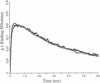
Abstract
A Monte Carlo method for modeling the neuromuscular junction is described in which the three-dimensional structure of the synapse can be specified. Complexities can be introduced into the acetylcholine kinetic model used with only a small increase in computing time. The Monte Carlo technique is shown to be superior to differential equation modeling methods (although less accurate) if a three-dimensional representation of synaptic geometry is desired. The conceptual development of the model is presented and the accuracy estimated. The consequences of manipulations such as varying the spacing of secondary synaptic folds or that between the release of multiple quantal packets of acetylcholine, are also presented. Increasing the spacing between folds increases peak current. Decreased spacing of adjacent quantal release sites increases the potentiation of peak current.
Full text
PDF

















Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams P. R. An analysis of the dose-response curve at voltage-clamped frog-endplates. Pflugers Arch. 1975 Oct 28;360(2):145–153. doi: 10.1007/BF00580537. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson C. R., Stevens C. F. Voltage clamp analysis of acetylcholine produced end-plate current fluctuations at frog neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1973 Dec;235(3):655–691. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Betz W., Sakmann B. Effects of proteolytic enzymes on function and structure of frog neuromuscular junctions. J Physiol. 1973 May;230(3):673–688. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blount P., Merlie J. P. Molecular basis of the two nonequivalent ligand binding sites of the muscle nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. Neuron. 1989 Sep;3(3):349–357. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90259-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cull-Candy S. G., Miledi R., Uchitel O. D. Diffusion of acetylcholine in the synaptic cleft of normal and myasthenia gravis human endplates. Nature. 1980 Jul 31;286(5772):500–502. doi: 10.1038/286500a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dionne V. E. Characterization of drug iontophoresis with a fast microassay technique. Biophys J. 1976 Jul;16(7):705–717. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(76)85723-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECCLES J. C., JAEGER J. C. The relationship between the mode of operation and the dimensions of the junctional regions at synapses and motor end-organs. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1958 Jan 1;148(930):38–56. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1958.0003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall Z. W., Kelly R. B. Enzymatic detachment of endplate acetylcholinesterase from muscle. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jul 14;232(28):62–63. doi: 10.1038/newbio232062a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartman D. S., Claudio T. Coexpression of two distinct muscle acetylcholine receptor alpha-subunits during development. Nature. 1990 Jan 25;343(6256):372–375. doi: 10.1038/343372a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartzell H. C., Kuffler S. W., Yoshikami D. Post-synaptic potentiation: interaction between quanta of acetylcholine at the skeletal neuromuscular synapse. J Physiol. 1975 Oct;251(2):427–463. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRNJEVIC K., MITCHELL J. F. Diffusion of acetylcholine in agar gels and in the isolated rat diaphragm. J Physiol. 1960 Oct;153:562–572. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. The binding of acetylcholine to receptors and its removal from the synaptic cleft. J Physiol. 1973 Jun;231(3):549–574. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labarca P., Montal M. S., Lindstrom J. M., Montal M. The occurrence of long openings in the purified cholinergic receptor channel increases with acetylcholine concentration. J Neurosci. 1985 Dec;5(12):3409–3413. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.05-12-03409.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Land B. R., Harris W. V., Salpeter E. E., Salpeter M. M. Diffusion and binding constants for acetylcholine derived from the falling phase of miniature endplate currents. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(5):1594–1598. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.5.1594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Land B. R., Salpeter E. E., Salpeter M. M. Acetylcholine receptor site density affects the rising phase of miniature endplate currents. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3736–3740. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Land B. R., Salpeter E. E., Salpeter M. M. Kinetic parameters for acetylcholine interaction in intact neuromuscular junction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):7200–7204. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.7200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews-Bellinger J., Salpeter M. M. Distribution of acetylcholine receptors at frog neuromuscular junctions with a discussion of some physiological implications. J Physiol. 1978 Jun;279:197–213. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMahan U. J., Sanes J. R., Marshall L. M. Cholinesterase is associated with the basal lamina at the neuromuscular junction. Nature. 1978 Jan 12;271(5641):172–174. doi: 10.1038/271172a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robitaille R., Tremblay J. P., Grenon G. Non-uniform distribution of miniature endplate potential amplitudes along the length of the frog neuromuscular junction. Neurosci Lett. 1987 Feb 24;74(2):187–192. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(87)90147-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheridan R. E., Lester H. A. Rates and equilibria at the acetylcholine receptor of Electrophorus electroplaques: a study of neurally evoked postsynaptic currents and of voltage-jump relaxations. J Gen Physiol. 1977 Aug;70(2):187–219. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sine S. M., Taylor P. The relationship between agonist occupation and the permeability response of the cholinergic receptor revealed by bound cobra alpha-toxin. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 10;255(21):10144–10156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tremblay J. P., Robitaille R., Martineau O., Labrecque C., Fahim M. A. Proximodistal gradients of the postjunctional folds at the frog neuromuscular junction: a scanning electron microscopic study. Neuroscience. 1989;30(2):535–550. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(89)90271-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Udgaonkar J. B., Hess G. P. Acetylcholine receptor kinetics: chemical kinetics. J Membr Biol. 1986;93(2):93–109. doi: 10.1007/BF01870803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vigny M., Bon S., Massoulié J., Leterrier F. Active-site catalytic efficiency of acetylcholinesterase molecular forms in Electrophorus, torpedo, rat and chicken. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Apr 17;85(2):317–323. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12241.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wathey J. C., Nass M. M., Lester H. A. Numerical reconstruction of the quantal event at nicotinic synapses. Biophys J. 1979 Jul;27(1):145–164. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(79)85208-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]