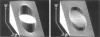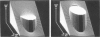Abstract
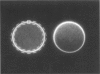
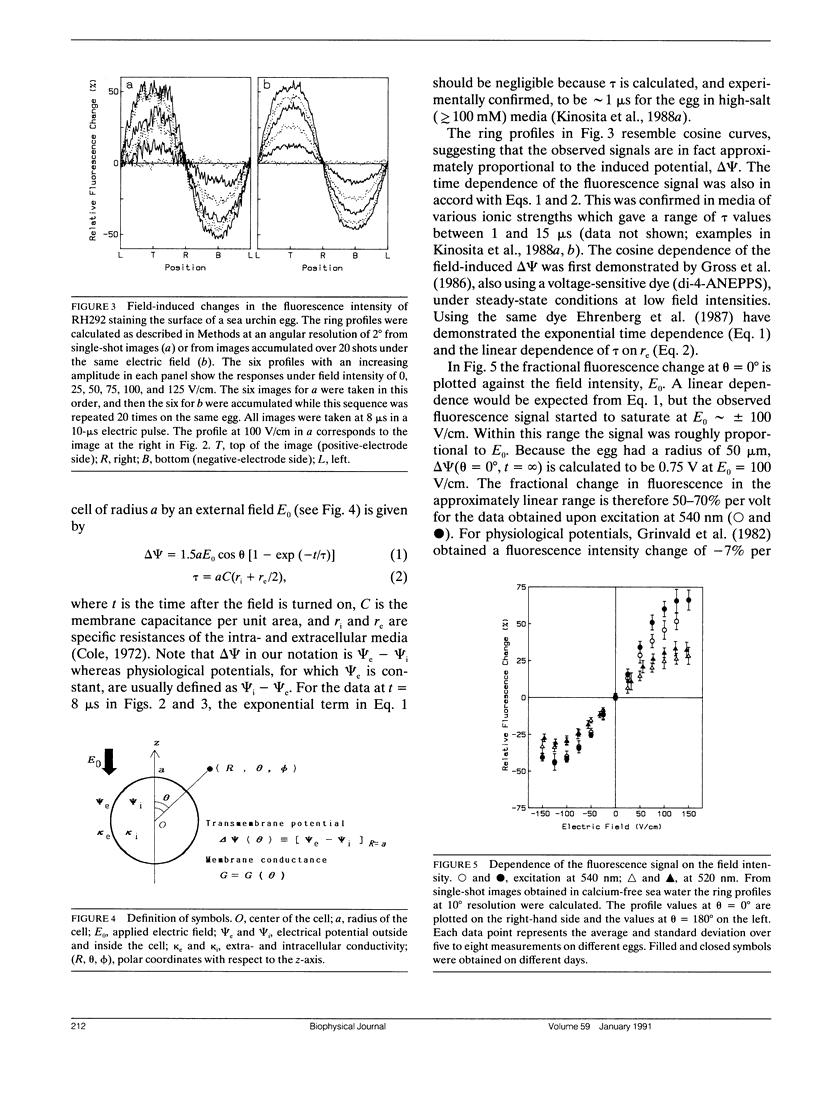
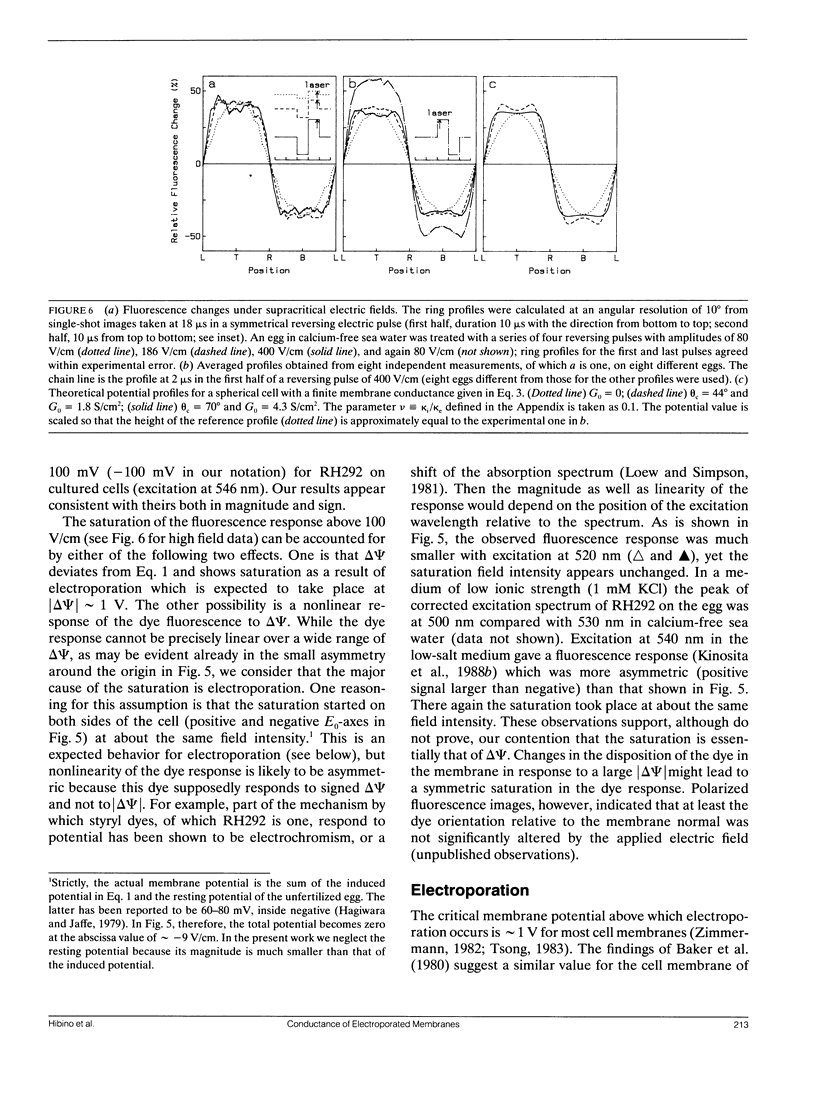
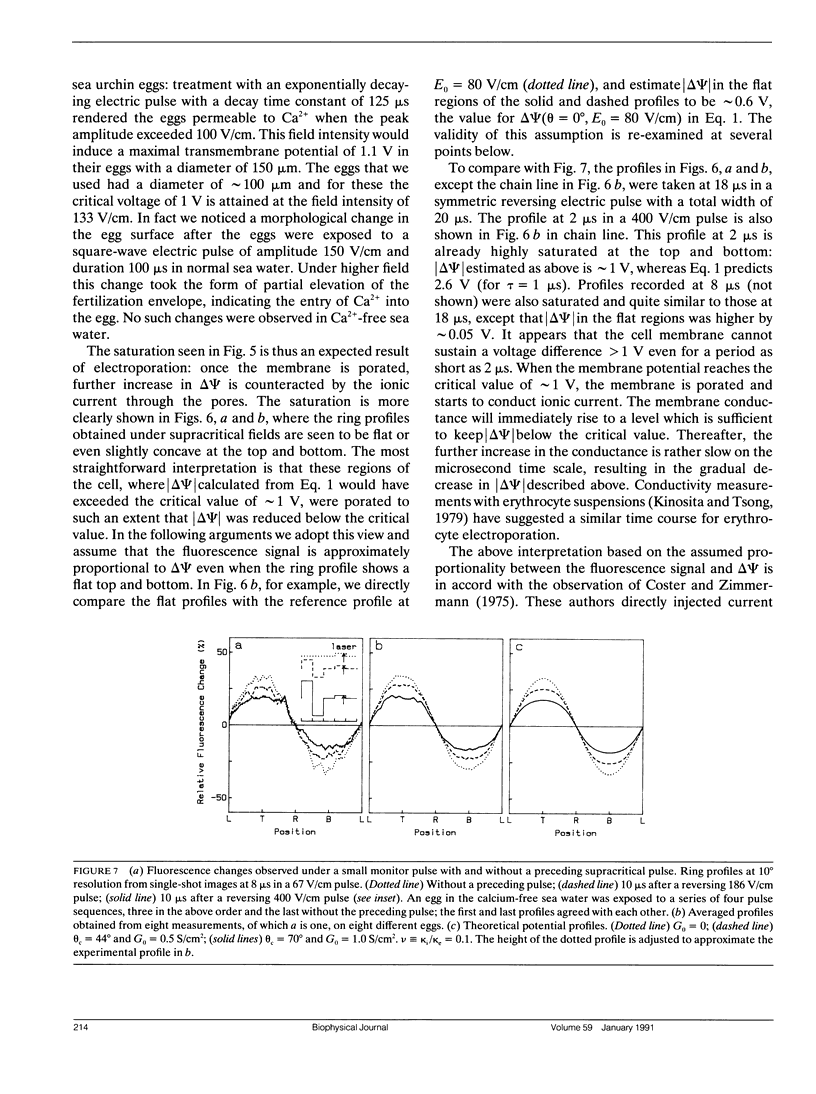
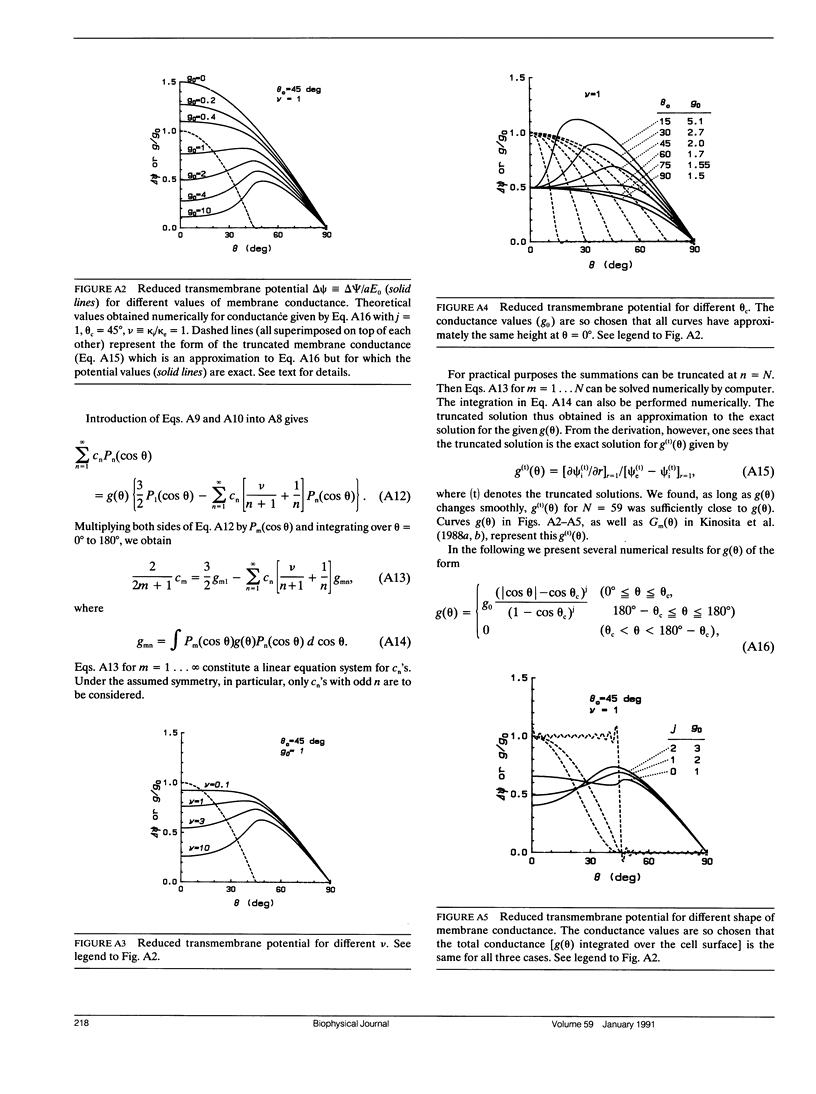
Transmembrane potential was induced in a sea urchin egg by applying a microsecond electric pulse across the cell. The potential was imaged at a submicrosecond time resolution by staining the cell membrane with the voltage-sensitive fluorescent dye RH292. Under moderate electric fields, the spatial distribution of the induced potential as well as its time dependence were in accord with the theoretical prediction in which the cell membrane was regarded as an insulator. At higher field intensities, however, the potential apparently did not fully develop and tended to saturate above a certain level. The saturation is ascribed to the introduction of a large electrical conductance, in the form of aqueous openings, in the membrane by the action of the induced potential (electroporation). Comparison of the experimental and theoretical potential profiles indicates that the two regions of the membrane that opposed the electrodes acquired a high membrane conductance of the order of 1 S/cm2 within 2 microseconds from the onset of the external field. The conductance was similar in the two regions, although permeability in the two regions of the membrane long after the pulse treatment appeared quite different.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Coster H. G., Simmermann U. The mechanism of electrical breakdown in the membranes of Valonai utricularis. J Membr Biol. 1975 Jun 3;22(1):73–90. doi: 10.1007/BF01868164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrenberg B., Farkas D. L., Fluhler E. N., Lojewska Z., Loew L. M. Membrane potential induced by external electric field pulses can be followed with a potentiometric dye. Biophys J. 1987 May;51(5):833–837. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(87)83410-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinvald A., Hildesheim R., Farber I. C., Anglister L. Improved fluorescent probes for the measurement of rapid changes in membrane potential. Biophys J. 1982 Sep;39(3):301–308. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(82)84520-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross D., Loew L. M., Webb W. W. Optical imaging of cell membrane potential changes induced by applied electric fields. Biophys J. 1986 Aug;50(2):339–348. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(86)83467-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara S., Jaffe L. A. Electrical properties of egg cell membranes. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1979;8:385–416. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.08.060179.002125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinosita K., Jr, Ashikawa I., Saita N., Yoshimura H., Itoh H., Nagayama K., Ikegami A. Electroporation of cell membrane visualized under a pulsed-laser fluorescence microscope. Biophys J. 1988 Jun;53(6):1015–1019. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(88)83181-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinosita K., Jr, Tsong T. T. Hemolysis of human erythrocytes by transient electric field. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 May;74(5):1923–1927. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.5.1923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinosita K., Jr, Tsong T. Y. Formation and resealing of pores of controlled sizes in human erythrocyte membrane. Nature. 1977 Aug 4;268(5619):438–441. doi: 10.1038/268438a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinosita K., Jr, Tsong T. Y. Voltage-induced conductance in human erythrocyte membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Jul 5;554(2):479–497. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(79)90386-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinosita K., Jr, Tsong T. Y. Voltage-induced pore formation and hemolysis of human erythrocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Dec 1;471(2):227–242. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90252-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loew L. M., Simpson L. L. Charge-shift probes of membrane potential: a probable electrochromic mechanism for p-aminostyrylpyridinium probes on a hemispherical lipid bilayer. Biophys J. 1981 Jun;34(3):353–365. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(81)84854-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossignol D. P., Decker G. L., Lennarz W. J., Tsong T. Y., Teissie J. Induction of calcium-dependent, localized cortical granule breakdown in sea-urchin eggs by voltage pulsation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Dec 19;763(4):346–355. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(83)90096-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sowers A. E. Fusion events and nonfusion contents mixing events induced in erythrocyte ghosts by an electric pulse. Biophys J. 1988 Oct;54(4):619–626. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(88)82997-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsong T. Y. Voltage modulation of membrane permeability and energy utilization in cells. Biosci Rep. 1983 Jun;3(6):487–505. doi: 10.1007/BF01120693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmermann U. Electric field-mediated fusion and related electrical phenomena. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Nov 30;694(3):227–277. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(82)90007-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]