Abstract
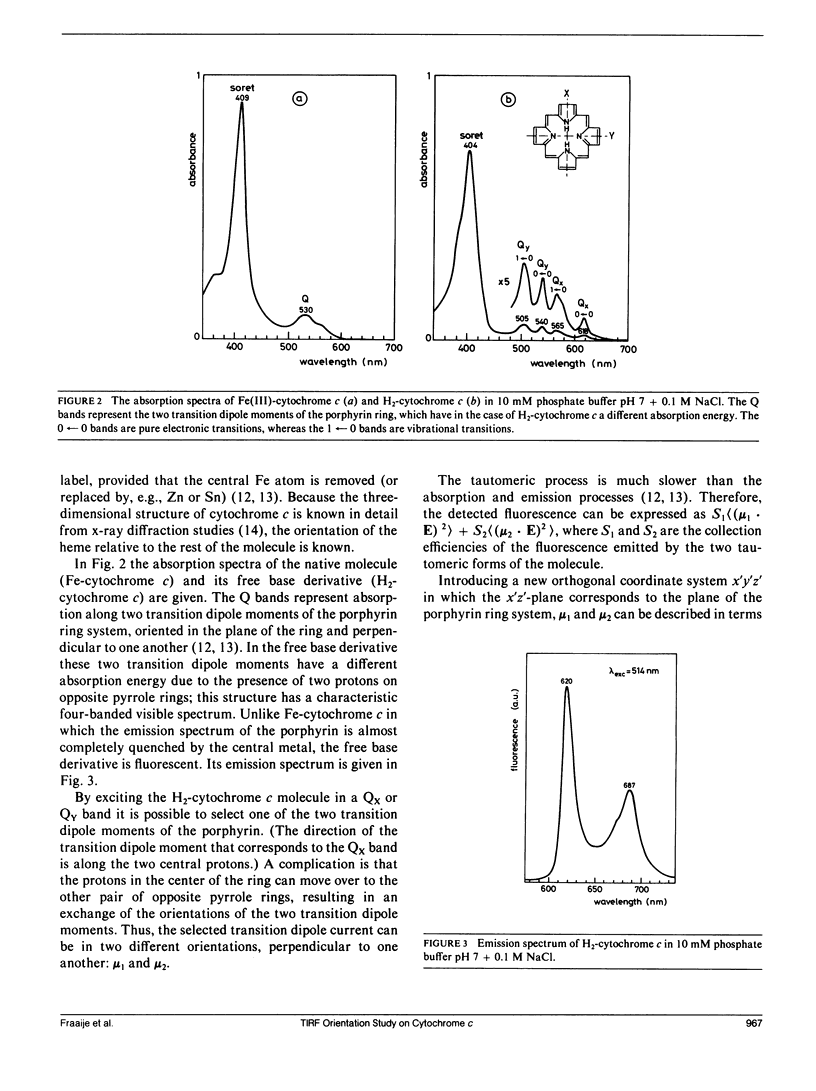
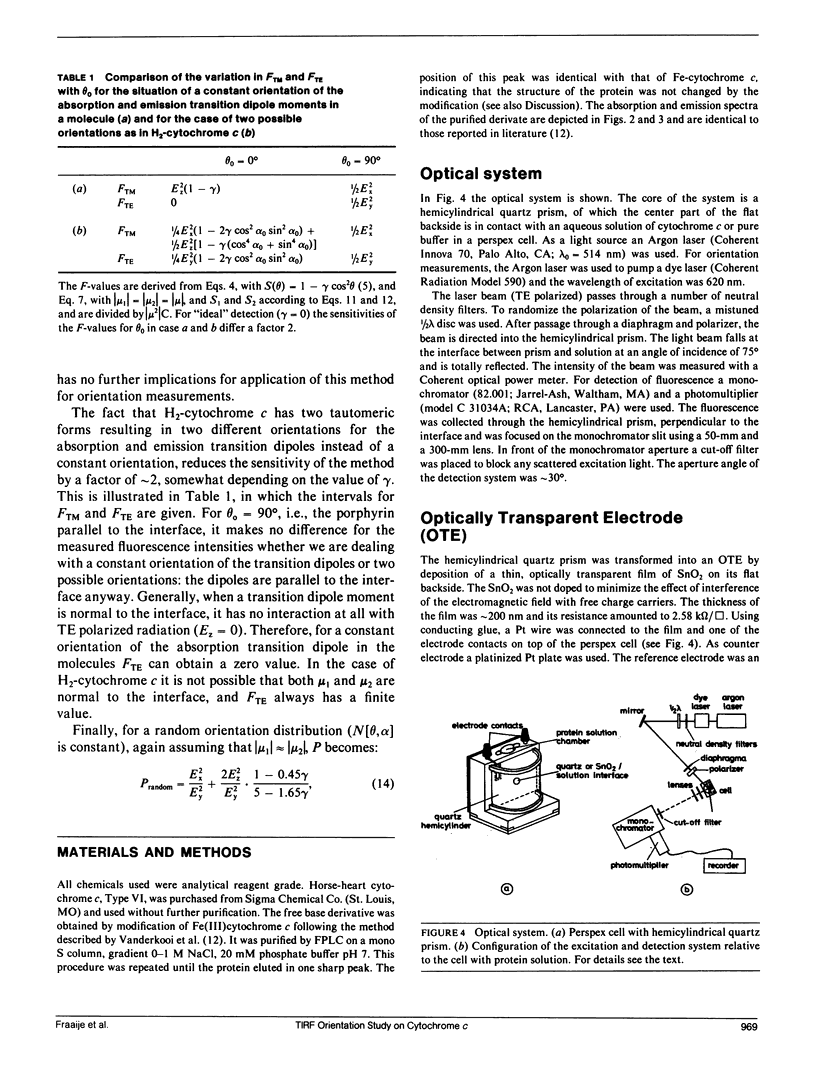
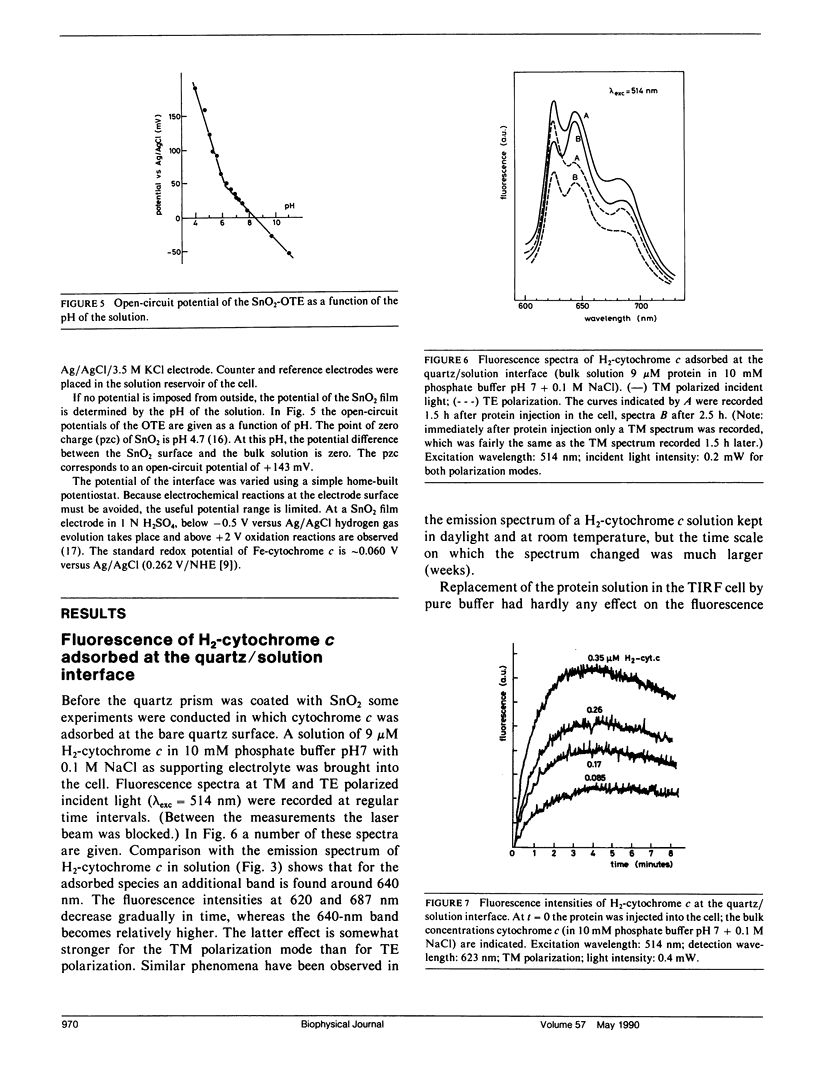
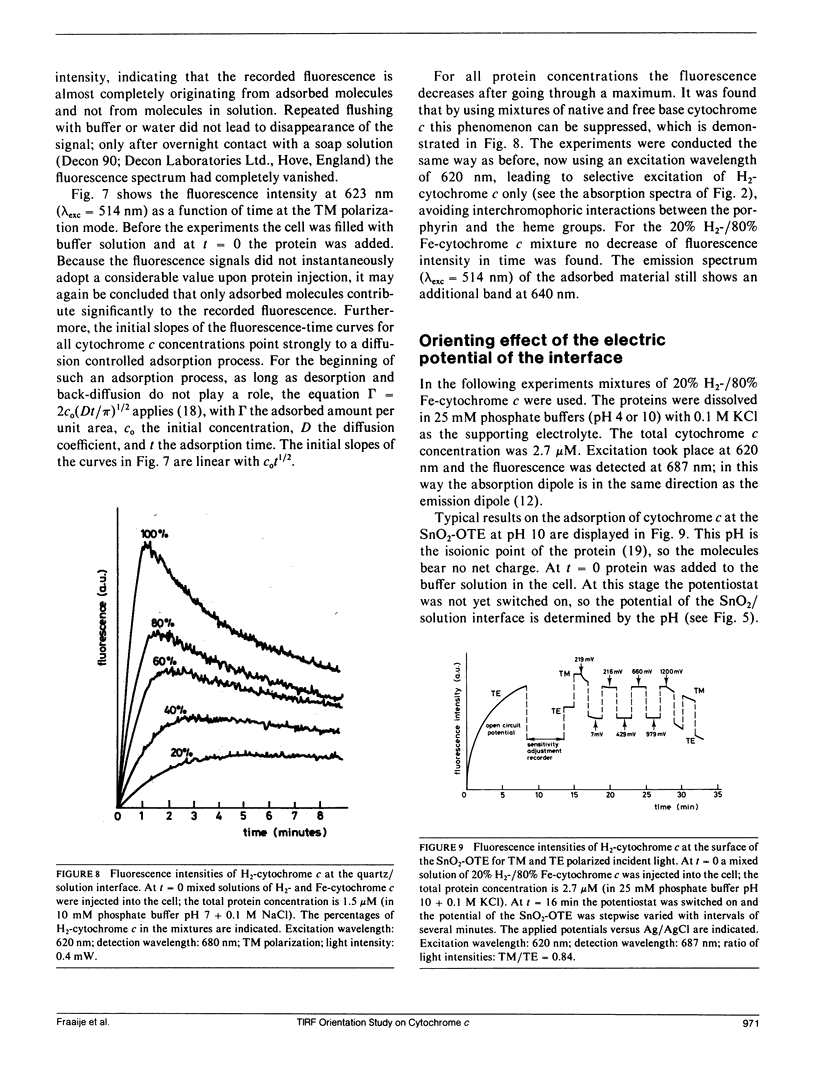
A method for determination of the orientation of adsorbed structure-stable proteins using Total Internal Reflection Fluorescence is outlined. The theory has been elaborated for orientation studies on adsorbed free base cytochrome c, of which the prophyrin can be used as an intrinsic fluorescent label. The ratio of fluorescence intensities at two polarization modes of the incident light (the transverse magnetic and the transverse electric polarization mode, respectively) gives a relation between the orientation angles of the porphyrin relative to the interface. As an illustration of the theory, experimental results on the adsorption of cytochrome c at an optically transparent SnO2 film electrode are presented. It is concluded that the orientation of the molecules can only be affected by the interfacial potential during the process of adsorption, but, once adsorbed, the orientation cannot be changed anymore by variation of the potential.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Axelrod D., Burghardt T. P., Thompson N. L. Total internal reflection fluorescence. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1984;13:247–268. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.13.060184.001335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burghardt T. P., Thompson N. L. Effect of planar dielectric interfaces on fluorescence emission and detection. Evanescent excitation with high-aperture collection. Biophys J. 1984 Dec;46(6):729–737. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84071-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickerson R. E., Takano T., Eisenberg D., Kallai O. B., Samson L., Cooper A., Margoliash E. Ferricytochrome c. I. General features of the horse and bonito proteins at 2.8 A resolution. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 10;246(5):1511–1535. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher W. R., Taniuchi H., Anfinsen C. B. On the role of heme in the formation of the structure of cytochrome c. J Biol Chem. 1973 May 10;248(9):3188–3195. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heineman W. R., Norris B. J., Goelz J. F. Measurement of enzyme E'values by optically transparent thin layer electrochemical cells. Anal Chem. 1975 Jan;47(1):79–84. doi: 10.1021/ac60351a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koppenol W. H., Margoliash E. The asymmetric distribution of charges on the surface of horse cytochrome c. Functional implications. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 25;257(8):4426–4437. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norde W. Adsorption of proteins from solution at the solid-liquid interface. Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 1986 Sep;25(4):267–340. doi: 10.1016/0001-8686(86)80012-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson N. L., Burghardt T. P., Axelrod D. Measuring surface dynamics of biomolecules by total internal reflection fluorescence with photobleaching recovery or correlation spectroscopy. Biophys J. 1981 Mar;33(3):435–454. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(81)84905-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson N. L., Burghardt T. P. Total internal reflection fluorescence. Measurement of spatial and orientational distributions of fluorophores near planar dielectric interfaces. Biophys Chem. 1986 Nov;25(1):91–97. doi: 10.1016/0301-4622(86)85069-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson N. L., McConnell H. M., Burhardt T. P. Order in supported phospholipid monolayers detected by the dichroism of fluorescence excited with polarized evanescent illumination. Biophys J. 1984 Dec;46(6):739–747. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84072-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanderkooi J. M., Adar F., Erecińska M. Metallocytochromes c: characterization of electronic absorption and emission spectra of Sn4+ and Zn2+ cytochromes c. Eur J Biochem. 1976 May 1;64(2):381–387. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10312.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanderkooi J. M., Erecińska M. Cytochrome c interaction with membranes. Absorption and emission spectra and binding characteristics of iron-free cytochrome c. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Dec 1;60(1):199–207. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb20992.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vos K., Laane C., Weijers S. R., Van Hoek A., Veeger C., Visser A. J. Time-resolved fluorescence and circular dichroism of porphyrin cytochrome c and Zn-porphyrin cytochrome c incorporated in reversed micelles. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Dec 1;169(2):259–268. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb13606.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


