Abstract
A model of transducin activation is constructed from its partial reactions (formation of metarhodopsin II, association, and dissociation of the rhodopsin-transducin complex). The kinetic equations of the model are solved both numerically and, for small photoactivation, analytically. From data on the partial reactions in vitro, rate and activation energy profile of amplified transducin turnover are modeled and compared with measured light-scattering signals of transducin activation in intact retinal rods. The data leave one free parameter, the rate of association between transducin and rhodopsin. Best fit is achieved for an activation energy of 35 kJ/mol, indicating lateral membrane diffusion of the proteins as its main determinant. The absolute value of the association rate is discussed in terms of the success of collisions to form the catalytic complex. It is greater than 30% for the intact retina and 10 times lower after permeabilization with staphylococcus aureus alpha-toxin. Dissociation rates for micromolar guanosinetriphosphale (GTP) (Kohl, B., and K. P. Hofmann, 1987. Biophys. J. 52:271-277) must be extrapolated linearly up to the millimolar range to explain the rapid transducin turnover in situ. This is interpreted by an unstable rhodopsin-transducin-GTP transient state. At the time of maximal turnover after a flash, the rate of activation is determined as 30, 120, 800, 2,500, and 4,000 activated transducins per photoactivated rhodopsin and second at 5, 10, 20, 30, 37 degrees C, respectively.
Full text
PDF



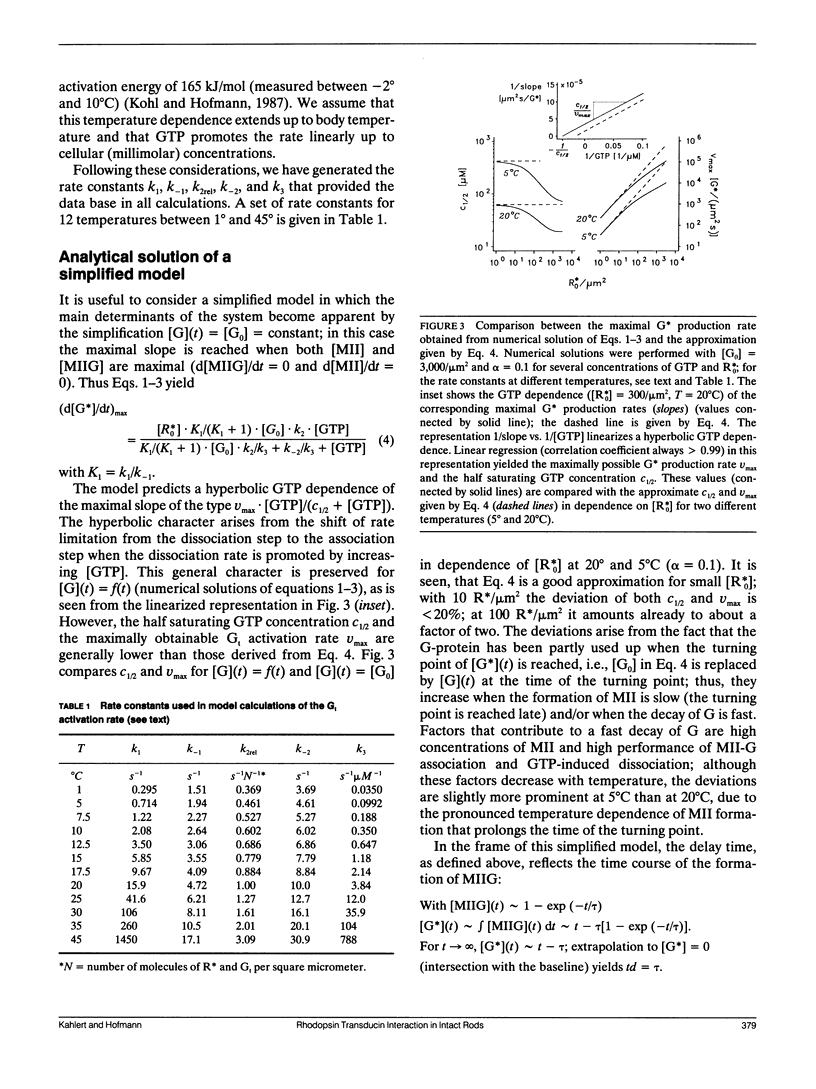

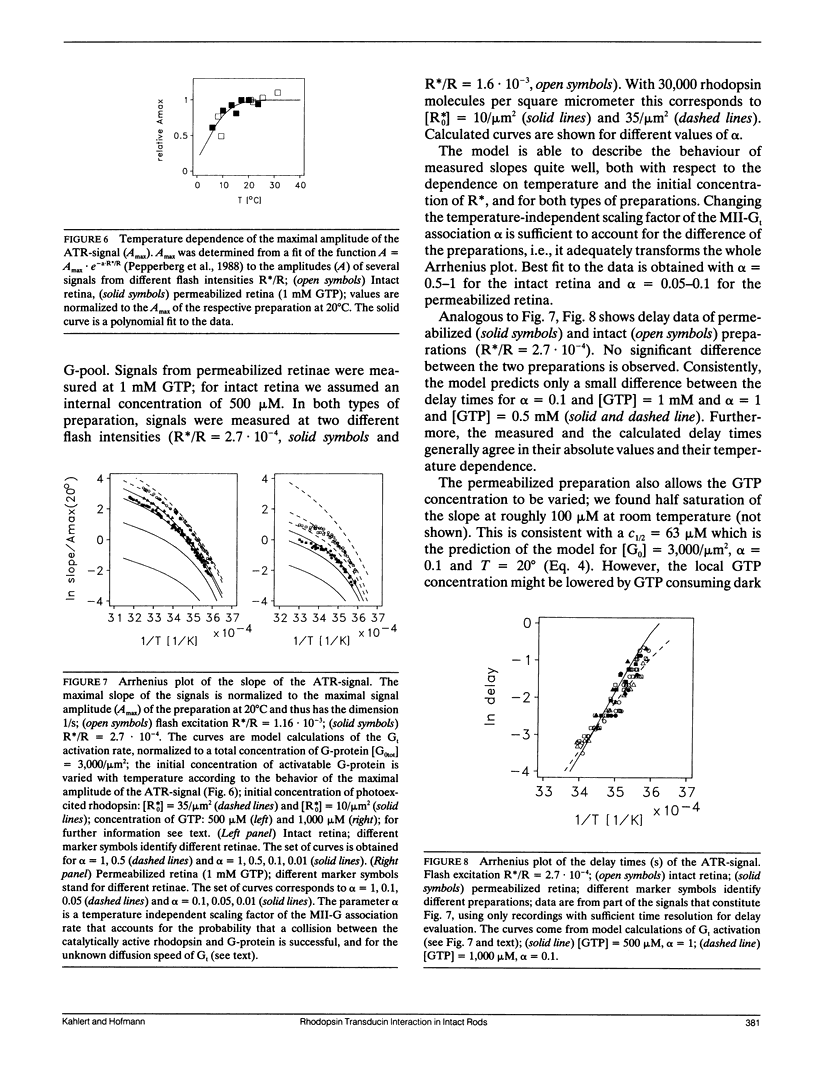





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Attwood P. V., Gutfreund H. The application of pressure relaxation to the study of the equilibrium between metarhodopsin I and II from bovine retinas. FEBS Lett. 1980 Oct 6;119(2):323–326. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80281-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baylor D. A., Lamb T. D., Yau K. W. Responses of retinal rods to single photons. J Physiol. 1979 Mar;288:613–634. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg H. C., Purcell E. M. Physics of chemoreception. Biophys J. 1977 Nov;20(2):193–219. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(77)85544-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruckert F., Vuong T. M., Chabre M. Light and GTP dependence of transducin solubility in retinal rods. Further analysis by near infra-red light scattering. Eur Biophys J. 1988;16(4):207–218. doi: 10.1007/BF00261263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caretta A., Stein P. J. cGMP- and phosphodiesterase-dependent light-scattering changes in rod disk membrane vesicles: relationship to disk vesicle-disk vesicle aggregation. Biochemistry. 1985 Sep 24;24(20):5685–5692. doi: 10.1021/bi00341a060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chabre M., Deterre P. Molecular mechanism of visual transduction. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Feb 1;179(2):255–266. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb14549.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chabre M. X-ray diffraction studies of retinal rods. I. Structure of the disc membrane, effect of illumination. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Mar 25;382(3):322–335. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(75)90274-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C. H., Takeuchi H., Ito T., Machida K., Ohnishi S. Lateral mobility of erythrocyte membrane proteins studied by the fluorescence photobleaching recovery technique. J Biochem. 1981 Oct;90(4):997–1004. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a133586. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cone R. A. Rotational diffusion of rhodopsin in the visual receptor membrane. Nat New Biol. 1972 Mar 15;236(63):39–43. doi: 10.1038/newbio236039a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawis S. M., Graeff R. M., Heyman R. A., Walseth T. F., Goldberg N. D. Regulation of cyclic GMP metabolism in toad photoreceptors. Definition of the metabolic events subserving photoexcited and attenuated states. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 25;263(18):8771–8785. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drzymala R. E., Weiner H. L., Dearry C. A., Liebman P. A. A barrier to lateral diffusion of porphyropsin in Necturus rod outer segment disks. Biophys J. 1984 Apr;45(4):683–692. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84210-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emeis D., Hofmann K. P. Shift in the relation between flash-induced metarhodopsin I and metarhodpsin II within the first 10% rhodopsin bleaching in bovine disc membranes. FEBS Lett. 1981 Dec 28;136(2):201–207. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80618-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emeis D., Kühn H., Reichert J., Hofmann K. P. Complex formation between metarhodopsin II and GTP-binding protein in bovine photoreceptor membranes leads to a shift of the photoproduct equilibrium. FEBS Lett. 1982 Jun 21;143(1):29–34. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80266-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Füssle R., Bhakdi S., Sziegoleit A., Tranum-Jensen J., Kranz T., Wellensiek H. J. On the mechanism of membrane damage by Staphylococcus aureus alpha-toxin. J Cell Biol. 1981 Oct;91(1):83–94. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.1.83. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. G proteins: transducers of receptor-generated signals. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:615–649. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamm H. E., Deretic D., Arendt A., Hargrave P. A., Koenig B., Hofmann K. P. Site of G protein binding to rhodopsin mapped with synthetic peptides from the alpha subunit. Science. 1988 Aug 12;241(4867):832–835. doi: 10.1126/science.3136547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann W., Siebert F., Hofmann K. P., Kreutz W. Two distinct rhodopsin molecules within the disc membrane of vertebrate rod outer segments. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Sep 7;503(3):450–461. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(78)90144-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann K. P., Uhl R., Hoffmann W., Kreutz W. Measurements on fast light-induced light-scattering and -absorption changes in outer segments of vertebrate light sensitive rod cells. Biophys Struct Mech. 1976 Apr 15;2(1):61–77. doi: 10.1007/BF00535653. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahlert M., König B., Hofmann K. P. Displacement of rhodopsin by GDP from three-loop interaction with transducin depends critically on the diphosphate beta-position. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 5;265(31):18928–18932. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamps K. M., Reichert J., Hofmann K. P. Light-induced activation of the rod phosphodiesterase leads to a rapid transient increase of near-infrared light scattering. FEBS Lett. 1985 Aug 19;188(1):15–20. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80866-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohl B., Hofmann K. P. Temperature dependence of G-protein activation in photoreceptor membranes. Transient extra metarhodopsin II on bovine disk membranes. Biophys J. 1987 Aug;52(2):271–277. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(87)83214-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- König B., Arendt A., McDowell J. H., Kahlert M., Hargrave P. A., Hofmann K. P. Three cytoplasmic loops of rhodopsin interact with transducin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(18):6878–6882. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.18.6878. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kühn H., Bennett N., Michel-Villaz M., Chabre M. Interactions between photoexcited rhodopsin and GTP-binding protein: kinetic and stoichiometric analyses from light-scattering changes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):6873–6877. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.6873. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb T. D. Sources of noise in photoreceptor transduction. J Opt Soc Am A. 1987 Dec;4(12):2295–2300. doi: 10.1364/josaa.4.002295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis J. W., Miller J. L., Mendel-Hartvig J., Schaechter L. E., Kliger D. S., Dratz E. A. Sensitive light scattering probe of enzymatic processes in retinal rod photoreceptor membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(3):743–747. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.3.743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liebman P. A., Entine G. Lateral diffusion of visual pigment in photorecptor disk membranes. Science. 1974 Aug 2;185(4149):457–459. doi: 10.1126/science.185.4149.457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liebman P. A., Parker K. R., Dratz E. A. The molecular mechanism of visual excitation and its relation to the structure and composition of the rod outer segment. Annu Rev Physiol. 1987;49:765–791. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.49.030187.004001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liebman P. A., Pugh E. N., Jr Gain, speed and sensitivity of GTP binding vs PDE activation in visual excitation. Vision Res. 1982;22(12):1475–1480. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(82)90212-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkes J. H., Liebman P. A. Temperature and pH dependence of the metarhodopsin I-metarhodopsin II kinetics and equilibria in bovine rod disk membrane suspensions. Biochemistry. 1984 Oct 9;23(21):5054–5061. doi: 10.1021/bi00316a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepperberg D. R., Kahlert M., Krause A., Hofmann K. P. Photic modulation of a highly sensitive, near-infrared light-scattering signal recorded from intact retinal photoreceptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(15):5531–5535. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.15.5531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters R., Cherry R. J. Lateral and rotational diffusion of bacteriorhodopsin in lipid bilayers: experimental test of the Saffman-Delbrück equations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(14):4317–4321. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.14.4317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poo M., Cone R. A. Lateral diffusion of rhodopsin in the photoreceptor membrane. Nature. 1974 Feb 15;247(5441):438–441. doi: 10.1038/247438a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saxton M. J., Owicki J. C. Concentration effects on reactions in membranes: rhodopsin and transducin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Feb 13;979(1):27–34. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(89)90519-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schleicher A., Franke R., Hofmann K. P., Finkelmann H., Welte W. Deoxylysolecithin and a new biphenyl detergent as solubilizing agents for bovine rhodopsin. Functional test by formation of metarhodopsin II and binding of G-protein. Biochemistry. 1987 Sep 8;26(18):5908–5916. doi: 10.1021/bi00392a050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stryer L. Cyclic GMP cascade of vision. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1986;9:87–119. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.09.030186.000511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaz W. L., Criado M., Madeira V. M., Schoellmann G., Jovin T. M. Size dependence of the translational diffusion of large integral membrane proteins in liquid-crystalline phase lipid bilayers. A study using fluorescence recovery after photobleaching. Biochemistry. 1982 Oct 26;21(22):5608–5612. doi: 10.1021/bi00265a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vuong T. M., Chabre M., Stryer L. Millisecond activation of transducin in the cyclic nucleotide cascade of vision. Nature. 1984 Oct 18;311(5987):659–661. doi: 10.1038/311659a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


