Abstract
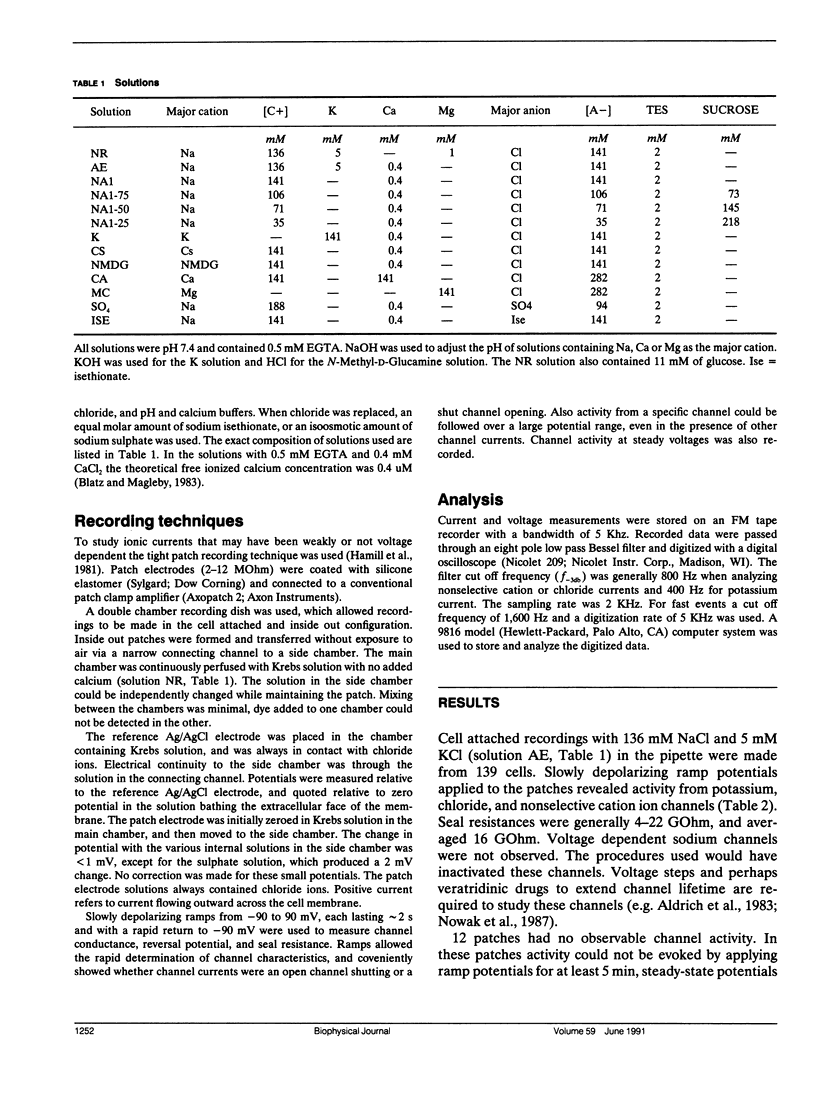
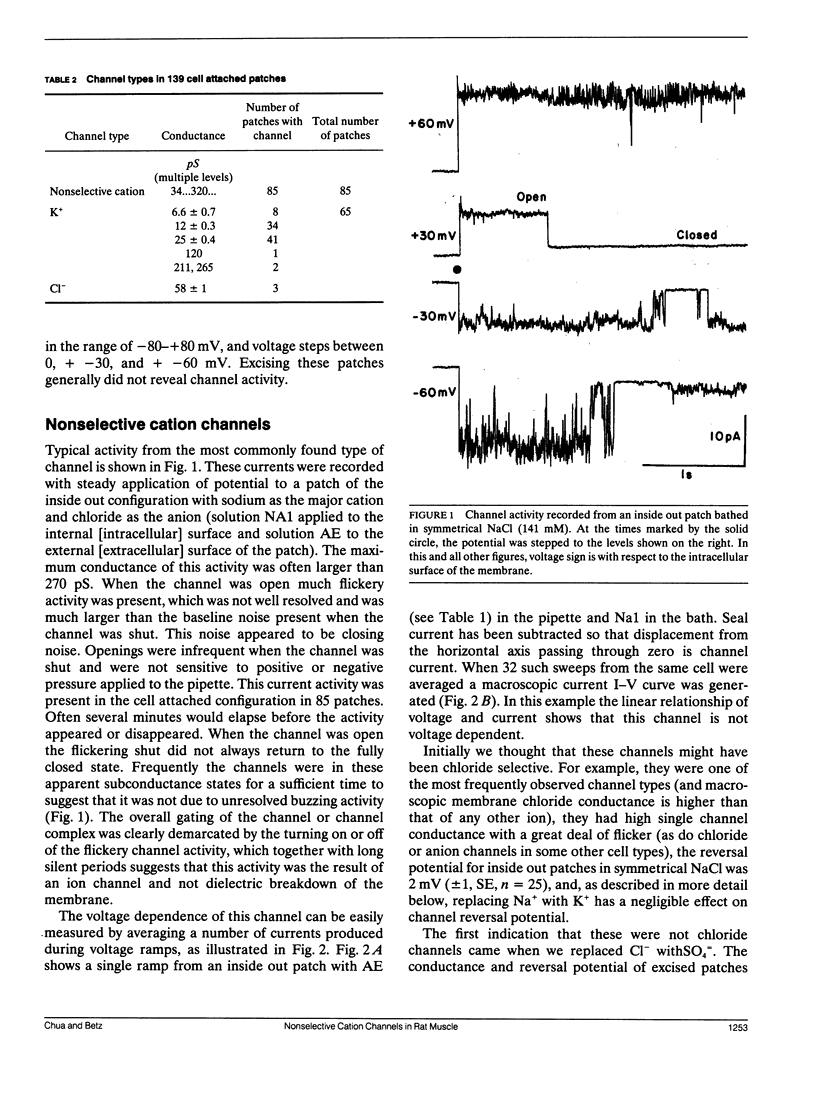
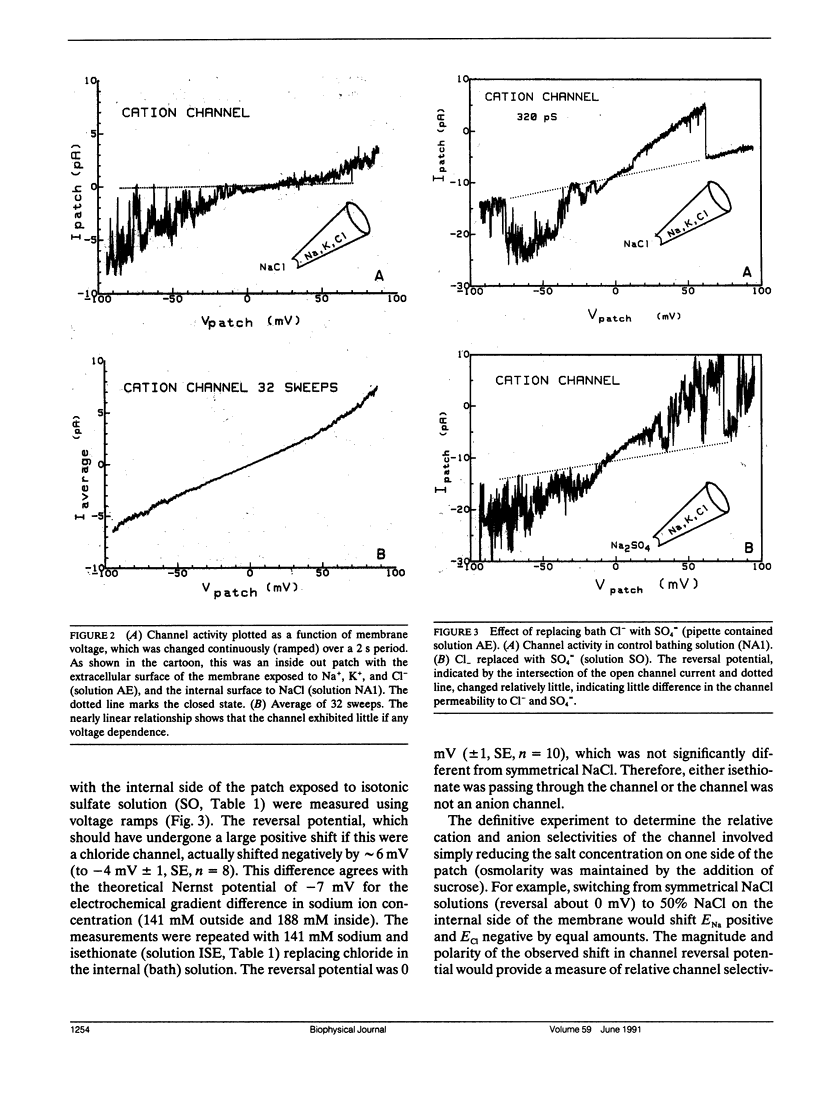
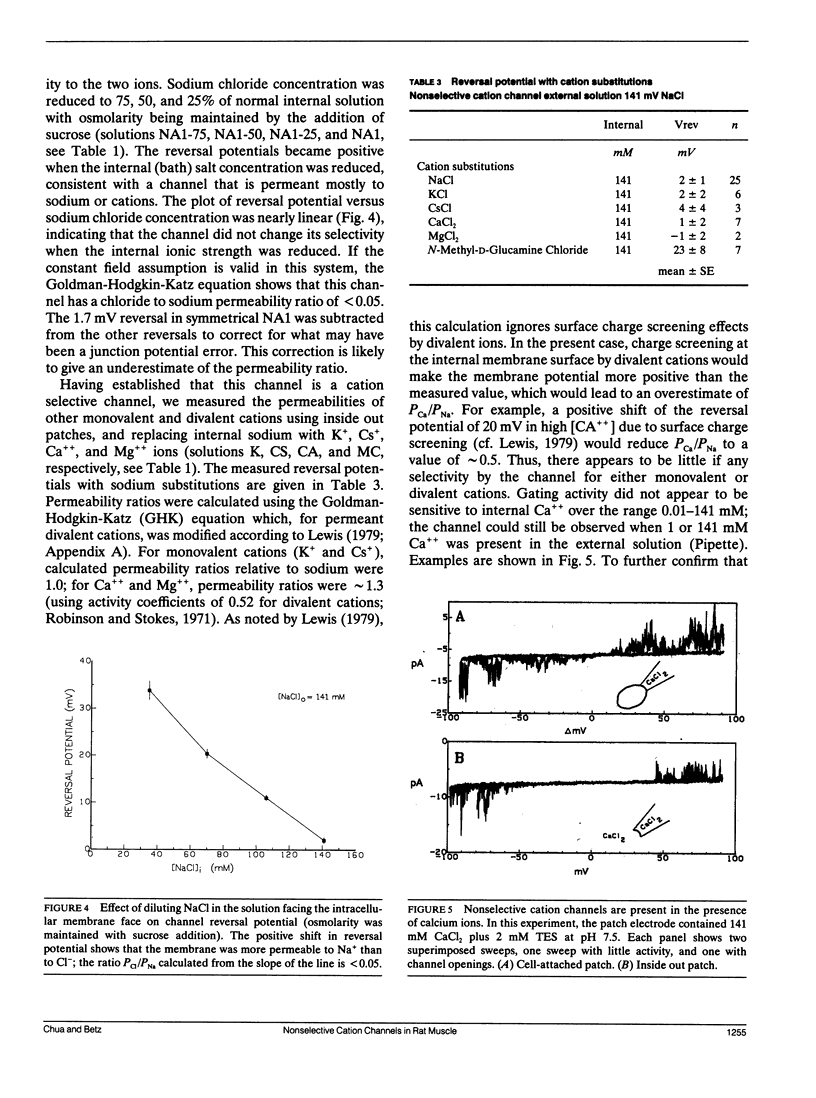
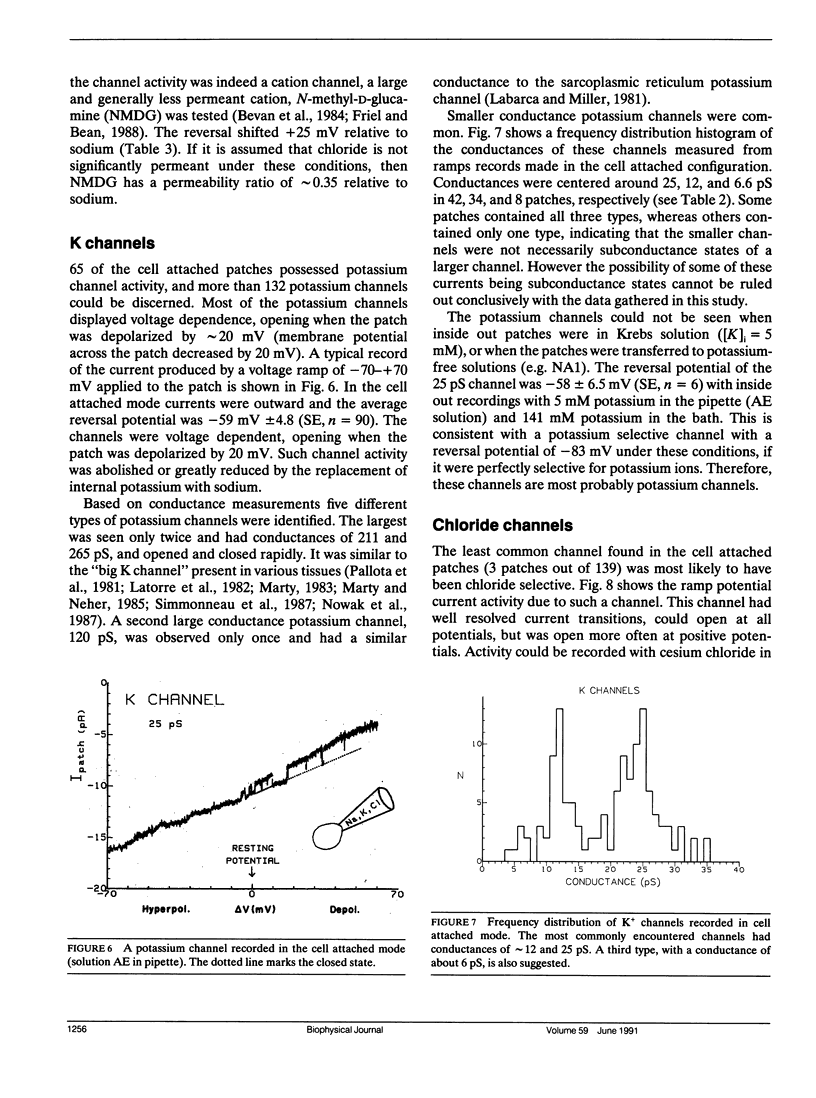
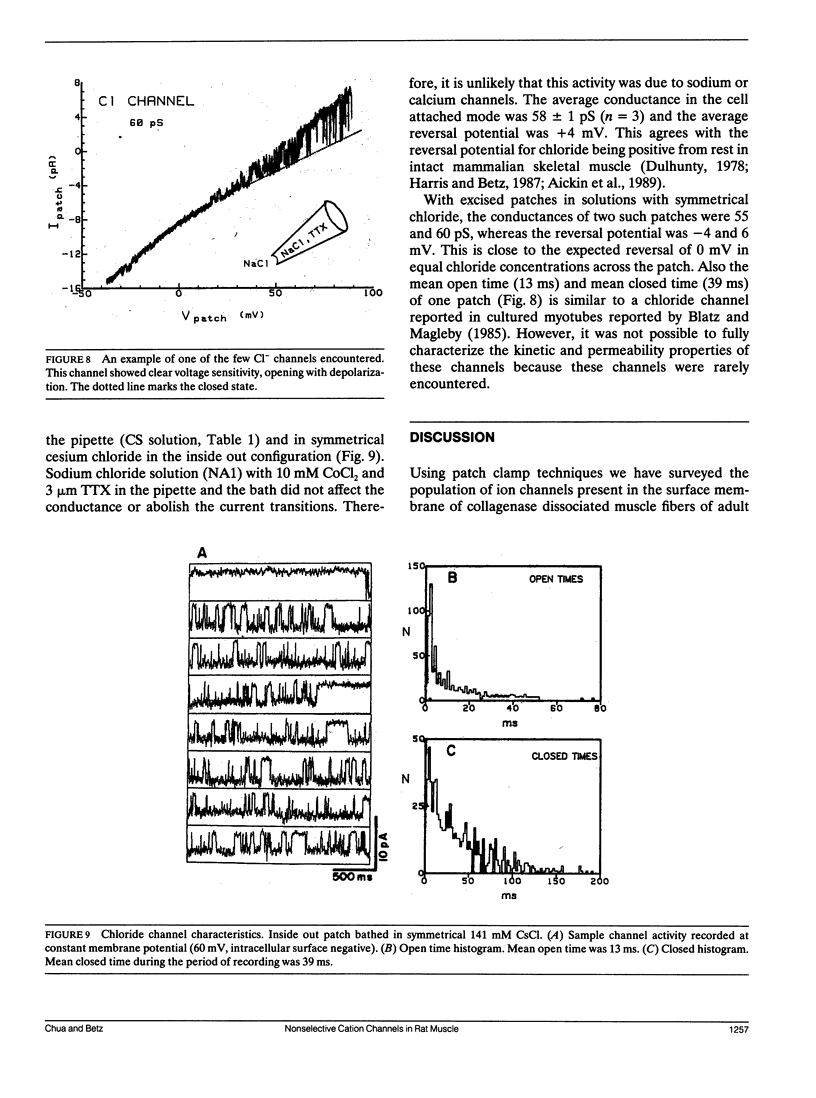
The channels present on the surface membrane of isolated rat flexor digitorum brevis muscle fibers were surveyed using the patch clamp technique. 85 out of 139 fibers had a novel channel which excluded the anions chloride, sulfate, and isethionate with a permeability ratio of chloride to sodium of less than 0.05. The selectivity sequence for cations was Na+ = K+ = Cs+ greater than Ca++ = Mg++ greater than N-Methyl-D-Glucamine. The channel remained closed for long periods, and had a large conductance of approximately 320 pS with several subconductance states at approximately 34 pS levels. Channel activity was not voltage dependent and the reversal potential for cations in muscle fibers of approximately 0 mV results in the channel's behaving as a physiological leakage conductance. Voltage activated potassium channels were present in 65 of the cell attached patches and had conductances of mostly 6, 12, and 25 pS. The voltage sensitivity of the potassium channels was consistent with that of the delayed rectifier current. Only three patches contained chloride channels. The scarcity of chloride channels despite the known high chloride conductance of skeletal muscle suggests that most of the chloride channels must be located in the transverse tubular system.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adrian R. H., Freygang W. H. The potassium and chloride conductance of frog muscle membrane. J Physiol. 1962 Aug;163(1):61–103. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1962.sp006959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aickin C. C., Betz W. J., Harris G. L. Intracellular chloride and the mechanism for its accumulation in rat lumbrical muscle. J Physiol. 1989 Apr;411:437–455. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017582. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aldrich R. W., Corey D. P., Stevens C. F. A reinterpretation of mammalian sodium channel gating based on single channel recording. Nature. 1983 Dec 1;306(5942):436–441. doi: 10.1038/306436a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Almers W., McCleskey E. W., Palade P. T. A non-selective cation conductance in frog muscle membrane blocked by micromolar external calcium ions. J Physiol. 1984 Aug;353:565–583. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bekoff A., Betz W. J. Physiological properties of dissociated muscle fibres obtained from innervated and denervated adult rat muscle. J Physiol. 1977 Sep;271(1):25–40. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bevan S., Gray P. T., Ritchie J. M. A calcium-activated cation-selective channel in rat cultured Schwann cells. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1984 Sep 22;222(1228):349–355. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1984.0068. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blatz A. L., Magleby K. L. Single chloride-selective channels active at resting membrane potentials in cultured rat skeletal muscle. Biophys J. 1985 Jan;47(1):119–123. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(85)83884-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blatz A. L., Magleby K. L. Single voltage-dependent chloride-selective channels of large conductance in cultured rat muscle. Biophys J. 1983 Aug;43(2):237–241. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(83)84344-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton T. B., Vaughan-Jones R. D. Continuous direct measurement of intracellular chloride and pH in frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1977 Sep;270(3):801–833. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colquhoun D., Neher E., Reuter H., Stevens C. F. Inward current channels activated by intracellular Ca in cultured cardiac cells. Nature. 1981 Dec 24;294(5843):752–754. doi: 10.1038/294752a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dulhunty A. F. Distribution of potassium and chloride permeability over the surface and T-tubule membranes of mammalian skeletal muscle. J Membr Biol. 1979 Apr 9;45(3-4):293–310. doi: 10.1007/BF01869290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dulhunty A. F. The dependence of membrane potential on extracellular chloride concentration in mammalian skeletal muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1978 Mar;276:67–82. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dulhunty A. Effect of chloride withdrawal on the geometry of the T-tubules in amphibian and mammalian muscle. J Membr Biol. 1982;67(2):81–90. doi: 10.1007/BF01868650. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erxleben C. Stretch-activated current through single ion channels in the abdominal stretch receptor organ of the crayfish. J Gen Physiol. 1989 Dec;94(6):1071–1083. doi: 10.1085/jgp.94.6.1071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friel D. D., Bean B. P. Two ATP-activated conductances in bullfrog atrial cells. J Gen Physiol. 1988 Jan;91(1):1–27. doi: 10.1085/jgp.91.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guharay F., Sachs F. Stretch-activated single ion channel currents in tissue-cultured embryonic chick skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1984 Jul;352:685–701. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HOROWICZ P. The influence of potassium and chloride ions on the membrane potential of single muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1959 Oct;148:127–160. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006278. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUTTER O. F., NOBLE D. The chloride conductance of frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1960 Apr;151:89–102. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Sakmann B. Multiple conductance states of single acetylcholine receptor channels in embryonic muscle cells. Nature. 1981 Dec 3;294(5840):462–464. doi: 10.1038/294462a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris G. L., Betz W. J. Evidence for active chloride accumulation in normal and denervated rat lumbrical muscle. J Gen Physiol. 1987 Jul;90(1):127–144. doi: 10.1085/jgp.90.1.127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horn R., Patlak J. Single channel currents from excised patches of muscle membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6930–6934. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutter O. F., Warner A. E. The voltage dependence of the chloride conductance of frog muscle. J Physiol. 1972 Dec;227(1):275–290. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp010032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krouse M. E., Schneider G. T., Gage P. W. A large anion-selective channel has seven conductance levels. Nature. 1986 Jan 2;319(6048):58–60. doi: 10.1038/319058a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labarca P. P., Miller C. A K+-selective, three-state channel from fragmented sarcoplasmic reticulum of frog leg muscle. J Membr Biol. 1981;61(1):31–38. doi: 10.1007/BF01870750. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latorre R., Coronado R., Vergara C. K+ channels gated by voltage and ions. Annu Rev Physiol. 1984;46:485–495. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.46.030184.002413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latorre R., Vergara C., Hidalgo C. Reconstitution in planar lipid bilayers of a Ca2+-dependent K+ channel from transverse tubule membranes isolated from rabbit skeletal muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(3):805–809. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.3.805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis C. A. Ion-concentration dependence of the reversal potential and the single channel conductance of ion channels at the frog neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1979 Jan;286:417–445. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipton S. A. Antibody activates cationic channels via second messenger Ca2+. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Mar 27;856(1):59–67. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(86)90010-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marty A., Neher E. Potassium channels in cultured bovine adrenal chromaffin cells. J Physiol. 1985 Oct;367:117–141. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama Y., Peterson O. H. Single-channel currents in isolated patches of plasma membrane from basal surface of pancreatic acini. Nature. 1982 Sep 9;299(5879):159–161. doi: 10.1038/299159a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowak L., Ascher P., Berwald-Netter Y. Ionic channels in mouse astrocytes in culture. J Neurosci. 1987 Jan;7(1):101–109. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-01-00101.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palade P. T., Barchi R. L. Characteristics of the chloride conductance in muscle fibers of the rat diaphragm. J Gen Physiol. 1977 Mar;69(3):325–342. doi: 10.1085/jgp.69.3.325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pallotta B. S., Magleby K. L., Barrett J. N. Single channel recordings of Ca2+-activated K+ currents in rat muscle cell culture. Nature. 1981 Oct 8;293(5832):471–474. doi: 10.1038/293471a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Partridge L. D., Swandulla D. Single Ca-activated cation channels in bursting neurons of Helix. Pflugers Arch. 1987 Dec;410(6):627–631. doi: 10.1007/BF00581323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prod'hom B., Pietrobon D., Hess P. Direct measurement of proton transfer rates to a group controlling the dihydropyridine-sensitive Ca2+ channel. Nature. 1987 Sep 17;329(6136):243–246. doi: 10.1038/329243a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quandt F. N., MacVicar B. A. Calcium activated potassium channels in cultured astrocytes. Neuroscience. 1986 Sep;19(1):29–41. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(86)90003-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz W., Passow H. Ca2+-activated K+ channels in erythrocytes and excitable cells. Annu Rev Physiol. 1983;45:359–374. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.45.030183.002043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigworth F. J. Open channel noise. I. Noise in acetylcholine receptor currents suggests conformational fluctuations. Biophys J. 1985 May;47(5):709–720. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(85)83968-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonneau M., Distasi C., Tauc L., Barbin G. Potassium channels in mouse neonate dorsal root ganglion cells: a patch-clamp study. Brain Res. 1987 Jun 2;412(2):224–232. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(87)91128-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swandulla D., Lux H. D. Activation of a nonspecific cation conductance by intracellular Ca2+ elevation in bursting pacemaker neurons of Helix pomatia. J Neurophysiol. 1985 Dec;54(6):1430–1443. doi: 10.1152/jn.1985.54.6.1430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yellen G. Single Ca2+-activated nonselective cation channels in neuroblastoma. Nature. 1982 Mar 25;296(5855):357–359. doi: 10.1038/296357a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


