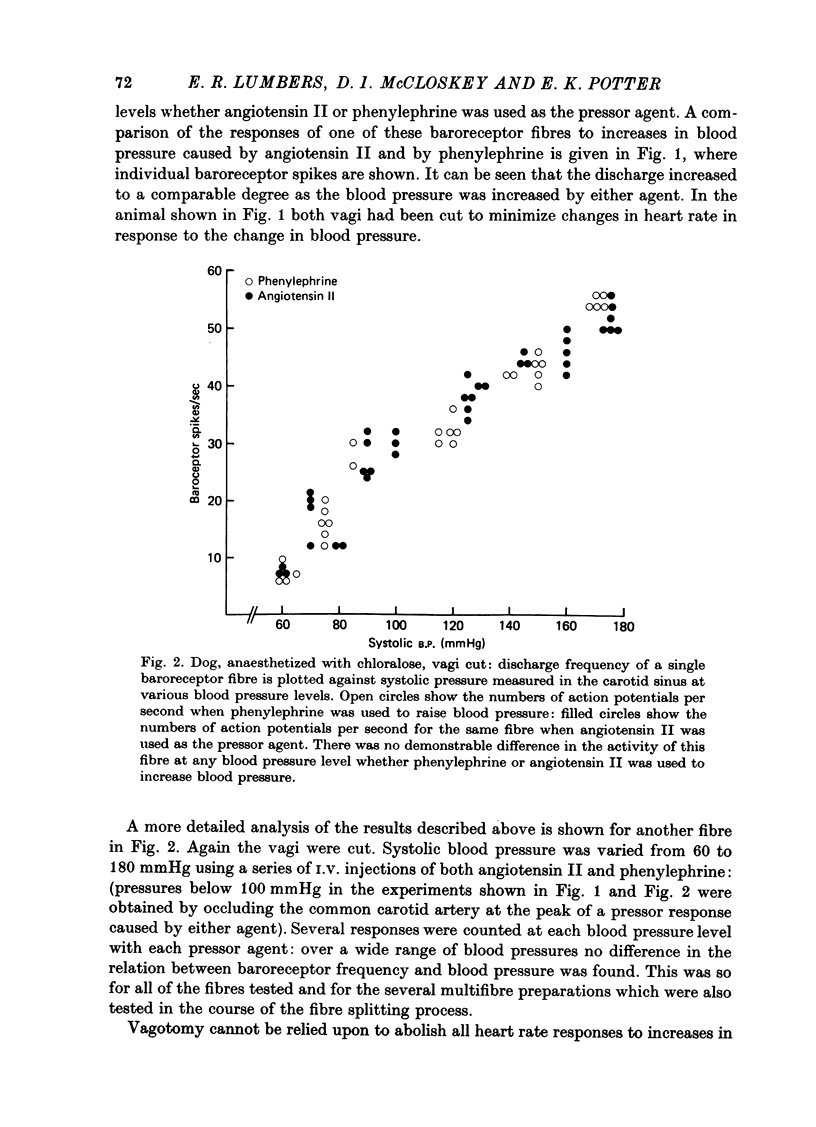
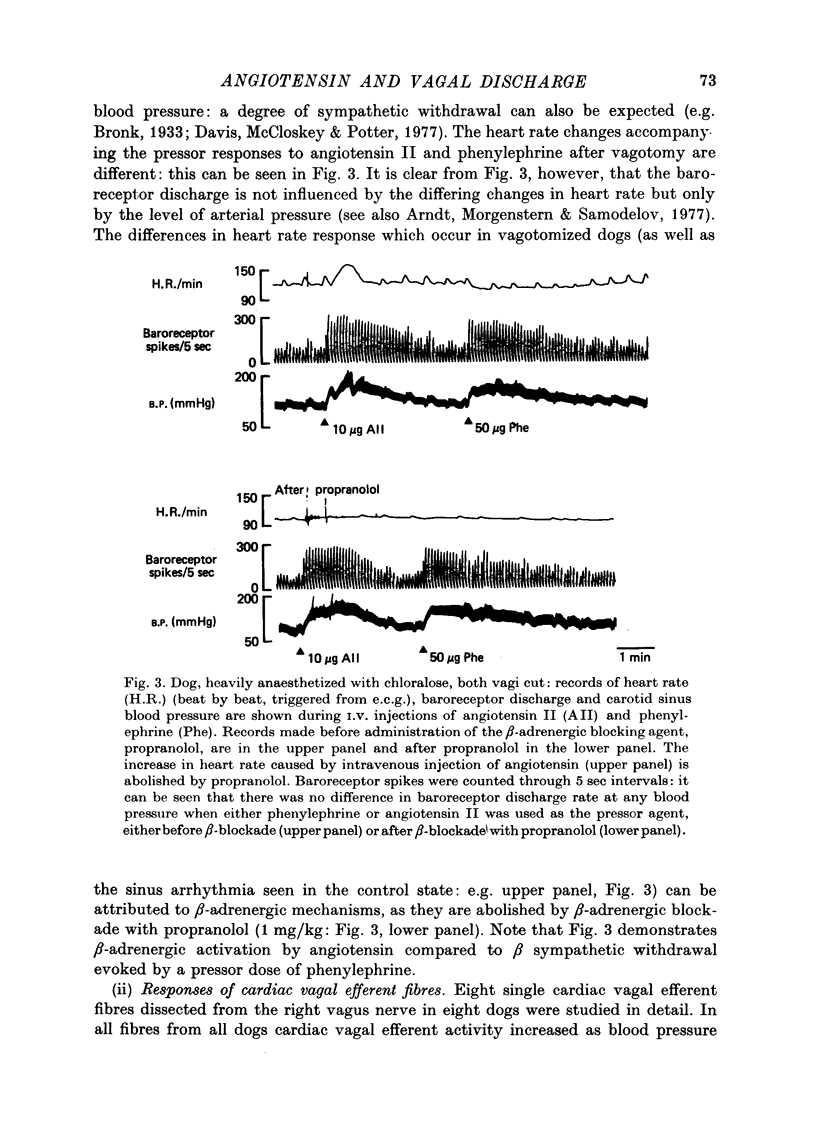
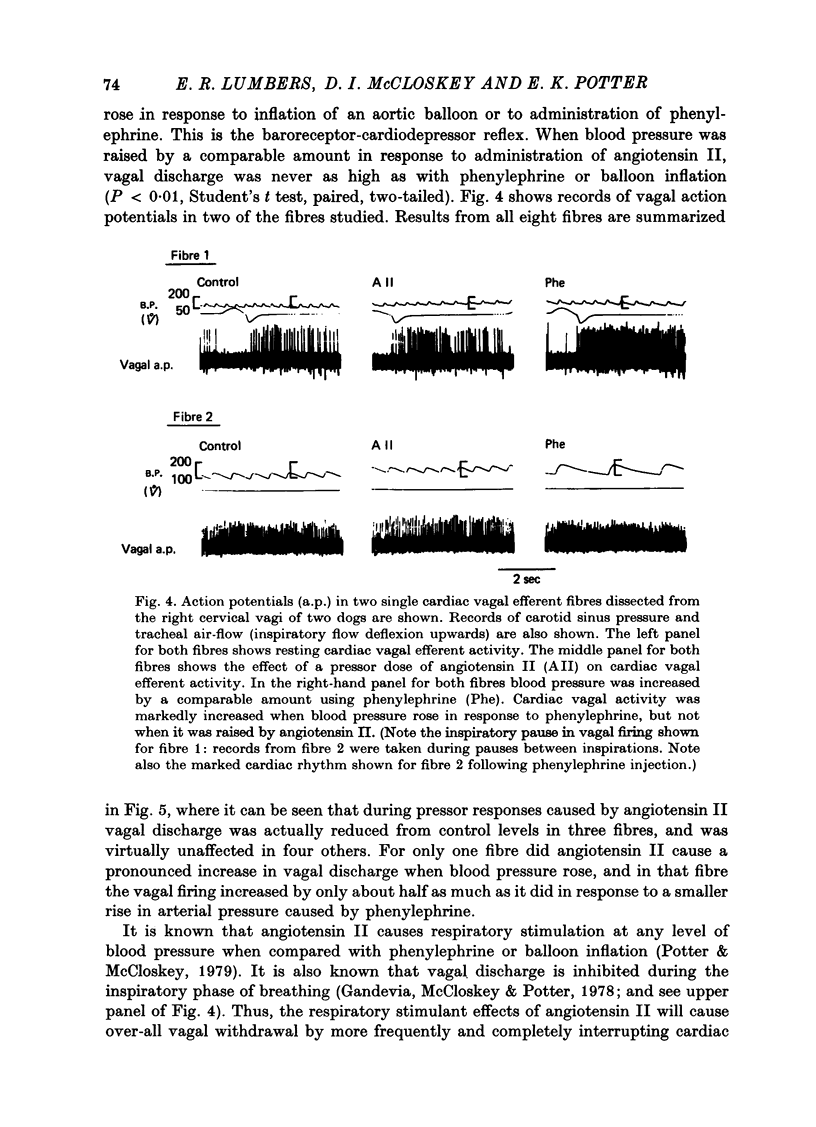
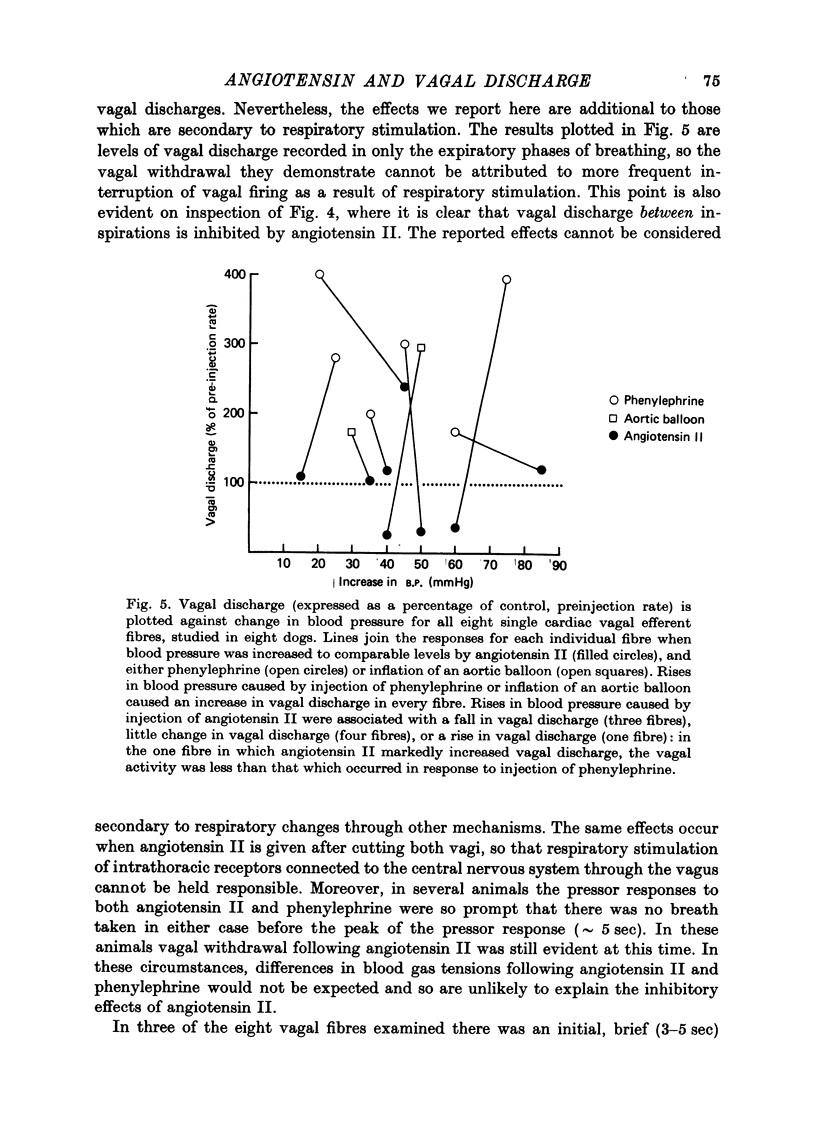
1. Action potentials were recorded in single baroreceptor fibres dissected from the carotid sinus nerves in dogs during increases in blood pressure caused by I.V. injection of angiotensin II, and by I.V. injection of phenylephrine or inflation of an aortic balloon. Action potentials were recorded in single cardiac efferent fibres dissected from the right cervical vagus nerve in other dogs during increases in blood pressure caused by angiotensin II, and by phenylephrine or by inflation of an aortic balloon. 2. There was no difference in the discharge frequency of single carotid sinus baroreceptor fibres at any blood pressure when phenylephrine, balloon inflation, or angiotensin II were used to raise the pressure. 3. Activity in single cardiac vagal efferent fibres was increased when blood pressure was increased by phenylephrine or by inflation of an aortic balloon. However, when blood pressure rose by a comparable amount in response to angiotensin II, vagal firing decreased (three fibres), was little changed from control levels (four fibres), or increased less than it did in response to phenylephrine (one fibre). 4. It is concluded that while angiotensin II has no effect on baroreceptor sensitivity, it does inhibit vagal discharge which is evoked by stimulation of arterial baroreceptors.
Full text
PDF


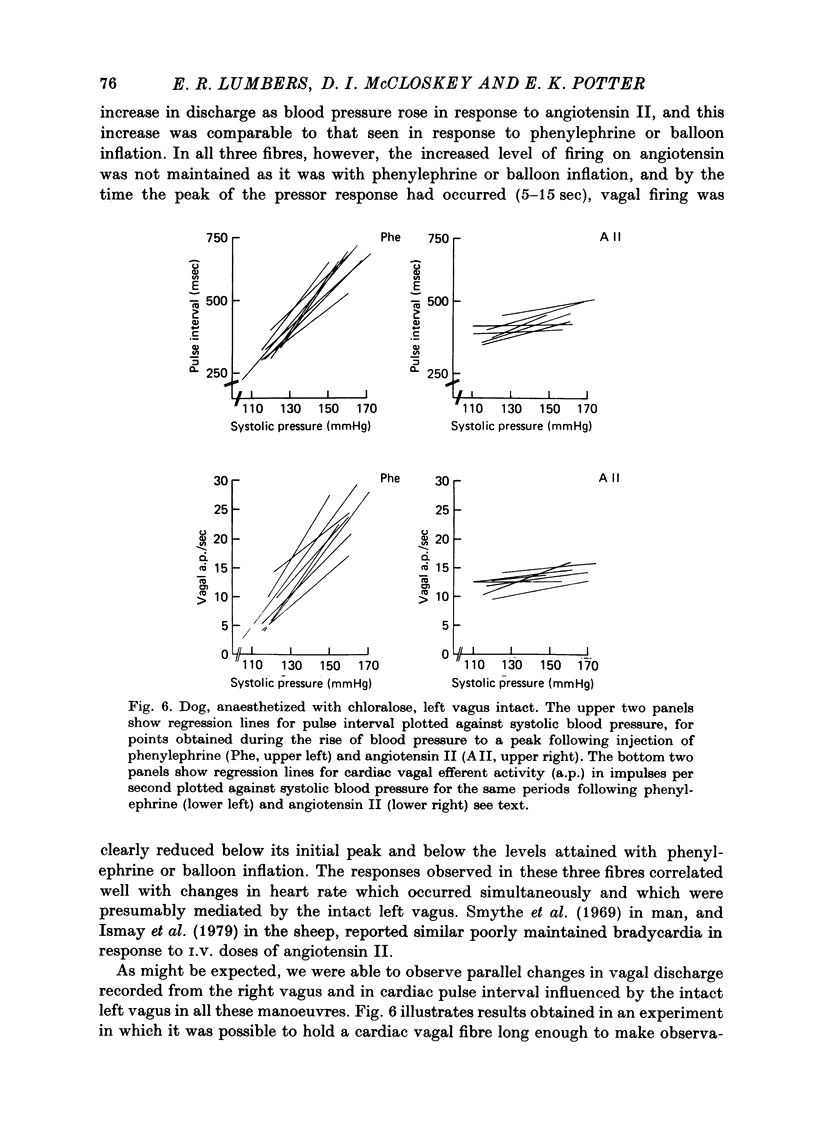



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arndt J. O., Morgenstern J., Samodelov L. The physiologically relevant information regarding systemic blood pressure encoded in the carotid sinus baroreceptor discharge pattern. J Physiol. 1977 Jul;268(3):775–791. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd G. W., Landon J., Peart W. S. Radioimmunoassay for determining plasms-levels of angiotensin II in man. Lancet. 1967 Nov 11;2(7524):1002–1005. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(67)90284-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bristow J. D., Brown E. B., Jr, Cunningham D. J., Goode R. C., Howson M. G., Sleight P. The effects of hypercapnia, hypoxia and ventilation on the baroreflex regulation of the pulse interval. J Physiol. 1971 Jul;216(2):281–302. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis A. L., McCloskey D. I., Potter E. K. Respiratory modulation of baroreceptor and chemoreceptor reflexes affecting heart rate through the sympathetic nervous system. J Physiol. 1977 Nov;272(3):691–703. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp012067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gandevia S. C., McCloskey D. I., Potter E. K. Inhibition of baroreceptor and chemoreceptor reflexes on heart rate by afferents from the lungs. J Physiol. 1978 Mar;276:369–381. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodge R. L., Ng K. K., Vane J. R. Disappearance of angiotensin from the circulation of the dog. Nature. 1967 Jul 8;215(5097):138–141. doi: 10.1038/215138a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- IRIUCHIJIMA J., KUMADA M. ACTIVITY OF SINGLE VAGAL FIBERS EFFERENT TO THE HEART. Jpn J Physiol. 1964 Oct 15;14:479–487. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.14.479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ismay M. J., Lumbers E. R., Stevens A. D. The action of angiotensin II on the baroreflex response of the conscious ewe and the conscious fetus. J Physiol. 1979 Mar;288:467–479. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JEWETT D. L. ACTIVITY OF SINGLE EFFERENT FIBRES IN THE CERVICAL VAGUS NERVE OF THE DOG, WITH SPECIAL REFERENCE TO POSSIBLE CARDIO-INHIBITORY FIBRES. J Physiol. 1964 Dec;175:321–357. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1964.sp007520. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
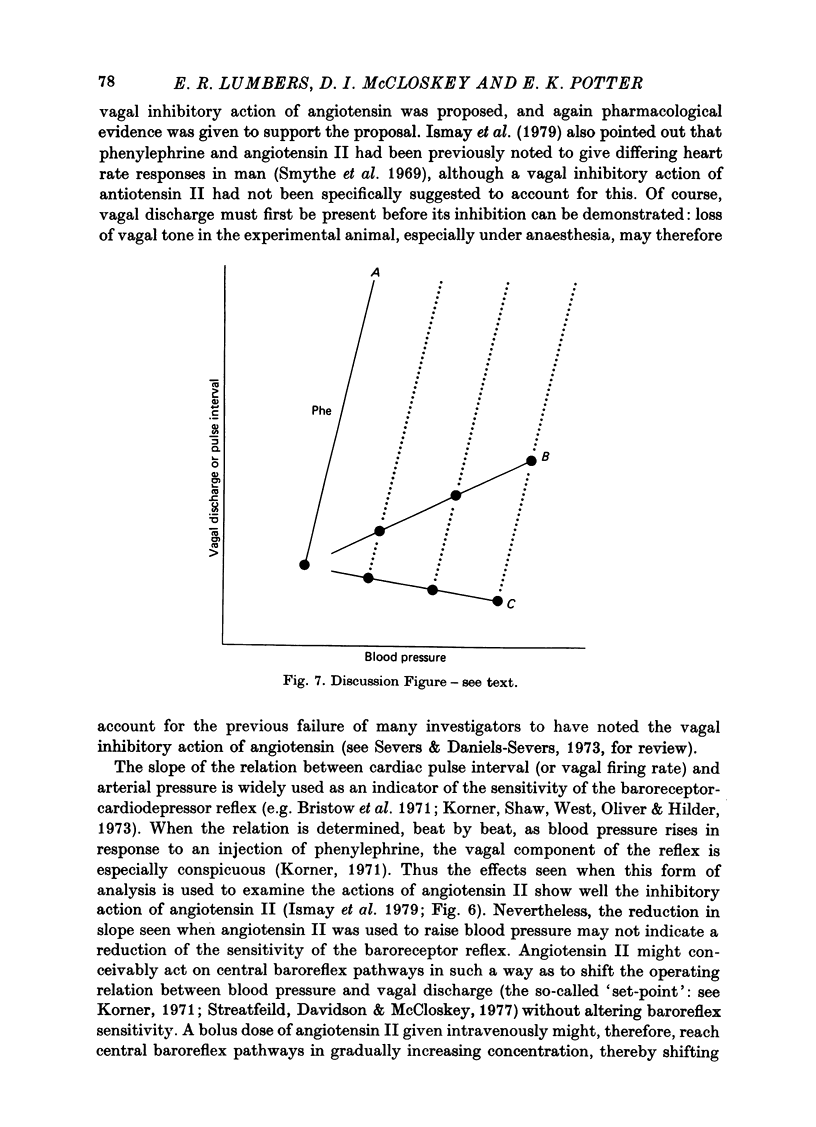
- Korner P. I. Integrative neural cardiovascular control. Physiol Rev. 1971 Apr;51(2):312–367. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1971.51.2.312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korner P. I., Shaw J., West M. J., Oliver J. R., Hilder R. G. Integrative reflex control of heart rate in the rabbit during hypoxia and hyperventilation. Circ Res. 1973 Jul;33(1):63–73. doi: 10.1161/01.res.33.1.63. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lumbers E. R., Reid G. C. Effects of vaginal delivery and caesarian section on plasma renin activity and angiotensin II levels in human umbilical cord blood. Biol Neonate. 1977;31(1-2):127–133. doi: 10.1159/000240953. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCCUBBIN J. W., PAGE I. H., BUMPUS F. M. Effect of synthetic angiotonin on the carotid sinus. Circ Res. 1957 Jul;5(4):458–460. doi: 10.1161/01.res.5.4.458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter E. K., McCloskey D. I. Respiratory stimulation by angiotensin II. Respir Physiol. 1979 Apr;36(3):367–373. doi: 10.1016/0034-5687(79)90048-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scroop G. C., Lowe R. D. Efferent pathways of the cardiovascular response to vertebral artery infusions of angiotensin in the dog. Clin Sci. 1969 Dec;37(3):605–619. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Severs W. B., Daniels-Severs A. E. Effects of angiotensin on the central nervous system. Pharmacol Rev. 1973 Sep;25(3):415–449. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smyth H. S., Sleight P., Pickering G. W. Reflex regulation of arterial pressure during sleep in man. A quantitative method of assessing baroreflex sensitivity. Circ Res. 1969 Jan;24(1):109–121. doi: 10.1161/01.res.24.1.109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streatfeild K. A., Davidson N. S., McCloskey D. I. Muscular reflex and baroreflex influences on heart rate during isometric contractions. Cardiovasc Res. 1977 Mar;11(2):87–93. doi: 10.1093/cvr/11.2.87. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweet C. S., Brody M. J. Central inhibition of reflex vasodilatation by angiotensin and reduced renal pressure. Am J Physiol. 1970 Dec;219(6):1751–1758. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1970.219.6.1751. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VARMA S., JOHNSEN S. D., SHERMAN D. E., YOUMANS W. B. Mechanisms of inhibition of heart rate by phenylephrine. Circ Res. 1960 Nov;8:1182–1186. doi: 10.1161/01.res.8.6.1182. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


