Abstract
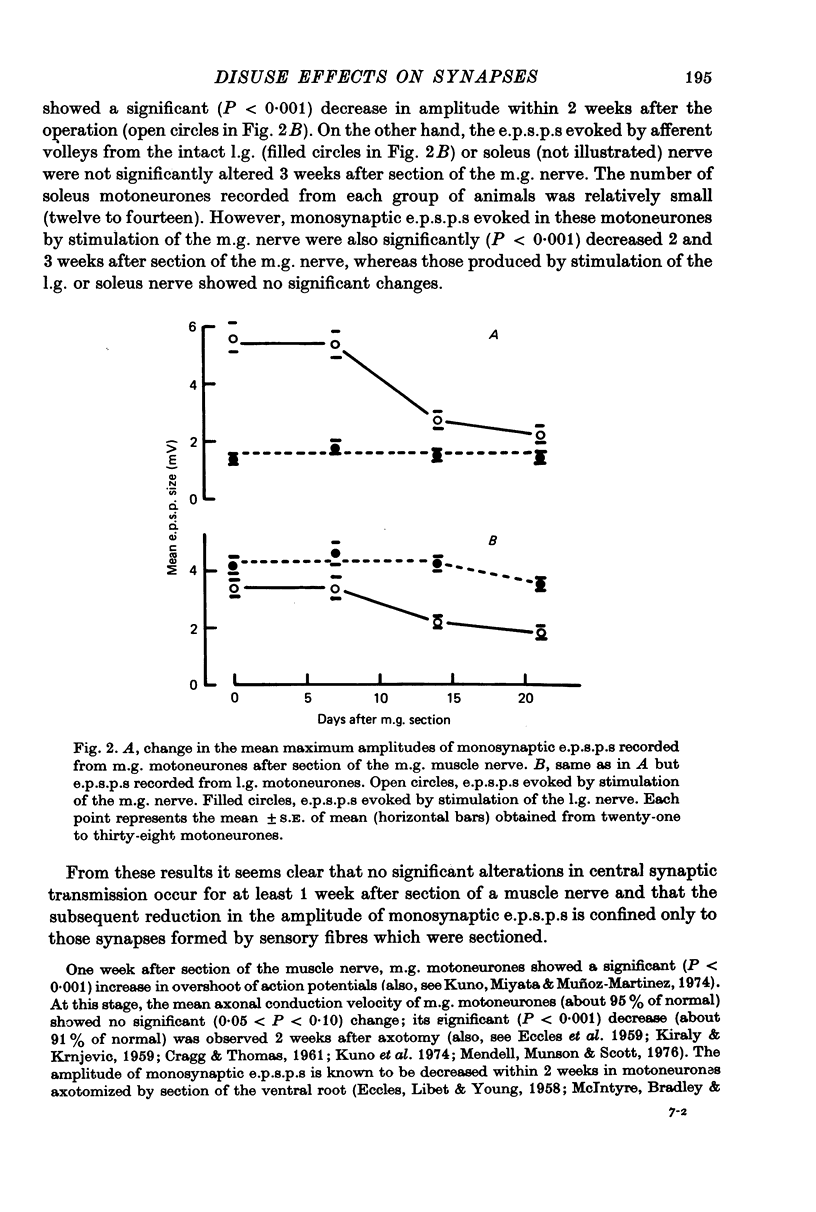
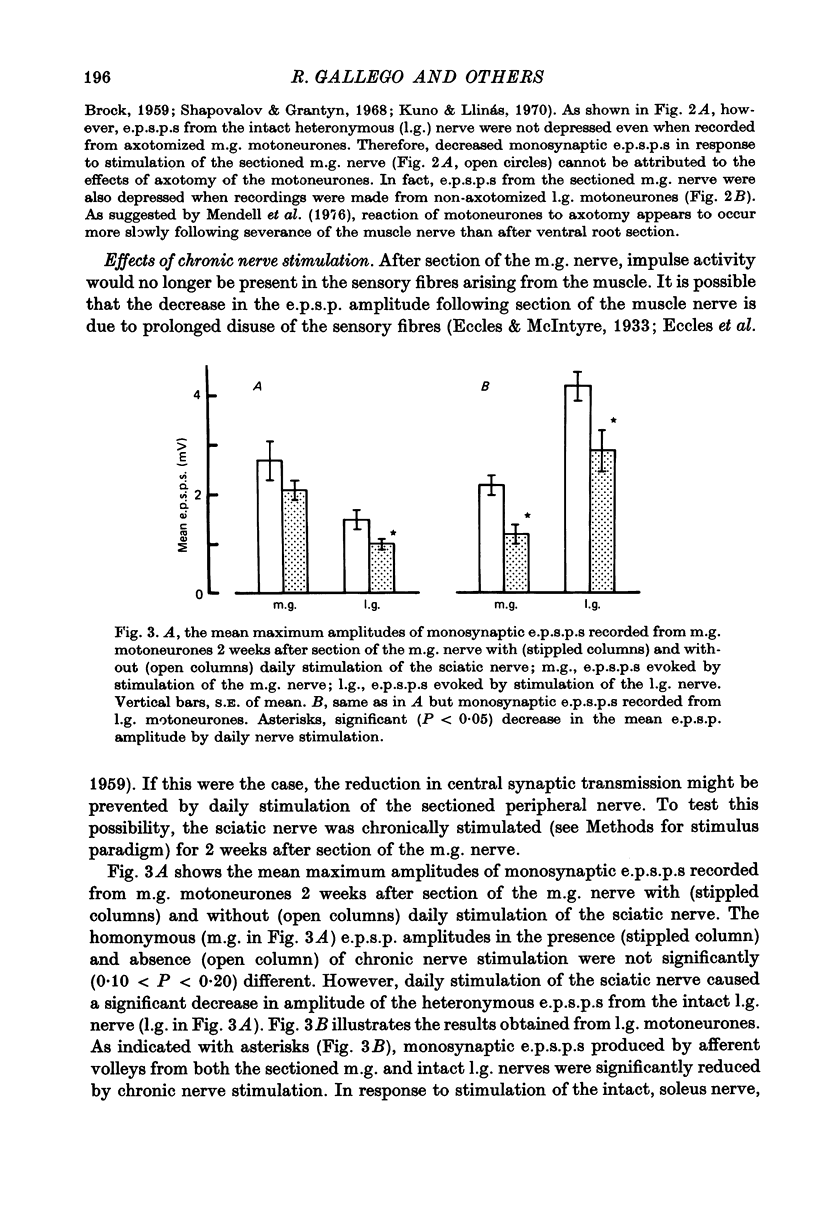
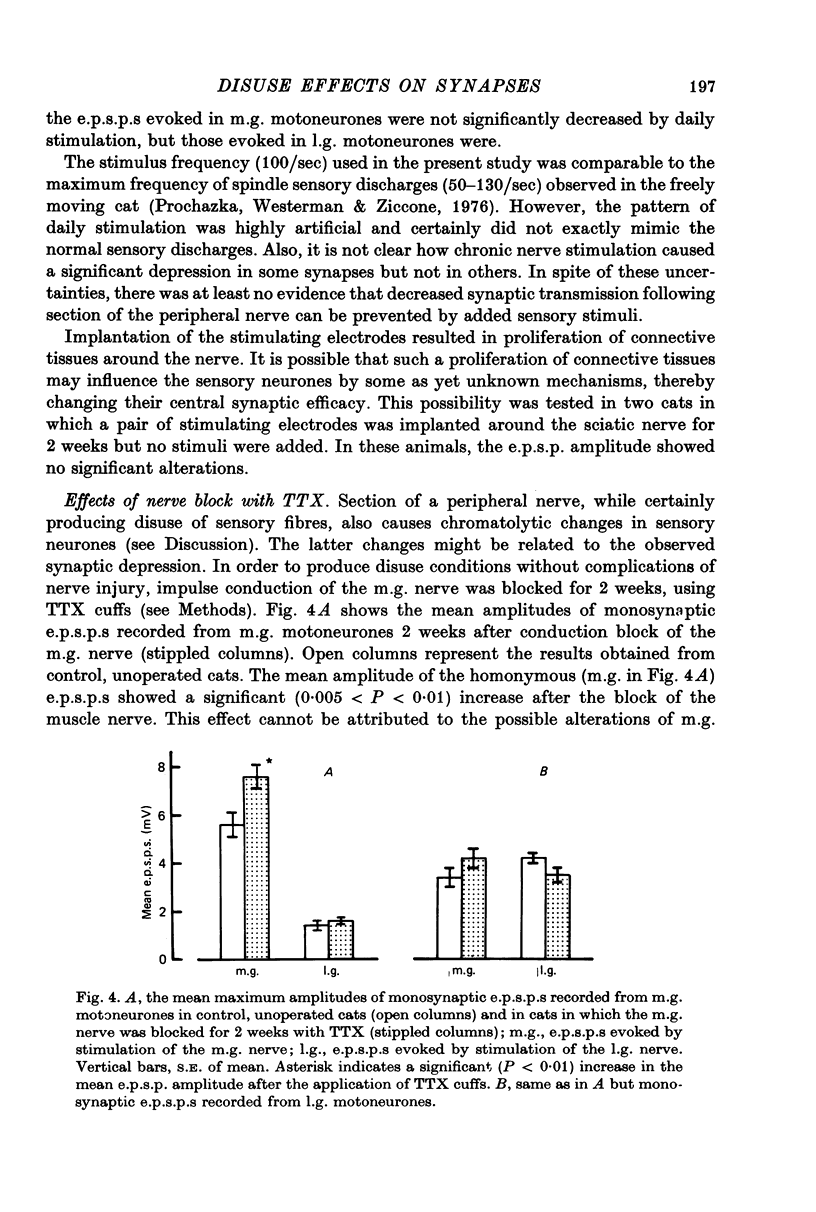
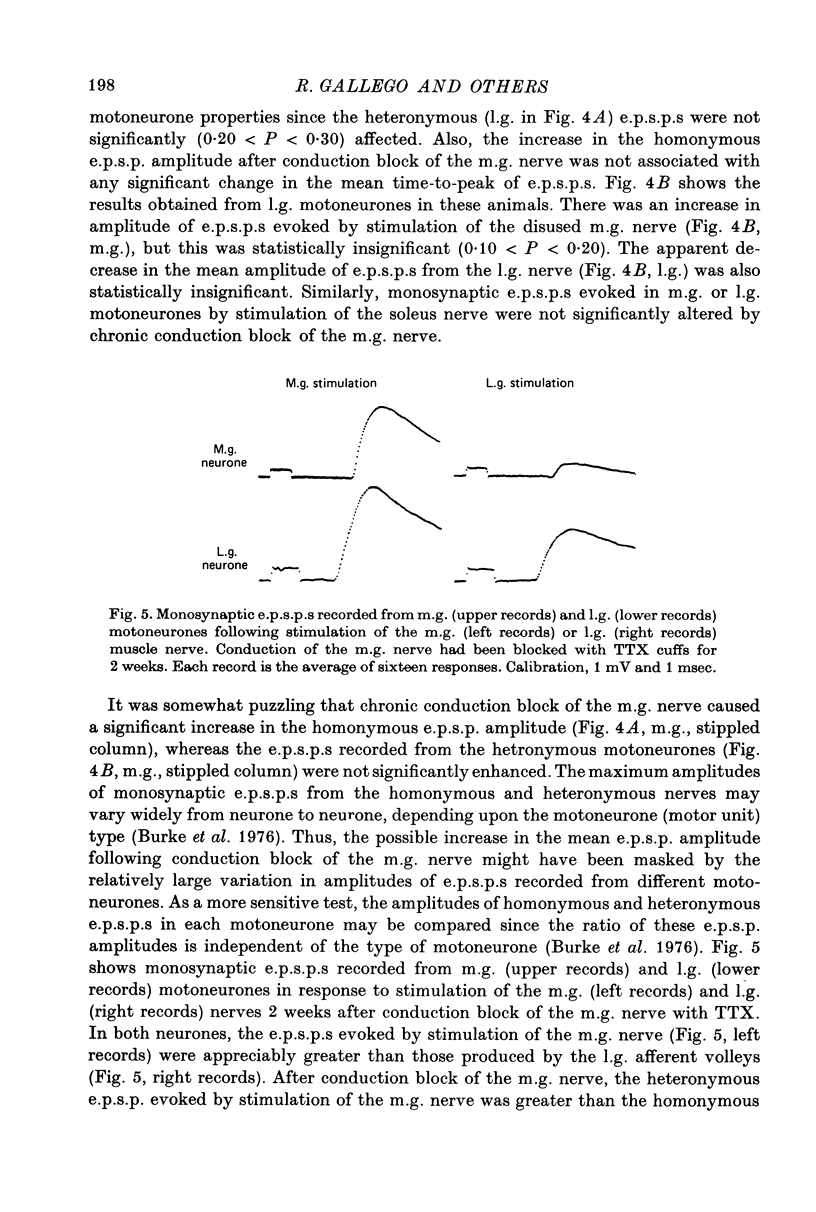
1. Monosynaptic excitatory post-synaptic potentials (e.p.s.p.s) were recorded from triceps surae motoneurones in the cat following section or chronic conduction block of the medial gastrocnemius (m.g.) nerve with tetrodotoxin (TTX) or after daily stimulation of the sciatic nerve. 2. The mean maximum amplitudes of homonymous and heteronymous monosynaptic e.p.s.p.s evoked by stimulation of the mg. nerve were reduced significantly between 1 and 2 weeks after section of the muscle nerve. The mean amplitudes of monosynaptic e.p.s.p.s produced in the same motoneurones by afferent volleys from the intact synergists showed no significant alterations. 3. Reduction of the amplitude of monosynaptic e.p.s.p.s. evoked by the sectioned m.g. afferent volleys was not prevented by daily stimulation of the sciatic nerve. The chronic stimulation of the sciatic nerve did not increase the amplitude of monosynaptic e.p.s.p.s evoked by stimulation of the intact, lateral gastrocnemius (l.g.) or soleus nerve. 4. Chronic conduction block of the intact m.g. nerve with TTX cuffs for 2 weeks resulted in a significant increase in the homonymous e.p.s.p. amplitude. The amplitude of the heteronymous e.p.s.p.s evoked in the same m.g. motoneurones by stimulation of the intact l.g. or soleus nerve showed no significant changes. 5. It is concluded that decreased central synaptic transmission following section of the peripheral nerve is not due to elimination of impulse activity (disuse) of the sensory input and that prolonged disuse of the sensory fibres causes an increase, rather than a decrease, in central synaptic efficacy.
Full text
PDF



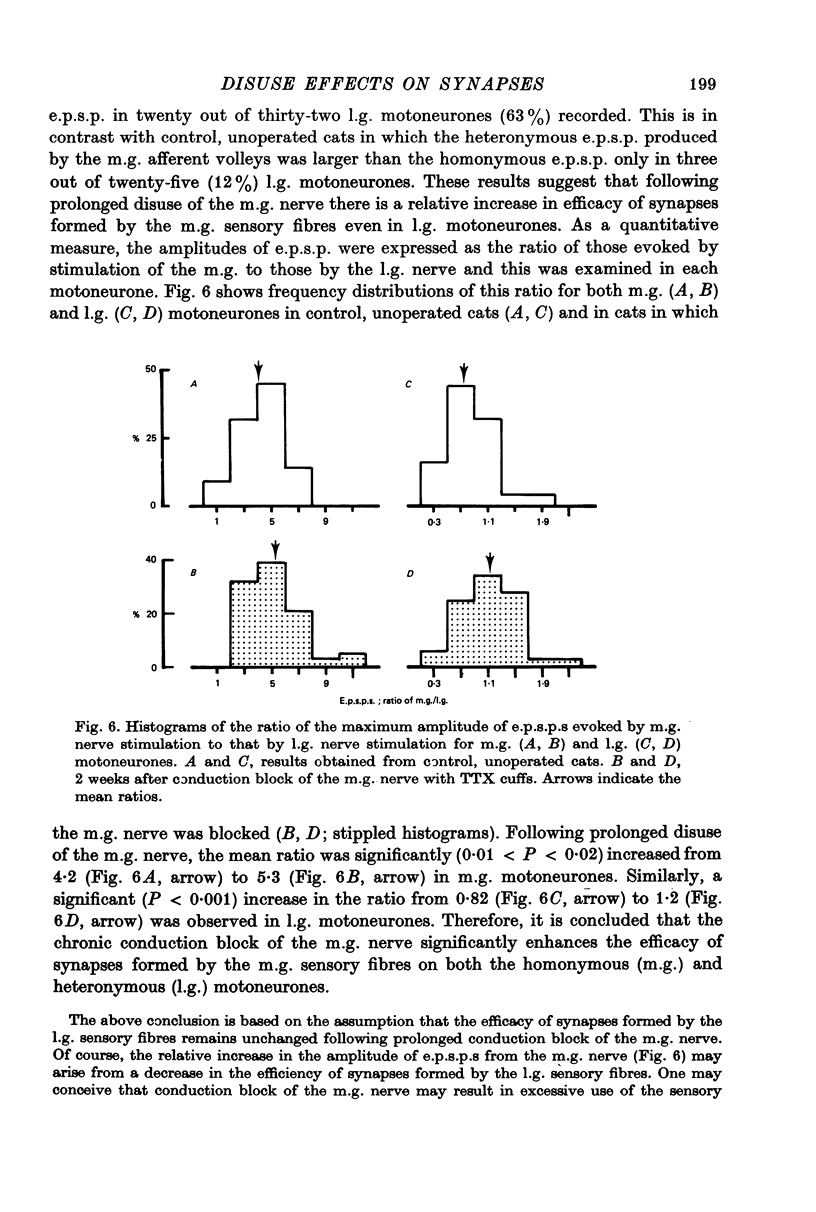
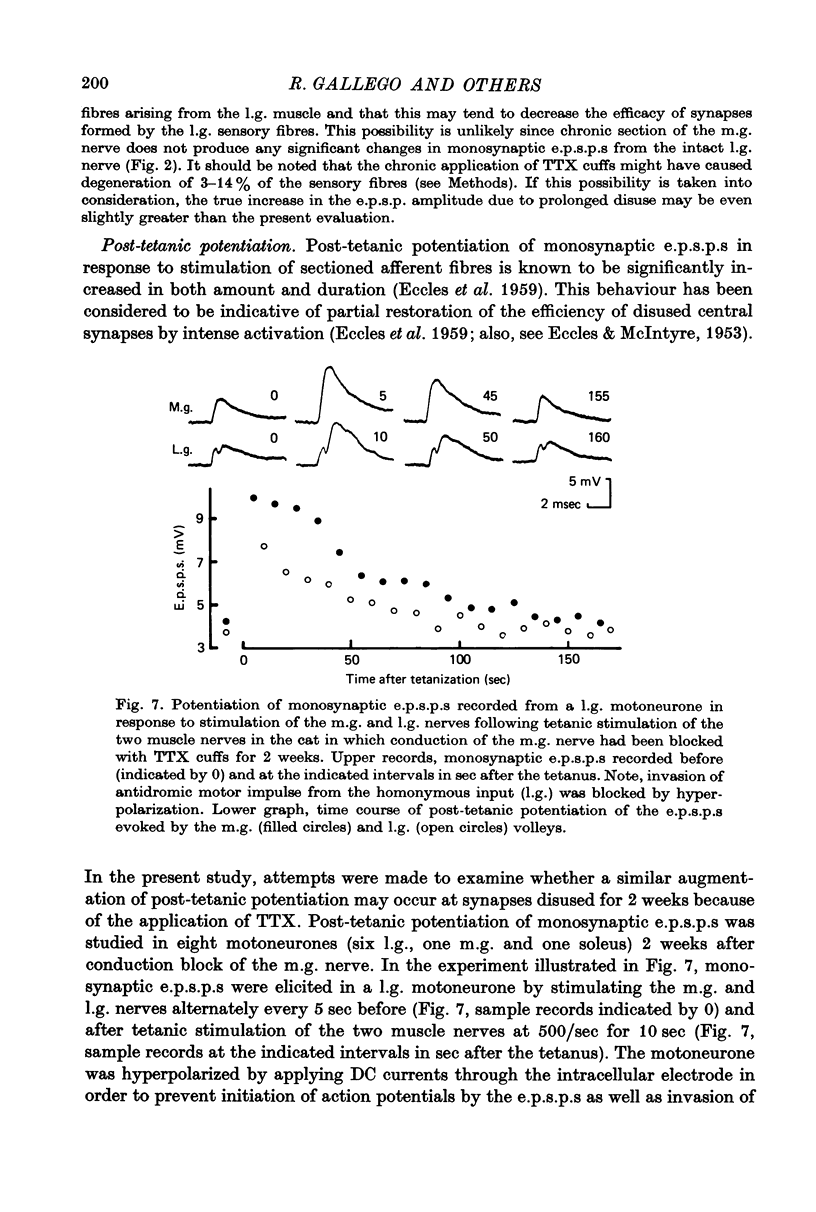





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson H. K. The nature of the lesions which hinder the development of nerve-cells and their processes. J Physiol. 1902 Dec 15;28(6):499–513. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1902.sp000931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson K. E., Edström A. Effects of nerve blocking agents on fast axonal transport of proteins in frog sciatic nerves in vitro. Brain Res. 1973 Feb 14;50(1):125–134. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(73)90599-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERANEK R., HNIK P. Long-term effects of tenotomy on spinal monosynaptic response in the cat. Science. 1959 Oct 16;130(3381):981–982. doi: 10.1126/science.130.3381.981-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke R. E. Group Ia synaptic input to fast and slow twitch motor units of cat triceps surae. J Physiol. 1968 Jun;196(3):605–630. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke R. E., Rymer W. Z. Relative strength of synaptic input from short-latency pathways to motor units of defined type in cat medial gastrocnemius. J Neurophysiol. 1976 May;39(3):447–458. doi: 10.1152/jn.1976.39.3.447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAVANAUGH M. W. Quantitative effects of the peripheral innervation area on nerves and spinal ganglion cells. J Comp Neurol. 1951 Apr;94(2):181–219. doi: 10.1002/cne.900940203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COOMBS J. S., ECCLES J. C., FATT P. Excitatory synaptic action in motoneurones. J Physiol. 1955 Nov 28;130(2):374–395. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1955.sp005413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COOMBS J. S., ECCLES J. C., FATT P. The electrical properties of the motoneurone membrane. J Physiol. 1955 Nov 28;130(2):291–325. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1955.sp005411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRAGG B. G., THOMAS P. K. Changes in conduction velocity and fibre size proximal to peripheral nerve lesions. J Physiol. 1961 Jul;157:315–327. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1961.sp006724. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carmel P. W., Stein B. M. Cell changes in sensory ganglia following proximal and distal nerve section in the monkey. J Comp Neurol. 1969 Feb;135(2):145–166. doi: 10.1002/cne.901350203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Csillik B., Knyihár E., Elshiekh A. A. Degenerative atrophy of central terminals of primary sensory neurons induced by blockade of axoplasmic transport in peripheral nerves. Experientia. 1977 May 15;33(5):656–657. doi: 10.1007/BF01946557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czéh G., Gallego R., Kudo N., Kuno M. Evidence for the maintenance of motoneurone properties by muscle activity. J Physiol. 1978 Aug;281:239–252. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czéh G., Kudo N., Kuno M. Membrane properties and conduction velocity in sensory neurones following central or peripheral axotomy. J Physiol. 1977 Aug;270(1):165–180. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011944. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECCLES J. C., ECCLES R. M., LUNDBERG A. The convergence of monosynaptic excitatory afferents on to many different species of alpha motoneurones. J Physiol. 1957 Jun 18;137(1):22–50. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005794. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECCLES J. C., KRNJEVIC K., MILEDI R. Delayed effects of peripheral severance of afferent nerve fibres on the efficacy of their central synapses. J Physiol. 1959 Jan 28;145(1):204–220. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006136. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECCLES J. C., LIBET B., YOUNG R. R. The behaviour of chromatolysed motoneurones studied by intracellular recording. J Physiol. 1958 Aug 29;143(1):11–40. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1958.sp006041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECCLES J. C., McINTYRE A. K. The effects of disuse and of activity on mammalian spinal reflexes. J Physiol. 1953 Sep;121(3):492–516. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1953.sp004961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards F. R., Redman S. J., Walmsley B. The effect of polarizing currents on unitary Ia excitatory post-synaptic potentials evoked in spinal motoneurones. J Physiol. 1976 Aug;259(3):705–723. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fein H. Passing current through recording glass micro-pipette electrodes. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 1966 Oct;13(4):211–212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldfard J., Muller R. U. Occurrence of heteronymous monosynaptic reflexes following tenotomy. Brain Res. 1971 May 21;28(3):553–555. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(71)90065-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HNIK P., BERANEK R., VYKLICKY L., ZELENA J. Sensory outflow from chronically tenotomized muscles. Physiol Bohemoslov. 1963;12:23–29. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOZAK W., WESTERMAN R. A. Plastic changes of spinal monosynaptic responses from tenotomized muscles in cats. Nature. 1961 Mar 4;189:753–755. doi: 10.1038/189753b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuno M., Llinás R. Alterations of synaptic action in chromatolysed motoneurones of the cat. J Physiol. 1970 Nov;210(4):823–838. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuno M., Miyahara J. T. Analysis of synaptic efficacy in spinal motoneurones from 'quantum' aspects. J Physiol. 1969 Apr;201(2):479–493. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008768. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuno M., Miyata Y., Muñoz-Martinez E. J. Differential reaction of fast and slow alpha-motoneurones to axotomy. J Physiol. 1974 Aug;240(3):725–739. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavoie P. A., Collier B., Tenehouse A. Comparison of alpha-bungarotoxin binding to skeletal muscles after inactivity or denervation. Nature. 1976 Mar 25;260(5549):349–350. doi: 10.1038/260349a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McINTYRE A. K., BRADLEY K., BROCK L. G. Responses of motoneurons undergoing chromatolysis. J Gen Physiol. 1959 May 20;42(5):931–958. doi: 10.1085/jgp.42.5.931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendell L. M., Munson J. B., Scott J. G. Alterations of synapses on axotomized motoneurones. J Physiol. 1976 Feb;255(1):67–79. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011270. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson P. G., Frank K. Anomalous rectification in cat spinal motoneurons and effect of polarizing currents on excitatory postsynaptic potential. J Neurophysiol. 1967 Sep;30(5):1097–1113. doi: 10.1152/jn.1967.30.5.1097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ochs S., Hollingsworth D. Dependence of fast axoplasmic transport in nerve on oxidative metabolism. J Neurochem. 1971 Jan;18(1):107–114. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1971.tb00172.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pestronk A., Drachman D. B., Griffin J. W. Effect of muscle disuse on acetylcholine receptors. Nature. 1976 Mar 25;260(5549):352–353. doi: 10.1038/260352a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prochazka A., Westerman R. A., Ziccone S. P. Discharges of single hindlimb afferents in the freely moving cat. J Neurophysiol. 1976 Sep;39(5):1090–1104. doi: 10.1152/jn.1976.39.5.1090. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins N., Nelson P. G. Tenotomy and the spinal monosynaptic reflex. Exp Neurol. 1970 Apr;27(1):66–75. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(70)90202-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapovalov A. I., Grantyn' A. A. Nadsegmentarnye sinapticheskie vliianiia na khromatolizirovannye motoneirony. Biofizika. 1968 Mar-Apr;13(2):260–269. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapovalov A. I., Kurchavyi G. G. Effects of trans-membrane polarization and TEA injection on monosynaptic actions from motor cortex, red nucleus and group Ia afferents on lumbar motoneurons in the monkey. Brain Res. 1974 Dec 20;82(1):49–67. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(74)90892-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh J. V., Jr, Burke R. E., Rymer W. Z., Tsairis P. Effect of compensatory hypertrophy studied in individual motor units in medial gastrocnemius muscle of the cat. J Neurophysiol. 1978 Mar;41(2):496–508. doi: 10.1152/jn.1978.41.2.496. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werman R., Carlen P. L. Unusual behavior of the La EPSP in cat spinal motoneurons. Brain Res. 1976 Aug 13;112(2):395–401. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90294-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


