Abstract
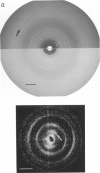
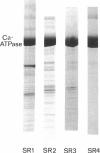
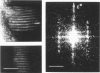
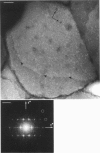
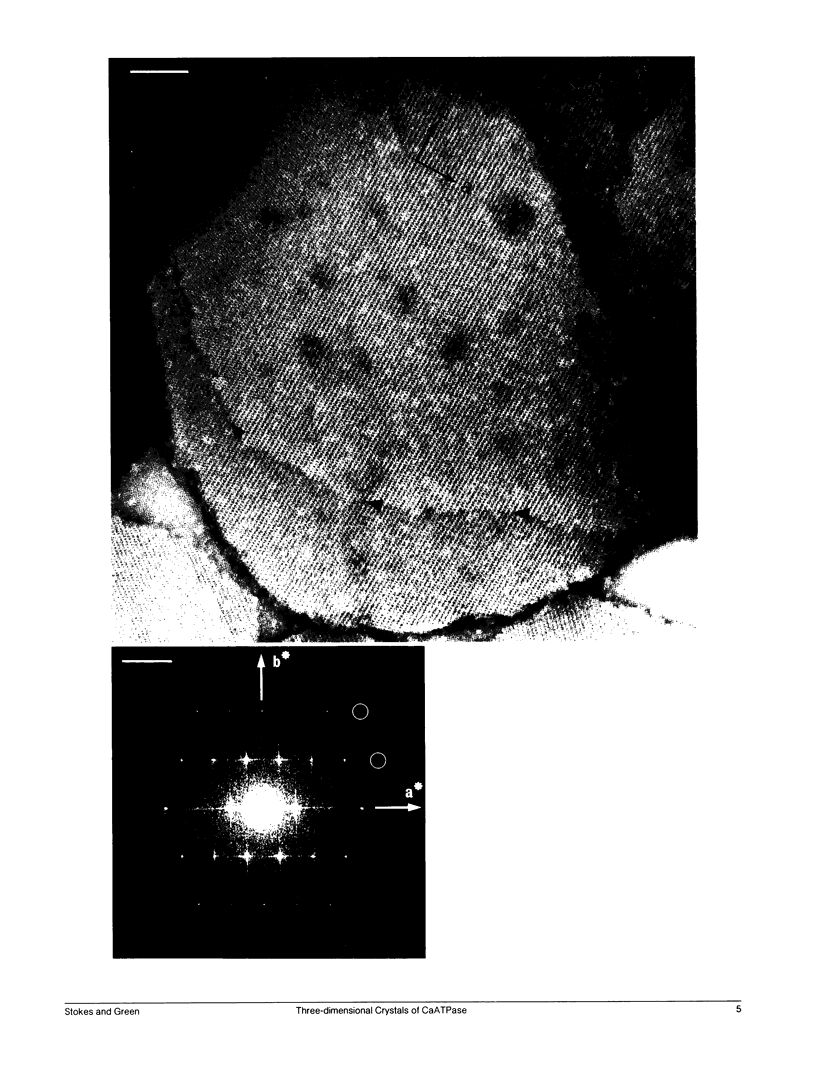
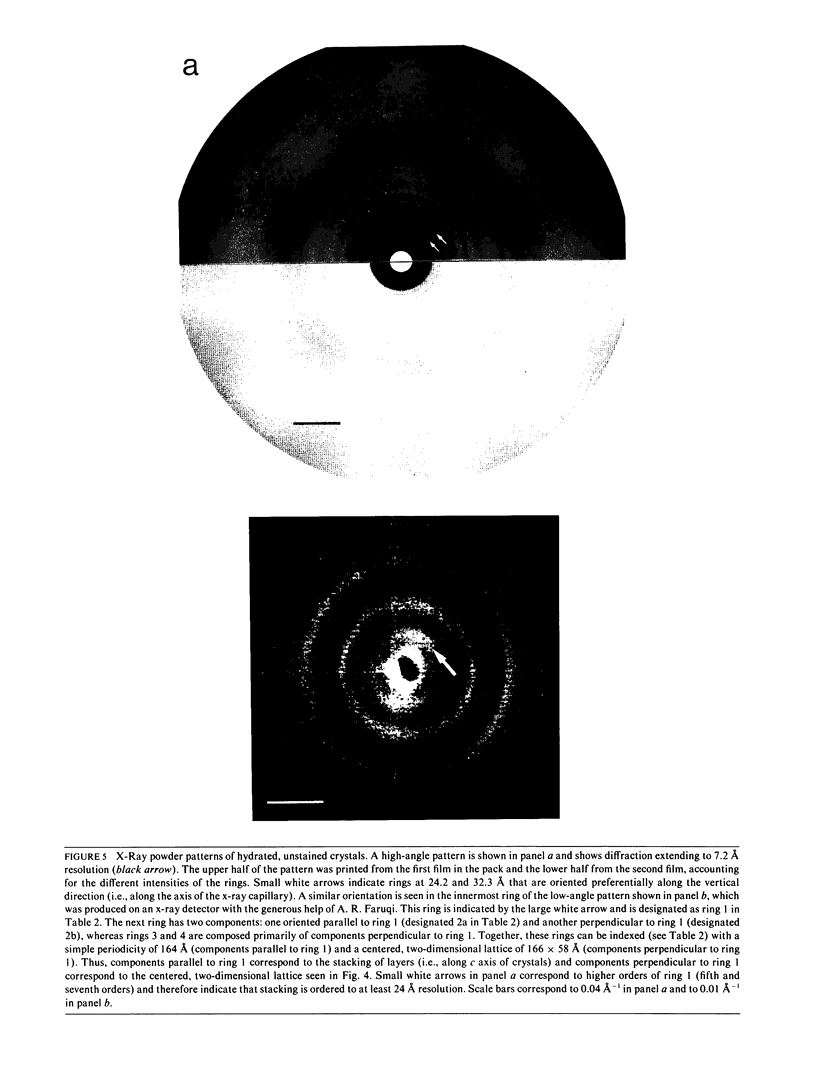
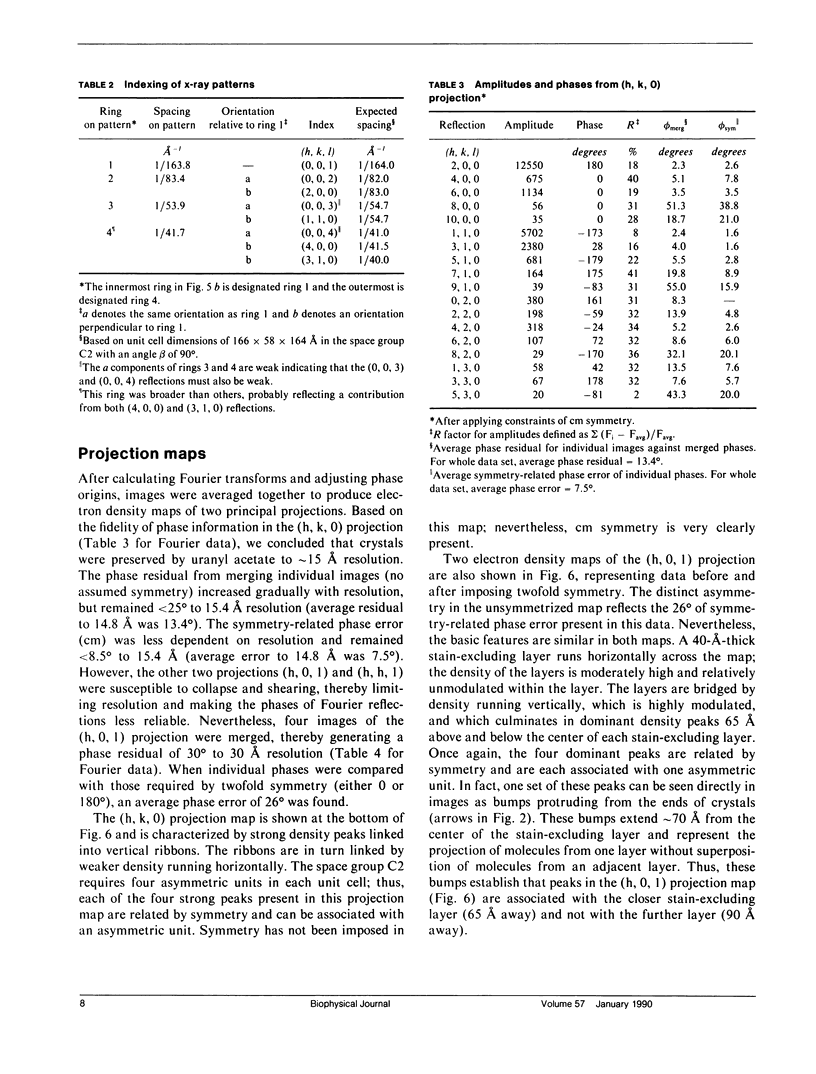
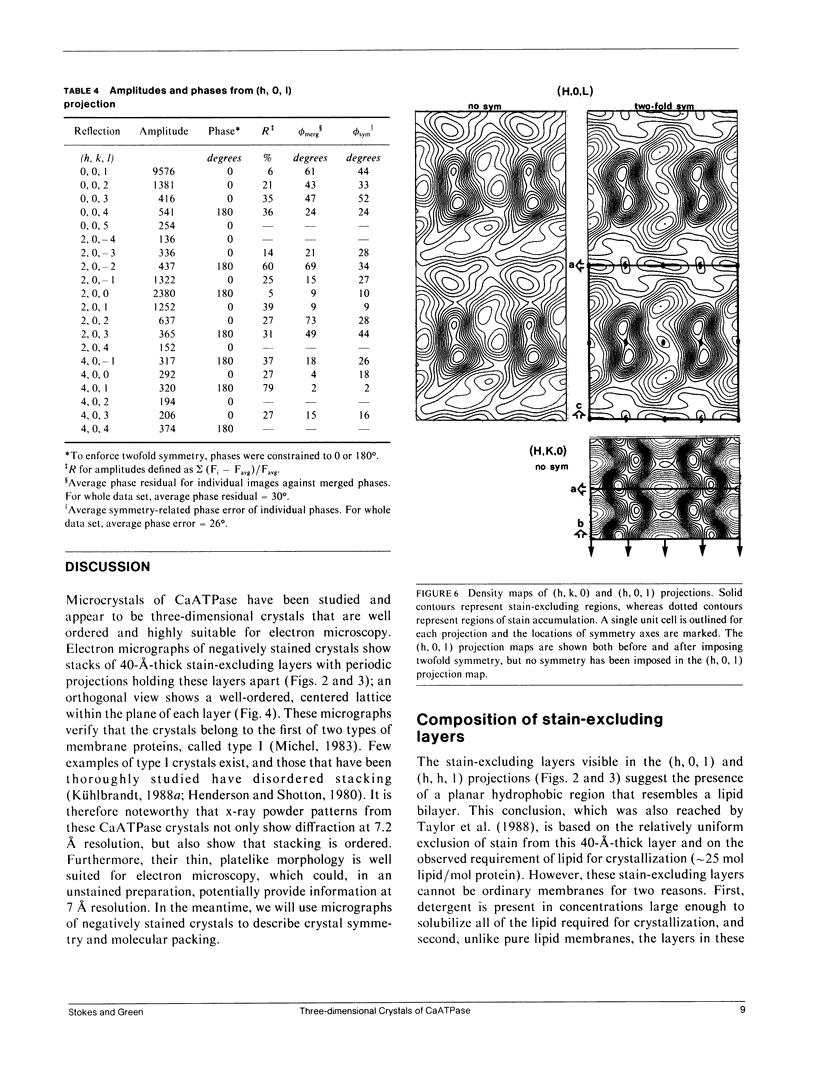
Structural studies of CaATPase from sarcoplasmic reticulum have so far been restricted to low resolution due to the poor order of two-dimensional crystal forms. However, we report that three-dimensional microcrystals of detergent-solubilized CaATPase diffract to 7.2 A in x-ray powder patterns and may therefore provide an opportunity to study CaATPase structure at higher resolutions. In the present study, we have characterized the symmetry and molecular packing of negatively stained crystals by electron microscopy (em). By altering the detergent-to-lipid ratio, different sized crystals were produced, which adhere to an em grid in different orientations. Thus, we obtained micrographs of three different projections and from these determined unit cell dimensions to be 151 X 51 X 158 A and the three-dimensional space group to be C2 with an angle beta very close to 90 degrees; x-ray powder patterns of hydrated, unstained crystals yielded dimensions of 166 X 58 X 164 A. Micrographs from each of two principal projections were averaged to produce two-dimensional density maps. Based on these maps and on the previously determined low-resolution structure of CaATPase, a packing diagram for these three-dimensional crystals is presented and major intermolecular contacts are proposed.
Full text
PDF





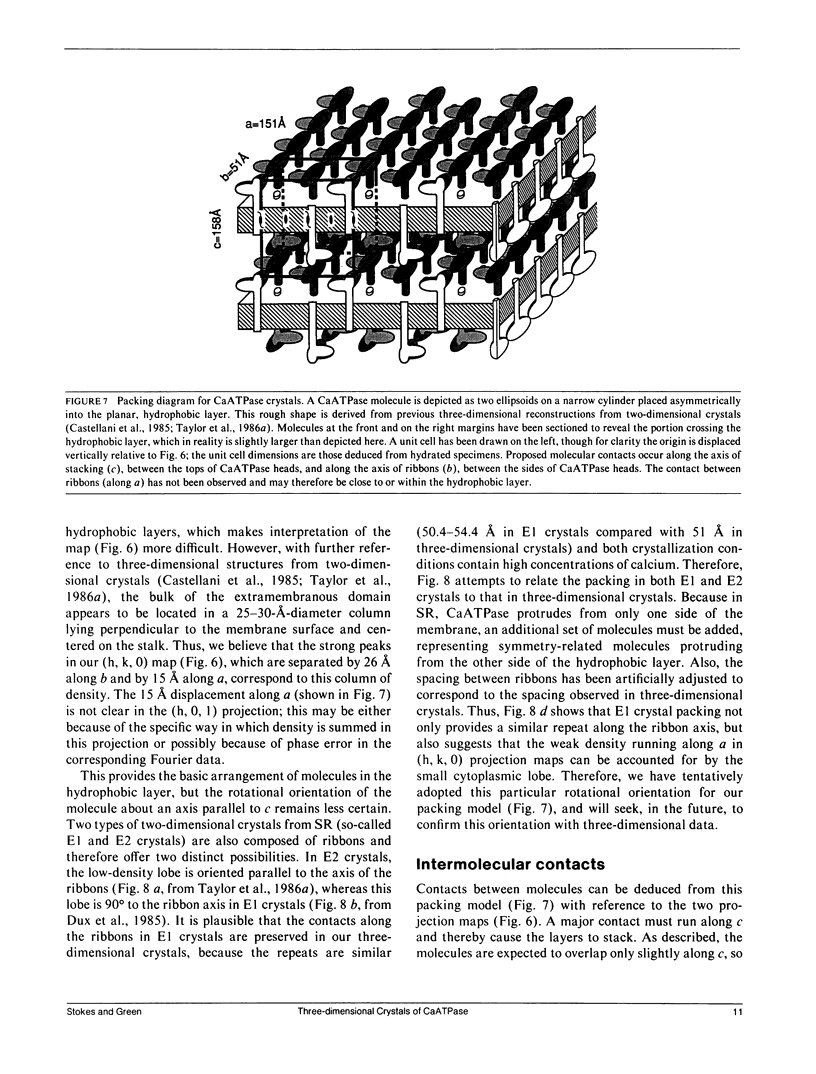
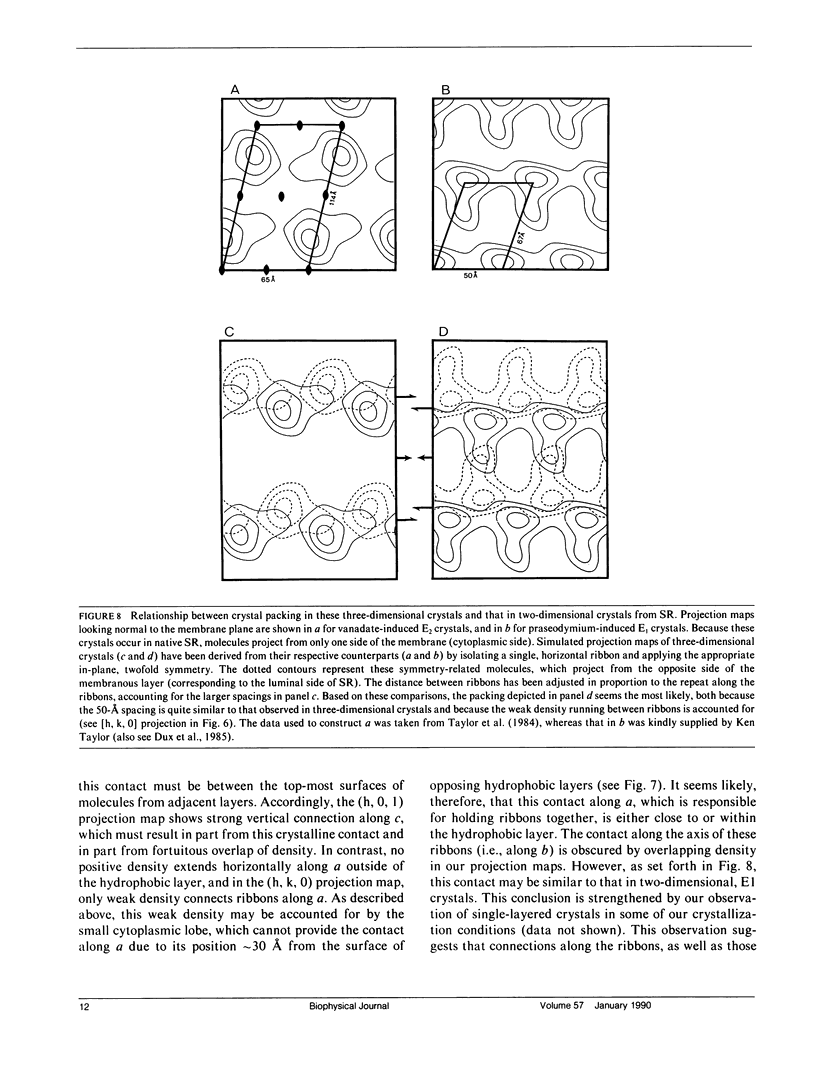


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arndt U. W., Leigh J. B., Mallett J. F., Twinn K. E. A mechanical microdensitometer. J Sci Instrum. 1969 May;2(5):385–387. doi: 10.1088/0022-3735/2/5/301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castellani L., Hardwicke P. M., Vibert P. Dimer ribbons in the three-dimensional structure of sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Mol Biol. 1985 Oct 5;185(3):579–594. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90073-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke D. M., Loo T. W., Inesi G., MacLennan D. H. Location of high affinity Ca2+-binding sites within the predicted transmembrane domain of the sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase. Nature. 1989 Jun 8;339(6224):476–478. doi: 10.1038/339476a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coll R. J., Murphy A. J. Purification of the CaATPase of sarcoplasmic reticulum by affinity chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 25;259(22):14249–14254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dux L., Pikula S., Mullner N., Martonosi A. Crystallization of Ca2+-ATPase in detergent-solubilized sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 15;262(14):6439–6442. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dux L., Taylor K. A., Ting-Beall H. P., Martonosi A. Crystallization of the Ca2+-ATPase of sarcoplasmic reticulum by calcium and lanthanide ions. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 25;260(21):11730–11743. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garavito R. M., Jenkins J., Jansonius J. N., Karlsson R., Rosenbusch J. P. X-ray diffraction analysis of matrix porin, an integral membrane protein from Escherichia coli outer membranes. J Mol Biol. 1983 Feb 25;164(2):313–327. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(83)90079-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson R., Shotton D. Crystallization of purple membrane in three dimensions. J Mol Biol. 1980 May 15;139(2):99–109. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90298-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbette L., DeFoor P., Fleischer S., Pascolini D., Scarpa A., Blasie J. K. The separate profile structures of the functional calcium pump protein and the phospholipid bilayer within isolated sarcoplasmic reticulum membranes determined by X-ray and neutron diffraction. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Jul 11;817(1):103–122. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(85)90073-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inesi G. Mechanism of calcium transport. Annu Rev Physiol. 1985;47:573–601. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.47.030185.003041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kühlbrandt W. Structure of light-harvesting chlorophyll a/b protein complex from plant photosynthetic membranes at 7 A resolution in projection. J Mol Biol. 1988 Aug 20;202(4):849–864. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90563-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüdi H., Hasselbach W. Preparation of a highly concentrated, completely monomeric, active sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Nov 21;821(1):137–141. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(85)90164-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLennan D. H. Purification and properties of an adenosine triphosphatase from sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1970 Sep 10;245(17):4508–4518. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martonosi A. Sarcoplasmic reticulum. IV. Solubilization of microsomal adenosine triphosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1968 Jan 10;243(1):71–81. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama K., MacLennan D. H. Mutation of aspartic acid-351, lysine-352, and lysine-515 alters the Ca2+ transport activity of the Ca2+-ATPase expressed in COS-1 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(10):3314–3318. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.10.3314. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews B. W. Solvent content of protein crystals. J Mol Biol. 1968 Apr 28;33(2):491–497. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90205-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClare C. W. An accurate and convenient organic phosphorus assay. Anal Biochem. 1971 Feb;39(2):527–530. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(71)90443-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller K. Structural dimorphism of bile salt/lecithin mixed micelles. A possible regulatory mechanism for cholesterol solubility in bile? X-ray structure analysis. Biochemistry. 1981 Jan 20;20(2):404–414. doi: 10.1021/bi00505a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor K. A., Dux L., Martonosi A. Three-dimensional reconstruction of negatively stained crystals of the Ca2+-ATPase from muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Mol Biol. 1986 Feb 5;187(3):417–427. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90442-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor K. A., Glaeser R. M. Electron microscopy of frozen hydrated biological specimens. J Ultrastruct Res. 1976 Jun;55(3):448–456. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(76)80099-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor K. A., Ho M. H., Martonosi A. Image analysis of the Ca2+-ATPase from sarcoplasmic reticulum. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1986;483:31–43. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1986.tb34493.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor K. A., Mullner N., Pikula S., Dux L., Peracchia C., Varga S., Martonosi A. Electron microscope observations on Ca2+-ATPase microcrystals in detergent-solubilized sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 15;263(11):5287–5294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor K., Dux L., Martonosi A. Structure of the vanadate-induced crystals of sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase. J Mol Biol. 1984 Mar 25;174(1):193–204. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90372-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unwin P. N., Henderson R. Molecular structure determination by electron microscopy of unstained crystalline specimens. J Mol Biol. 1975 May 25;94(3):425–440. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90212-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]