Abstract
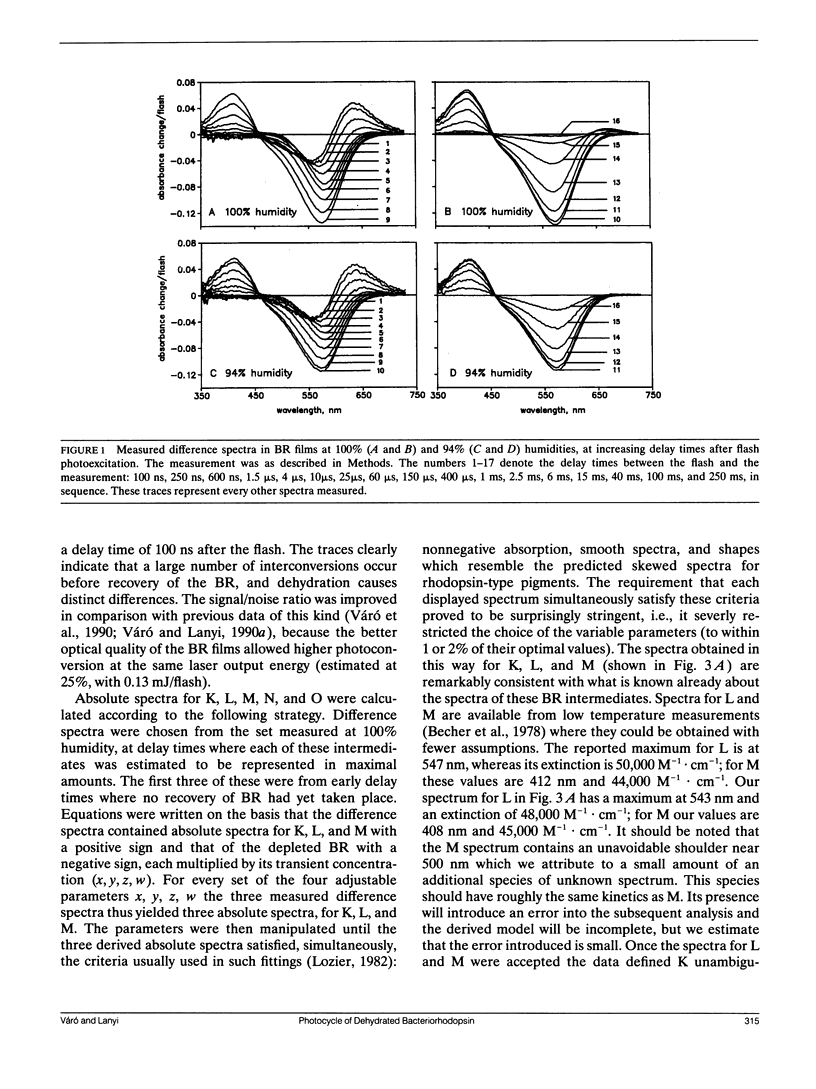
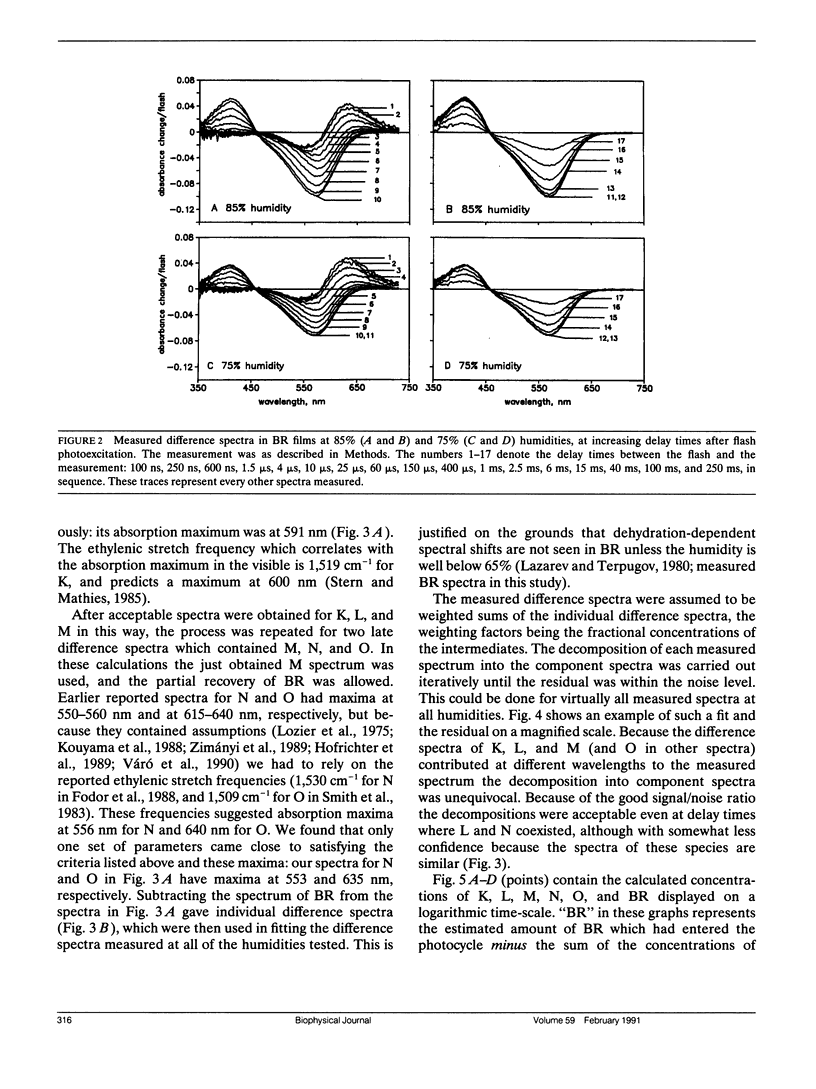
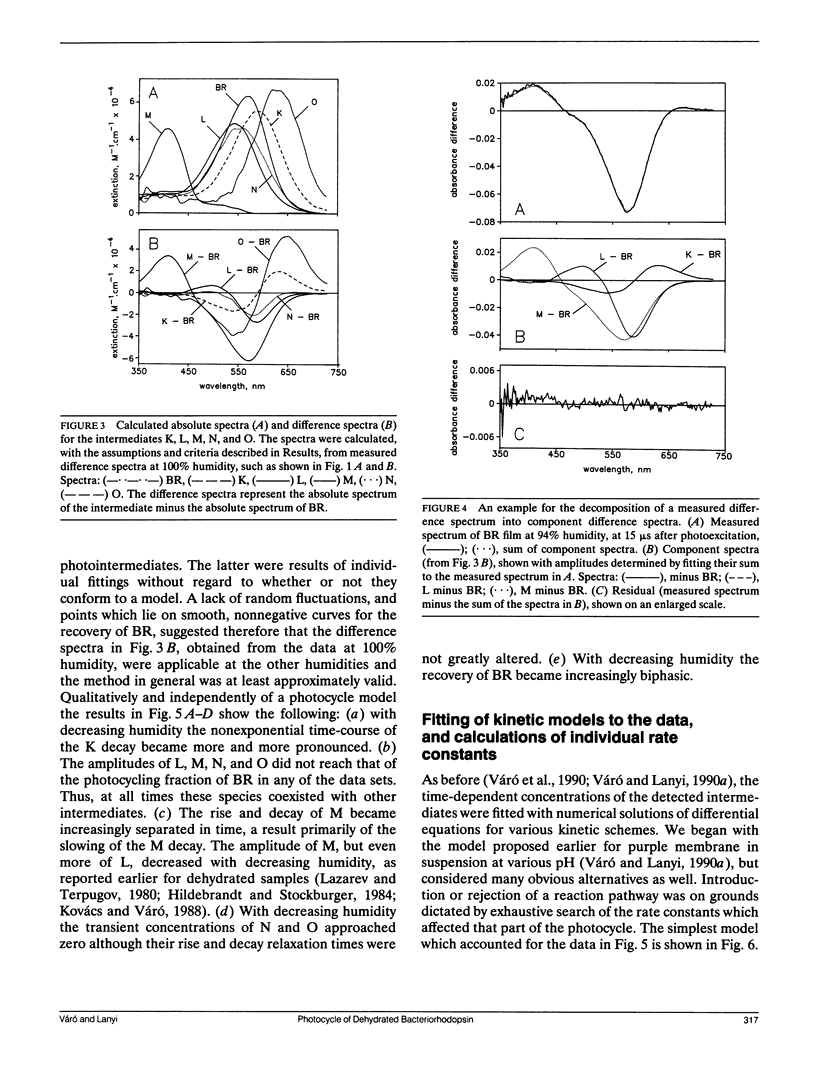
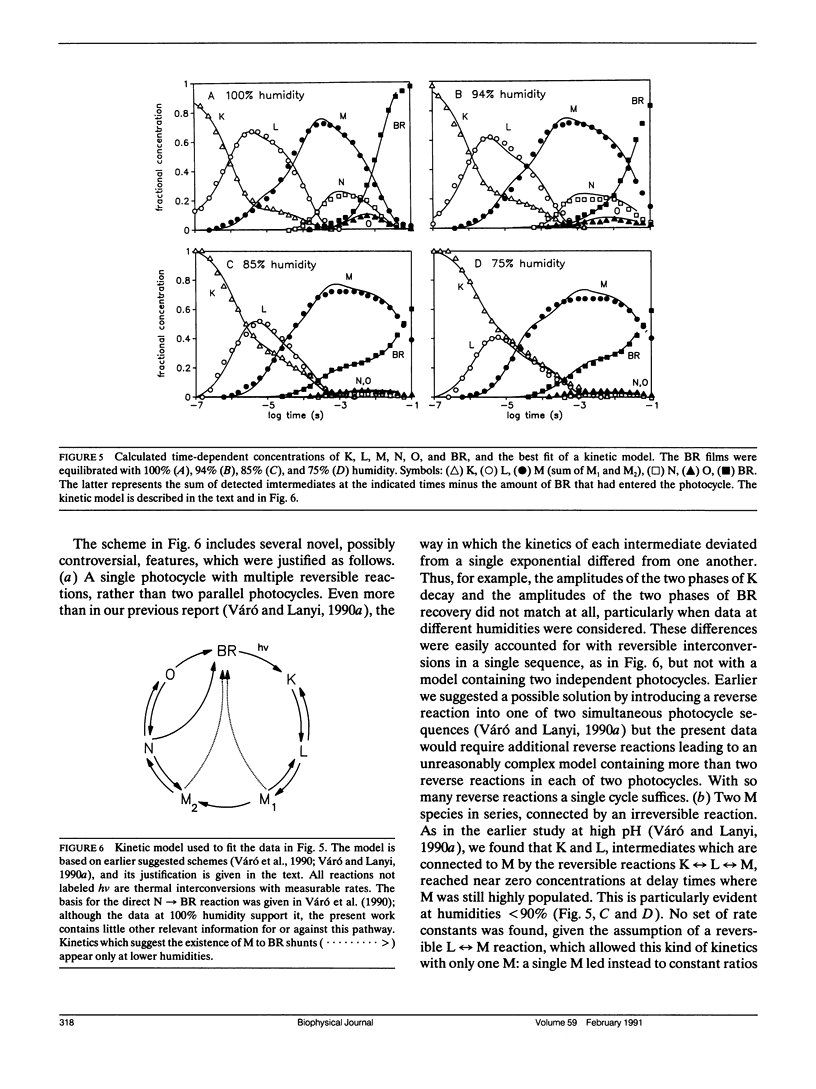
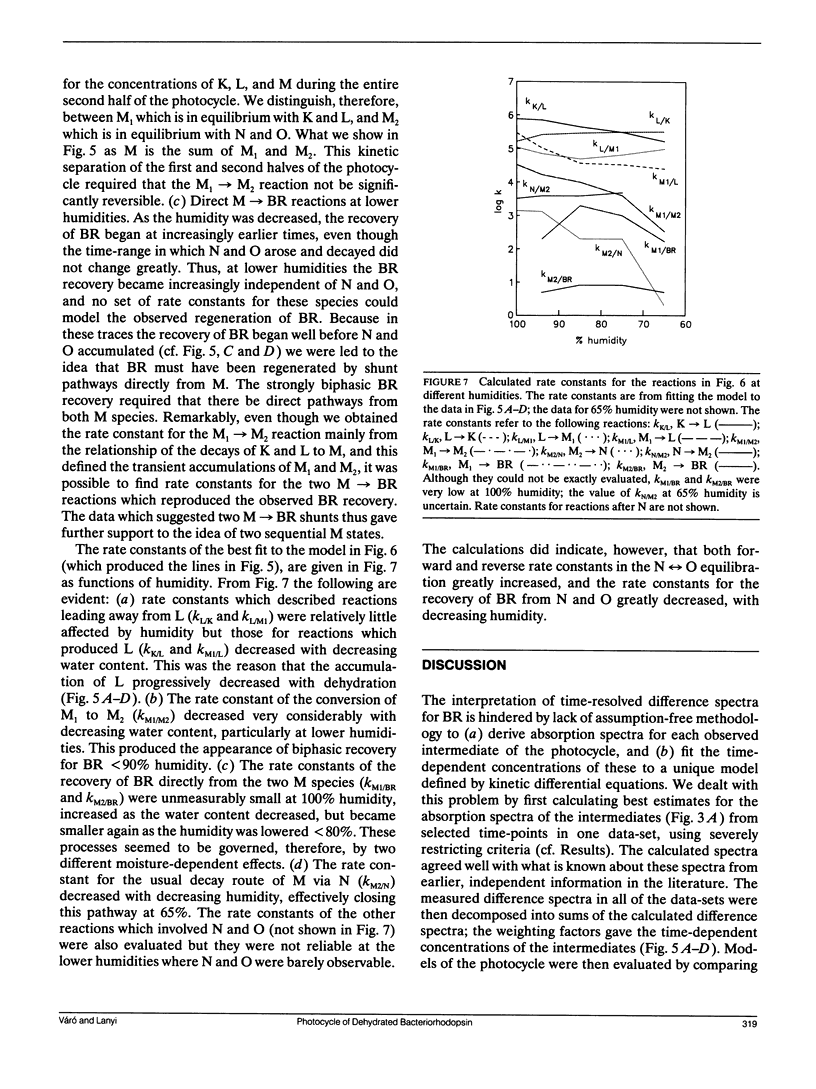
The photoreaction of bacteriorhodopsin was studied in moderately dehydrated films (relative humidities between 100 and 65%). Time-resolved difference spectra from a gated optical multichannel analyzer, between 100 ns and 100 ms after photoexcitation, were decomposed into sums of difference spectra of the intermediates K, L, M, N, and O, and the kinetics obtained were fitted to various alternative schemes. The data confirm the model of a single reaction sequence with reversible reactions we proposed recently for purple membrane suspensions (Váró, G., and J. K. Lanyi. Biochemistry. 1990. 29:2241-2250) but including reversibility also for the reaction K in equilibrium with L in addition to L in equilibrium with M, M in equilibrium with N, and N in equilibrium with O. With increasing dehydration the kinetics were increasingly dominated by the reverse reactions. As before, fitting the data required the existence of two M species in series: L in equilibrium with M1 in equilibrium with M2 in equilibrium with N. The M1 in equilibrium with M2 reaction was greatly slowed at lower humidities. This step might be the switch for the unidirectional transfer of protons. With increasing dehydration recovery of BR occurred less and less via the N intermediate and increasingly via direct shunts from the two M species. As indicated earlier by electrical measurements with similarly dried bacteriorhodopsin films (Váró, G., and L. Keszthelyi, 1983. Biophys. J. 43:47-51). The latter are pathways not necessarily associated with net proton translocation.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ames J. B., Fodor S. P., Gebhard R., Raap J., van den Berg E. M., Lugtenburg J., Mathies R. A. Bacteriorhodopsin's M412 intermediate contains a 13-cis, 14-s-trans, 15-anti-retinal Schiff base chromophore. Biochemistry. 1989 May 2;28(9):3681–3687. doi: 10.1021/bi00435a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ames J. B., Mathies R. A. The role of back-reactions and proton uptake during the N----O transition in bacteriorhodopsin's photocycle: a kinetic resonance Raman study. Biochemistry. 1990 Aug 7;29(31):7181–7190. doi: 10.1021/bi00483a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becher B., Tokunaga F., Ebrey T. G. Ultraviolet and visible absorption spectra of the purple membrane protein and the photocycle intermediates. Biochemistry. 1978 Jun 13;17(12):2293–2300. doi: 10.1021/bi00605a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braiman M. S., Mogi T., Marti T., Stern L. J., Khorana H. G., Rothschild K. J. Vibrational spectroscopy of bacteriorhodopsin mutants: light-driven proton transport involves protonation changes of aspartic acid residues 85, 96, and 212. Biochemistry. 1988 Nov 15;27(23):8516–8520. doi: 10.1021/bi00423a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butt H. J., Fendler K., Bamberg E., Tittor J., Oesterhelt D. Aspartic acids 96 and 85 play a central role in the function of bacteriorhodopsin as a proton pump. EMBO J. 1989 Jun;8(6):1657–1663. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03556.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butt H. J., Fendler K., Dér A., Bamberg E. Temperature jump study of charge translocation during the bacteriorhodopsin photocycle. Biophys J. 1989 Nov;56(5):851–859. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(89)82731-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chernavskii D. S., Chizhov I. V., Lozier R. H., Murina T. M., Prokhorov A. M., Zubov B. V. Kinetic model of bacteriorhodopsin photocycle: pathway from M state to bR. Photochem Photobiol. 1989 May;49(5):649–653. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1989.tb08437.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fodor S. P., Ames J. B., Gebhard R., van den Berg E. M., Stoeckenius W., Lugtenburg J., Mathies R. A. Chromophore structure in bacteriorhodopsin's N intermediate: implications for the proton-pumping mechanism. Biochemistry. 1988 Sep 6;27(18):7097–7101. doi: 10.1021/bi00418a064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerwert K., Hess B., Soppa J., Oesterhelt D. Role of aspartate-96 in proton translocation by bacteriorhodopsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(13):4943–4947. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.13.4943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerwert K., Siebert F. Evidence for light-induced 13-cis, 14-s-cis isomerization in bacteriorhodopsin obtained by FTIR difference spectroscopy using isotopically labelled retinals. EMBO J. 1986 Apr;5(4):805–811. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04285.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofrichter J., Henry E. R., Lozier R. H. Photocycles of bacteriorhodopsin in light- and dark-adapted purple membrane studied by time-resolved absorption spectroscopy. Biophys J. 1989 Oct;56(4):693–706. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(89)82716-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holz M., Drachev L. A., Mogi T., Otto H., Kaulen A. D., Heyn M. P., Skulachev V. P., Khorana H. G. Replacement of aspartic acid-96 by asparagine in bacteriorhodopsin slows both the decay of the M intermediate and the associated proton movement. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2167–2171. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe J. S., Glaeser R. M. Difference Fourier analysis of "surface features" of bacteriorhodopsin using glucose-embedded and frozen-hydrated purple membrane. Ultramicroscopy. 1987;23(1):17–28. doi: 10.1016/0304-3991(87)90223-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khorana H. G. Bacteriorhodopsin, a membrane protein that uses light to translocate protons. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 5;263(16):7439–7442. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korenstein R., Hess B. Hydration effects on cis--trans isomerization of bacteriorhodopsin. FEBS Lett. 1977 Oct 1;82(1):7–11. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80874-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korenstein R., Hess B. Hydration effects on the photocycle of bacteriorhodopsin in thin layers of purple membrane. Nature. 1977 Nov 10;270(5633):184–186. doi: 10.1038/270184a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kouyama T., Nasuda-Kouyama A., Ikegami A., Mathew M. K., Stoeckenius W. Bacteriorhodopsin photoreaction: identification of a long-lived intermediate N (P,R350) at high pH and its M-like photoproduct. Biochemistry. 1988 Aug 9;27(16):5855–5863. doi: 10.1021/bi00416a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarev Y. A., Terpugov E. L. Effect of water on the structure of bacteriorhodopsin and photochemical processes in purple membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 May 9;590(3):324–338. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(80)90203-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lozier R. H., Bogomolni R. A., Stoeckenius W. Bacteriorhodopsin: a light-driven proton pump in Halobacterium Halobium. Biophys J. 1975 Sep;15(9):955–962. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(75)85875-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lozier R. H., Niederberger W., Bogomolni R. A., Hwang S., Stoeckenius W. Kinetics and stoichiometry of light-induced proton release and uptake from purple membrane fragments, Halobacterium halobium cell envelopes, and phospholipid vesicles containing oriented purple membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Sep 13;440(3):545–556. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(76)90041-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oesterhelt D., Stoeckenius W. Isolation of the cell membrane of Halobacterium halobium and its fractionation into red and purple membrane. Methods Enzymol. 1974;31:667–678. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)31072-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oesterhelt D., Tittor J. Two pumps, one principle: light-driven ion transport in halobacteria. Trends Biochem Sci. 1989 Feb;14(2):57–61. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(89)90044-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otto H., Marti T., Holz M., Mogi T., Lindau M., Khorana H. G., Heyn M. P. Aspartic acid-96 is the internal proton donor in the reprotonation of the Schiff base of bacteriorhodopsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(23):9228–9232. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.23.9228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otto H., Marti T., Holz M., Mogi T., Stern L. J., Engel F., Khorana H. G., Heyn M. P. Substitution of amino acids Asp-85, Asp-212, and Arg-82 in bacteriorhodopsin affects the proton release phase of the pump and the pK of the Schiff base. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(3):1018–1022. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.3.1018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogan P. K., Zaccai G. Hydration in purple membrane as a function of relative humidity. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jan 5;145(1):281–284. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90344-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. O., Courtin J., van den Berg E., Winkel C., Lugtenburg J., Herzfeld J., Griffin R. G. Solid-state 13C NMR of the retinal chromophore in photointermediates of bacteriorhodopsin: characterization of two forms of M. Biochemistry. 1989 Jan 10;28(1):237–243. doi: 10.1021/bi00427a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. O., Myers A. B., Pardoen J. A., Winkel C., Mulder P. P., Lugtenburg J., Mathies R. Determination of retinal Schiff base configuration in bacteriorhodopsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):2055–2059. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.2055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoeckenius W., Lozier R. H., Bogomolni R. A. Bacteriorhodopsin and the purple membrane of halobacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Mar 14;505(3-4):215–278. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(79)90006-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tavan P., Schulten K., Oesterhelt D. The effect of protonation and electrical interactions on the stereochemistry of retinal schiff bases. Biophys J. 1985 Mar;47(3):415–430. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(85)83933-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tittor J., Soell C., Oesterhelt D., Butt H. J., Bamberg E. A defective proton pump, point-mutated bacteriorhodopsin Asp96----Asn is fully reactivated by azide. EMBO J. 1989 Nov;8(11):3477–3482. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08512.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Váró G., Duschl A., Lanyi J. K. Interconversions of the M, N, and O intermediates in the bacteriorhodopsin photocycle. Biochemistry. 1990 Apr 17;29(15):3798–3804. doi: 10.1021/bi00467a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Váró G., Eisenstein L. Infrared studies of water induced conformational changes in bacteriorhodopsin. Eur Biophys J. 1987;14(3):163–168. doi: 10.1007/BF00253841. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Váró G., Keszthelyi L. Arrhenius parameters of the bacteriorhodopsin photocycle in dried oriented samples. Biophys J. 1985 Feb;47(2 Pt 1):243–246. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3495(85)83897-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Váró G., Keszthelyi L. Photoelectric signals from dried oriented purple membranes of Halobacterium halobium. Biophys J. 1983 Jul;43(1):47–51. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(83)84322-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Váró G., Lanyi J. K. Pathways of the rise and decay of the M photointermediate(s) of bacteriorhodopsin. Biochemistry. 1990 Mar 6;29(9):2241–2250. doi: 10.1021/bi00461a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Váró G., Lanyi J. K. Protonation and deprotonation of the M, N, and O intermediates during the bacteriorhodopsin photocycle. Biochemistry. 1990 Jul 24;29(29):6858–6865. doi: 10.1021/bi00481a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaccai G., Gilmore D. J. Areas of hydration in the purple membrane of Halobacterium halobium: a neutron diffraction study. J Mol Biol. 1979 Aug 5;132(2):181–191. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90390-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaccai G. Structure and hydration of purple membranes in different conditions. J Mol Biol. 1987 Apr 5;194(3):569–572. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90683-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimányi L., Keszthelyi L., Lanyi J. K. Transient spectroscopy of bacterial rhodopsins with an optical multichannel analyzer. 1. Comparison of the photocycles of bacteriorhodopsin and halorhodopsin. Biochemistry. 1989 Jun 13;28(12):5165–5172. doi: 10.1021/bi00438a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


