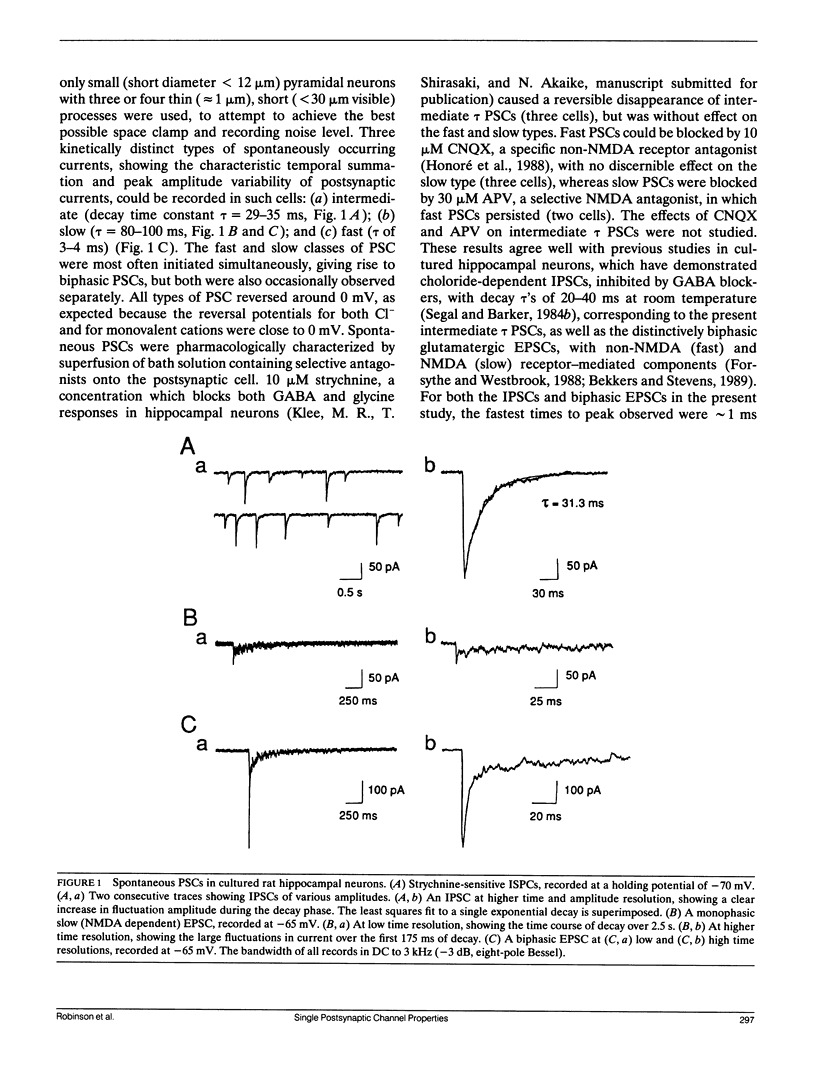
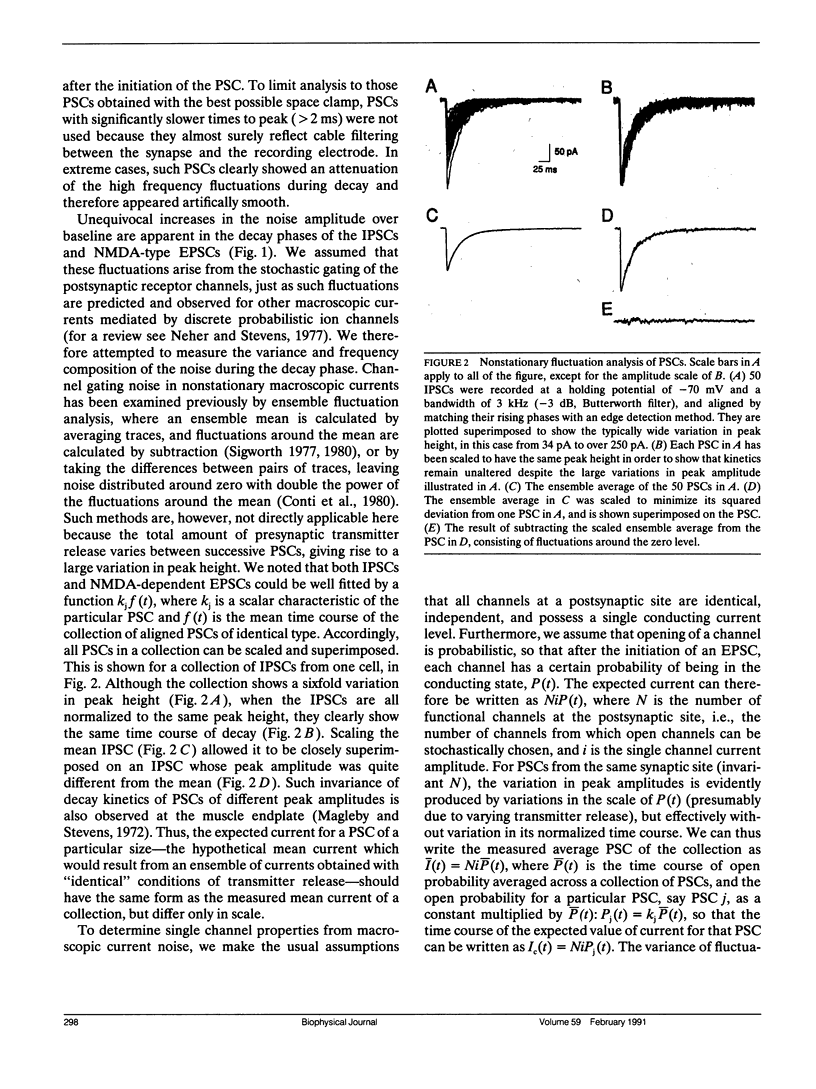
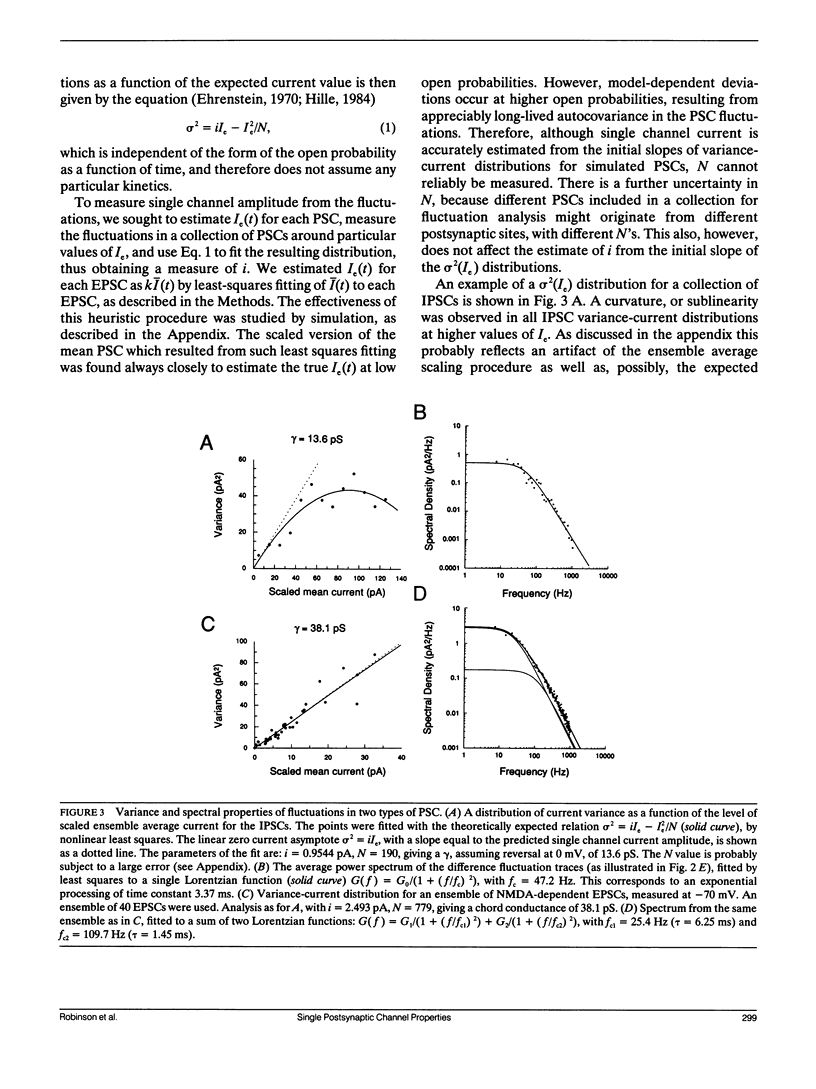
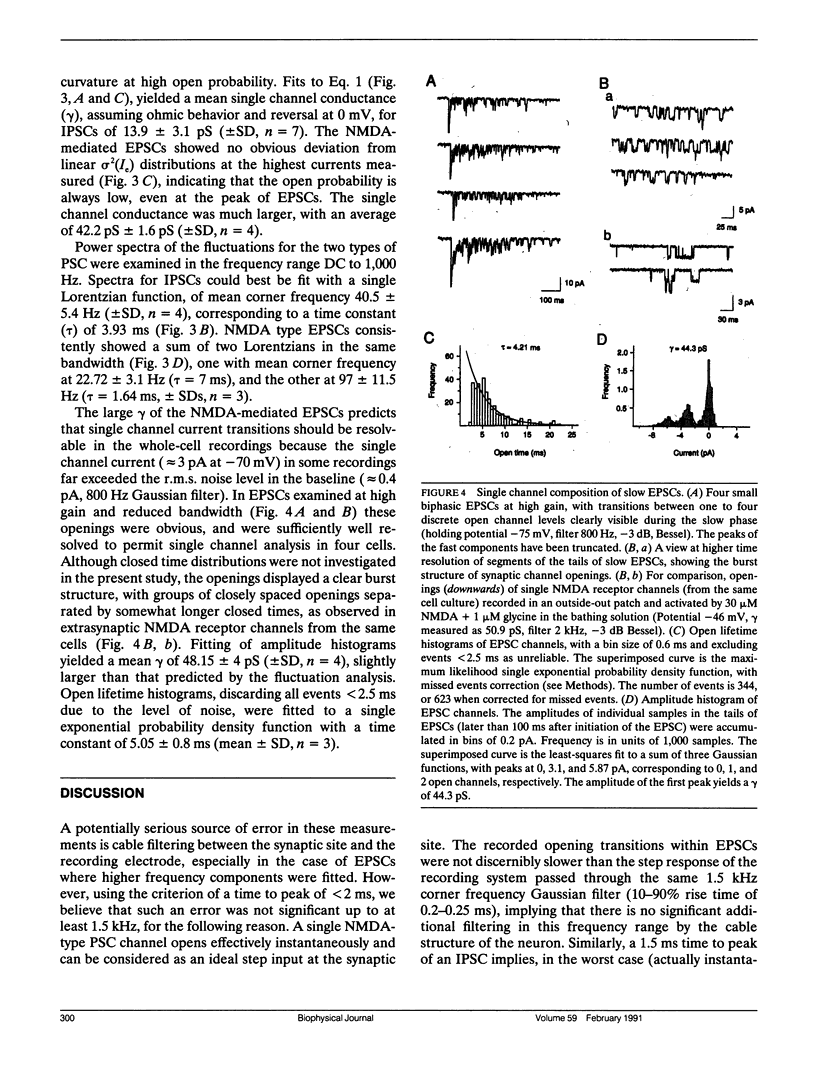
Abstract
In order to measure unitary properties of receptor channels at the postsynaptic site, the noise within the decay phases of inhibitory postsynaptic currents (IPSCs) and of N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA)-dependent excitatory postsynaptic currents (EPSCs) in rat hippocampal neurons was studied by nonstationary fluctuation analysis. Least squares scaling of the mean current was used to circumvent the wide variation in amplitude of postsynaptic currents. The variance of fluctuations around the expected current was analyzed to calculate single channel conductance, and fluctuation kinetics were studied with power spectra. The single channel conductance underlying the IPSC was measured as 14 pS, whereas that underlying the EPSC was 42 pS. Openings of the EPSC channel could also be resolved directly in low-noise whole-cell recordings, allowing verification of the accuracy of the fluctuation analysis. The results are the first measurements of the properties of single postsynaptic channels activated during synaptic currents, and suggest that the technique can be widely applicable in investigations of synaptic mechanism and plasticity.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ascher P., Bregestovski P., Nowak L. N-methyl-D-aspartate-activated channels of mouse central neurones in magnesium-free solutions. J Physiol. 1988 May;399:207–226. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017076. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ascher P., Nowak L. Quisqualate- and kainate-activated channels in mouse central neurones in culture. J Physiol. 1988 May;399:227–245. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bekkers J. M., Stevens C. F. NMDA and non-NMDA receptors are co-localized at individual excitatory synapses in cultured rat hippocampus. Nature. 1989 Sep 21;341(6239):230–233. doi: 10.1038/341230a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett P. B., Kass R., Begenisich T. Nonstationary fluctuation analysis of the delayed rectifier K channel in cardiac Purkinje fibers. Actions of norepinephrine on single-channel current. Biophys J. 1989 Apr;55(4):731–738. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(89)82872-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bormann J., Hamill O. P., Sakmann B. Mechanism of anion permeation through channels gated by glycine and gamma-aminobutyric acid in mouse cultured spinal neurones. J Physiol. 1987 Apr;385:243–286. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collingridge G. L., Gage P. W., Robertson B. Inhibitory post-synaptic currents in rat hippocampal CA1 neurones. J Physiol. 1984 Nov;356:551–564. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015482. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collingridge G. L., Lester R. A. Excitatory amino acid receptors in the vertebrate central nervous system. Pharmacol Rev. 1989 Jun;41(2):143–210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conti F., Neumcke B., Nonner W., Stämpfli R. Conductance fluctuations from the inactivation process of sodium channels in myelinated nerve fibres. J Physiol. 1980 Nov;308:217–239. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cull-Candy S. G., Howe J. R., Ogden D. C. Noise and single channels activated by excitatory amino acids in rat cerebellar granule neurones. J Physiol. 1988 Jun;400:189–222. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dilger J. P., Brett R. S. Direct measurement of the concentration- and time-dependent open probability of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor channel. Biophys J. 1990 Apr;57(4):723–731. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82593-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrenstein G., Lecar H., Nossal R. The nature of the negative resistance in bimolecular lipid membranes containing excitability-inducing material. J Gen Physiol. 1970 Jan;55(1):119–133. doi: 10.1085/jgp.55.1.119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faber D. S., Funch P. G., Korn H. Evidence that receptors mediating central synaptic potentials extend beyond the postsynaptic density. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(10):3504–3508. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.10.3504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischbach G. D., Schuetze S. M. A post-natal decrease in acetylcholine channel open time at rat end-plates. J Physiol. 1980 Jun;303:125–137. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsythe I. D., Westbrook G. L. Slow excitatory postsynaptic currents mediated by N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors on cultured mouse central neurones. J Physiol. 1988 Feb;396:515–533. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp016975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honoré T., Davies S. N., Drejer J., Fletcher E. J., Jacobsen P., Lodge D., Nielsen F. E. Quinoxalinediones: potent competitive non-NMDA glutamate receptor antagonists. Science. 1988 Aug 5;241(4866):701–703. doi: 10.1126/science.2899909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe J. R., Colquhoun D., Cull-Candy S. G. On the kinetics of large-conductance glutamate-receptor ion channels in rat cerebellar granule neurons. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1988 May 23;233(1273):407–422. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1988.0030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahr C. E., Stevens C. F. Glutamate activates multiple single channel conductances in hippocampal neurons. Nature. 1987 Feb 5;325(6104):522–525. doi: 10.1038/325522a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. A., Baughman R. W. NMDA- and non-NMDA-receptor components of excitatory synaptic potentials recorded from cells in layer V of rat visual cortex. J Neurosci. 1988 Sep;8(9):3522–3534. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.08-09-03522.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerma J., Kushner L., Zukin R. S., Bennett M. V. N-methyl-D-aspartate activates different channels than do kainate and quisqualate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(6):2083–2087. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.6.2083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magleby K. L., Stevens C. F. A quantitative description of end-plate currents. J Physiol. 1972 May;223(1):173–197. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marr D., Hildreth E. Theory of edge detection. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1980 Feb 29;207(1167):187–217. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1980.0020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neher E., Sakmann B. Noise analysis of drug induced voltage clamp currents in denervated frog muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1976 Jul;258(3):705–729. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011442. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neher E., Stevens C. F. Conductance fluctuations and ionic pores in membranes. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1977;6:345–381. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.06.060177.002021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowak L., Bregestovski P., Ascher P., Herbet A., Prochiantz A. Magnesium gates glutamate-activated channels in mouse central neurones. Nature. 1984 Feb 2;307(5950):462–465. doi: 10.1038/307462a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozawa S., Yuzaki M. Patch-clamp studies of chloride channels activated by gamma-aminobutyric acid in cultured hippocampal neurones of the rat. Neurosci Res. 1984 Oct;1(5):275–293. doi: 10.1016/0168-0102(84)90034-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal M., Barker J. L. Rat hippocampal neurons in culture: properties of GABA-activated Cl- ion conductance. J Neurophysiol. 1984 Mar;51(3):500–515. doi: 10.1152/jn.1984.51.3.500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal M., Barker J. L. Rat hippocampal neurons in culture: voltage-clamp analysis of inhibitory synaptic connections. J Neurophysiol. 1984 Sep;52(3):469–487. doi: 10.1152/jn.1984.52.3.469. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigworth F. J. Interpreting power spectra from nonstationary membrane current fluctuations. Biophys J. 1981 Aug;35(2):289–300. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(81)84790-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigworth F. J. Sodium channels in nerve apparently have two conductance states. Nature. 1977 Nov 17;270(5634):265–267. doi: 10.1038/270265a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigworth F. J. The variance of sodium current fluctuations at the node of Ranvier. J Physiol. 1980 Oct;307:97–129. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013426. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinbach J. H. Structural and functional diversity in vertebrate skeletal muscle nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Annu Rev Physiol. 1989;51:353–365. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.51.030189.002033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang C. M., Dichter M., Morad M. Quisqualate activates a rapidly inactivating high conductance ionic channel in hippocampal neurons. Science. 1989 Mar 17;243(4897):1474–1477. doi: 10.1126/science.2467378. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


