Abstract
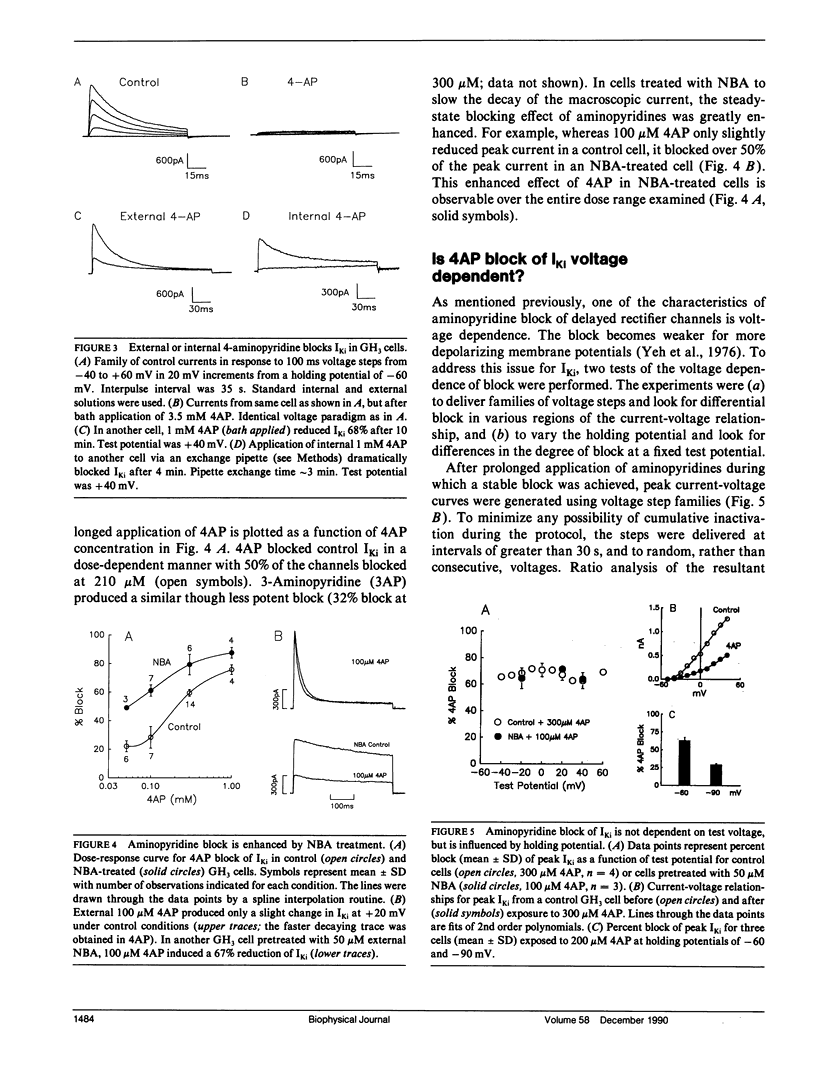
The blocking action of aminopyridines on an inactivating K current (lKi) in GH3 pituitary cells was studied before and after altering the macroscopic decay of the current with N-bromoacetamide (NBA). The first depolarizing pulse delivered either seconds or minutes after beginning 4-aminopyridine (4AP) application, elicited a current with both a more rapid decay and a reduced peak amplitude. The rapid decay (or time-dependent block) was especially prominent in NBA-treated cells. With continued drug application, subsequent test pulses revealed a stable block of peak current, greater in NBA-treated than control cells. Recovery from block was enhanced by hyperpolarizing holding potentials and by the first depolarizing pulse delivered after prolonged recovery intervals. Unlike aminopyridine block of other K currents, there was no convincing evidence for voltage shifts in activation or inactivation, or for voltage and frequency-dependent unblock. Increasing the open probability of the channels did, however, facilitate the block. Although the behavior of currents in 4AP was suggestive of "open channel block," the block was not produced by 4-aminopyridine methiodide, a positively charged aminopyridine. Moreover, because partial block and recovery occurred without opening the channels we suggest that aminopyridines bind to, or near, this K channel, that this binding is enhanced by opening the channel, and that a conformational change is induced which mimics inactivation. Because recovery from block is enhanced by negative potentials, we suggest that aminopyridine molecules may become "trapped" by inactivation awaiting the slow process of reactivation to escape their binding sites.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armstrong C. M., Bezanilla F. Inactivation of the sodium channel. II. Gating current experiments. J Gen Physiol. 1977 Nov;70(5):567–590. doi: 10.1085/jgp.70.5.567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong C. M., Croop R. S. Simulation of Na channel inactivation by thiazine dyes. J Gen Physiol. 1982 Nov;80(5):641–662. doi: 10.1085/jgp.80.5.641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong C. M. Interaction of tetraethylammonium ion derivatives with the potassium channels of giant axons. J Gen Physiol. 1971 Oct;58(4):413–437. doi: 10.1085/jgp.58.4.413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bondy C. A., Russell J. T. Dendrotoxin and 4-aminopyridine potentiate neurohypophysial hormone secretion during low frequency electrical stimulation. Brain Res. 1988 Jun 21;453(1-2):397–400. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(88)90187-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cahalan M. D. Local anesthetic block of sodium channels in normal and pronase-treated squid giant axons. Biophys J. 1978 Aug;23(2):285–311. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(78)85449-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chabala L. D. The kinetics of recovery and development of potassium channel inactivation in perfused squid (Loligo pealei) giant axons. J Physiol. 1984 Nov;356:193–220. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandy K. G., DeCoursey T. E., Cahalan M. D., McLaughlin C., Gupta S. Voltage-gated potassium channels are required for human T lymphocyte activation. J Exp Med. 1984 Aug 1;160(2):369–385. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.2.369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cull-Candy S. G., Miledi R., Parker I. Single glutamate-activated channels recorded from locust muscle fibres with perfused patch-clamp electrodes. J Physiol. 1981 Dec;321:195–210. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez J. M., Fox A. P., Krasne S. Membrane patches and whole-cell membranes: a comparison of electrical properties in rat clonal pituitary (GH3) cells. J Physiol. 1984 Nov;356:565–585. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hescheler J., Pelzer D., Trube G., Trautwein W. Does the organic calcium channel blocker D600 act from inside or outside on the cardiac cell membrane? Pflugers Arch. 1982 Jun;393(4):287–291. doi: 10.1007/BF00581411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hille B. Local anesthetics: hydrophilic and hydrophobic pathways for the drug-receptor reaction. J Gen Physiol. 1977 Apr;69(4):497–515. doi: 10.1085/jgp.69.4.497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiraoka M., Kawano S. Mechanism of increased amplitude and duration of the plateau with sudden shortening of diastolic intervals in rabbit ventricular cells. Circ Res. 1987 Jan;60(1):14–26. doi: 10.1161/01.res.60.1.14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Josephson I. R., Sanchez-Chapula J., Brown A. M. Early outward current in rat single ventricular cells. Circ Res. 1984 Feb;54(2):157–162. doi: 10.1161/01.res.54.2.157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirsch G. E., Narahashi T. Site of action and active form of aminopyridines in squid axon membranes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1983 Jul;226(1):174–179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirsch G. E., Yeh J. Z., Oxford G. S. Modulation of aminopyridine block of potassium currents in squid axon. Biophys J. 1986 Oct;50(4):637–644. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(86)83503-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matteson D. R., Carmeliet P. Modification of K channel inactivation by papain and N-bromoacetamide. Biophys J. 1988 Apr;53(4):641–645. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(88)83143-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen J. D. The determination of the stability constant for calcium-EGTA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Nov 18;451(1):321–325. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(76)90282-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oxford G. S., Wagoner P. K. The inactivating K+ current in GH3 pituitary cells and its modification by chemical reagents. J Physiol. 1989 Mar;410:587–612. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oxford G. S., Yeh J. Z. Interactions of monovalent cations with sodium channels in squid axon. I. Modification of physiological inactivation gating. J Gen Physiol. 1985 Apr;85(4):583–602. doi: 10.1085/jgp.85.4.583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sand O., Haug E., Gautvik K. M. Effects of thyroliberin and 4-aminopyridine on action potentials and prolactin release and synthesis in rat pituitary cells in culture. Acta Physiol Scand. 1980 Mar;108(3):247–252. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1980.tb06530.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schofield J. G., Saith S. Potentiation of bovine growth hormone release by an inhibitor of potassium channels. Eur J Pharmacol. 1981 Dec 17;76(4):431–434. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(81)90116-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thesleff S. Aminopyridines and synaptic transmission. Neuroscience. 1980;5(8):1413–1419. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(80)90002-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson S. Aminopyridine block of transient potassium current. J Gen Physiol. 1982 Jul;80(1):1–18. doi: 10.1085/jgp.80.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeh J. Z., Narahashi T. Kinetic analysis of pancuronium interaction with sodium channels in squid axon membranes. J Gen Physiol. 1977 Mar;69(3):293–323. doi: 10.1085/jgp.69.3.293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeh J. Z., Oxford G. S., Wu C. H., Narahashi T. Dynamics of aminopyridine block of potassium channels in squid axon membrane. J Gen Physiol. 1976 Nov;68(5):519–535. doi: 10.1085/jgp.68.5.519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


