Abstract
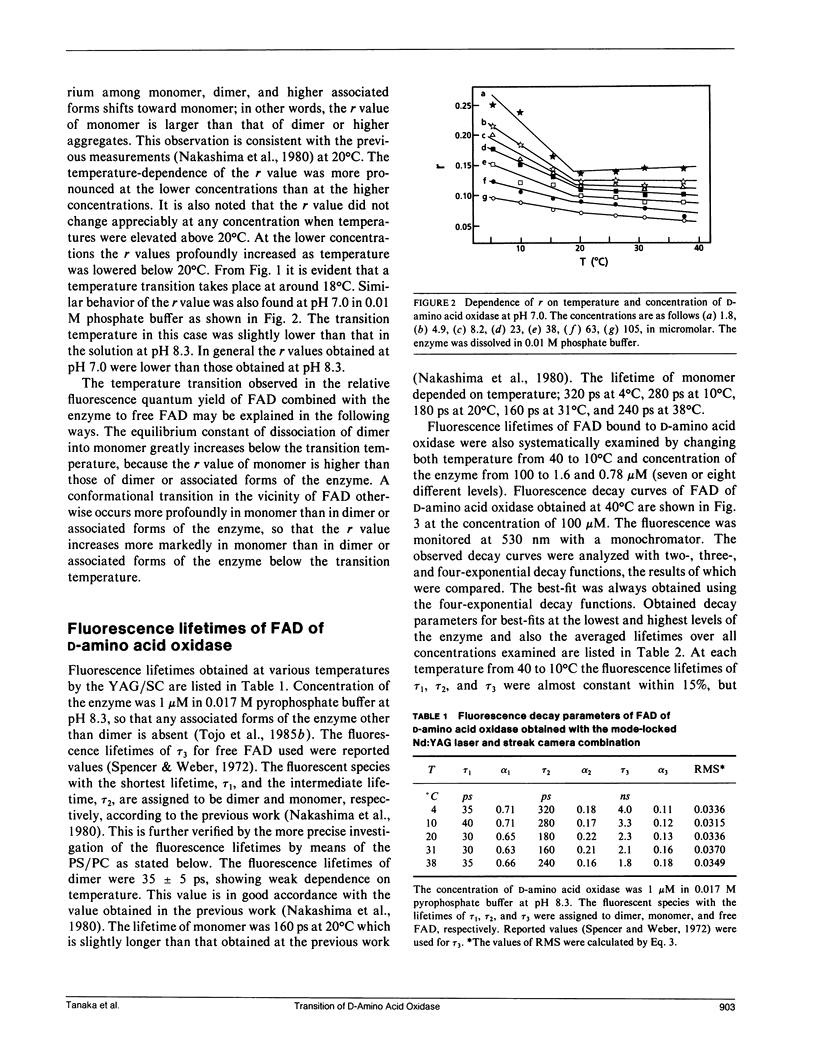
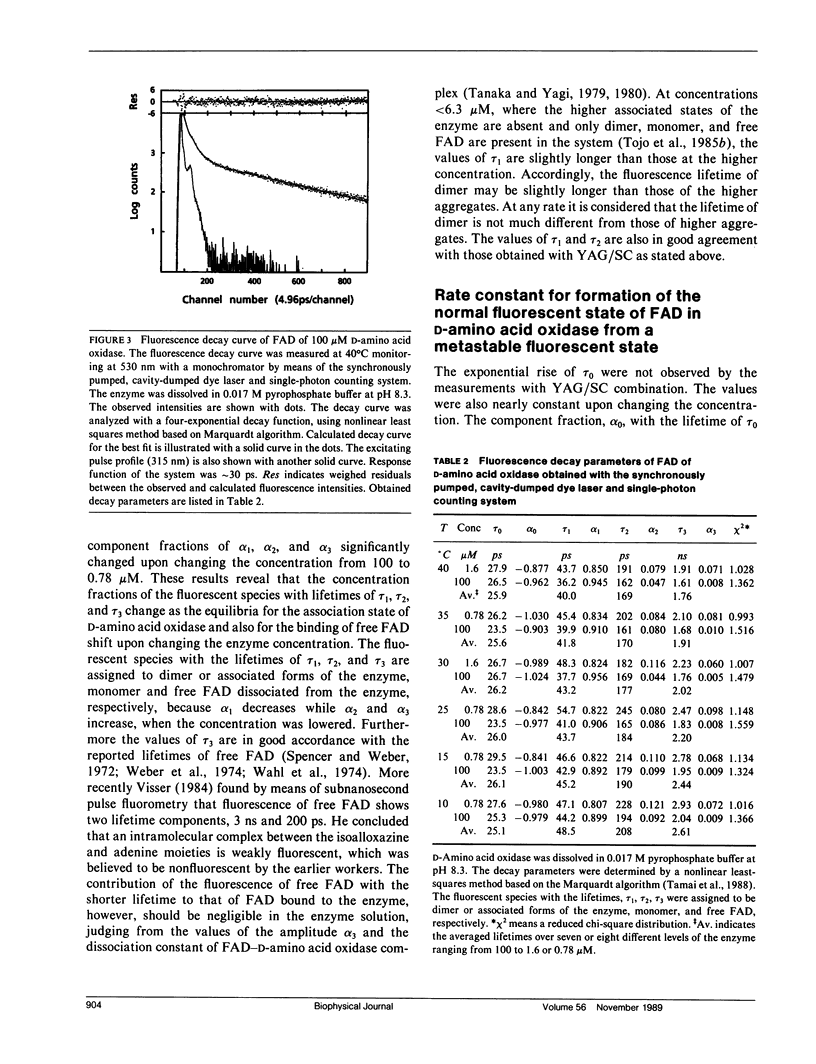
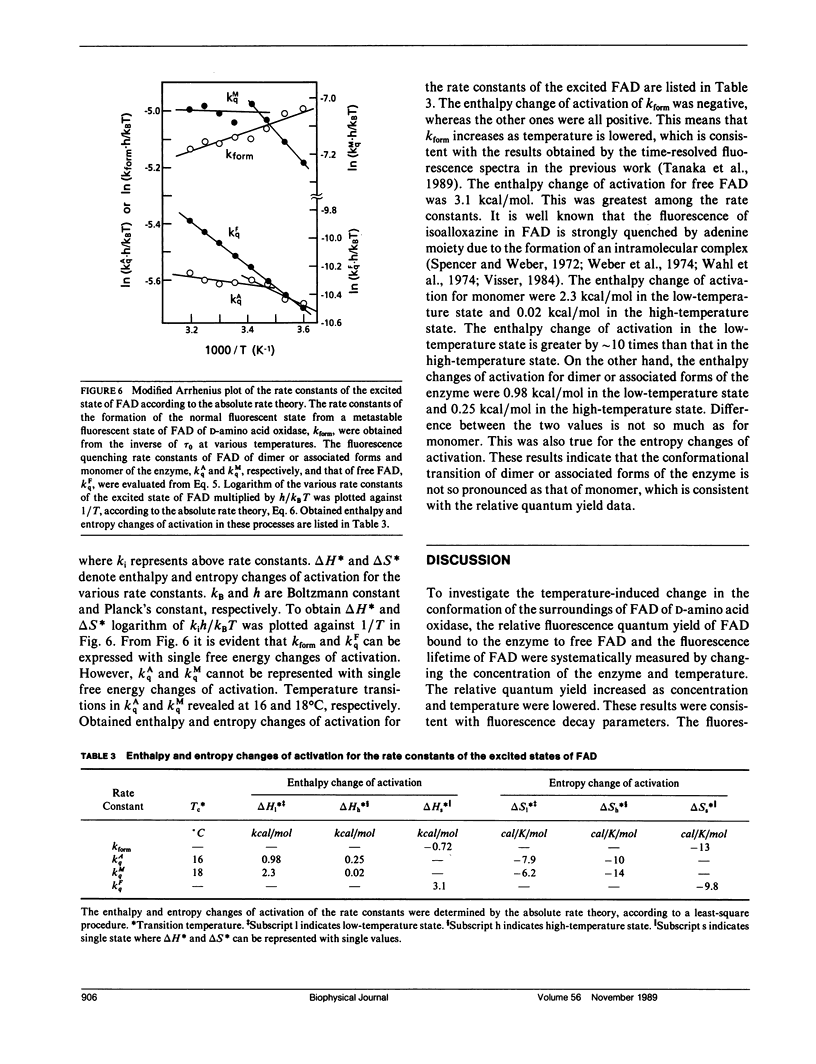
A temperature-dependent change in the microenvironment of the coenzyme, FAD, of D-amino acid oxidase was investigated by means of steady-state and picosecond time-resolved fluorescence spectroscopy. Relative emission quantum yields from FAD bound to D-amino acid oxidase revealed the temperature transition when concentration of the enzyme was lowered. The observed fluorescence decay curves were well described with four-exponential decay functions. The amplitude of the shortest lifetime (tau 0), approximately 25 ps, was always negative, which indicates that the fluorescence of D-amino acid oxidase at approximately 520 nm appears after a metastable state of the excited isoalloxazine decays. The other components with positive amplitudes were assigned to dimer or associated forms of the enzyme, monomer, and free FAD dissociated from the enzyme. Ethalpy and entropy changes of intermediate states in the quenching processes were evaluated according to the absolute rate theory. The temperature transition was much more pronounced in the monomer than in the dimer or associated forms of the enzyme.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Antonini E., Brunori M., Bruzzesi R., Chiancone E., Massey V. Association-dissociation phenomena of D-amino acid oxidase. J Biol Chem. 1966 May 25;241(10):2358–2366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHARLWOOD P. A., PALMER G., BENNETT R. Association phenomena in the ultracentrifugal behaviour of D-amino acid oxidase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1961 Jun 10;50:17–22. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(61)91054-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzpatrick P. F., Massey V. The kinetic mechanism of D-amino acid oxidase with D-alpha-aminobutyrate as substrate. Effect of enzyme concentration on the kinetics. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 10;257(21):12916–12923. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fonda M. L., Anderson B. M. D-amino acid oxidase. 3. Studies of flavin adenine dinucleotide binding. J Biol Chem. 1968 Nov 10;243(21):5635–5643. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henn S. W., Ackers G. K. Molecular sieve studies of interacting protein systems. IV. Molecular size of the D-amino acid oxidase apoenzyme subunit. J Biol Chem. 1969 Jan 25;244(2):465–470. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henn S. W., Ackers G. K. Molecular sieve studies of interacting protein systems. V. Association of subunits of D-amino acid oxidase apoenzyme. Biochemistry. 1969 Sep;8(9):3829–3838. doi: 10.1021/bi00837a049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horiike K., Shiga K., Isomoto A., Yamano T. Effect of quasi-substrate on the monomer-dimer equilibrium of D-amino acid oxidase. J Biochem. 1974 Apr;75(4):925–929. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a130466. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horiike K., Shiga K., Isomoto A., Yamano T. Interaction between D-amino acid oxidase and small molecules. J Biochem. 1976 Nov;80(5):1073–1083. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a131363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horiike K., Shiga K., Nishina Y., Isomoto A., Yamano T. Association-dissociation of the flavoprotein hog kidney D-amino acid oxidase. Determination of the monomer-dimer equilibrium constant and the energetics of subunit association. J Biochem. 1977 Nov;82(5):1247–1255. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a131812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karen A., Ikeda N., Mataga N., Tanaka F. Picosecond laser photolysis studies of fluorescence quenching mechanisms of flavin: a direct observation of indole-flavin singlet charge transfer state formation in solutions and flavoenzymes. Photochem Photobiol. 1983 May;37(5):495–502. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1983.tb04507.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koster J. F., Veeger C. The relation between temperature-inducible allosteric effects and the activation energies of amino-acid oxidases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Aug 27;167(1):48–63. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(68)90276-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MASSEY V., SWOBODA B. E. THE FLAVIN COMPOSITION OF PIG HEART MUSCLE PREPARATIONS. Biochem Z. 1963;338:474–484. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massey V., Curti B., Ganther H. A temperature-dependent conformational change in D-amino acid oxidase and its effect on catalysis. J Biol Chem. 1966 May 25;241(10):2347–2357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miura R., Miyake Y. 13C-NMR studies of porcine kidney D-amino acid oxidase reconstituted with 13C-enriched flavin adenine dinucleotide. Effects of competitive inhibitors. J Biochem. 1987 Mar;101(3):581–589. doi: 10.1093/jb/101.3.581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakashima N., Yoshihara K., Tanaka F., Yagi K. Picosecond fluorescence lifetime of the coenzyme of D-amino acid oxidase. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jun 10;255(11):5261–5263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishimoto K., Watanabe Y., Yagi K. Hydrogen bonding of flavoprotein. I. Effect of hydrogen bonding on electronic spectra of flavoprotein. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Sep 11;526(1):34–41. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(78)90287-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rawitch A. B., Weber G. The reversible association of lysozyme and thyroglobulin. Cooperative binding by near-neighbor interactions. J Biol Chem. 1972 Feb 10;247(3):680–685. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiga K., Isomoto A., Horiike K., Yamano T. A study of the equilibrium between the monomer and the dimer of D-amino-acid oxidase. J Biochem. 1973 Sep;74(3):481–488. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a130267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiga K., Shiga T. The kinetic features of monomers and dimers in high- and low-temperature conformational states of D-amino acid oxidase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Apr 15;263(2):294–303. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(72)90082-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturtevant J. M., Mateo P. L. Proposed temperature-dependent conformational transition in D-amino acid oxidase: a differential scanning microcalorimetric study. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2584–2587. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka F., Tamai N., Yamazaki I. Picosecond-resolved fluorescence spectra of D-amino-acid oxidase. A new fluorescent species of the coenzyme. Biochemistry. 1989 May 16;28(10):4259–4262. doi: 10.1021/bi00436a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka F., Yagi K. Cooperative binding of coenzyme in D-amino acid oxidase. Biochemistry. 1979 Apr 17;18(8):1531–1536. doi: 10.1021/bi00575a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tojo H., Horiike K., Shiga K., Nishina Y., Watari H., Yamano T. Self-association mode of a flavoenzyme D-amino acid oxidase from hog kidney. I. Analysis of apparent weight-average molecular weight data for the apoenzyme in terms of models. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 15;260(23):12607–12614. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tojo H., Horiike K., Shiga K., Nishina Y., Watari H., Yamano T. Self-association mode of a flavoenzyme D-amino acid oxidase from hog kidney. II. Stoichiometry of holoenzyme association and energetics of subunit association. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 15;260(23):12615–12621. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Visser A. J. Kinetics of stacking interactions in flavin adenine dinucleotide from time-resolved flavin fluorescence. Photochem Photobiol. 1984 Dec;40(6):703–706. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1984.tb04640.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEBER G. Polarization of the fluorescence of macromolecules. I. Theory and experimental method. Biochem J. 1952 May;51(2):145–155. doi: 10.1042/bj0510145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl P., Auchet J. C., Visser A. J., Müller F. Time resolved fluorescence of flavin adenine dinucleotide. FEBS Lett. 1974 Aug 15;44(1):67–70. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)80307-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber G., Tanaka F., Okamoto B. Y., Drickamer H. G. The effect of pressure on the molecular complex of isoalloxazine and adenine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1264–1266. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yagi K., Naoi M., Harada M., Okumura K., Hidaka H. Structure and function of D-amino acid oxidase. I. Further purification of hog kidney D-amino acid oxidase and its hydrodynamic and optical rotatory properties. J Biochem. 1967 May;61(5):580–597. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a128588. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yagi K., Ohishi N., Nishimoto K., Choi J. D., Song P. S. Effect of hydrogen bonding on electronic spectra and reactivity of flavins. Biochemistry. 1980 Apr 15;19(8):1553–1557. doi: 10.1021/bi00549a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yagi K., Oishi N. Structure and function of D-amino acid oxidase. IV. Electrophoretic and ultracentrifugal approach to the monomer-dimer equilibrium. J Biochem. 1972 Jun;71(6):993–998. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a129871. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yagi K., Tanaka F., Nakashima N., Yoshihara K. Picosecond laser fluorometry of FAD of D-amino acid oxidase-benzoate complex. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 25;258(6):3799–3802. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yagi K., Tanaka F., Oishi N. Structure and function of D-amino acid oxidase. IX. Changes in the fluorescence polarization of FAD upon complex formation. J Biochem. 1975 Feb;77(2):463–468. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a130746. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


