Abstract
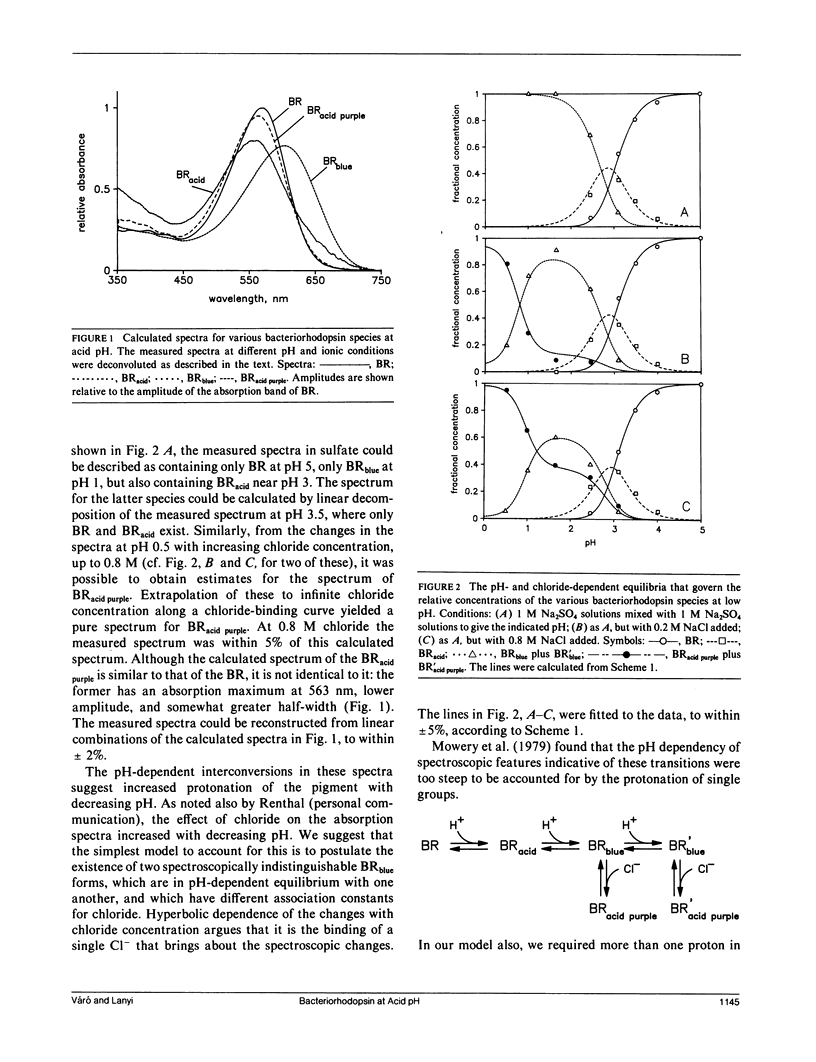
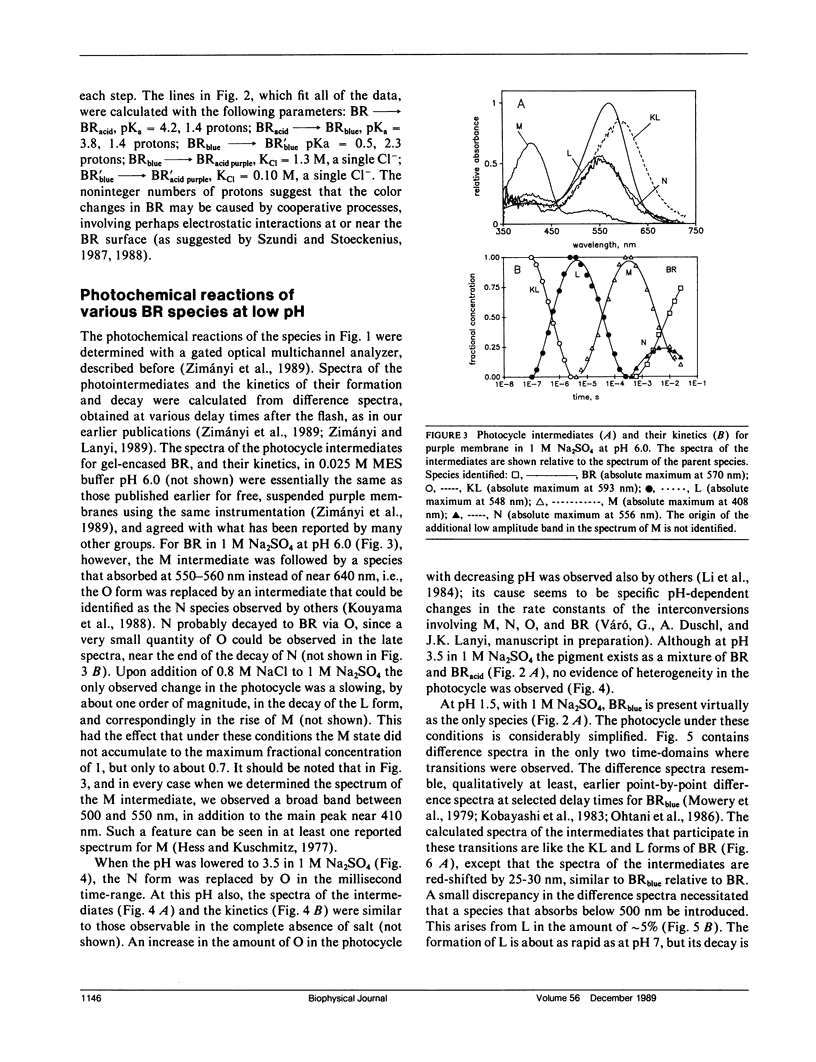
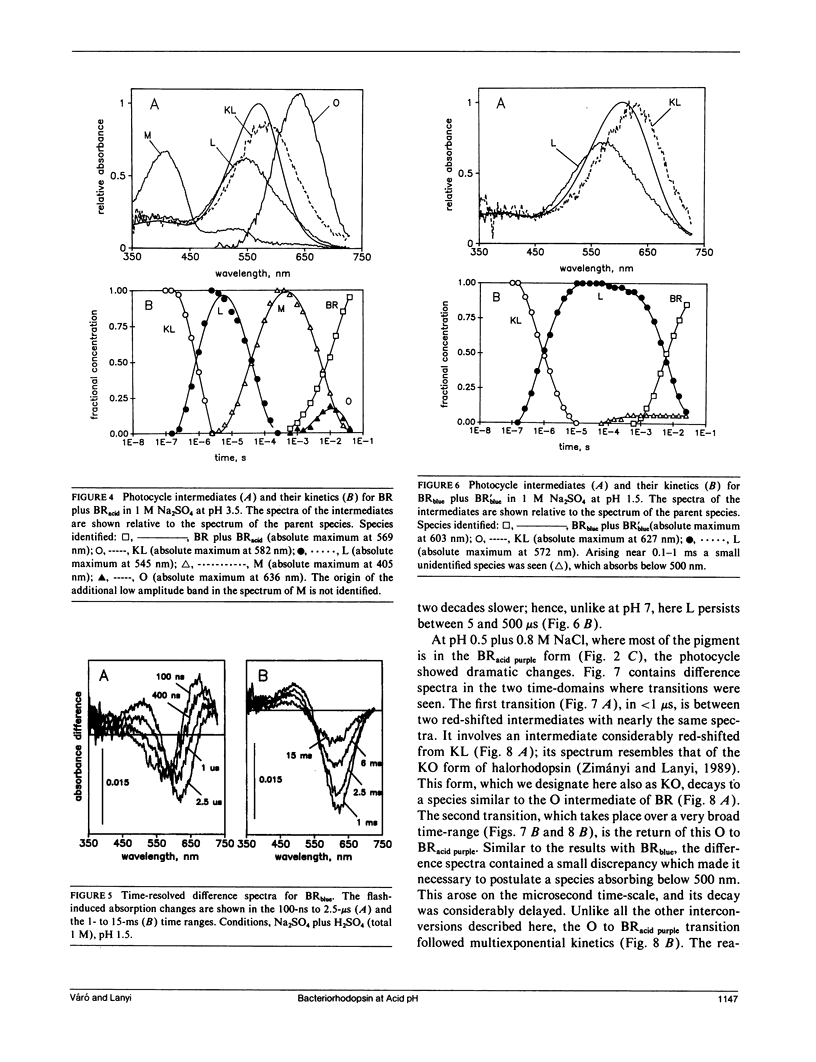
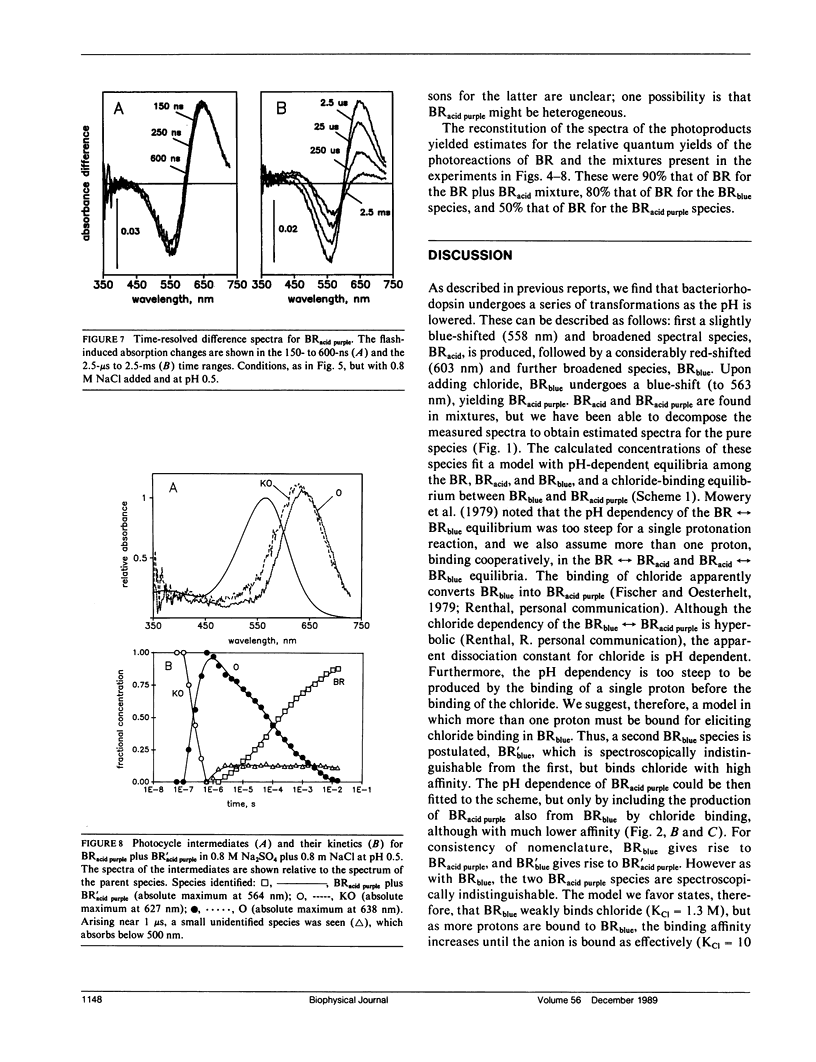
It has been known that bacteriorhodopsin, the retinal protein in purple membrane which functions as a light-driven proton pump, undergoes reversible spectroscopic changes at acid pH. The absorption spectra of various bacteriorhodopsin species were estimated from measured spectra of the mixtures that form at low pH, in the presence of sulfate and chloride. The dependency of these on pH and the concentration of Cl- fit a model in which progressive protonation of purple membrane produces "blue membrane", which will bind, with increasing affinity as the pH is lowered, chloride ions to produce "acid purple membrane." Transient spectroscopy with a multichannel analyzer identified the intermediates of the photocycles of these altered pigments, and described their kinetics. Blue membrane produced red-shifted KL-like and L-like products, but no other photointermediates, consistent with earlier suggestions. Unlike others, however, we found that acid purple membrane exhibited a very different photocycle: its first detected intermediate was not like KL in that it was much more red-shifted, and the only other intermediate detectable resembled the O species of the bacteriorhodopsin photocycle. An M-like intermediate, with a deprotonated Schiff base, was not found in either of these photocycles. There are remarkable similarities between the photoreactions of the acid forms of bacteriorhodopsin and the chloride transport system halorhodopsin, where the Schiff base deprotonation seems to be prevented by lack of suitable aspartate residues, rather than by low pH.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blanck A., Oesterhelt D. The halo-opsin gene. II. Sequence, primary structure of halorhodopsin and comparison with bacteriorhodopsin. EMBO J. 1987 Jan;6(1):265–273. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04749.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braiman M. S., Mogi T., Marti T., Stern L. J., Khorana H. G., Rothschild K. J. Vibrational spectroscopy of bacteriorhodopsin mutants: light-driven proton transport involves protonation changes of aspartic acid residues 85, 96, and 212. Biochemistry. 1988 Nov 15;27(23):8516–8520. doi: 10.1021/bi00423a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braiman M. S., Mogi T., Stern L. J., Hackett N. R., Chao B. H., Khorana H. G., Rothschild K. J. Vibrational spectroscopy of bacteriorhodopsin mutants: I. Tyrosine-185 protonates and deprotonates during the photocycle. Proteins. 1988;3(4):219–229. doi: 10.1002/prot.340030403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butt H. J., Fendler K., Bamberg E., Tittor J., Oesterhelt D. Aspartic acids 96 and 85 play a central role in the function of bacteriorhodopsin as a proton pump. EMBO J. 1989 Jun;8(6):1657–1663. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03556.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C. H., Chen J. G., Govindjee R., Ebrey T. Cation binding by bacteriorhodopsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):396–400. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C. H., Liu S. Y., Jonas R., Govindjee R. The pink membrane: the stable photoproduct of deionized purple membrane. Biophys J. 1987 Oct;52(4):617–623. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(87)83252-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chronister E. L., Corcoran T. C., Song L., El-Sayed M. A. On the molecular mechanisms of the Schiff base deprotonation during the bacteriorhodopsin photocycle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(22):8580–8584. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.22.8580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drachev L. A., Kaulen A. D., Skulachev V. P. Time resolution of the intermediate steps in the bacteriorhodopsin-linked electrogenesis. FEBS Lett. 1978 Mar 1;87(1):161–167. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80157-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dupuis P., Corcoran T. C., El-Sayed M. A. Importance of bound divalent cations to the tyrosine deprotonation during the photocycle of bacteriorhodopsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(11):3662–3664. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.11.3662. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duñach M., Padrós E., Seigneuret M., Rigaud J. L. On the molecular mechanism of the blue to purple transition of bacteriorhodopsin. UV-difference spectroscopy and electron spin resonance studies. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 5;263(16):7555–7559. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duñach M., Seigneuret M., Rigaud J. L., Padrós E. Influence of cations on the blue to purple transition of bacteriorhodopsin. Comparison of Ca2+ and Hg2+ binding and their effect on the surface potential. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 25;263(33):17378–17384. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edgerton M. E., Moore T. A., Greenwood C. Investigations into the effect of acid on the spectral and kinetic properties of purple membrane from Halobacterium halobium. Biochem J. 1980 Sep 1;189(3):413–420. doi: 10.1042/bj1890413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer U., Oesterhelt D. Chromophore equilibria in bacteriorhodopsin. Biophys J. 1979 Nov;28(2):211–230. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(79)85172-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hegemann P., Oesterbelt D., Steiner M. The photocycle of the chloride pump halorhodopsin. I: Azide-catalyzed deprotonation of the chromophore is a side reaction of photocycle intermediates inactivating the pump. EMBO J. 1985 Sep;4(9):2347–2350. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03937.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura Y., Ikegami A., Stoeckenius W. Salt and pH-dependent changes of the purple membrane absorption spectrum. Photochem Photobiol. 1984 Nov;40(5):641–646. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1984.tb05353.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kouyama T., Nasuda-Kouyama A., Ikegami A., Mathew M. K., Stoeckenius W. Bacteriorhodopsin photoreaction: identification of a long-lived intermediate N (P,R350) at high pH and its M-like photoproduct. Biochemistry. 1988 Aug 9;27(16):5855–5863. doi: 10.1021/bi00416a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanyi J. K. Light-dependent trans to cis isomerization of the retinal in halorhodopsin. FEBS Lett. 1984 Oct 1;175(2):337–342. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)80764-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanyi J. K. Mechanism of base-catalyzed Schiff base deprotonation in halorhodopsin. Biochemistry. 1986 Oct 21;25(21):6706–6711. doi: 10.1021/bi00369a057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanyi J. K., Vodyanoy V. Flash spectroscopic studies of the kinetics of the halorhodopsin photocycle. Biochemistry. 1986;25(6):1465–1470. doi: 10.1021/bi00354a042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Q., Govindjee R., Ebrey T. G. A correlation between proton pumping and the bacteriorhodopsin photocycle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(22):7079–7082. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.22.7079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda A., Iwasa T., Yoshizawa T. Formation of 9-cis- and 11-cis-retinal pigments from bacteriorhodopsin by irradiating purple membrane in acid. Biochemistry. 1980 Aug 5;19(16):3825–3831. doi: 10.1021/bi00557a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marinetti T., Subramaniam S., Mogi T., Marti T., Khorana H. G. Replacement of aspartic residues 85, 96, 115, or 212 affects the quantum yield and kinetics of proton release and uptake by bacteriorhodopsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(2):529–533. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.2.529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mogi T., Stern L. J., Hackett N. R., Khorana H. G. Bacteriorhodopsin mutants containing single tyrosine to phenylalanine substitutions are all active in proton translocation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(16):5595–5599. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.16.5595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mogi T., Stern L. J., Marti T., Chao B. H., Khorana H. G. Aspartic acid substitutions affect proton translocation by bacteriorhodopsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4148–4152. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mowery P. C., Lozier R. H., Chae Q., Tseng Y. W., Taylor M., Stoeckenius W. Effect of acid pH on the absorption spectra and photoreactions of bacteriorhodopsin. Biochemistry. 1979 Sep 18;18(19):4100–4107. doi: 10.1021/bi00586a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oesterhelt D., Stoeckenius W. Isolation of the cell membrane of Halobacterium halobium and its fractionation into red and purple membrane. Methods Enzymol. 1974;31:667–678. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)31072-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. O., Mathies R. A. Resonance Raman spectra of the acidified and deionized forms of bacteriorhodopsin. Biophys J. 1985 Feb;47(2 Pt 1):251–254. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3495(85)83899-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soppa J., Otomo J., Straub J., Tittor J., Meessen S., Oesterhelt D. Bacteriorhodopsin mutants of Halobacterium sp. GRB. II. Characterization of mutants. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 5;264(22):13049–13056. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoeckenius W., Bogomolni R. A. Bacteriorhodopsin and related pigments of halobacteria. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:587–616. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.003103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoeckenius W., Lozier R. H., Bogomolni R. A. Bacteriorhodopsin and the purple membrane of halobacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Mar 14;505(3-4):215–278. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(79)90006-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szundi I., Stoeckenius W. Effect of lipid surface charges on the purple-to-blue transition of bacteriorhodopsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(11):3681–3684. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.11.3681. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szundi I., Stoeckenius W. Purple-to-blue transition of bacteriorhodopsin in a neutral lipid environment. Biophys J. 1988 Aug;54(2):227–232. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(88)82951-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Váró G., Keszthelyi L. Photoelectric signals from dried oriented purple membranes of Halobacterium halobium. Biophys J. 1983 Jul;43(1):47–51. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(83)84322-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimányi L., Keszthelyi L., Lanyi J. K. Transient spectroscopy of bacterial rhodopsins with an optical multichannel analyzer. 1. Comparison of the photocycles of bacteriorhodopsin and halorhodopsin. Biochemistry. 1989 Jun 13;28(12):5165–5172. doi: 10.1021/bi00438a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimányi L., Lanyi J. K. Iso-halorhodopsin: a stable, 9-cis retinal containing photoproduct of halorhodopsin. Biophys J. 1987 Dec;52(6):1007–1013. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(87)83293-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimányi L., Lanyi J. K. Transient spectroscopy of bacterial rhodopsins with an optical multichannel analyzer. 2. Effects of anions on the halorhodopsin photocycle. Biochemistry. 1989 Jun 13;28(12):5172–5178. doi: 10.1021/bi00438a039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


