Abstract
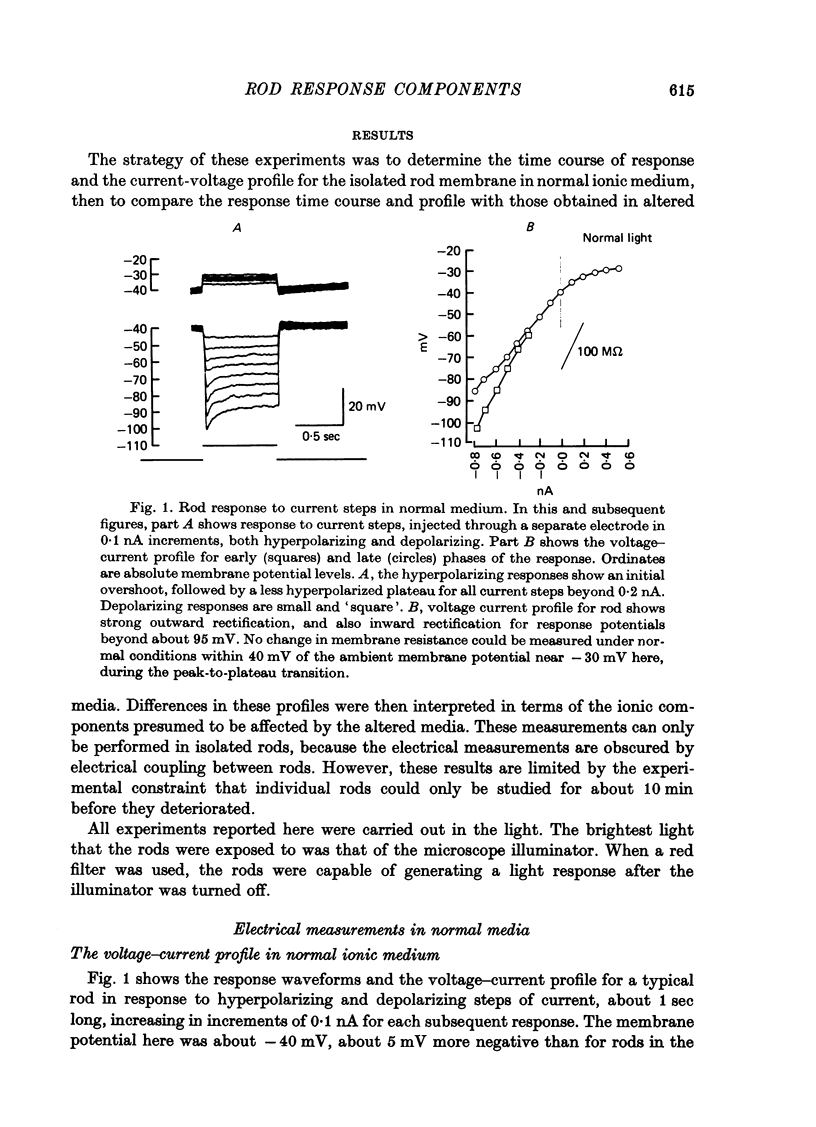
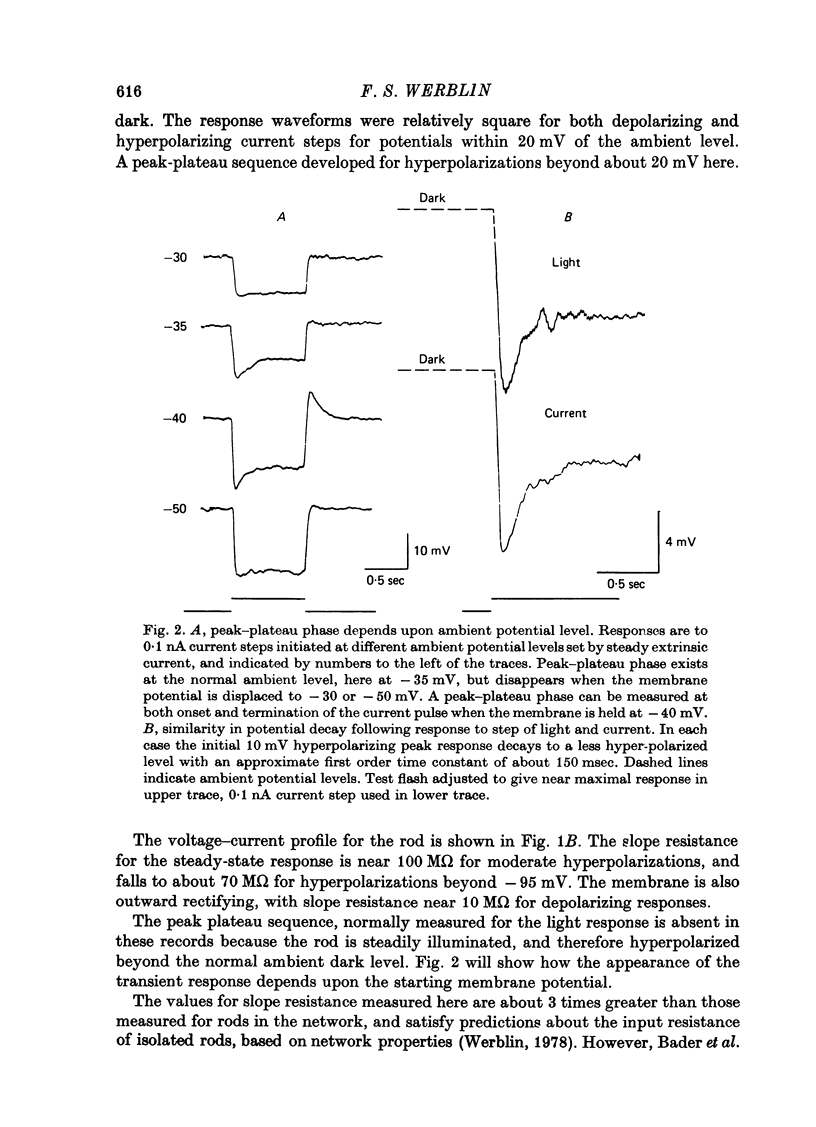
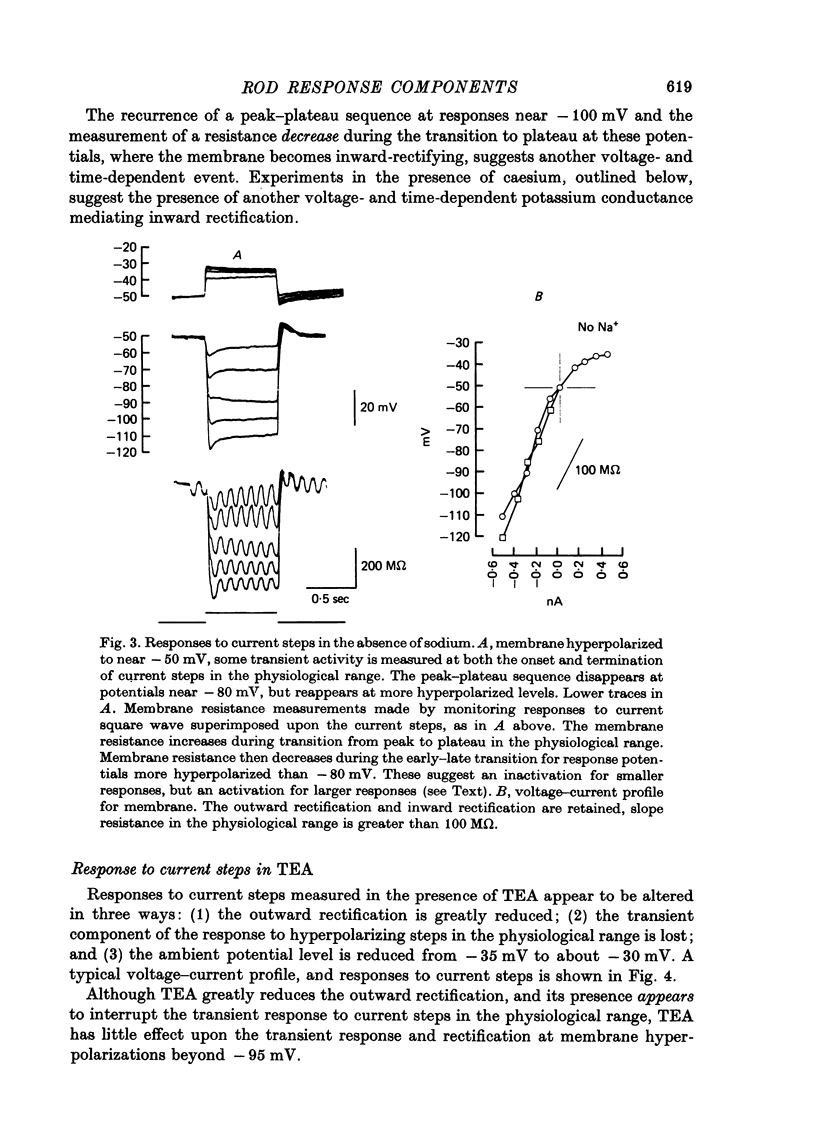
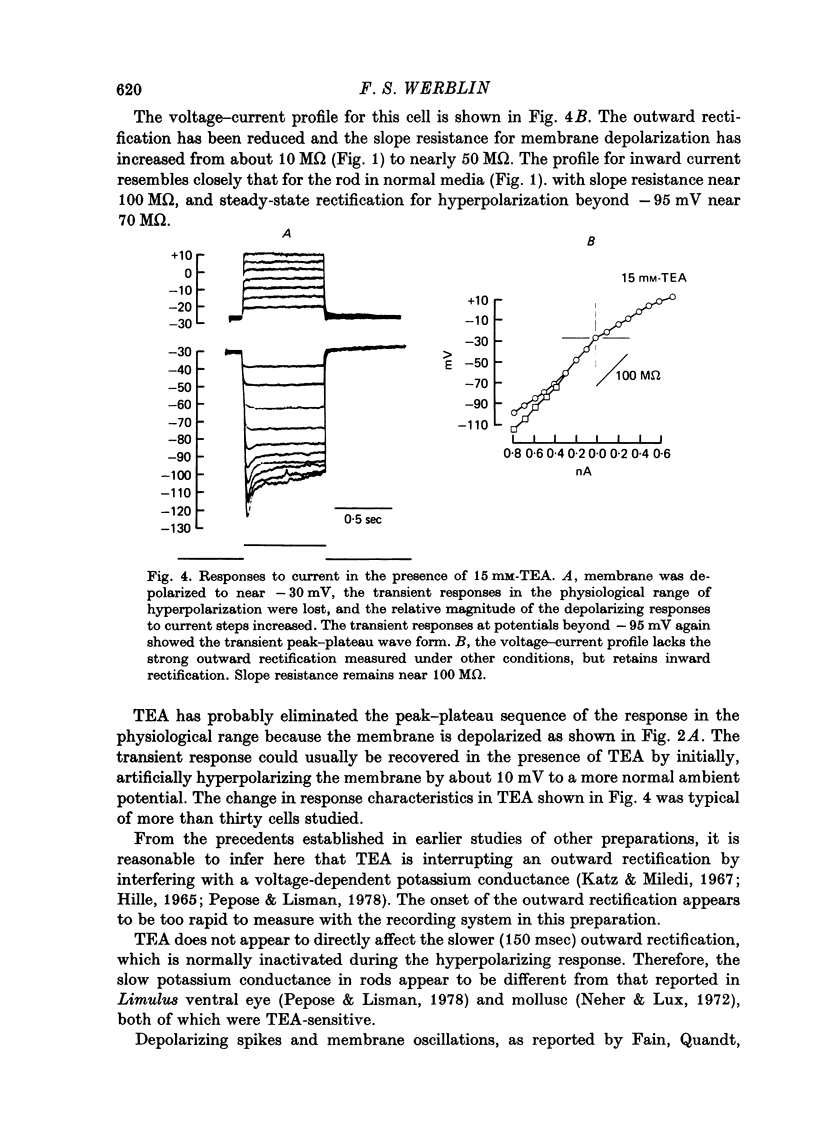
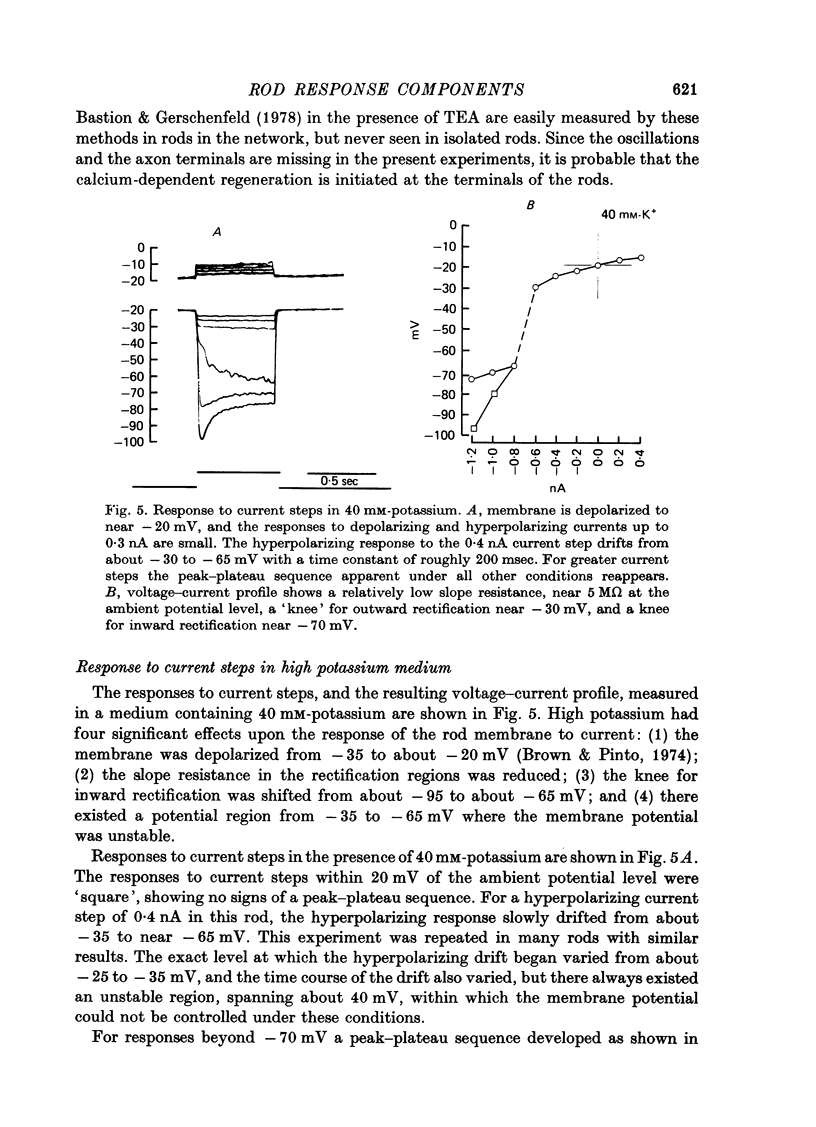
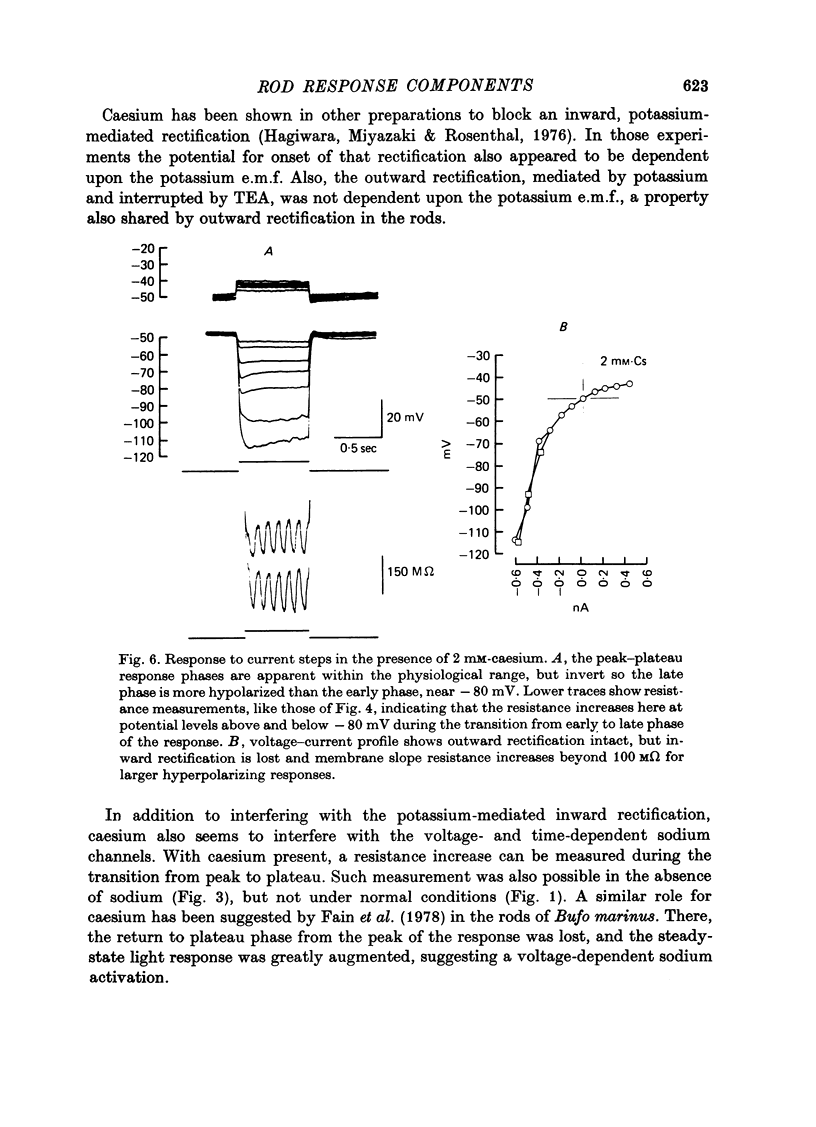
1. The electrical properties of individual rods, physically isolated from the rod network, were measured in terms of the time course of response and voltage-current relations derived from current steps. Properties were measured in normal and altered bathing media designed to reveal the ionic basis for the time and voltage dependent properties of the rod response. 2. In normal media the rod membrane was strongly outward-rectifying with slope resistance near 100 M omega when hyperpolarized, but near 10 M omega when depolarized from a typical ambient level near 35 mV. The membrane become inward rectifying for hyperpolarizations beyond -95 mV, with slope resistance near 70 M omega. 3. The normal hyperpolarizing overshoot associated with the rod response was strongly potential dependent: the overshoot in response to a current step disappeared when the membrane was first depolarized or hyperpolarized by more than about 10 mV from the -35 mV ambient potential level. The decay from overshoot elicited either by current or light, could be approximated with a first order time constant of about 150 msec. 4. In the absence of sodium the peak-plateau sequence remained intact. Membrane resistance increased during transition to the plateau. The plateau became more hyperpolarized than the early phase during responses beyond -75 mV. These results indicate a time- and voltage-dependent conductance other than sodium contributes to the peak-plateau response, probably potassium. 5. Outward rectification was greatly reduced in the presence of 15 mM-TEA, suggesting that it is mediated by potassium activation. 6. Inward rectification, and the associated transients near -95 mV were eliminated in the presence of 2 mM-caesium, suggesting that potassium conductance contributes to the time and voltage dependent inward rectification.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARMSTRONG C. M., BINSTOCK L. ANOMALOUS RECTIFICATION IN THE SQUID GIANT AXON INJECTED WITH TETRAETHYLAMMONIUM CHLORIDE. J Gen Physiol. 1965 May;48:859–872. doi: 10.1085/jgp.48.5.859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bader C. R., MacLeish P. R., Schwartz E. A. Responses to light of solitary rod photoreceptors isolated from tiger salamander retina. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3507–3511. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett E. F., Barret J. N. Separation of two voltage-sensitive potassium currents, and demonstration of a tetrodotoxin-resistant calcium current in frog motoneurones. J Physiol. 1976 Mar;255(3):737–774. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett M. V., Grundfest H. Analysis of depolarizing and hyperpolarizing inactivation responses in gymnotid electroplaques. J Gen Physiol. 1966 Sep;50(1):141–169. doi: 10.1085/jgp.50.1.141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. E., Pinto L. H. Ionic mechanism for the photoreceptor potential of the retina of Bufo marinus. J Physiol. 1974 Feb;236(3):575–591. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connor J. A., Stevens C. F. Voltage clamp studies of a transient outward membrane current in gastropod neural somata. J Physiol. 1971 Feb;213(1):21–30. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Copenhagen D. R., Owen W. G. Functional characteristics of lateral interactions between rods in the retina of the snapping turtle. J Physiol. 1976 Jul;259(2):251–282. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Detwiler P. B., Hodgkin A. L., McNaughton P. A. A surprising property of electrical spread in the network of rods in the turtle's retina. Nature. 1978 Aug 10;274(5671):562–565. doi: 10.1038/274562a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fain G. L., Gold G. H., Dowling J. E. Receptor coupling in the toad retina. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1976;40:547–561. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1976.040.01.051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fain G. L., Quandt F. N., Bastian B. L., Gerschenfeld H. M. Contribution of a caesium-sensitive conductance increase to the rod photoresponse. Nature. 1978 Mar 30;272(5652):466–469. doi: 10.1038/272467a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fain G. L., Quandt F. N., Gerschenfeld H. M. Calcium-dependent regenerative responses in rods. Nature. 1977 Oct 20;269(5630):707–710. doi: 10.1038/269707a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fain G. L. Sensitivity of toad rods: Dependence on wave-length and background illumination. J Physiol. 1976 Sep;261(1):71–101. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gay L. A., Stanfield P. R. Cs(+) causes a voltage-dependent block of inward K currents in resting skeletal muscle fibres. Nature. 1977 May 12;267(5607):169–170. doi: 10.1038/267169a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara S., Miyazaki S., Rosenthal N. P. Potassium current and the effect of cesium on this current during anomalous rectification of the egg cell membrane of a starfish. J Gen Physiol. 1976 Jun;67(6):621–638. doi: 10.1085/jgp.67.6.621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hille B. The selective inhibition of delayed potassium currents in nerve by tetraethylammonium ion. J Gen Physiol. 1967 May;50(5):1287–1302. doi: 10.1085/jgp.50.5.1287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. A study of synaptic transmission in the absence of nerve impulses. J Physiol. 1967 Sep;192(2):407–436. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lasansky A., Marchiafava P. L. Light-induced resistance changes in retinal rods and cones of the tiger salamander. J Physiol. 1974 Jan;236(1):171–191. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neher E., Lux H. D. Differential action of TEA + on two K + -current componentss of a molluscan neurone. Pflugers Arch. 1972;336(2):87–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00592924. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepose J. S., Lisman J. E. Voltage-sensitive potassium channels in Limulus ventral photoreceptors. J Gen Physiol. 1978 Jan;71(1):101–120. doi: 10.1085/jgp.71.1.101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz E. A. Electrical properties of the rod syncytium in the retina of the turtle. J Physiol. 1976 May;257(2):379–406. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson S. H. Three pharmacologically distinct potassium channels in molluscan neurones. J Physiol. 1977 Feb;265(2):465–488. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werblin F. S. Regenerative hyperpolarization in rods. J Physiol. 1975 Jan;244(1):53–81. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werblin F. S. Transmission along and between rods in the tiger salamander retina. J Physiol. 1978 Jul;280:449–470. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yau K. W., Lamb T. D., Baylor D. A. Light-induced fluctuations in membrane current of single toad rod outer segments. Nature. 1977 Sep 1;269(5623):78–80. doi: 10.1038/269078a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


