Abstract
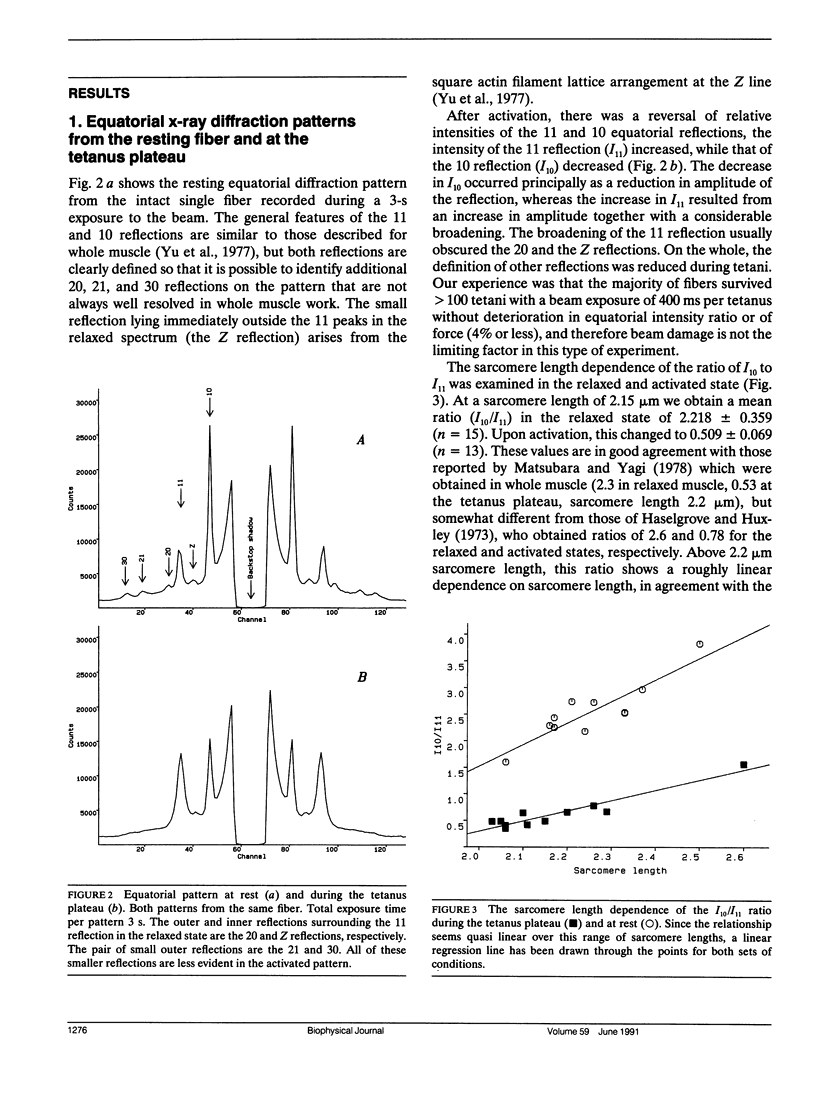
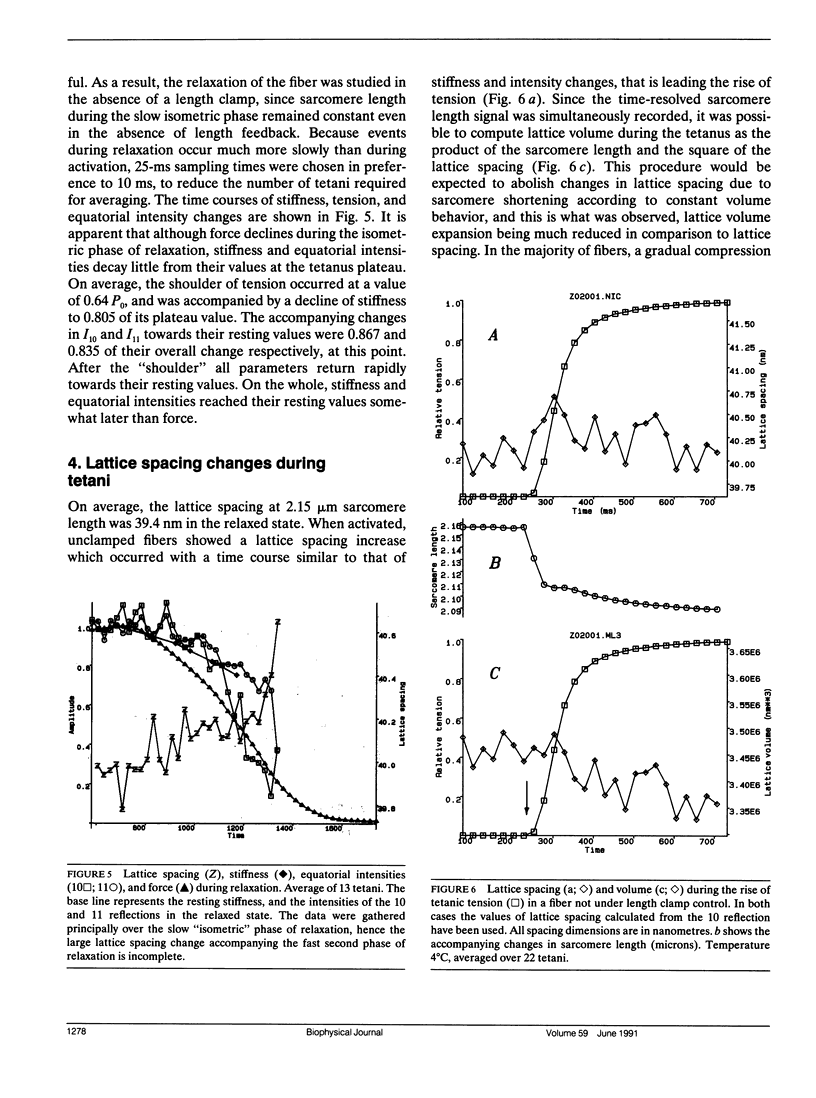
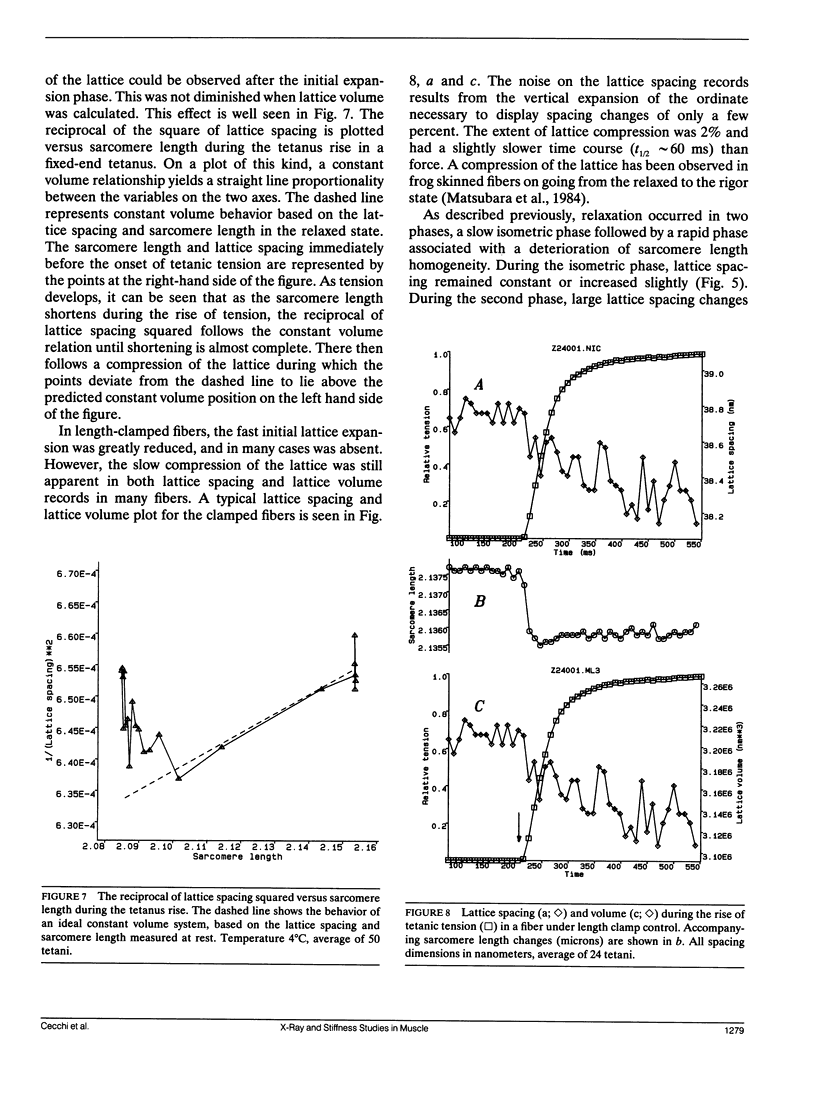
We report the first time-resolved x-ray diffraction studies on tetanized intact single muscle fibers of the frog. The 10, 11, 20, 21, 30, and Z equatorial reflections were clearly resolved in the relaxed fiber. The preparation readily withstood 100 1-s duration (0.4-s beam exposure) tetani at 4 degrees C (less than 4% decline of force and no deterioration in the 10, 11 equatorial intensity ratio at rest or during activation). Equatorial intensity changes (10 and 11) and fiber stiffness led tension (t1/2 lead 20 ms at 4 degrees C) during the tetanus rise and lagged during the isometric phase of relaxation. These findings support the existence of a low force cross-bridge state during the rise of tetanic tension and isometric relaxation that is not evident at the tetanus plateau. In "fixed end" tetani lattice expansion occurred with a time course similar to stiffness during the tetanus rise. During relaxation, lattice spacing increased slightly, while the sarcomere length remained isometric, but underwent large changes after the "shoulder" of tension. Under length clamp control, lattice expansion during the tetanus rise was reduced or abolished, and compression (2%) of the lattice was observed. A lattice compression is predicted by certain cross-bridge models of force generation (Schoenberg, M. 1980. Biophys. J. 30:51-68; Schoenberg, M. 1980. Biophys. J. 30:69-78).
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ADRIAN R. H. The effect of internal and external potassium concentration on the membrane potential of frog muscle. J Physiol. 1956 Sep 27;133(3):631–658. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagni M. A., Cecchi G., Schoenberg M. A model of force production that explains the lag between crossbridge attachment and force after electrical stimulation of striated muscle fibers. Biophys J. 1988 Dec;54(6):1105–1114. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(88)83046-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannell M. B. Effect of tetanus duration on the free calcium during the relaxation of frog skeletal muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1986 Jul;376:203–218. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cecchi G., Colomo F., Lombardi V. A loudspeaker servo system for determination of mechanical characteristics of isolated muscle fibres. Boll Soc Ital Biol Sper. 1976 May 30;52(10):733–736. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cecchi G., Colomo F., Lombardi V., Piazzesi G. Stiffness of frog muscle fibres during rise of tension and relaxation in fixed-end or length-clamped tetani. Pflugers Arch. 1987 Jun;409(1-2):39–46. doi: 10.1007/BF00584747. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cecchi G., Griffiths P. J., Taylor S. Muscular contraction: kinetics of crossbridge attachment studied by high-frequency stiffness measurements. Science. 1982 Jul 2;217(4554):70–72. doi: 10.1126/science.6979780. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cecchi G., Griffiths P. J., Taylor S. Stiffness and force in activated frog skeletal muscle fibers. Biophys J. 1986 Feb;49(2):437–451. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(86)83653-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chalovich J. M., Eisenberg E. The effect of troponin-tropomyosin on the binding of heavy meromyosin to actin in the presence of ATP. J Biol Chem. 1986 Apr 15;261(11):5088–5093. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- El-Saleh S. C., Thieret R., Johnson P., Potter J. D. Modification of Lys-237 on actin by 2,4-pentanedione. Alteration of the interaction of actin with tropomyosin. J Biol Chem. 1984 Sep 10;259(17):11014–11021. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford L. E., Huxley A. F., Simmons R. M. Tension responses to sudden length change in stimulated frog muscle fibres near slack length. J Physiol. 1977 Jul;269(2):441–515. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011911. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford L. E., Huxley A. F., Simmons R. M. Tension transients during the rise of tetanic tension in frog muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1986 Mar;372:595–609. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths P. J., Duchateau J. J., Maeda Y., Potter J. D., Ashley C. C. Mechanical characteristics of skinned and intact muscle fibres from the giant barnacle, Balanus nubilus. Pflugers Arch. 1990 Feb;415(5):554–565. doi: 10.1007/BF02583506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUXLEY A. F. Muscle structure and theories of contraction. Prog Biophys Biophys Chem. 1957;7:255–318. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUXLEY A. F., NIEDERGERKE R. Structural changes in muscle during contraction; interference microscopy of living muscle fibres. Nature. 1954 May 22;173(4412):971–973. doi: 10.1038/173971a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUXLEY H., HANSON J. Changes in the cross-striations of muscle during contraction and stretch and their structural interpretation. Nature. 1954 May 22;173(4412):973–976. doi: 10.1038/173973a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haselgrove J. C., Huxley H. E. X-ray evidence for radial cross-bridge movement and for the sliding filament model in actively contracting skeletal muscle. J Mol Biol. 1973 Jul 15;77(4):549–568. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90222-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haselgrove J. C. X-ray evidence for conformational changes in the myosin filaments of vertebrate striated muscle. J Mol Biol. 1975 Feb 15;92(1):113–143. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90094-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huxley A. F., Simmons R. M. Proposed mechanism of force generation in striated muscle. Nature. 1971 Oct 22;233(5321):533–538. doi: 10.1038/233533a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kress M., Huxley H. E., Faruqi A. R., Hendrix J. Structural changes during activation of frog muscle studied by time-resolved X-ray diffraction. J Mol Biol. 1986 Apr 5;188(3):325–342. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90158-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsubara I., Goldman Y. E., Simmons R. M. Changes in the lateral filament spacing of skinned muscle fibres when cross-bridges attach. J Mol Biol. 1984 Feb 15;173(1):15–33. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90401-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsubara I., Yagi N. A time-resolved X-ray diffraction study of muscle during twitch. J Physiol. 1978 May;278:297–307. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maéda Y., Boulin C., Gabriel A., Sumner I., Koch M. H. Intensity increases of actin layer-lines on activation of the Limulus muscle. Biophys J. 1986 Dec;50(6):1035–1042. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(86)83547-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoenberg M. Characterization of the myosin adenosine triphosphate (M.ATP) crossbridge in rabbit and frog skeletal muscle fibers. Biophys J. 1988 Jul;54(1):135–148. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(88)82938-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoenberg M. Geometrical factors influencing muscle force development. I. The effect of filament spacing upon axial forces. Biophys J. 1980 Apr;30(1):51–67. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(80)85076-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoenberg M. Geometrical factors influencing muscle force development. II. Radial forces. Biophys J. 1980 Apr;30(1):69–77. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(80)85077-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner P. D., Stone D. B. Calcium-sensitive binding of heavy meromyosin to regulated actin requires light chain 2 and the head-tail junction. Biochemistry. 1983 Mar 15;22(6):1334–1342. doi: 10.1021/bi00275a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu S. G., Kress M., Huxley H. E. X-ray diffraction studies of the structural state of crossbridges in skinned frog sartorius muscle at low ionic strength. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1987 Feb;8(1):39–54. doi: 10.1007/BF01767263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu L. C., Lymn R. W., Podolsky R. J. Characterization of a non-indexible equatorial x-ray reflection from frog sartorius muscle. J Mol Biol. 1977 Sep 25;115(3):455–464. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90165-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


