Abstract
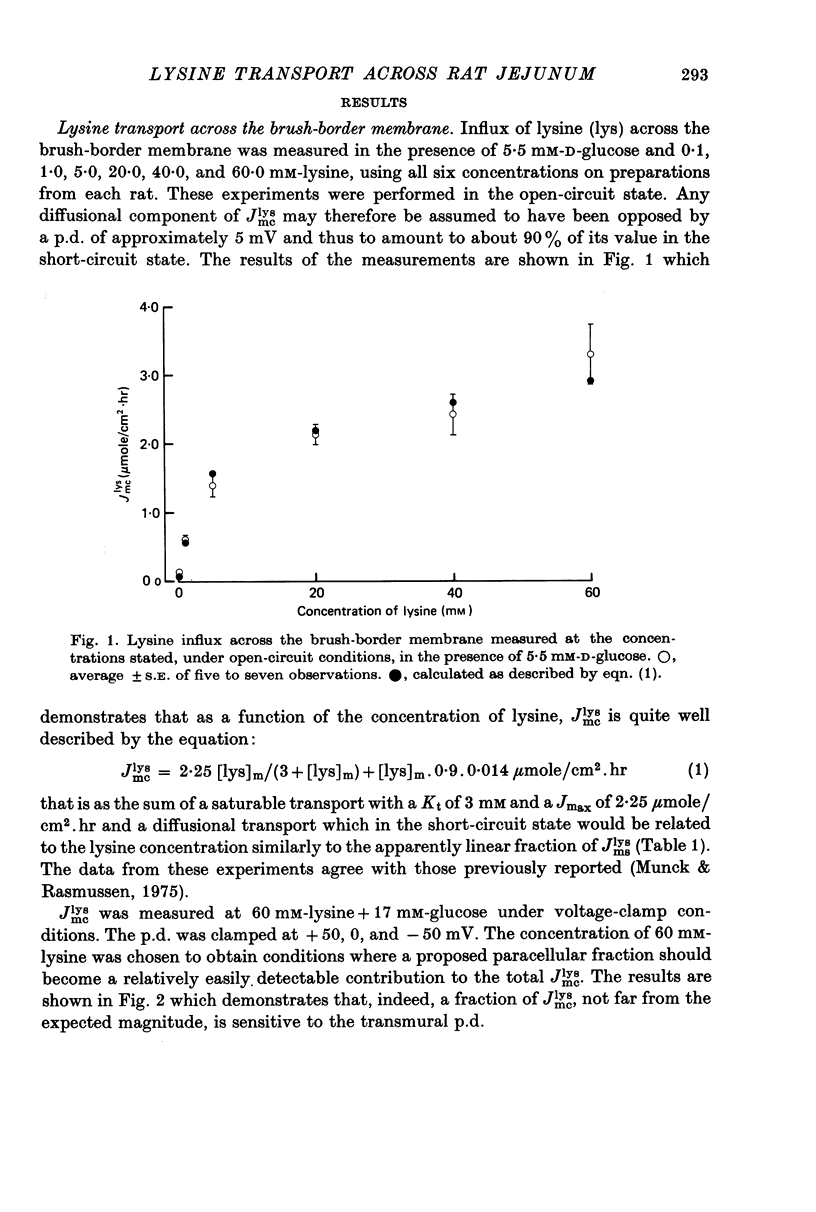
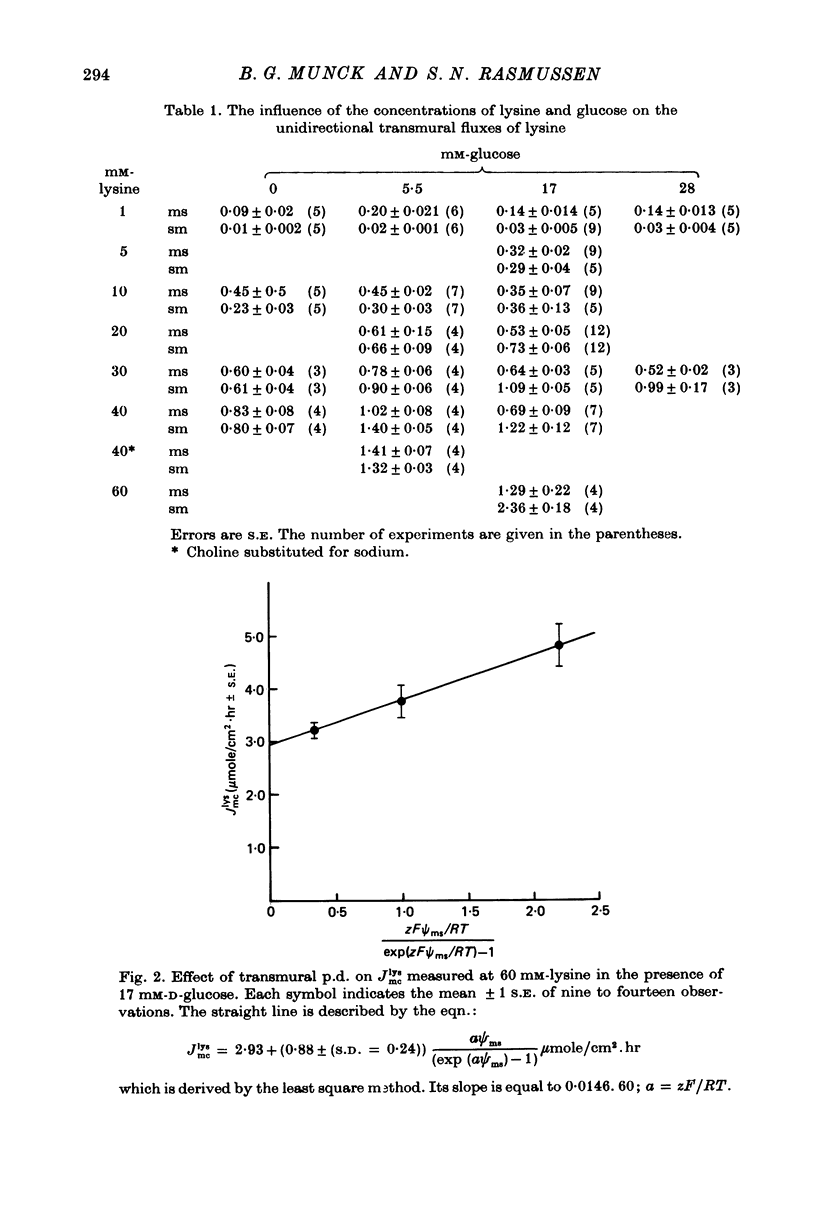
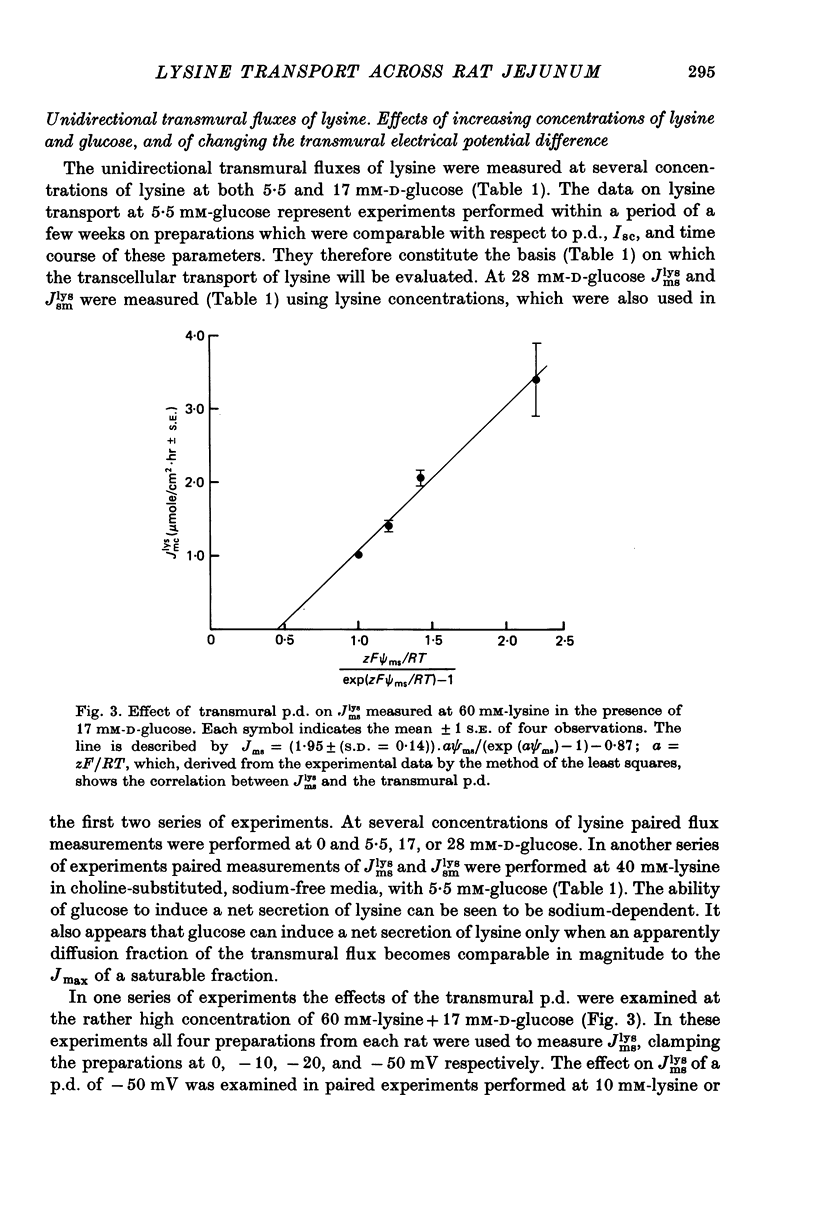
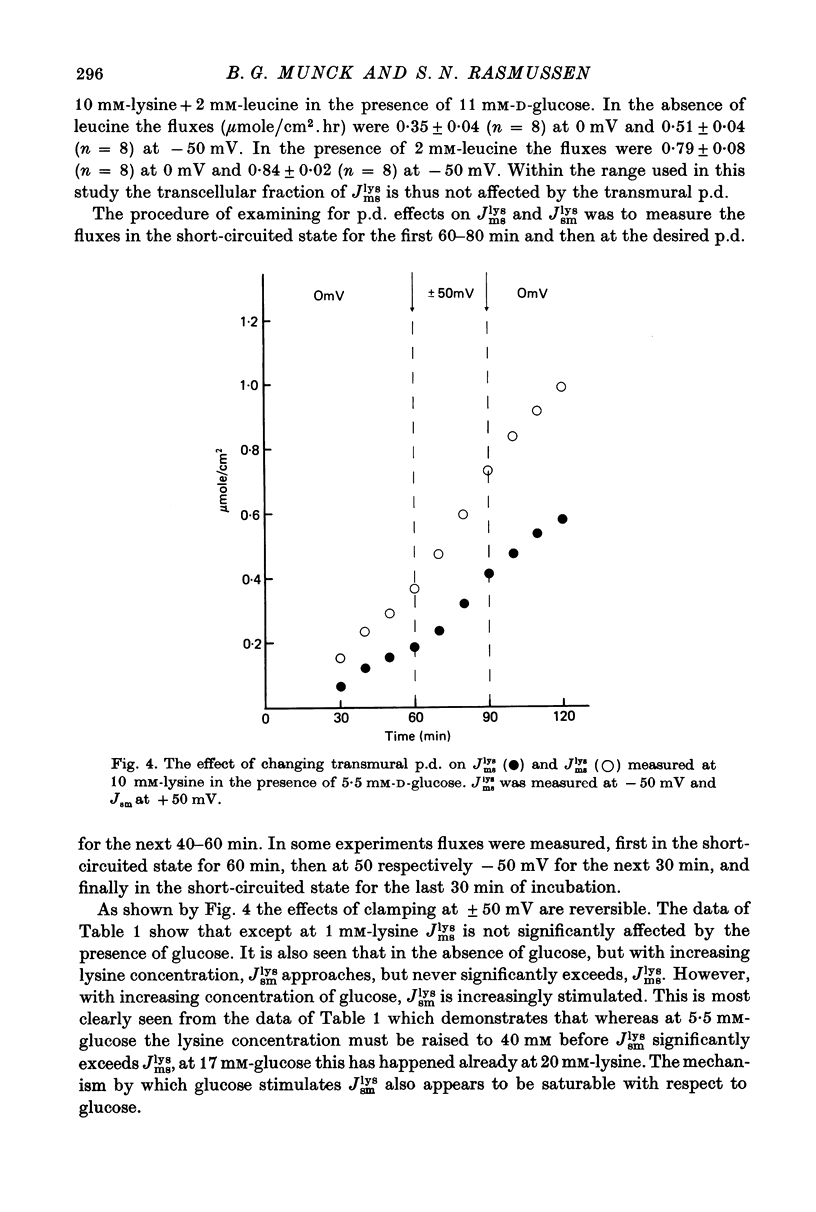
Transport of lysine across the rat jejunum has been studied measuring transmural fluxes, Jms and Jsm, under short-circuit conditions, influx across the brush-border membrane, Jmc, under open-circuit and voltage-clamp conditions, and steady-state uptake by the isolated mucosa. 1. Jlysmc can be described as the sum of a saturable process with a Kt of 3 mM and a Jmax of 2.25 micromole/cm2.hr and a diffusional component corresponding to a lysine permeability of 0.014 cm/hr. Also Jlysms is well described as the sum of a saturable process and a diffusional contribution described by the same permeability as for Jlysmc. 2. The effects of the transmural p.d. on Jlysmc indicate that at 60 mM this flux includes a diffusional contribution, which corresponds to a lysine permeability of 0.014 cm/hr. 3. The passage of an electrical current across the gut wall changes the electrical conductance as expected for a cation-selective epithelium. The effect of a mucosa to serosa current on the Jms value of mannitol provides confirmation of the expected current effect on transepithelial volume flow. These effects on conductance and solute flux, together with the electrostatic effect on lysine movements, suffice to account for the p.d. effects on Jmc, Jms, and Jsm of lysine. 4. Jlyssm is in a saturable manner stimulated by increasing concentrations of D-glucose. At higher (10 mM) concentrations of lysine this effect leads to a net secretion of lysine. Qualitatively and quantitatively these effects are consistent with the model of a glucose-induced fluid circuit between the mucosal solution and the lateral intercellular spaces. 5. All observations are consistent with a paracellular, transepithelial pathway for lysine, which includes the lateral intercellular spaces. 6. The transport of lysine across the basolateral membrane is analysed. Togethet the data on transcellular passage of lysine are very similar to those reported for rabbit ileum, except that more than one transport process could not be demonstrated.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bindslev N., Tormey J. M., Wright E. M. The effects of electrical and osmotic gradients on lateral intercellular spaces and membrane conductance in a low resistance epithelium. J Membr Biol. 1974;19(4):357–380. doi: 10.1007/BF01869986. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chez R. A., Palmer R. R., Schultz S. G., Curran P. F. Effect of inhibitors on alanine transport in isolated rabbit ileum. J Gen Physiol. 1967 Nov;50(10):2357–2375. doi: 10.1085/jgp.50.10.2357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desjeux J. F., Tai Y. H., Powell D. W., Curran P. F. Effects of cholera toxin on cellular and paracellular sodium fluxes in rabbit ileum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Oct 5;448(2):352–367. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90248-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickens F., Weil-Malherbe H. Metabolism of normal and tumour tissue: The metabolism of intestinal mucous membrane. Biochem J. 1941 Jan;35(1-2):7–15. doi: 10.1042/bj0350007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobson J. G., Jr, Kidder G. W., 3rd Edge damage effect in in vitro frog skin preparations. Am J Physiol. 1968 Apr;214(4):719–724. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1968.214.4.719. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frizzell R. A., Schultz S. G. Ionic conductances of extracellular shunt pathway in rabbit ileum. Influence of shunt on transmural sodium transport and electrical potential differences. J Gen Physiol. 1972 Mar;59(3):318–346. doi: 10.1085/jgp.59.3.318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munck B. G. Effects of sugar and amino acid transport on transepithelial fluxes of sodium and chloride of short circuited rat jejunum. J Physiol. 1972 Jun;223(3):699–717. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009870. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munck B. G., Rasmussen S. N. Characteristics of rat jejunal transport of tryptophan. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 May 6;389(2):261–280. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(75)90320-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munck B. G., Rasmussen S. N. Paracellular permeability of extracellular space markers across rat jejunum in vitro. Indication of a transepithelial fluid circuit. J Physiol. 1977 Oct;271(2):473–488. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp012009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munck B. G., Schultz S. G. Lysine transport across isolated rabbit ileum. J Gen Physiol. 1969 Feb;53(2):157–182. doi: 10.1085/jgp.53.2.157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munck B. G., Schultz S. G. Properties of the passive conductance pathway across in vitro rat jejunum. J Membr Biol. 1974;16(2):163–174. doi: 10.1007/BF01872412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Os C. H., Michels J. A., Slegers J. F. Effects of electrical gradients on volume flows across gall bladder epithelium. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Sep 7;443(3):545–555. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90472-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patlak C. S., Rapoport S. I. Theoretical analysis of net tracer flux due to volume circulation in a membrane with pores of different sizes. Relation to solute drag model. J Gen Physiol. 1971 Feb;57(2):113–124. doi: 10.1085/jgp.57.2.113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHULTZ S. G., ZALUSKY R. ION TRANSPORT IN ISOLATED RABBIT ILEUM. I. SHORT-CIRCUIT CURRENT AND NA FLUXES. J Gen Physiol. 1964 Jan;47:567–584. doi: 10.1085/jgp.47.3.567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz S. G., Curran P. F., Chez R. A., Fuisz R. E. Alanine and sodium fluxes across mucosal border of rabbit ileum. J Gen Physiol. 1967 May;50(5):1241–1260. doi: 10.1085/jgp.50.5.1241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright E. M. Diffusion potentials across the small intestine. Nature. 1966 Oct 8;212(5058):189–190. doi: 10.1038/212189a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



