Abstract
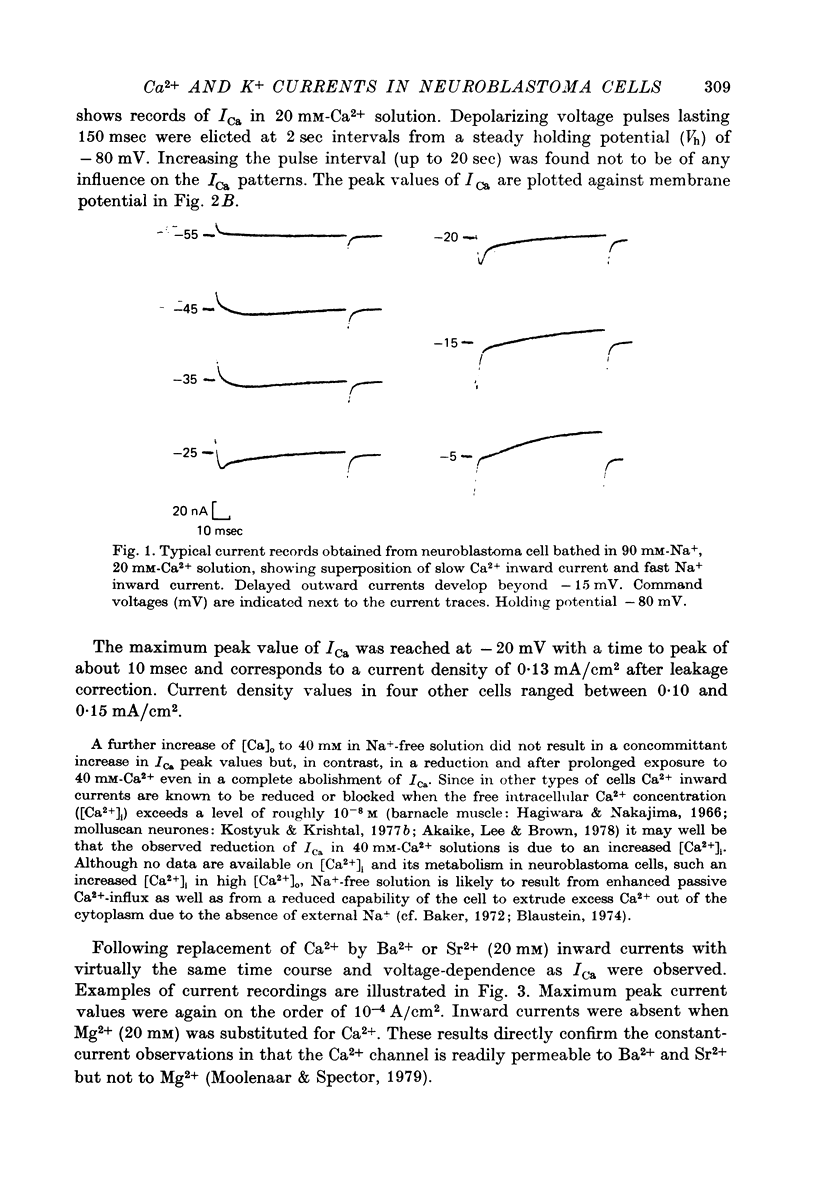
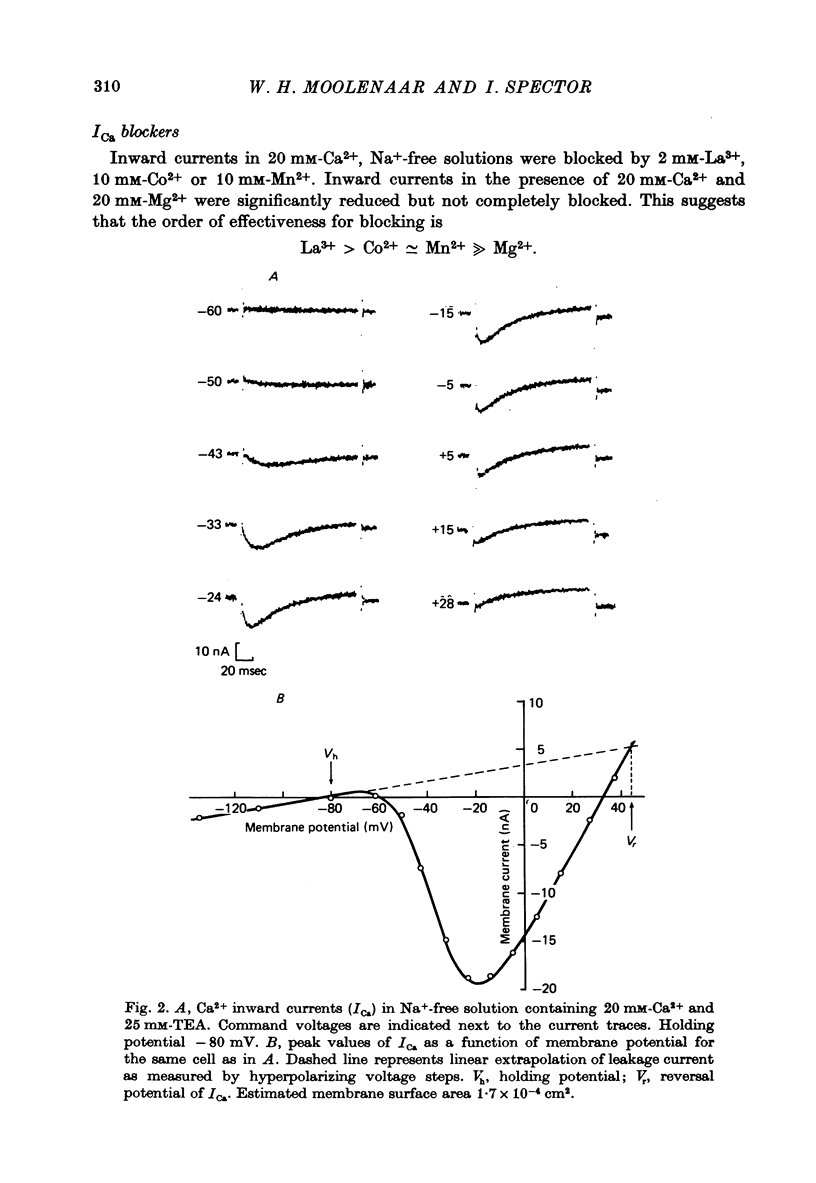
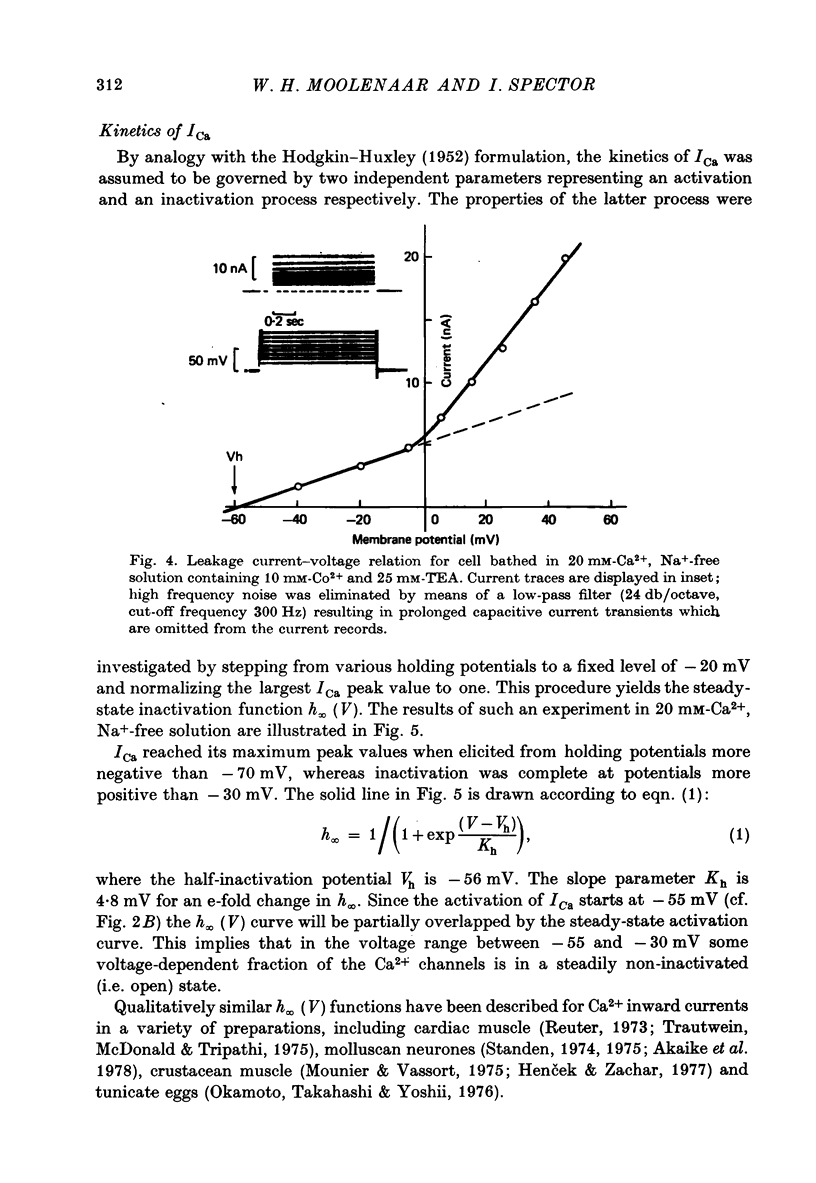
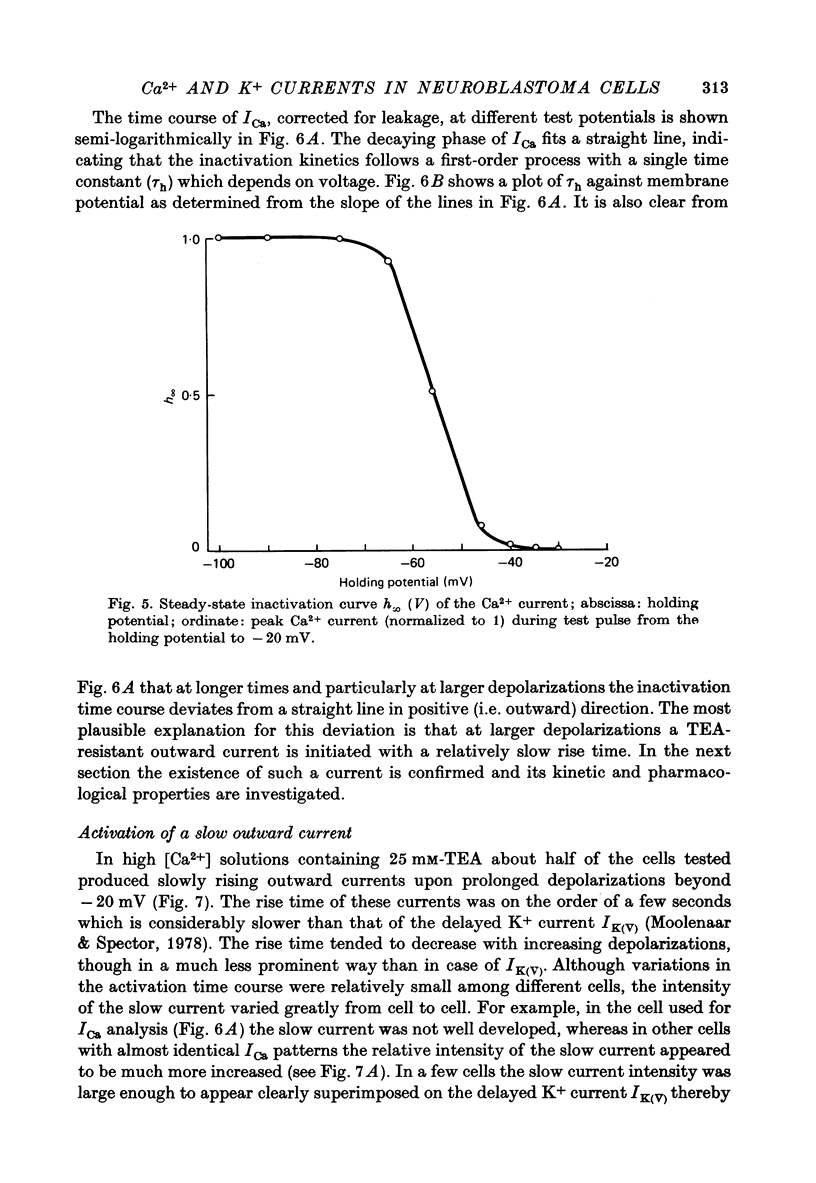
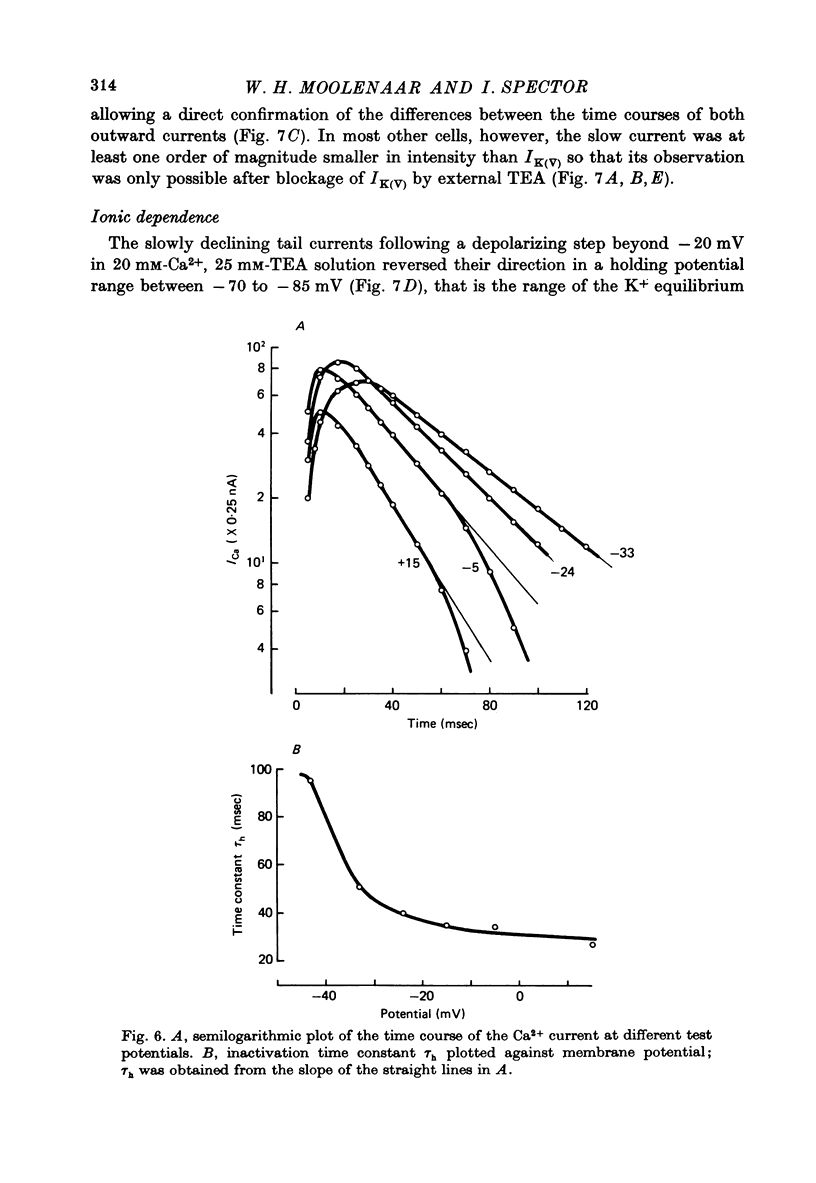
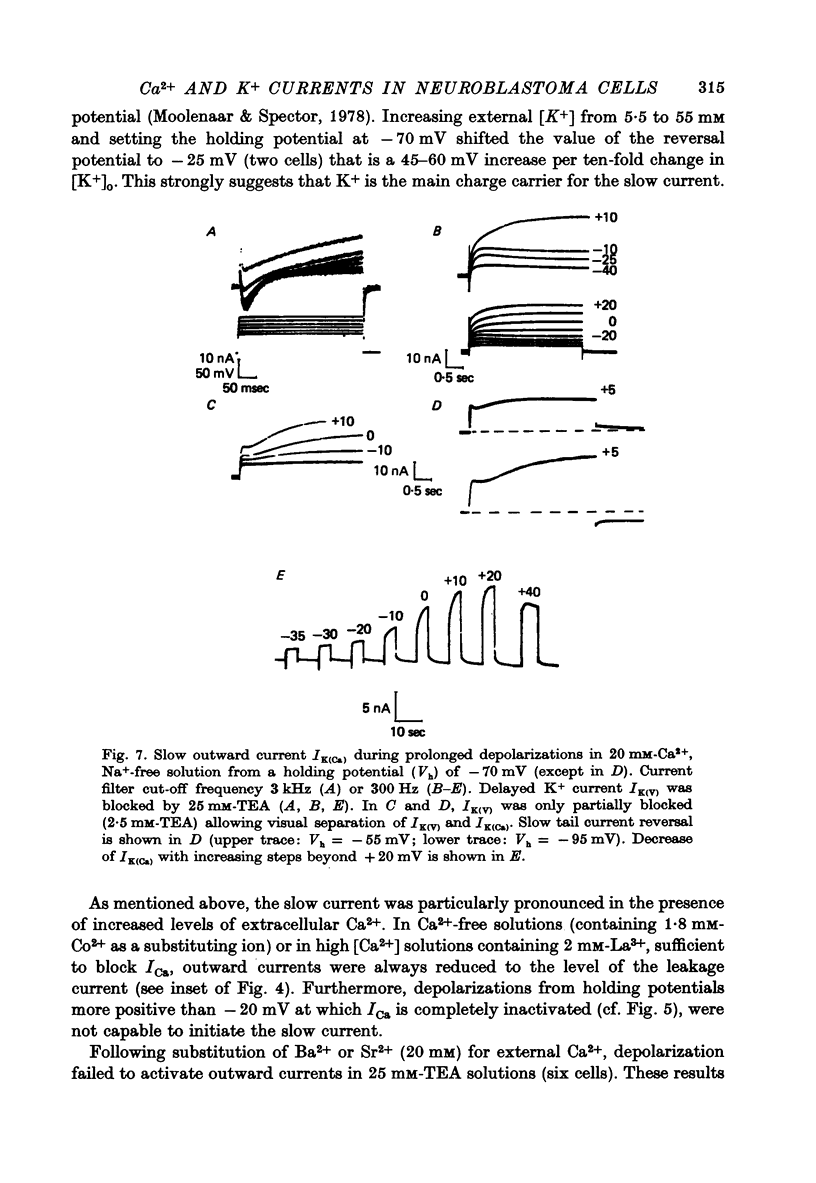
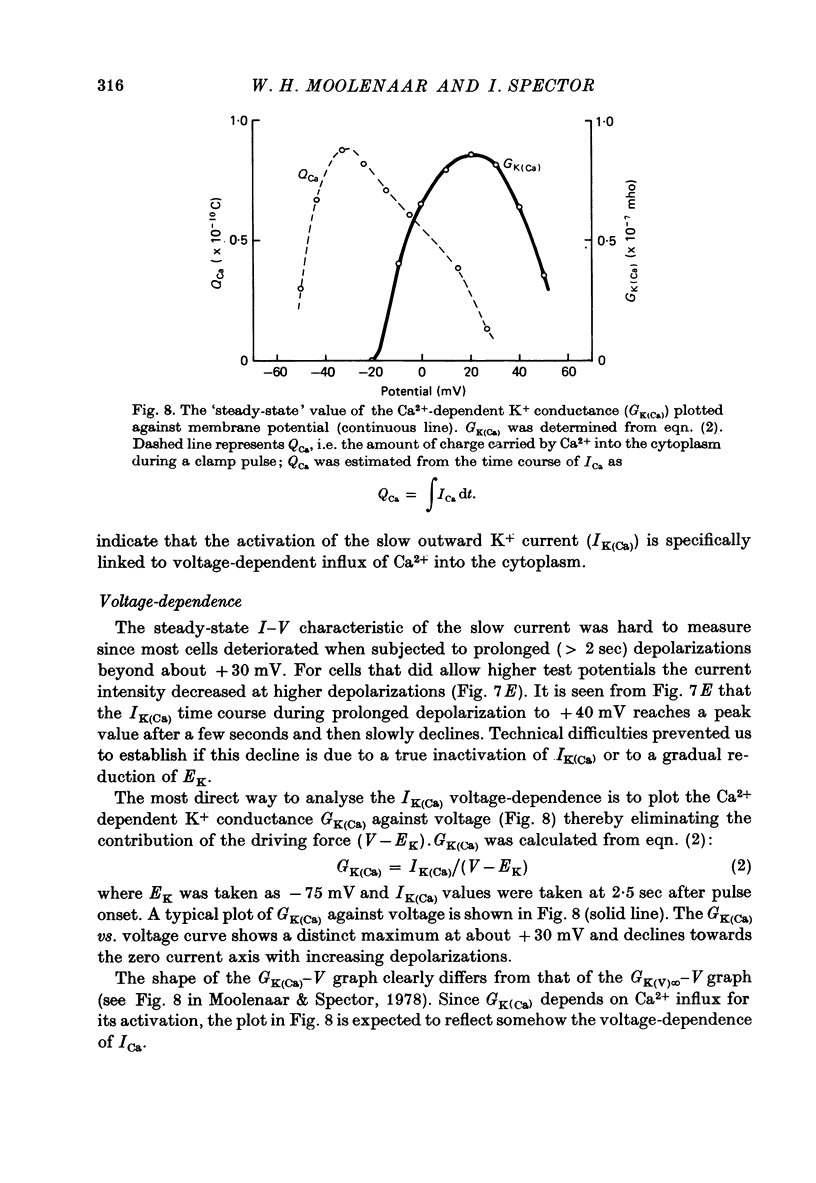
1. The Ca2+ inward current (ICa) and a slow outward current in differentiated cells of mouse neuroblastoma clone N1E-115 have been studied under voltage-clamp conditions. 2. ICa shows voltage- and time-dependent inactivation when evoked by step-wise depolarizations in Na+-free solution containing high [Ca2+] (20 nM) and tetraethylammonium (TEA, 25 mM). Ba2+ and Sr2+ can substitute for Ca2+. 3. Holding potentials below -70 mV maximal activate ICa. Half inactivation occurs at -56 mV and ICa is completely inactivated beyond holding levels of -30 mV. Maximum peak currents are of the order of 10(-4) A/cm2 and the reversal potential ranges from +40 to +60 mV. The ICa inactivation time course follows first-order kinetics with a voltage-depedent time constant ranging from 25 to 100 msec. 4. The striking resemblance between ICa and the Ca2+ current in the unfertilized mouse oocyte (Okamoto, Takahashi & Yamashita, 1977) is discussed. 5. A slow outward current with a rise time of several seconds is recorded on voltage steps beyond -20 mV in high [Ca2+] solutions. It is carried primarily by K+ on account of the value of the reversal potential and its dependence on [K]0. This K+ current is TEA-insensitive and is blocked by Ca2+ antagonists. 6. The slow K+ current (IK(Ca)) is suggested to be mediated by Ca2+ influx, but the voltage-dependence of the underlying conductance (GK(Ca)) differs significantly from the ICa voltage-dependence. 7. The results are consistent with the hypothesis that IK(Ca) depends both on ICa and on membrane potential. An alternative hypothesis is briefly discussed.
Full text
PDF









Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ADELMAN W. J., TAYLOR R. E. Leakage current rectification in the squid giant axon. Nature. 1961 Jun 3;190:883–885. doi: 10.1038/190883a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adrian R. H., Chandler W. K., Hodgkin A. L. Slow changes in potassium permeability in skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1970 Jul;208(3):645–668. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akaike N., Lee K. S., Brown A. M. The calcium current of Helix neuron. J Gen Physiol. 1978 May;71(5):509–531. doi: 10.1085/jgp.71.5.509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. F., Meves H., Ridgway E. B. Calcium entry in response to maintained depolarization of squid axons. J Physiol. 1973 Jun;231(3):527–548. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. F. Transport and metabolism of calcium ions in nerve. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1972;24:177–223. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(72)90007-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett E. F., Barret J. N. Separation of two voltage-sensitive potassium currents, and demonstration of a tetrodotoxin-resistant calcium current in frog motoneurones. J Physiol. 1976 Mar;255(3):737–774. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaustein M. P. The interrelationship between sodium and calcium fluxes across cell membranes. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1974;70:33–82. doi: 10.1007/BFb0034293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brehm P., Dunlap K., Eckert R. Calcium-dependent repolarization in Paramecium. J Physiol. 1978 Jan;274:639–654. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busis N. A., Weight F. F. Spike after-hyperpolarisation of a sympathetic neurone is calcium sensitive and is potentiated by theophylline. Nature. 1976 Sep 30;263(5576):434–436. doi: 10.1038/263434a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clusin W. T., Bennett M. V. Calcium-activated conductance in skate electroreceptors: voltage clamp experiments. J Gen Physiol. 1977 Feb;69(2):145–182. doi: 10.1085/jgp.69.2.145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckert R., Lux H. D. A voltage-sensitive persistent calcium conductance in neuronal somata of Helix. J Physiol. 1976 Jan;254(1):129–151. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckert R., Tillotson D. Potassium activation associated with intraneuronal free calcium. Science. 1978 Apr 28;200(4340):437–439. doi: 10.1126/science.644308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckert R., Tillotson D., Ridgway E. B. Voltage-dependent facilitation of Ca2+ entry in voltage-clamped, aequorin-injected molluscan neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Apr;74(4):1748–1752. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.4.1748. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulton B. P., Whittingham D. G. Activation of mammalian oocytes by intracellular injection of calcium. Nature. 1978 May 11;273(5658):149–151. doi: 10.1038/273149a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geduldig D., Gruener R. Voltage clamp of the Aplysia giant neurone: early sodium and calcium currents. J Physiol. 1970 Nov;211(1):217–244. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman L., Binstock L. Leak current rectification in Myxicola giant axons. Constant field and constant conductance components. J Gen Physiol. 1969 Dec;54(6):755–764. doi: 10.1085/jgp.54.6.755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman A. L., Thomas M. V. Changes in the intracellular concentration of free calcium ions in a pace-maker neurone, measured with the metallochromic indicator dye arsenazo III. J Physiol. 1978 Feb;275:357–376. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HUXLEY A. F. A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. J Physiol. 1952 Aug;117(4):500–544. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara S. Ca spike. Adv Biophys. 1973;4:71–102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara S., Fukuda J., Eaton D. C. Membrane currents carried by Ca, Sr, and Ba in barnacle muscle fiber during voltage clamp. J Gen Physiol. 1974 May;63(5):564–578. doi: 10.1085/jgp.63.5.564. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara S., Hayashi H., Takahashi K. Calcium and potassium currents of the membrane of a barnacle muscle fibre in relation to the calcium spike. J Physiol. 1969 Nov;205(1):115–129. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara S., Nakajima S. Effects of the intracellular Ca ion concentration upon the excitability of the muscle fiber membrane of a barnacle. J Gen Physiol. 1966 Mar;49(4):807–818. doi: 10.1085/jgp.49.4.807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara S., Takahashi K. Surface density of calcium ions and calcium spikes in the barnacle muscle fiber membrane. J Gen Physiol. 1967 Jan;50(3):583–601. doi: 10.1085/jgp.50.3.583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hencek M., Zachar J. Calcium currents and conductances in the msucle membrane of the crayfish. J Physiol. 1977 Jun;268(1):51–71. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011846. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyer C. B., Lux H. D. Control of the delayed outward potassium currents in bursting pace-maker neurones of the snail, Helix pomatia. J Physiol. 1976 Nov;262(2):349–382. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyer C. B., Lux H. D. Properties of a facilitating calcium current in pace-maker neurones of the snail, Helix pomatia. J Physiol. 1976 Nov;262(2):319–348. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isenberg G. Cardiac Purkinje fibres: [Ca2+]i controls the potassium permeability via the conductance components gK1 and gK2. Pflugers Arch. 1977 Oct 19;371(1-2):77–85. doi: 10.1007/BF00580775. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansen J. K., Nicholls J. G. Conductance changes, an electrogenic pump and the hyperpolarization of leech neurones following impulses. J Physiol. 1973 Mar;229(3):635–655. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. Tetrodotoxin-resistant electric activity in presynaptic terminals. J Physiol. 1969 Aug;203(2):459–487. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keynes R. D., Rojas E., Taylor R. E., Vergara J. Calcium and potassium systems of a giant barnacle muscle fibre under membrane potential control. J Physiol. 1973 Mar;229(2):409–455. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimhi Y., Palfrey C., Spector I., Barak Y., Littauer U. Z. Maturation of neuroblastoma cells in the presence of dimethylsulfoxide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Feb;73(2):462–466. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.2.462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostyuk P. G., Krishtal O. A. Effects of calcium and calcium-chelating agents on the inward and outward current in the membrane of mollusc neurones. J Physiol. 1977 Sep;270(3):569–580. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostyuk P. G., Krishtal O. A., Shakhovalov Y. A. Separation of sodium and calcium currents in the somatic membrane of mollusc neurones. J Physiol. 1977 Sep;270(3):545–568. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krnjević K., Puil E., Werman R. EGTA and motoneuronal after-potentials. J Physiol. 1978 Feb;275:199–223. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llinás R., Steinberg I. Z., Walton K. Presynaptic calcium currents and their relation to synaptic transmission: voltage clamp study in squid giant synapse and theoretical model for the calcium gate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Aug;73(8):2918–2922. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.8.2918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lux H. D., Eckert R. Inferred slow inward current in snail neurones. Nature. 1974 Aug 16;250(467):574–576. doi: 10.1038/250574a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meech R. W. Intracellular calcium injection causes increased potassium conductance in Aplysia nerve cells. Comp Biochem Physiol A Comp Physiol. 1972 Jun 1;42(2):493–499. doi: 10.1016/0300-9629(72)90128-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meech R. W., Standen N. B. Potassium activation in Helix aspersa neurones under voltage clamp: a component mediated by calcium influx. J Physiol. 1975 Jul;249(2):211–239. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meech R. W. The sensitivity of Helix aspersa neurones to injected calcium ions. J Physiol. 1974 Mar;237(2):259–277. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyake M. The development of action potential mechanism in a mouse neuronal cell line in vitro. Brain Res. 1978 Mar 24;143(2):349–354. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)90574-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moolenaar W. H., Spector I. Ionic currents in cultured mouse neuroblastoma cells under voltage-clamp conditions. J Physiol. 1978 May;278:265–286. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moolenaar W. H., Spector I. Membrane currents examined under voltage clamp in cultured neuroblastoma cells. Science. 1977 Apr 15;196(4287):331–333. doi: 10.1126/science.557842. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moolenaar W. H., Spector I. The calcium action potential and a prolonged calcium dependent after-hyperpolarization in mouse neuroblastoma cells. J Physiol. 1979 Jul;292:297–306. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mounier Y., Vassort G. Initial and delayed membrane currents in crab muscle fibre under voltage-clamp conditions. J Physiol. 1975 Oct;251(3):589–608. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto H., Takahashi K., Yamashita N. Ionic currents through the membrane of the mammalian oocyte and their comparison with those in the tunicate and sea urchin. J Physiol. 1977 May;267(2):465–495. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011822. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto H., Takahashi K., Yoshii M. Membrane currents of the tunicate egg under the voltage-clamp condition. J Physiol. 1976 Jan;254(3):607–638. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen H., Goodman D. B. Relationships between calcium and cyclic nucleotides in cell activation. Physiol Rev. 1977 Jul;57(3):421–509. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1977.57.3.421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reuter H. Divalent cations as charge carriers in excitable membranes. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1973;26:1–43. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(73)90016-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reuter H., Scholz H. A study of the ion selectivity and the kinetic properties of the calcium dependent slow inward current in mammalian cardiac muscle. J Physiol. 1977 Jan;264(1):17–47. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011656. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Standen N. B. Properties of a calcium channel in snail neurones. Nature. 1974 Jul 26;250(464):340–342. doi: 10.1038/250340a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Standen N. B. Voltage-clamp studies of the calcium inward current in an identified snail neurone: comparison with the sodium inward current. J Physiol. 1975 Jul;249(2):253–268. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson S. H. Three pharmacologically distinct potassium channels in molluscan neurones. J Physiol. 1977 Feb;265(2):465–488. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trautwein W., McDonald T. F., Tripathi O. Calcium conductance and tension in mammalian ventricular muscle. Pflugers Arch. 1975;354(1):55–74. doi: 10.1007/BF00584503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittam R. Control of membrane permeability to potassium in red blood cells. Nature. 1968 Aug 10;219(5154):610–610. doi: 10.1038/219610a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


