Abstract
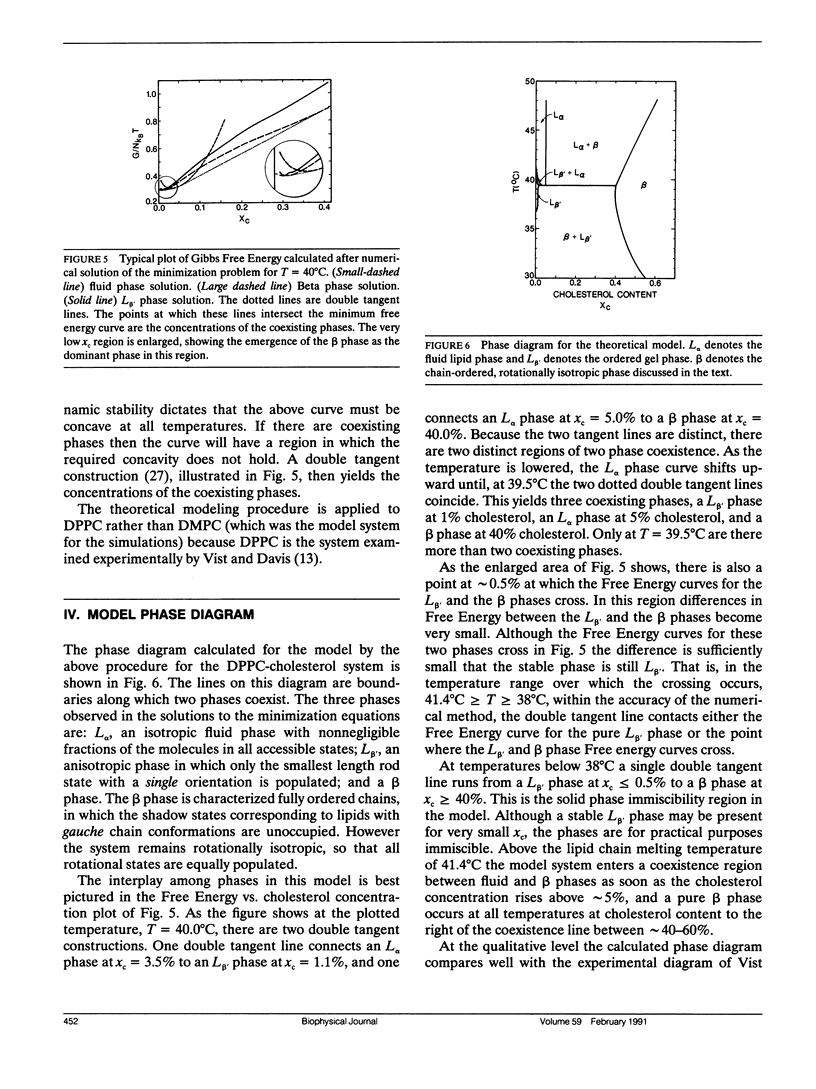
Results of Monte Carlo calculations of order parameter profiles of lipid chains interacting with cholesterol are presented. Cholesterol concentrations in the simulations are sufficiently large that it is possible to analyze profiles for chains which are near neighbors of two or more cholesterol molecules, chains which are neighbors to a single cholesterol, and chains which are not near any cholesterol molecules. The profiles, show that cholesterol acts to significantly decrease the ability of neighboring chains to undergo trans-gauche isomeric rotations, although these chains are not all forced into all-trans conformations. The effect is significantly greater for chains which are neighbors to more than one cholesterol. The Monte Carlo results are next used as a guide to develop a theoretical model for lipid-cholesterol mixtures. The properties of this model and the phase diagram which it predicts are described. The phase diagram is then compared with experimentally determined phase diagrams. The model calculations and the computer simulations upon which they are based yield a molecular mechanism for several of the observed phases exhibited by lipid-cholesterol mixtures. The theoretical model predicts that at low temperatures the system should exhibit solid phase immiscibility.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Delmelle M., Butler K. W., Smith I. C. Saturation transfer electron spin resonance spectroscopy as a probe of anisotropic motion in model membrane systems. Biochemistry. 1980 Feb 19;19(4):698–704. doi: 10.1021/bi00545a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demel R. A., Bruckdorfer K. R., van Deenen L. L. Structural requirements of sterols for the interaction with lecithin at the air water interface. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jan 17;255(1):311–320. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(72)90030-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estep T. N., Mountcastle D. B., Biltonen R. L., Thompson T. E. Studies on the anomalous thermotropic behavior of aqueous dispersions of dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine-cholesterol mixtures. Biochemistry. 1978 May 16;17(10):1984–1989. doi: 10.1021/bi00603a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein RE, Leibler S. Model for lamellar phases of interacting lipid membranes. Phys Rev Lett. 1988 Nov 7;61(19):2213–2216. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.61.2213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ipsen J. H., Karlström G., Mouritsen O. G., Wennerström H., Zuckermann M. J. Phase equilibria in the phosphatidylcholine-cholesterol system. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Nov 27;905(1):162–172. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(87)90020-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs R., Oldfield E. Deuterium nuclear magnetic resonance investigation of dimyristoyllecithin--dipalmitoyllecithin and dimyristoyllecithin--cholesterol mixtures. Biochemistry. 1979 Jul 24;18(15):3280–3285. doi: 10.1021/bi00582a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lentz B. R., Barrow D. A., Hoechli M. Cholesterol-phosphatidylcholine interactions in multilamellar vesicles. Biochemistry. 1980 Apr 29;19(9):1943–1954. doi: 10.1021/bi00550a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mabrey S., Sturtevant J. M. Investigation of phase transitions of lipids and lipid mixtures by sensitivity differential scanning calorimetry. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Nov;73(11):3862–3866. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.11.3862. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCullough WS, Scott HL. Statistical-Mechanical Theory of the Ripple Phase of Lipid Bilayers. Phys Rev Lett. 1990 Aug 13;65(7):931–934. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.65.931. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mortensen K., Pfeiffer W., Sackmann E., Knoll W. Structural properties of a phosphatidylcholine-cholesterol system as studied by small-angle neutron scattering: ripple structure and phase diagram. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Nov 22;945(2):221–245. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(88)90485-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peng Z. Y., Tjandra N., Simplaceanu V., Ho C. Slow motions in oriented phospholipid bilayers and effects of cholesterol or gramicidin. A 19F-NMR T1 rho study. Biophys J. 1989 Nov;56(5):877–885. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(89)82734-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Recktenwald D. J., McConnell H. M. Phase equilibria in binary mixtures of phosphatidylcholine and cholesterol. Biochemistry. 1981 Jul 21;20(15):4505–4510. doi: 10.1021/bi00518a042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman J. E., Engelman D. M. Molecular mechanism for the interaction of phospholipid with cholesterol. Nat New Biol. 1972 May 10;237(71):42–44. doi: 10.1038/newbio237042a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott H. L., Cheng W. H. A theoretical model for lipid mixtures, phase transitions, and phase diagrams. Biophys J. 1979 Oct;28(1):117–132. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(79)85163-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott H. L., Jr Phase transitions in lipid bilayers. A theoretical model for phosphatidylethanolamine and phosphatidic acid bilayers. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Nov 6;648(2):129–136. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(81)90027-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott H. L., Jr Phosphatidylcholine bilayers. A theoretical model which describes the main and the lower transitions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Apr 22;643(1):161–167. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(81)90228-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott H. L., Kalaskar S. Lipid chains and cholesterol in model membranes: a Monte Carlo Study. Biochemistry. 1989 May 2;28(9):3687–3691. doi: 10.1021/bi00435a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott H. L., Pearce P. A. Calculation of intermolecular interaction strengths in the P beta' phase in lipid bilayers. Implications for theoretical models. Biophys J. 1989 Feb;55(2):339–345. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(89)82810-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vist M. R., Davis J. H. Phase equilibria of cholesterol/dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine mixtures: 2H nuclear magnetic resonance and differential scanning calorimetry. Biochemistry. 1990 Jan 16;29(2):451–464. doi: 10.1021/bi00454a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]