Abstract
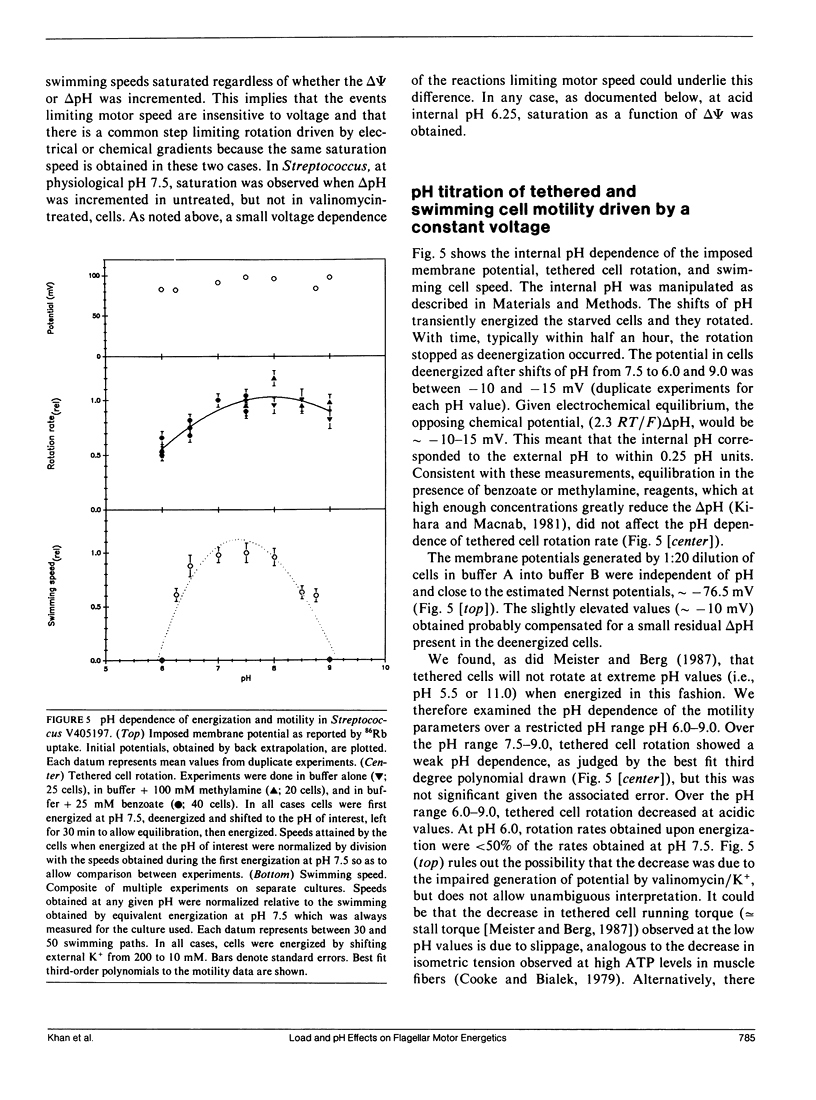
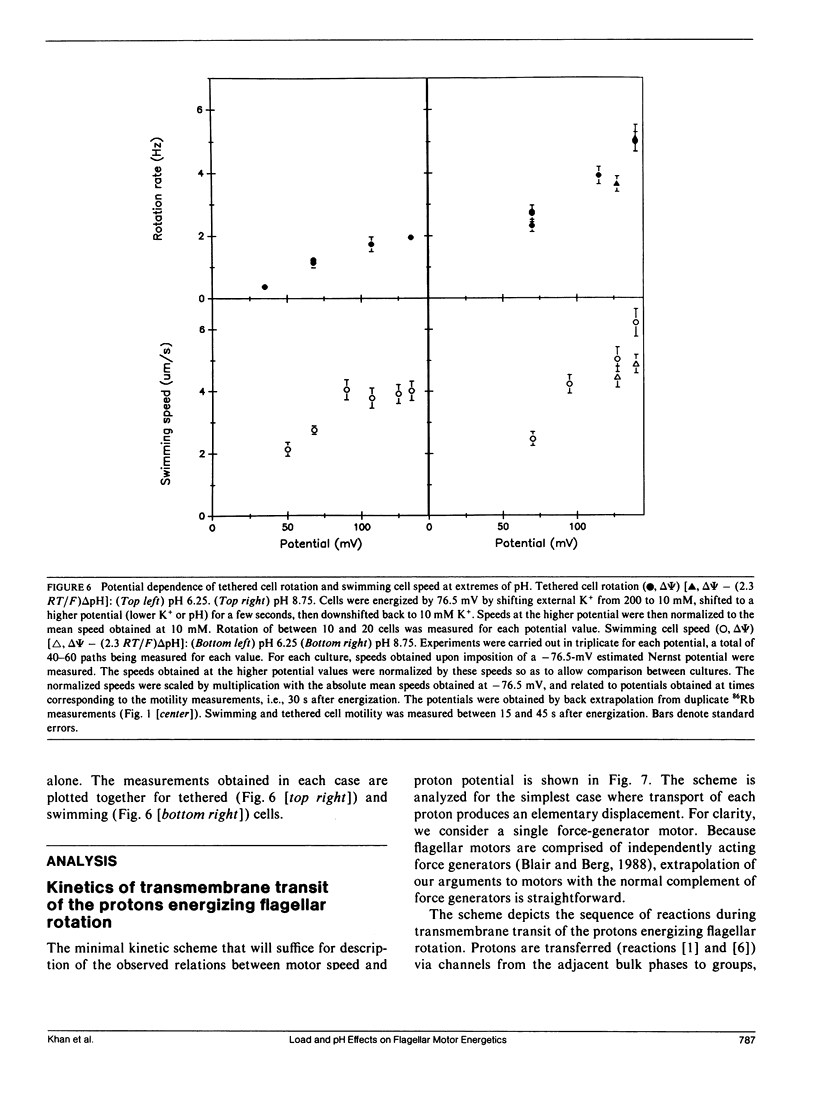
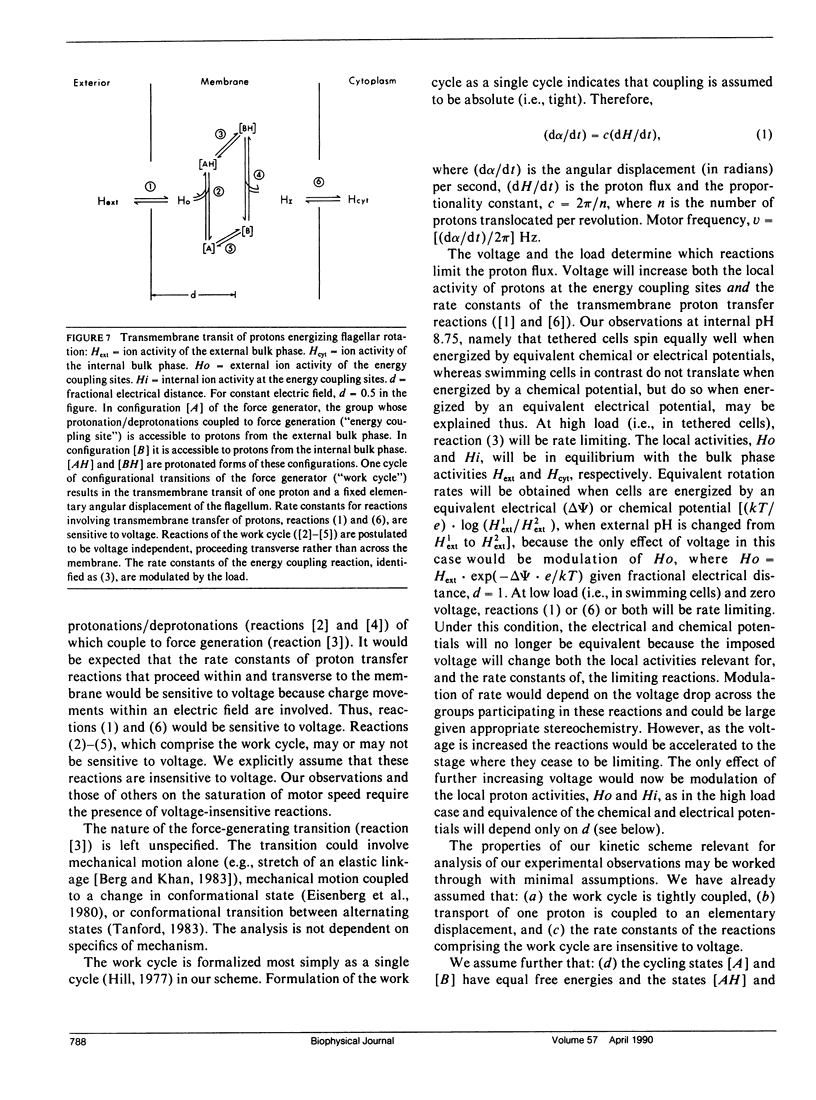
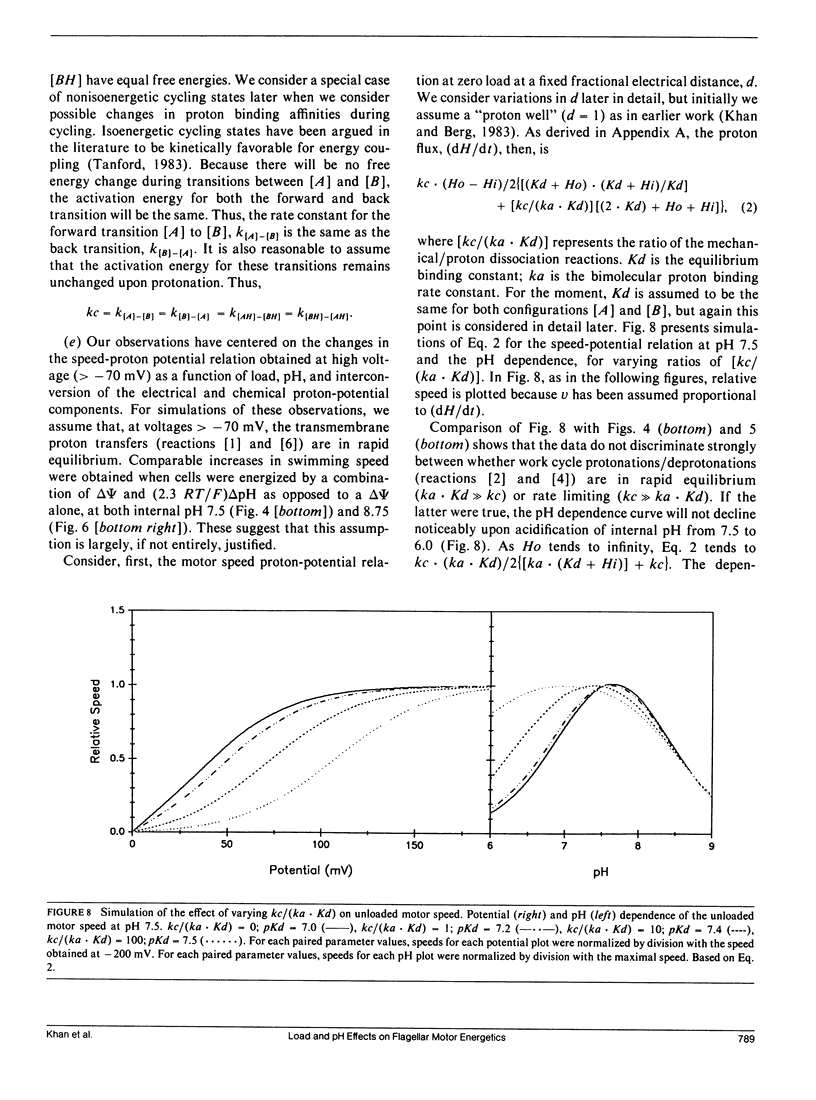
The effect of load and pH on the relation between proton potential and flagellar rotation has been studied in cells of a smooth-swimming Streptococcus strain. The driving potential, speeds of free-swimming bacteria, and rotation rates of bacteria tethered to glass by a single flagellum were measured. The relation between rotation rate of tethered bacteria and potential was remarkably linear up to nearly -200 mV. The relation between swimming speed and potential exhibited both saturation and threshold, as previously observed in other species. The form of these relations depended on pH. The equivalence of the electrical and chemical potential components of the proton potential in enabling swimming depended on the voltage. Our observations may be most simply accommodated by a kinetic scheme that links transmembrane proton transits to a tightly coupled work cycle. The properties of this scheme were elucidated by computer simulations of the experimental plots. These simulations indicated that the protonable groups that participate in the rate limiting reactions have a fractional electrical distance between three-fourths to all of the way toward the cytoplasm with a corresponding mean proton binding affinity of 10(-7.3)-10(-7.0) M, respectively.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bakker E. P., Mangerich W. E. Interconversion of components of the bacterial proton motive force by electrogenic potassium transport. J Bacteriol. 1981 Sep;147(3):820–826. doi: 10.1128/jb.147.3.820-826.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg H. C., Anderson R. A. Bacteria swim by rotating their flagellar filaments. Nature. 1973 Oct 19;245(5425):380–382. doi: 10.1038/245380a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg H. C., Block S. M. A miniature flow cell designed for rapid exchange of media under high-power microscope objectives. J Gen Microbiol. 1984 Nov;130(11):2915–2920. doi: 10.1099/00221287-130-11-2915. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg H. C. Dynamic properties of bacterial flagellar motors. Nature. 1974 May 3;249(452):77–79. doi: 10.1038/249077a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg H. C., Manson M. D., Conley M. P. Dynamics and energetics of flagellar rotation in bacteria. Symp Soc Exp Biol. 1982;35:1–31. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg H. C., Turner L. Movement of microorganisms in viscous environments. Nature. 1979 Mar 22;278(5702):349–351. doi: 10.1038/278349a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blair D. F., Berg H. C. Restoration of torque in defective flagellar motors. Science. 1988 Dec 23;242(4886):1678–1681. doi: 10.1126/science.2849208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conley M. P., Berg H. C. Chemical modification of Streptococcus flagellar motors. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jun;158(3):832–843. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.3.832-843.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke R., Bialek W. Contraction of glycerinated muscle fibers as a function of the ATP concentration. Biophys J. 1979 Nov;28(2):241–258. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(79)85174-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coronado R., Rosenberg R. L., Miller C. Ionic selectivity, saturation, and block in a K+-selective channel from sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Gen Physiol. 1980 Oct;76(4):425–446. doi: 10.1085/jgp.76.4.425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DePamphilis M. L., Adler J. Purification of intact flagella from Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1971 Jan;105(1):376–383. doi: 10.1128/jb.105.1.376-383.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dewey T. G., Hammes G. G. Steady state kinetics of ATP synthesis and hydrolysis catalyzed by reconstituted chloroplast coupling factor. J Biol Chem. 1981 Sep 10;256(17):8941–8946. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dibrov P. A., Kostryko V. A., Lazarova R. L., Skulachev V. P., Smirnova I. A. The sodium cycle. I. Na+-dependent motility and modes of membrane energization in the marine alkalotolerant vibrio Alginolyticus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Jul 23;850(3):449–457. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(86)90113-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dimmitt K., Simon M. Purification and thermal stability of intact Bacillus subtilis flagella. J Bacteriol. 1971 Jan;105(1):369–375. doi: 10.1128/jb.105.1.369-375.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg E., Hill T. L., Chen Y. Cross-bridge model of muscle contraction. Quantitative analysis. Biophys J. 1980 Feb;29(2):195–227. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(80)85126-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guffanti A. A., Clejan S., Falk L. H., Hicks D. B., Krulwich T. A. Isolation and characterization of uncoupler-resistant mutants of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1987 Oct;169(10):4469–4478. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.10.4469-4478.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirota N., Imae Y. Na+-driven flagellar motors of an alkalophilic Bacillus strain YN-1. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 10;258(17):10577–10581. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joys T. M. The flagellar filament protein. Can J Microbiol. 1988 Apr;34(4):452–458. doi: 10.1139/m88-078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kashket E. R., Barker S. L. Effects of potassium ions on the electrical and pH gradients across the membrane of Streptococcus lactis cells. J Bacteriol. 1977 Jun;130(3):1017–1023. doi: 10.1128/jb.130.3.1017-1023.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kashket E. R. The proton motive force in bacteria: a critical assessment of methods. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1985;39:219–242. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.39.100185.001251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan S. Analysis of bacterial flagellar rotation. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1988;10(1-2):38–46. doi: 10.1002/cm.970100108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan S., Berg H. C. Isotope and thermal effects in chemiosmotic coupling to the flagellar motor of Streptococcus. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):913–919. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90076-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan S., Dapice M., Reese T. S. Effects of mot gene expression on the structure of the flagellar motor. J Mol Biol. 1988 Aug 5;202(3):575–584. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90287-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan S., Macnab R. M. Proton chemical potential, proton electrical potential and bacterial motility. J Mol Biol. 1980 Apr 15;138(3):599–614. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(80)80019-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan S., Meister M., Berg H. C. Constraints on flagellar rotation. J Mol Biol. 1985 Aug 20;184(4):645–656. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90310-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kihara M., Macnab R. M. Chemotaxis of Salmonella typhimurium toward citrate. J Bacteriol. 1979 Oct;140(1):297–300. doi: 10.1128/jb.140.1.297-300.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Läuger P. Ion transport and rotation of bacterial flagella. Nature. 1977 Jul 28;268(5618):360–362. doi: 10.1038/268360a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Läuger P. Torque and rotation rate of the bacterial flagellar motor. Biophys J. 1988 Jan;53(1):53–65. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(88)83065-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maloney P. C. Energy coupling to ATP synthesis by the proton-translocating ATPase. J Membr Biol. 1982;67(1):1–12. doi: 10.1007/BF01868643. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maloney P. C., Schattschneider S. Voltage sensitivity of the proton-translocating adenosine 5'-triphosphatase in Streptococcus lactis. FEBS Lett. 1980 Feb 11;110(2):337–340. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80106-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manson M. D., Tedesco P. M., Berg H. C. Energetics of flagellar rotation in bacteria. J Mol Biol. 1980 Apr 15;138(3):541–561. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(80)80017-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manson M. D., Tedesco P., Berg H. C., Harold F. M., Van der Drift C. A protonmotive force drives bacterial flagella. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jul;74(7):3060–3064. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.7.3060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meister M., Berg H. C. The stall torque of the bacterial flagellar motor. Biophys J. 1987 Sep;52(3):413–419. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(87)83230-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meister M., Caplan S. R., Berg H. C. Dynamics of a tightly coupled mechanism for flagellar rotation. Bacterial motility, chemiosmotic coupling, protonmotive force. Biophys J. 1989 May;55(5):905–914. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(89)82889-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meister M., Lowe G., Berg H. C. The proton flux through the bacterial flagellar motor. Cell. 1987 Jun 5;49(5):643–650. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90540-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller C. Bis-quaternary ammonium blockers as structural probes of the sarcoplasmic reticulum K+ channel. J Gen Physiol. 1982 May;79(5):869–891. doi: 10.1085/jgp.79.5.869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oosawa F., Hayashi S. The loose coupling mechanism in molecular machines of living cells. Adv Biophys. 1986;22:151–183. doi: 10.1016/0065-227x(86)90005-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramos S., Schuldiner S., Kaback H. R. The electrochemical gradient of protons and its relationship to active transport in Escherichia coli membrane vesicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jun;73(6):1892–1896. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.6.1892. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravid S., Matsumura P., Eisenbach M. Restoration of flagellar clockwise rotation in bacterial envelopes by insertion of the chemotaxis protein CheY. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(19):7157–7161. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.19.7157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shioi J. I., Matsuura S., Imae Y. Quantitative measurements of proton motive force and motility in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1980 Dec;144(3):891–897. doi: 10.1128/jb.144.3.891-897.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugiyama S., Cragoe E. J., Jr, Imae Y. Amiloride, a specific inhibitor for the Na+-driven flagellar motors of alkalophilic Bacillus. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 15;263(17):8215–8219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundberg S. A., Alam M., Spudich J. L. Excitation signal processing times in Halobacterium halobium phototaxis. Biophys J. 1986 Nov;50(5):895–900. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(86)83530-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanford C. Mechanism of free energy coupling in active transport. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:379–409. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.002115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanford C. Steady state of an ATP-driven calcium pump: limitations on kinetic and thermodynamic parameters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(20):6161–6165. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.20.6161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokuda H., Unemoto T. Characterization of the respiration-dependent Na+ pump in the marine bacterium Vibrio alginolyticus. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 10;257(17):10007–10014. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. J. Proton circuits in biological energy interconversions. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1988;17:71–97. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.17.060188.000443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodhull A. M. Ionic blockage of sodium channels in nerve. J Gen Physiol. 1973 Jun;61(6):687–708. doi: 10.1085/jgp.61.6.687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yellen G. Permeation in potassium channels: implications for channel structure. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1987;16:227–246. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.16.060187.001303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaritsky A., Kihara M., Macnab R. M. Measurement of membrane potential in Bacillus subtilis: a comparison of lipophilic cations, rubidium ion, and a cyanine dye as probes. J Membr Biol. 1981;63(3):215–231. doi: 10.1007/BF01870983. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


