Abstract
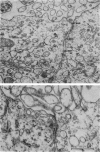
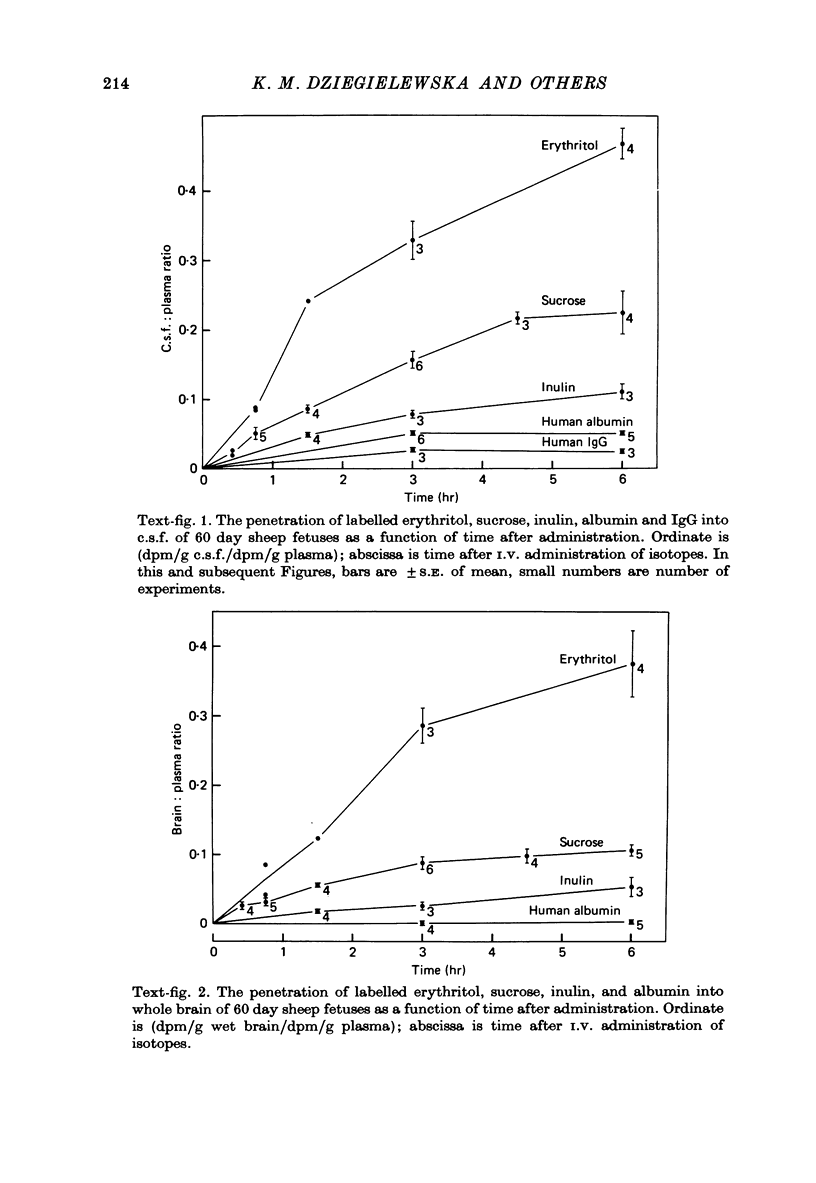
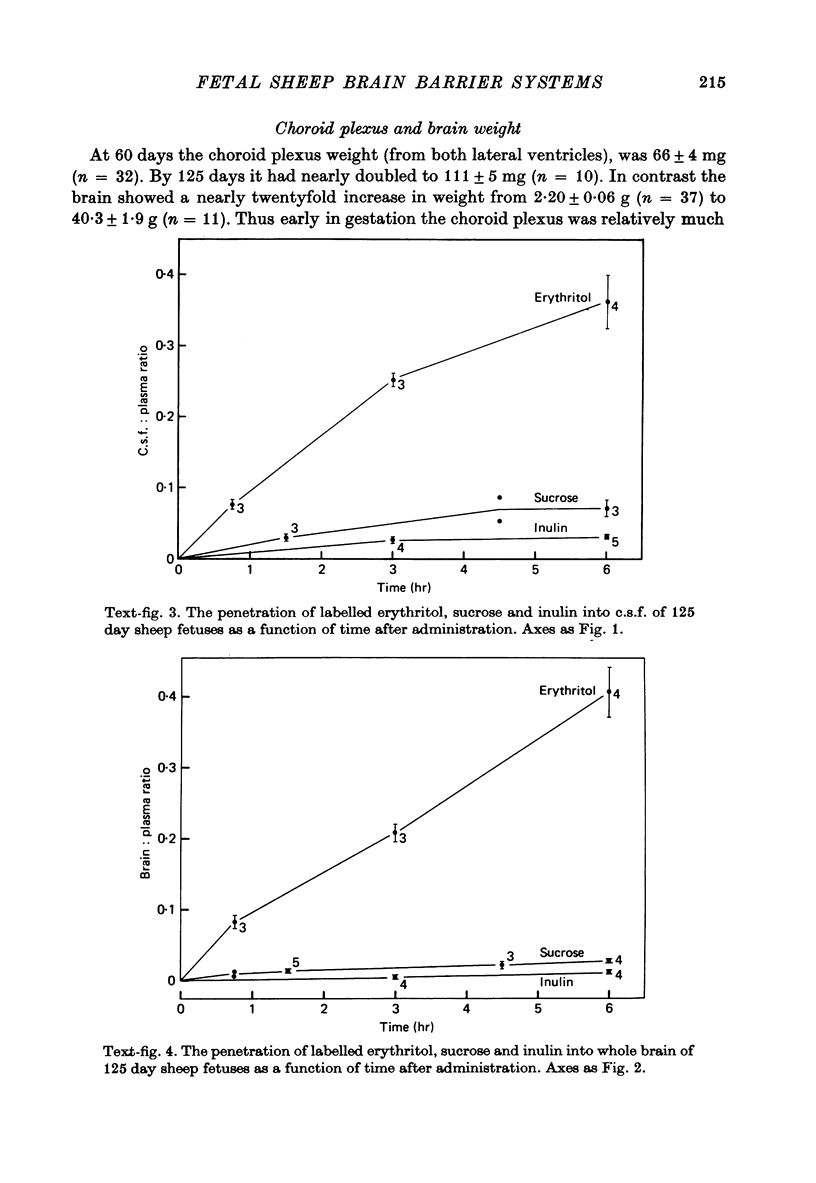
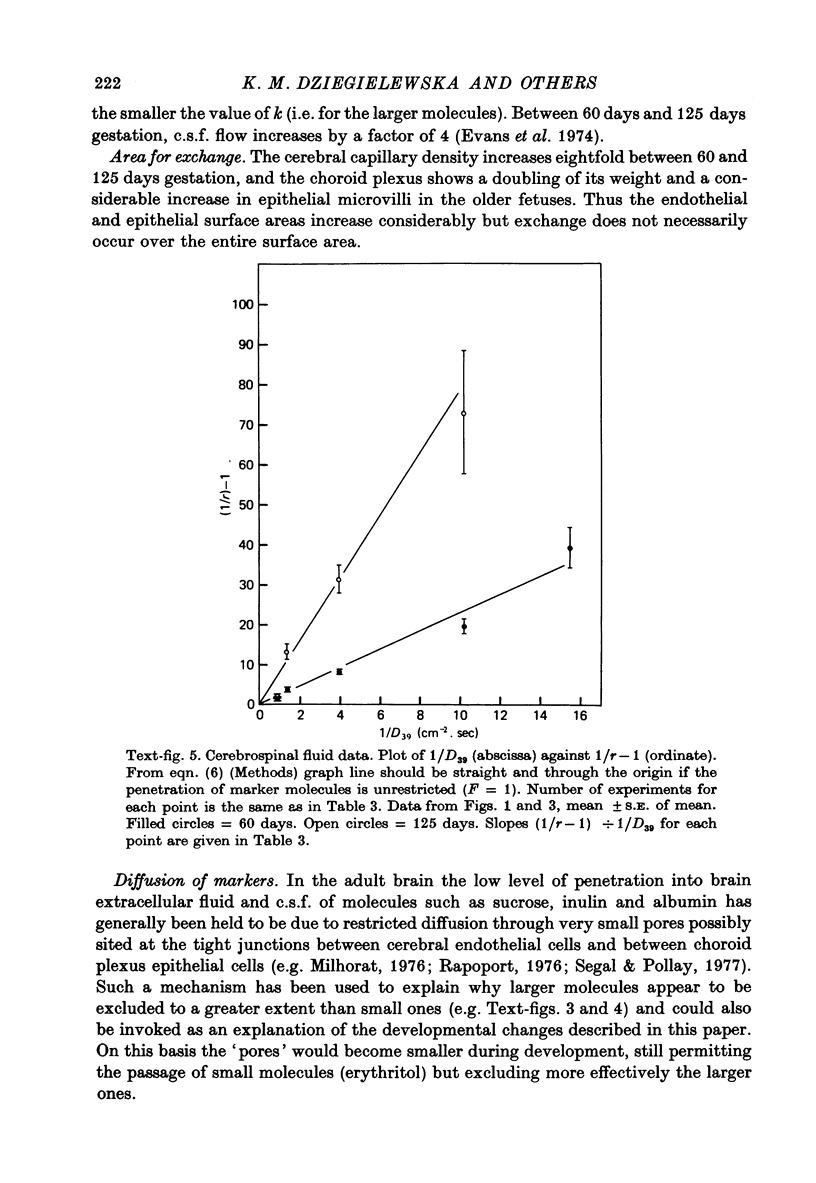
1. The development of the blood-brain and blood-c.s.f barriers to lipid insoluble substances of different molecular radii has been studied in fetal sheep, early (60 days) and late (125 days) in gestation, using labelled erythritol (C14), sucrose (3H or 14C), inulin (3H or 14C) and albumin (125I), or albumin and IgG detected by immunoassay. 2. Morphological studies of fetal brain and choroid plexus at the same gestational stages were carried out using thin section electron microscopy and the freeze fracture techniques. 3. Penetration of markers into c.s.f. was substantially greater at 60 days than at 125 days, but at both ages the steady-state level achieved appeared to be related to molecular size. 4. A simple model describing penetration from blood into c.s.f. at 60 days is proposed. It involves the assumption that c.s.f. and brain extracellular fluid are effectively separate compartments; morphological and permeability data which supports this assumption is presented. The data for c.s.f. at 60 days are consistent with the suggestion that the markers penetrate into c.s.f. by diffusion and are not restricted by small pores in the interface between blood and c.s.f. 5. The reduction in penetration which occurred by 125 days for all markers except erythritol appears to be accounted for by an increase in the sink effect and a decrease in the effective surface area for exchange between blood and c.s.f. 6. Intercellular tight junctions of both cerebral endothelial cells and choroid plexus epithelial cells were well formed at 60 days gestation. There was no change in junctional characteristics previously thought to correlate with transepithelial permeability (tight junction depth and strand number) between the two ages studied, although there were marked changes in permeability. 7. Evidence is advanced in support of the hypothesis that in the fetus much of the penetration of lipid insoluble non-polar substances across the blood-c.s.f. barrier and perhaps across the blood-brain barrier occurs via a transcellular route consisting of a system of tubulo-cisternal endoplasmic reticulum. Penetration via the choroid plexus appears to be the dominant route for penetration from blood into c.s.f. in the 60 day fetus.
Full text
PDF























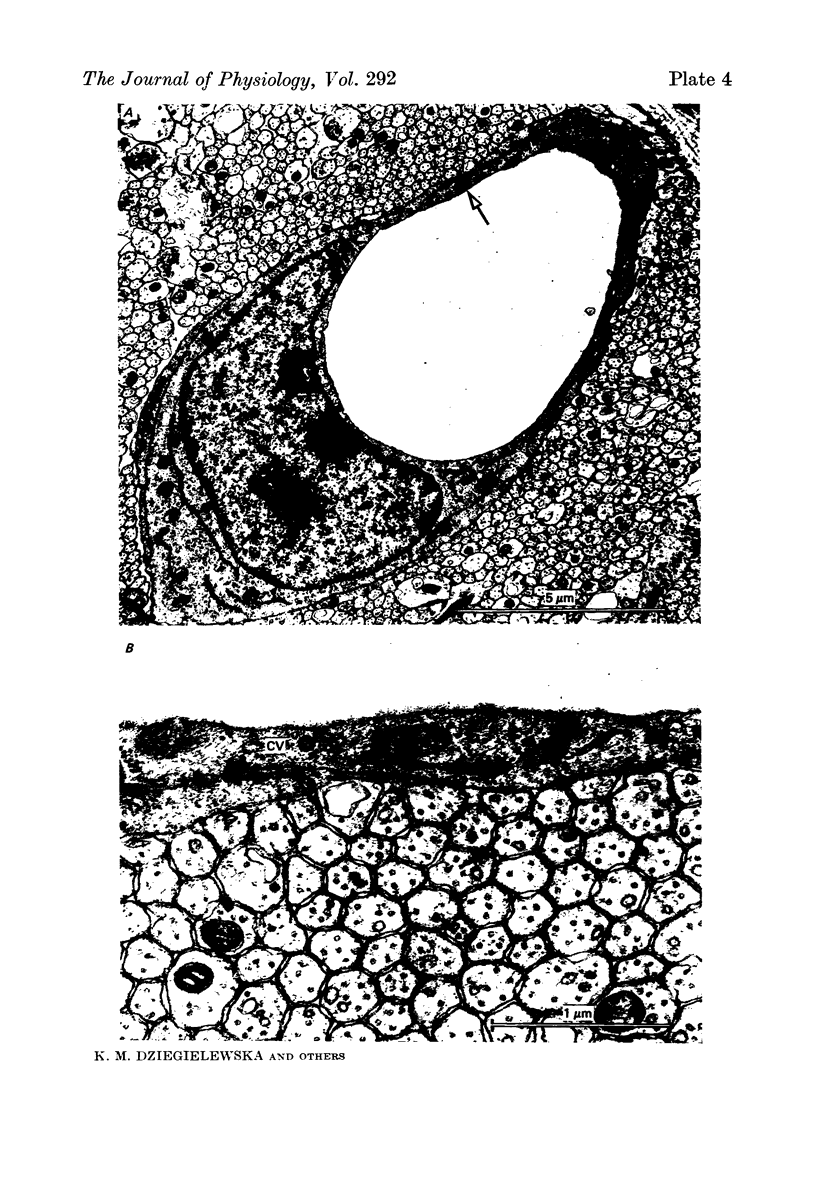


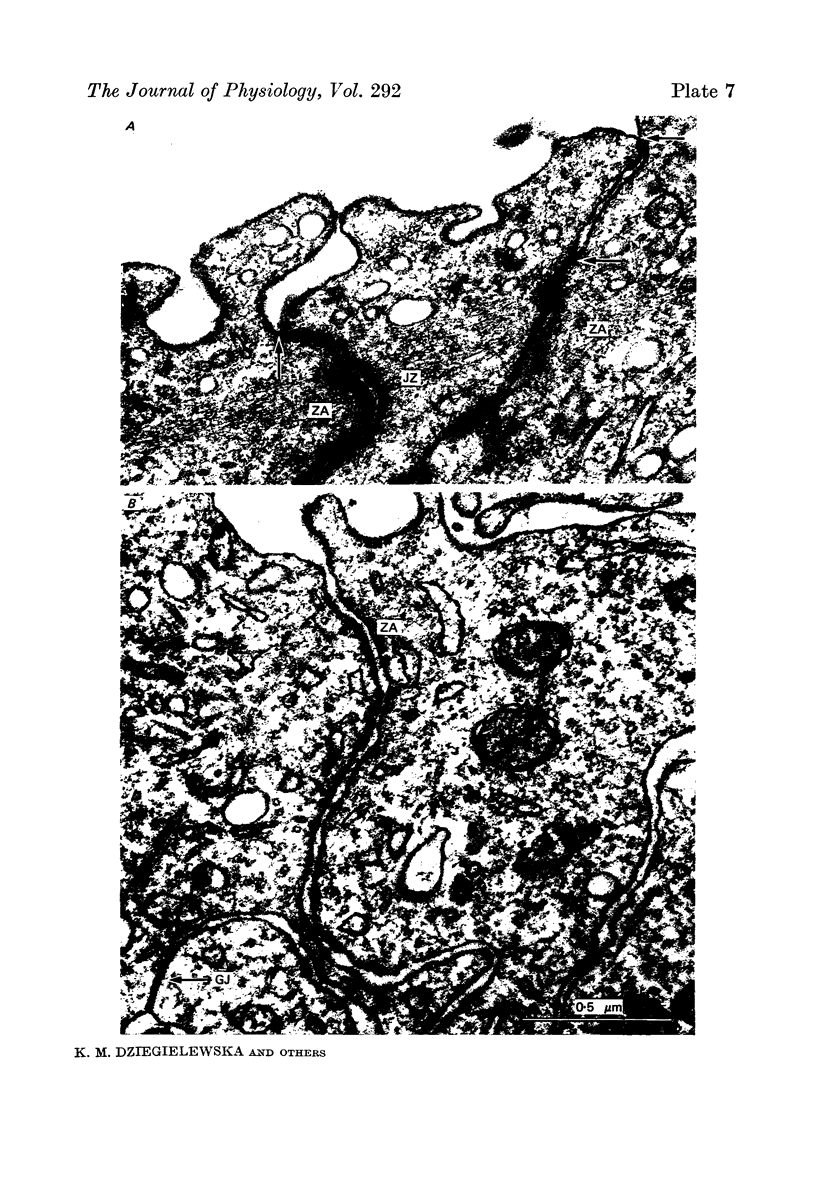

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amtorp O. Transfer of I125-albumin from blood into brain and cerebrospinal fluid in newborn and juvenile rats. Acta Physiol Scand. 1976 Mar;96(3):399–406. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1976.tb10208.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anchel H., Lindsley D. B. Differentiation of two reticulo-hypothalamic systems regulating hippocampal activity. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1972 Mar;32(3):209–226. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(72)90171-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bass N. H., Lundborg P. Postnatal development of bulk flow in the cerebrospinal fluid system of the albino rat: clearance of carboxyl-( 14 C)inulin after intrathecal infusion. Brain Res. 1973 Mar 30;52:323–332. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(73)90668-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker N. H., Novikoff A. B., Zimmerman H. M. Fine structure observations of the uptake of intravenously injected peroxidase by the rat choroid plexus. J Histochem Cytochem. 1967 Mar;15(3):160–165. doi: 10.1177/15.3.160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birge W. J., Rose A. D., Haywood J. R., Doolin P. F. Development of the blood-cerebrospinal fluid barrier to proteins and differentiation of cerebrospinal fluid in the chick embryo. Dev Biol. 1974 Dec;41(2):245–254. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(74)90303-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradbury M. W., Crowder J., Desai S., Reynolds J. M., Reynolds M., Saunders N. R. Electrolytes and water in the brain and cerebrospinal fluid of the foetal sheep and guinea-pig. J Physiol. 1972 Dec;227(2):591–610. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp010049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Branton D., Bullivant S., Gilula N. B., Karnovsky M. J., Moor H., Mühlethaler K., Northcote D. H., Packer L., Satir B., Satir P. Freeze-etching nomenclature. Science. 1975 Oct 3;190(4209):54–56. doi: 10.1126/science.1166299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Branton D. Fracture faces of frozen membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 May;55(5):1048–1056. doi: 10.1073/pnas.55.5.1048. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brightman M. W., Reese T. S. Junctions between intimately apposed cell membranes in the vertebrate brain. J Cell Biol. 1969 Mar;40(3):648–677. doi: 10.1083/jcb.40.3.648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bär T., Wolff J. R. The formation of capillary basement membranes during internal vascularization of the rat's cerebral cortex. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1972;133(2):231–248. doi: 10.1007/BF00307145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caulfield J. P., Farquhar M. G. The permeability of glomerular capillaries to graded dextrans. Identification of the basement membrane as the primary filtration barrier. J Cell Biol. 1974 Dec;63(3):883–903. doi: 10.1083/jcb.63.3.883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claude P., Goodenough D. A. Fracture faces of zonulae occludentes from "tight" and "leaky" epithelia. J Cell Biol. 1973 Aug;58(2):390–400. doi: 10.1083/jcb.58.2.390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAITZ H. M., POWELL T. P. Studies of the connexions of the fornix system. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1954 Feb;17(1):75–82. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.17.1.75. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DARIAN-SMITH I., PHILLIPS G., RYAN R. D. FUNCTIONAL ORGANIZATION IN THE TRIGEMINAL MAIN SENSORY AND ROSTRAL SPINAL NUCLEI OF THE CAT. J Physiol. 1963 Aug;168:129–146. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFrance J. F., Shimono T., Kitai S. T. Anatomical distribution of the hippocampal fibers afferent to the lateral septal nucleus. Brain Res. 1971 Nov;34(1):176–180. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(71)90359-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFrance J. F., Shimono T., Kitai S. T. Hippocampal inputs to the lateral septal nucleus: patterns of facilitation and inhibition. Brain Res. 1972 Feb 25;37(2):333–339. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(72)90681-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFrance J. F., Yoshihara H., Chronister R. B. Electrophysiological studies of the septal nuclei. II. The medial septal region. Exp Neurol. 1978 Jan 1;58(1):14–31. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(78)90117-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFrance J. F., Yoshihara H., Chronister R. B. Electrophysiological studies of the septal nuclei: I. The lateral septal region. Exp Neurol. 1976 Nov;53(2):399–419. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(76)90081-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFrance J. F., Yoshihara H., McCrea R. A., Kitai S. T. Pharmacology of the inhibiton in the lateral septal region. Exp Neurol. 1975 Sep;48(3 Pt 1):502–523. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(75)90009-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFrance J. F., Yoshihara H. Medial forebrain bundle projections to the nucleus of the diagonal band of Broca. Experientia. 1975 Jul 15;31(7):809–810. doi: 10.1007/BF01938477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delorme P. Différenciation ultrastructurale des jonctions intercellulaires de l'endothélium des capillaires télencéphaliques chez l'embron de poulet. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1972;133(4):571–582. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doolin P. F., Birge W. J. Ultrastructural differentiation of the junctional complex of the avian choroidal epithelium. J Comp Neurol. 1969 Jul;136(3):253–267. doi: 10.1002/cne.901360302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edinger H., Siegel A., Troiano R. Single unit analysis of the hippocampal projections to the septum in the cat. Exp Neurol. 1973 Dec;41(3):569–583. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(73)90051-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eto T., Omae T., Yamamoto T. An electron microscope study of hypertensive encephalopathy in the rat with renal hypertension. Arch Histol Jpn. 1971 Jun;33(2):133–143. doi: 10.1679/aohc1950.33.133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans C. A., Reynolds J. M., Reynolds M. L., Saunders N. R., Segal M. B. The development of a blood-brain barrier mechanism in foetal sheep. J Physiol. 1974 Apr;238(2):371–386. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010530. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans C. A., Reynolds J. M., Reynolds M. L., Saunders N. R. The effect of hypercapnia on a blood-brain barrier mechanism in foetal and new-born sheep. J Physiol. 1976 Mar;255(3):701–714. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felgenhauer K. Protein size and cerebrospinal fluid composition. Klin Wochenschr. 1974 Dec 15;52(24):1158–1164. doi: 10.1007/BF01466734. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson R. K., Woodbury D. M. Penetration of 14C-inulin and 14C-sucrose into brain, cerebrospinal fluid, and skeletal muscle of developing rats. Exp Brain Res. 1969;7(3):181–194. doi: 10.1007/BF00239028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeman W. J., Patel H. H. Extraneuronal potential fields evoked in septal region of cat by stimulation of fornix. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1968 May;24(5):444–457. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(68)90104-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREEN J. D., ARDUINI A. A. Hippocampal electrical activity in arousal. J Neurophysiol. 1954 Nov;17(6):533–557. doi: 10.1152/jn.1954.17.6.533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto P. H. Intracellular channels as a route for protein passage in the capillary endothelium of the shark brain. Am J Anat. 1972 May;134(1):41–57. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001340105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayward J. N., Vincent J. D. Osmosensitive single neurones in the hypothalamus of unanaesthetized monkeys. J Physiol. 1970 Nov;210(4):947–972. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hosain F., McIntyre P. A., Poulose K., Stern H. S., Wagner H. N., Jr Binding of trace amounts of ionic indium-113m to plasma transferrin. Clin Chim Acta. 1969 Apr;24(1):69–75. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(69)90142-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KILLAM E. K. Drug action on the brain-stem reticular formation. Pharmacol Rev. 1962 Jun;14:175–223. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEE J. C., OLSZEWSKI J. Penetration of radioactive bovine albumin from cerebrospinal fluid into brain tissue. Neurology. 1960 Sep;10:814–822. doi: 10.1212/wnl.10.9.814. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIERSE W. DIE KAPILLARDICHTE IM WIRBELTIERGEHIRN. Acta Anat (Basel) 1963;54:1–31. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lange W., Halata Z. Die Ultrastruktur der Kapillaren der Kleinhirnrinde und das perikapilläre Gewebe. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1972;128(1):83–99. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee B. B., Mandl G., Stean J. P. Micro-electrode tip position marking in nervous tissue: a new dye method. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1969 Dec;27(6):610–613. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(69)90075-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis P. R., Shute C. C. The cholinergic limbic system: projections to hippocampal formation, medial cortex, nuclei of the ascending cholinergic reticular system, and the subfornical organ and supra-optic crest. Brain. 1967 Sep;90(3):521–540. doi: 10.1093/brain/90.3.521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUGNAINI E., WALBERG F. THE FINE STRUCTURE OF THE CAPPILLARIES AND THEIR SURROUNDINGS IN THE CEREBRAL HEMISPHERES OF MYXINE GLUTINOSA (L.). Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1965 May 6;66(3):333–351. doi: 10.1007/BF00334716. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini G., Carbonara A. O., Heremans J. F. Immunochemical quantitation of antigens by single radial immunodiffusion. Immunochemistry. 1965 Sep;2(3):235–254. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(65)90004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLennan H., Miller J. J. The hippocampal control of neuronal discharges in the septum of the rat. J Physiol. 1974 Mar;237(3):607–624. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meschia G., Makowski E. L., Battaglia F. C. The use of indwelling catheters in the uterine and umbilical veins of sheep for a description of fetal acid-base balance and oxygenation. Yale J Biol Med. 1969 Dec;42(3-4):154–165. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milhorat T. H. Structure and function of the choroid plexus and other sites of cerebrospinal fluid formation. Int Rev Cytol. 1976;47:225–288. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)60090-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mollgård K., Saunders N. R. A possible transepithelial pathway via endoplasmic reticulum in foetal sheep choroid plexus. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1977 Nov 14;199(1135):321–326. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1977.0142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mollgøard K., Saunders N. R. Complex tight junctions of epithelial and of endothelial cells in early foetal brain. J Neurocytol. 1975 Aug;4(4):453–468. doi: 10.1007/BF01261375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Møllgård K., Milinowska D. H., Saunders N. R. Lack of correlation between tight junction morphology and permeability properties in developing choroid plexus. Nature. 1976 Nov 18;264(5583):293–294. doi: 10.1038/264293a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Normand I. C., Olver R. E., Reynolds E. O., Strang L. B. Permeability of lung capillaries and alveoli to non-electrolytes in the foetal lamb. J Physiol. 1971 Dec;219(2):303–330. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldendorf W. H., Davson H. Brain extracellular space and the sink action of cerebrospinal fluid. Measurement of rabbit brain extracellular space using sucrose labeled with carbon 14. Arch Neurol. 1967 Aug;17(2):196–205. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1967.00470260086010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olver R. E., Strang L. B. Ion fluxes across the pulmonary epithelium and the secretion of lung liquid in the foetal lamb. J Physiol. 1974 Sep;241(2):327–357. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PETSCHE H., STUMPF C., GOGOLAK G. [The significance of the rabbit's septum as a relay station between the midbrain and the hippocampus. I. The control of hippocampus arousal activity by the septum cells]. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1962 Apr;14:202–211. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(62)90030-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pappas G. D. Some morphological considerations of the blood-brain barrier. J Neurol Sci. 1970 Mar;10(3):241–246. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(70)90152-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinto da Silva P., Branton D. Membrane splitting in freeze-ethching. Covalently bound ferritin as a membrane marker. J Cell Biol. 1970 Jun;45(3):598–605. doi: 10.1083/jcb.45.3.598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell E. W., Clark W. M., Mukawa J. An evoked potential study of limbic projections to nuclei of the cat septum. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1968 Sep;25(3):266–273. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(68)90025-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reese T. S., Karnovsky M. J. Fine structural localization of a blood-brain barrier to exogenous peroxidase. J Cell Biol. 1967 Jul;34(1):207–217. doi: 10.1083/jcb.34.1.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STUMPF C. THE FAST COMPONENT IN THE ELECTRICAL ACTIVITY OF RABBIT'S HIPPOCAMPUS. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1965 Apr;18:477–486. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(65)90128-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saunders N. R. Ontogeny of the blood-brain barrier. Exp Eye Res. 1977;25 (Suppl):523–550. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4835(77)80046-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal M. B., Pollay M. The secretion of cerebrospinal fluid. Exp Eye Res. 1977;25 (Suppl):127–148. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4835(77)80012-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaywitz B. A., Katzman R., Escriva A. CSF formation and 24Na clearance in normal and hydrocephalic kittens during ventriculocisternal perfusion. Neurology. 1969 Dec;19(12):1159–1168. doi: 10.1212/wnl.19.12.1159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel A., Tassoni J. P. Differential efferent projections from the ventral and dorsal hippocampus of the cat. Brain Behav Evol. 1971;4(3):185–200. doi: 10.1159/000125433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TENNYSON V. M., PAPPAS G. D. FINE STRUCTURE OF THE DEVELOPING TELENCEPHALIC AND MYELENCEPHALIC CHOROID PLEXUS IN THE RABBIT. J Comp Neurol. 1964 Dec;123:379–411. doi: 10.1002/cne.901230307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VALENSTEIN E. S., NAUTA W. J. A comparison of the distribution of the fornix system in the rat, guinea pig, cat, and monkey. J Comp Neurol. 1959 Dec;113:337–363. doi: 10.1002/cne.901130302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOLFF J. [Contributions to the ultrastructure of the capillaries in the normal cerebral cortex]. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1963;60:409–431. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westergaard E., Brightman M. W. Transport of proteins across normal cerebral arterioles. J Comp Neurol. 1973 Nov 1;152(1):17–44. doi: 10.1002/cne.901520103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westergaard E. Enhanced vesicular transport of exogenous peroxidase across cerebral vessels, induced by serotonin. Acta Neuropathol. 1975;32(1):27–42. doi: 10.1007/BF00686065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson C. L., Motter B. C., Lindsley D. B. Influences of hypothalamic stimulation upon septal and hippocampal electrical activity in the cat. Brain Res. 1976 Apr 30;107(1):55–68. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90095-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright E. M. Mechanisms of ion transport across the choroid plexus. J Physiol. 1972 Oct;226(2):545–571. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright E. M., Pietras R. J. Routes of nonelectrolyte permeation across epithelial membranes. J Membr Biol. 1974 Jul 12;17(3):293–312. doi: 10.1007/BF01870189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]