Abstract
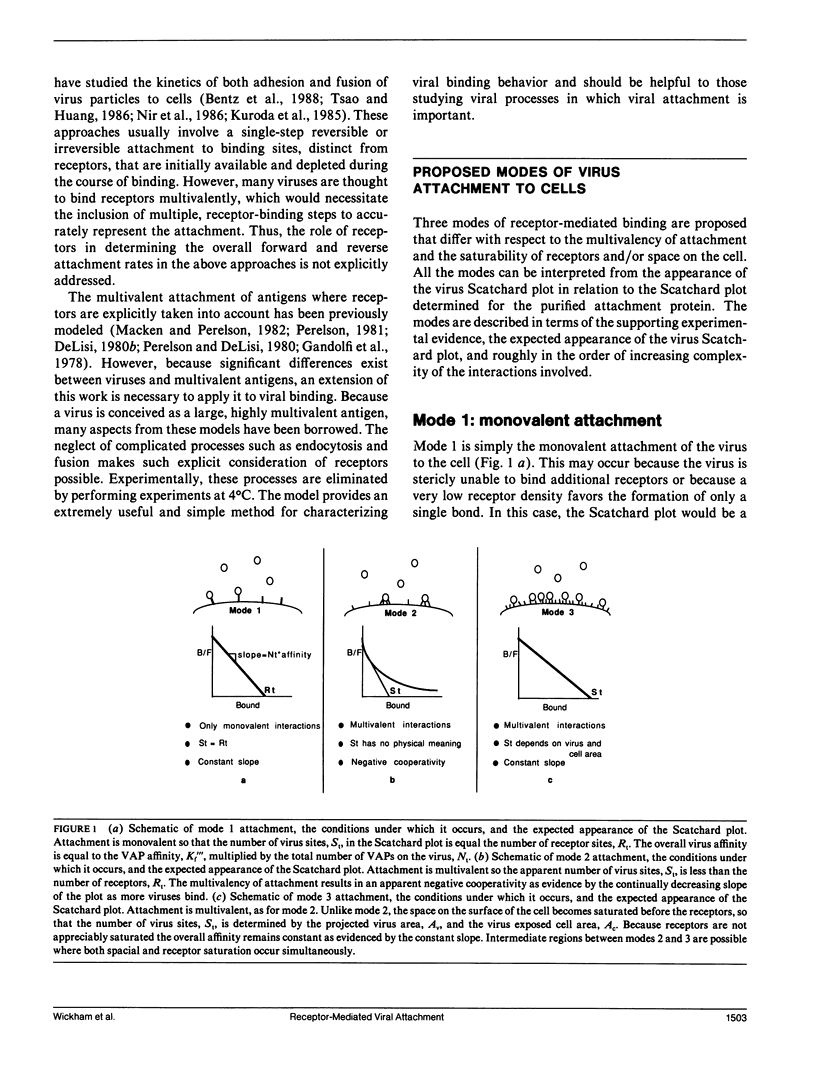
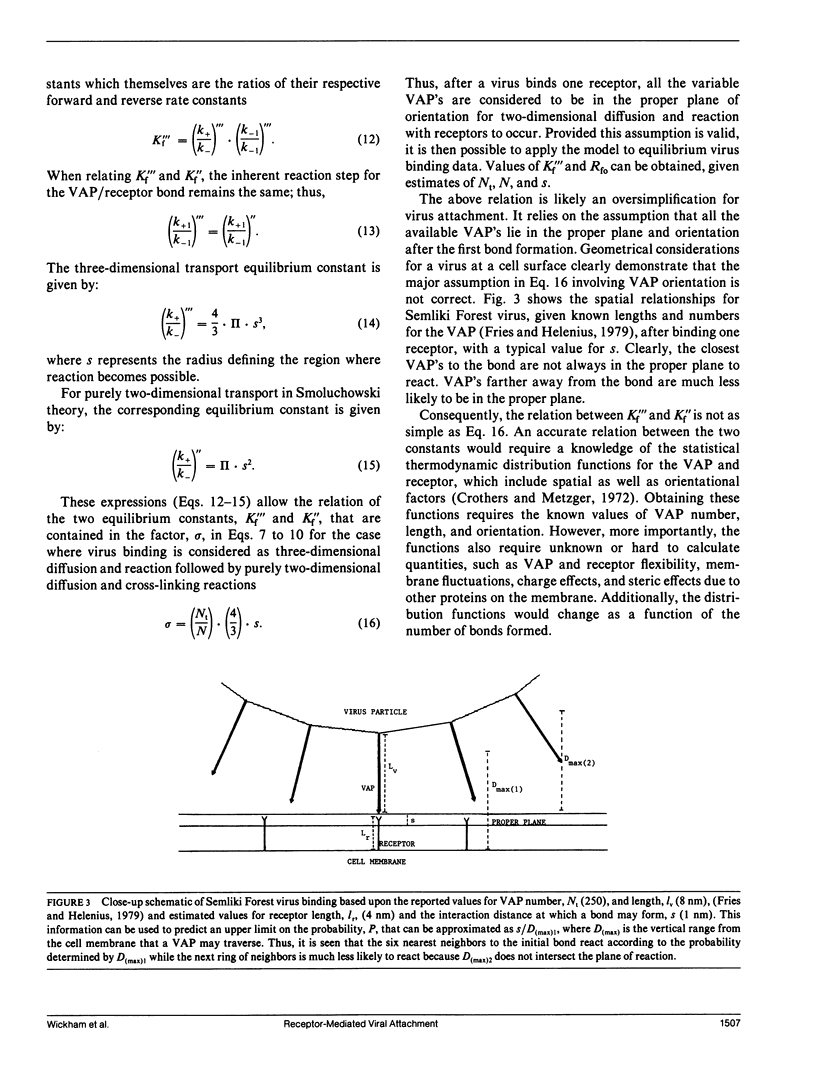
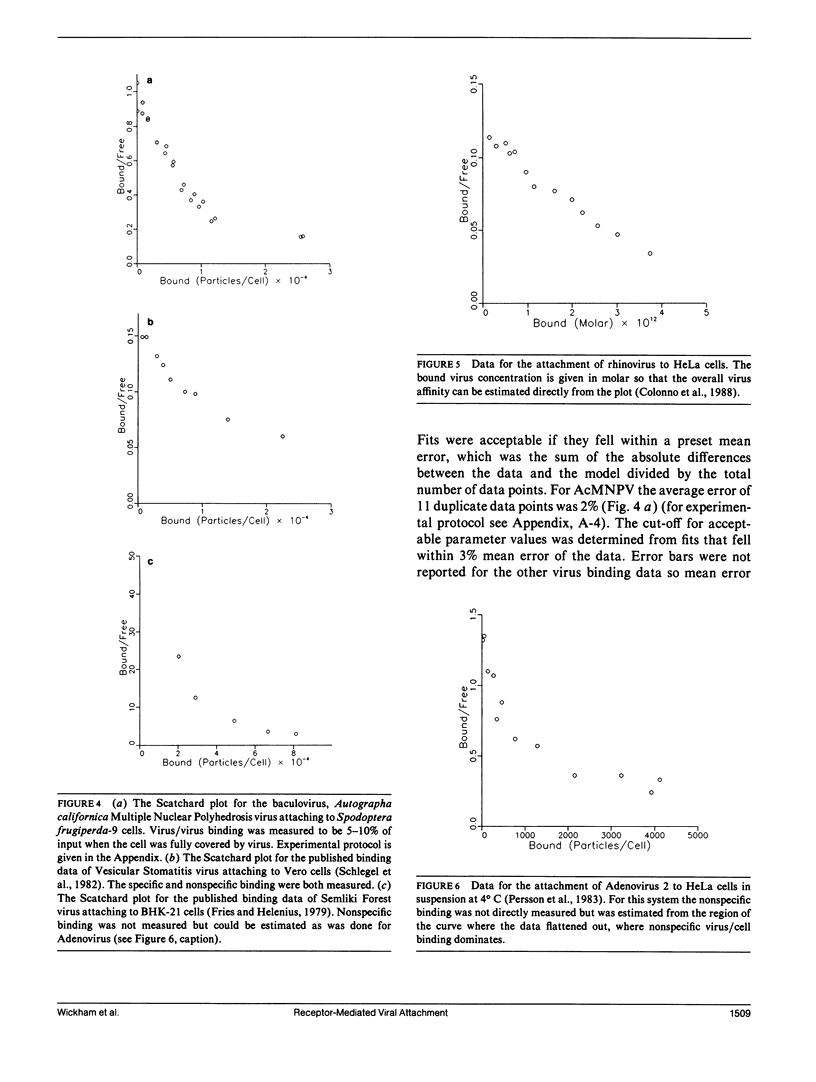
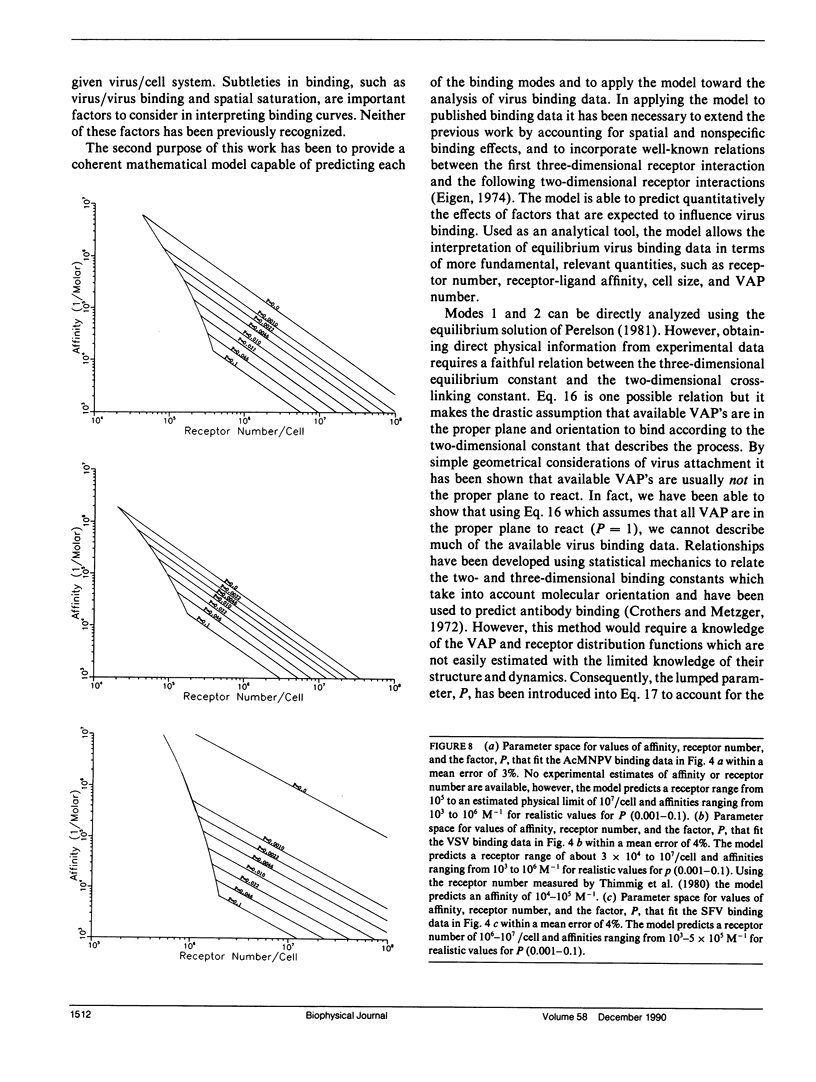
Viruses are multivalent particles that attach to cells through one or more bonds between viral attachment proteins (VAP) and specific cellular receptors. Three modes of virus binding are presented that can explain the diversity in binding data observed among viruses. They are based on multivalency of attachment and spatial versus receptor saturation effects which are easily distinguished based upon simple criteria. Mode 1 involves only monovalent virus/receptor binding. Modes 2 and 3 involve multivalent bonds between the virus and cell; however, in mode 3 space on the cell surface becomes saturated before receptors. A model is developed for viral attachment that accounts for nonspecific binding, receptor/virus interactions, and spatial saturation effects. The model can describe each mode in different limits and can be applied to virus binding data to extract key physical information such as receptor number and affinity. These values are used to postulate the type of VAP/receptor interaction involved and to predict binding at different parameter values. For the mode 2 binding of Adenovirus 2, the model predicts a receptor number of 4-15 x 10(3) on HeLa cells and an affinity of 2-6 x 10(7) M-1 which closely approximate experimental estimates. For the binding of three, broad-host-range, enveloped viruses, Semliki Forest virus, Vesicular Stomatitis virus, and the baculovirus, Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus, the model predicts receptor numbers of 10(5) or greater and affinities in the range of 10(4) to 10(5) M-1. These values are indicative of a VAP/oligosaccharide interaction which has been documented for a number of other viruses. Experimental evidence is presented that is the first to demonstrate that baculovirus binding is mediated by a cell surface receptor.
Full text
PDF











Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alcamí A., Carrascosa A. L., Viñuela E. Saturable binding sites mediate the entry of African swine fever virus into Vero cells. Virology. 1989 Feb;168(2):393–398. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90281-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell G. I. Models for the specific adhesion of cells to cells. Science. 1978 May 12;200(4342):618–627. doi: 10.1126/science.347575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bentz J., Nir S., Covell D. G. Mass action kinetics of virus-cell aggregation and fusion. Biophys J. 1988 Sep;54(3):449–462. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(88)82978-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boldt D. H., Lyons R. D. Fractionation of human lymphocytes with plant lectins. I. Structural and functional characteristics of lymphocyte subclasses isolated by an affinity technique using Lens culinaris lectin. Cell Immunol. 1979 Mar 1;43(1):82–93. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(79)90152-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bukrinskaya A. G. Penetration of viral genetic material into host cell. Adv Virus Res. 1982;27:141–204. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60435-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cahan L. D., Singh R., Paulson J. C. Sialyloligosaccharide receptors of binding variants of polyoma virus. Virology. 1983 Oct 30;130(2):281–289. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90083-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colonno R. J., Condra J. H., Mizutani S., Callahan P. L., Davies M. E., Murcko M. A. Evidence for the direct involvement of the rhinovirus canyon in receptor binding. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(15):5449–5453. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.15.5449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crothers D. M., Metzger H. The influence of polyvalency on the binding properties of antibodies. Immunochemistry. 1972 Mar;9(3):341–357. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(72)90097-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalgleish A. G., Beverley P. C., Clapham P. R., Crawford D. H., Greaves M. F., Weiss R. A. The CD4 (T4) antigen is an essential component of the receptor for the AIDS retrovirus. Nature. 1984 Dec 20;312(5996):763–767. doi: 10.1038/312763a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLisi C. The biophysics of ligand-receptor interactions. Q Rev Biophys. 1980 May;13(2):201–230. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500001657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein R. L., Powers M. L., Rogart R. B., Weiner H. L. Binding of 125I-labeled reovirus to cell surface receptors. Virology. 1984 Feb;133(1):46–55. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90424-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fries E., Helenius A. Binding of Semliki Forest virus and its spike glycoproteins to cells. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Jun;97(1):213–220. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13105.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gandolfi A., Giovenco M. A. Reversible binding of multivalent antigen in the control of B lymphocyte activation. J Theor Biol. 1978 Oct 21;74(4):513–521. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(78)90238-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haywood A. M. Characteristics of Sendai virus receptors in a model membrane. J Mol Biol. 1974 Mar 15;83(4):427–436. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90504-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helenius A., Marsh M. Endocytosis of enveloped animal viruses. Ciba Found Symp. 1982;(92):59–76. doi: 10.1002/9780470720745.ch4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helenius A., Morein B., Fries E., Simons K., Robinson P., Schirrmacher V., Terhorst C., Strominger J. L. Human (HLA-A and HLA-B) and murine (H-2K and H-2D) histocompatibility antigens are cell surface receptors for Semliki Forest virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):3846–3850. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.3846. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoekstra D., Klappe K., de Boer T., Wilschut J. Characterization of the fusogenic properties of Sendai virus: kinetics of fusion with erythrocyte membranes. Biochemistry. 1985 Aug 27;24(18):4739–4745. doi: 10.1021/bi00339a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klatzmann D., Champagne E., Chamaret S., Gruest J., Guetard D., Hercend T., Gluckman J. C., Montagnier L. T-lymphocyte T4 molecule behaves as the receptor for human retrovirus LAV. Nature. 1984 Dec 20;312(5996):767–768. doi: 10.1038/312767a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamarre D., Ashkenazi A., Fleury S., Smith D. H., Sekaly R. P., Capon D. J. The MHC-binding and gp120-binding functions of CD4 are separable. Science. 1989 Aug 18;245(4919):743–746. doi: 10.1126/science.2549633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lentz T. L., Burrage T. G., Smith A. L., Crick J., Tignor G. H. Is the acetylcholine receptor a rabies virus receptor? Science. 1982 Jan 8;215(4529):182–184. doi: 10.1126/science.7053569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipkind M., Urbakh V. Dependence of virus adsorption to the cell surface on the input multiplicity of infection. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1988 Nov;269(4):501–505. doi: 10.1016/s0176-6724(88)80072-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macken C. A., Perelson A. S. Aggregation of cell surface receptors by multivalent ligands. J Math Biol. 1982;14(3):365–370. doi: 10.1007/BF00275399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maddon P. J., Dalgleish A. G., McDougal J. S., Clapham P. R., Weiss R. A., Axel R. The T4 gene encodes the AIDS virus receptor and is expressed in the immune system and the brain. Cell. 1986 Nov 7;47(3):333–348. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90590-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh M., Helenius A. Virus entry into animal cells. Adv Virus Res. 1989;36:107–151. doi: 10.1016/S0065-3527(08)60583-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh M. The entry of enveloped viruses into cells by endocytosis. Biochem J. 1984 Feb 15;218(1):1–10. doi: 10.1042/bj2180001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morishima T., McClintock P. R., Billups L. C., Notkins A. L. Expression and modulation of virus receptors on lymphoid and myeloid cells: relationship to infectivity. Virology. 1982 Jan 30;116(2):605–618. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90152-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nir S., Klappe K., Hoekstra D. Mass action analysis of kinetics and extent of fusion between Sendai virus and phospholipid vesicles. Biochemistry. 1986 Dec 16;25(25):8261–8266. doi: 10.1021/bi00373a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldstone M. B., Tishon A., Dutko F. J., Kennedy S. I., Holland J. J., Lampert P. W. Does the major histocompatibility complex serve as a specific receptor for Semliki Forest virus? J Virol. 1980 Apr;34(1):256–265. doi: 10.1128/jvi.34.1.256-265.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulson J. C., Sadler J. E., Hill R. L. Restoration of specific myxovirus receptors to asialoerythrocytes by incorporation of sialic acid with pure sialyltransferases. J Biol Chem. 1979 Mar 25;254(6):2120–2124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persson R., Svensson U., Everitt E. Virus receptor interaction in the adenovirus system. II. Capping and cooperative binding of virions on HeLa cells. J Virol. 1983 Jun;46(3):956–963. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.3.956-963.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philipson L., Lonberg-Holm K., Pettersson U. Virus-receptor interaction in an adenovirus system. J Virol. 1968 Oct;2(10):1064–1075. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.10.1064-1075.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers G. N., Paulson J. C., Daniels R. S., Skehel J. J., Wilson I. A., Wiley D. C. Single amino acid substitutions in influenza haemagglutinin change receptor binding specificity. Nature. 1983 Jul 7;304(5921):76–78. doi: 10.1038/304076a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlegel R., Willingham M. C., Pastan I. H. Saturable binding sites for vesicular stomatitis virus on the surface of Vero cells. J Virol. 1982 Sep;43(3):871–875. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.3.871-875.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svensson U. Role of vesicles during adenovirus 2 internalization into HeLa cells. J Virol. 1985 Aug;55(2):442–449. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.2.442-449.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tardieu M., Epstein R. L., Weiner H. L. Interaction of viruses with cell surface receptors. Int Rev Cytol. 1982;80:27–61. doi: 10.1016/S0074-7696(08)60366-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor H. P., Cooper N. R. Human cytomegalovirus binding to fibroblasts is receptor mediated. J Virol. 1989 Sep;63(9):3991–3998. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.9.3991-3998.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thimmig R. L., Hughes J. V., Kinders R. J., Milenkovic A. G., Johnson T. C. Isolation of the glycoprotein of vesicular stomatitis virus and its binding to cell surfaces. J Gen Virol. 1980 Oct;50(2):279–291. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-50-2-279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsao Y. S., Huang L. Kinetic studies of Sendai virus-target membrane interactions: independent analysis of binding and fusion. Biochemistry. 1986 Jul 1;25(13):3971–3976. doi: 10.1021/bi00361a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weis W., Brown J. H., Cusack S., Paulson J. C., Skehel J. J., Wiley D. C. Structure of the influenza virus haemagglutinin complexed with its receptor, sialic acid. Nature. 1988 Jun 2;333(6172):426–431. doi: 10.1038/333426a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. M., Littman D. R. Viral receptors of the immunoglobulin superfamily. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):725–728. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90674-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wunner W. H., Reagan K. J., Koprowski H. Characterization of saturable binding sites for rabies virus. J Virol. 1984 Jun;50(3):691–697. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.3.691-697.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada S., Ohnishi S. Vesicular stomatitis virus binds and fuses with phospholipid domain in target cell membranes. Biochemistry. 1986 Jun 17;25(12):3703–3708. doi: 10.1021/bi00360a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


