Abstract
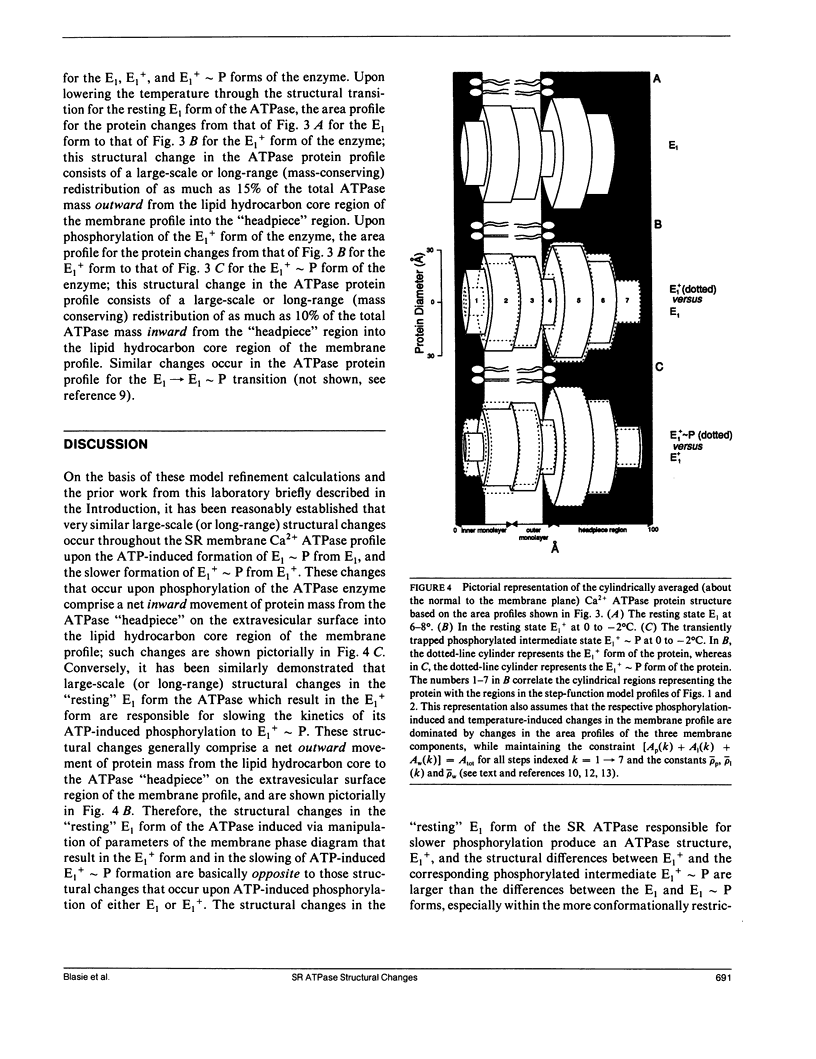
Model refinement calculations utilizing the results from time-resolved x-ray diffraction studies indicate that specific, large-scale changes (i.e., structural changes over a large length scale or long range) occur throughout the cylindrically averaged profile structure of the sarcoplasmic reticulum ATPase upon its phosphorylation during calcium active transport. Several physical-chemical factors, all of which slow the kinetics of phosphoenzyme formation, induce specific, large-scale changes throughout the profile structure of the unphosphorylated enzyme that in general are opposite to those observed upon phosphorylation. These results suggest that such large-scale structural changes in the ATPase occurring upon its phosphorylation are required for its calcium transport function.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Asturias F. J., Blasie J. K. Effect of Mg2+ concentration on Ca2+ uptake kinetics and structure of the sarcoplasmic reticulum membrane. Biophys J. 1989 Apr;55(4):739–753. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(89)82873-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blasie J. K., Herbette L. G., Pascolini D., Skita V., Pierce D. H., Scarpa A. Time-resolved x-ray diffraction studies of the sarcoplasmic reticulum membrane during active transport. Biophys J. 1985 Jul;48(1):9–18. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(85)83756-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blasie J. K., Herbette L., Pachence J. Biological membrane structure as "seen" by X-ray and neutron diffraction techniques. J Membr Biol. 1985;86(1):1–7. doi: 10.1007/BF01871604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blasie J. K., Pachence J. M., Herbette L. G. Neutron diffraction and the decomposition of membrane scattering profiles into the scattering profiles of their molecular components. Basic Life Sci. 1984;27:201–210. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4899-0375-4_12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebashi S., Endo M., Otsuki I. Control of muscle contraction. Q Rev Biophys. 1969 Nov;2(4):351–384. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500001190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez-Belda F., Kurzmack M., Inesi G. A comparative study of calcium transients by isotopic tracer, metallochromic indicator, and intrinsic fluorescence in sarcoplasmic reticulum ATPase. J Biol Chem. 1984 Aug 10;259(15):9687–9698. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbette L., DeFoor P., Fleischer S., Pascolini D., Scarpa A., Blasie J. K. The separate profile structures of the functional calcium pump protein and the phospholipid bilayer within isolated sarcoplasmic reticulum membranes determined by X-ray and neutron diffraction. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Jul 11;817(1):103–122. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(85)90073-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbette L., Scarpa A., Blasie J. K., Wang C. T., Hymel L., Seelig J., Fleischer S. The determination of the separate Ca2+ pump protein and phospholipid profile structures within reconstituted sarcoplasmic reticulum membranes via X-ray and neutron diffraction. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 May 5;730(2):369–378. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(83)90354-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meissner G., Conner G. E., Fleischer S. Isolation of sarcoplasmic reticulum by zonal centrifugation and purification of Ca 2+ -pump and Ca 2+ -binding proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Mar 16;298(2):246–269. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90355-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pachence J. M., Dutton P. L., Blasie J. K. The reaction center profile structure derived from neutron diffraction. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Apr 13;635(2):267–283. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(81)90026-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pascolini D., Blasie J. K., Gruner S. M. A 12 A resolution X-ray diffraction study of the profile structure of isolated bovine retinal rod outer segment disk membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Oct 17;777(1):9–20. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(84)90491-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pascolini D., Blasie J. K. Moderate resolution profile structure of the sarcoplasmic reticulum membrane under low temperature conditions for the transient trapping of E1 approximately P. Biophys J. 1988 Oct;54(4):669–678. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(88)83002-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pascolini D., Herbette L. G., Skita V., Asturias F., Scarpa A., Blasie J. K. Changes in the sarcoplasmic reticulum membrane profile induced by enzyme phosphorylation to E1 approximately P at 16 A resolution via time-resolved x-ray diffraction. Biophys J. 1988 Oct;54(4):679–687. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(88)83003-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce D. H., Scarpa A., Topp M. R., Blasie J. K. Kinetics of calcium uptake by isolated sarcoplasmic reticulum vesicles using flash photolysis of caged adenosine 5'-triphosphate. Biochemistry. 1983 Nov 8;22(23):5254–5261. doi: 10.1021/bi00292a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce D. H., Scarpa A., Trentham D. R., Topp M. R., Blasie J. K. Comparison of the kinetics of calcium transport in vesicular dispersions and oriented multilayers of isolated sarcoplasmic reticulum membranes. Biophys J. 1983 Dec;44(3):365–373. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(83)84310-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Meis L., Vianna A. L. Energy interconversion by the Ca2+-dependent ATPase of the sarcoplasmic reticulum. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:275–292. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.001423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]