Abstract
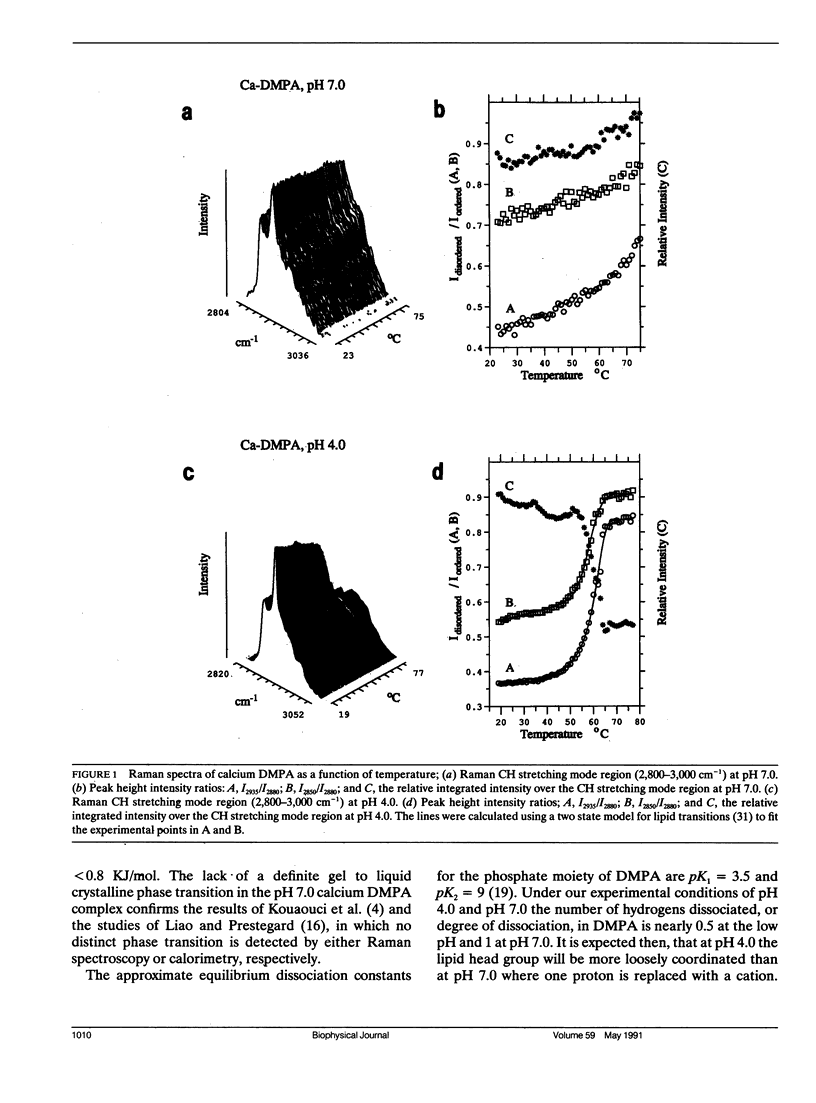
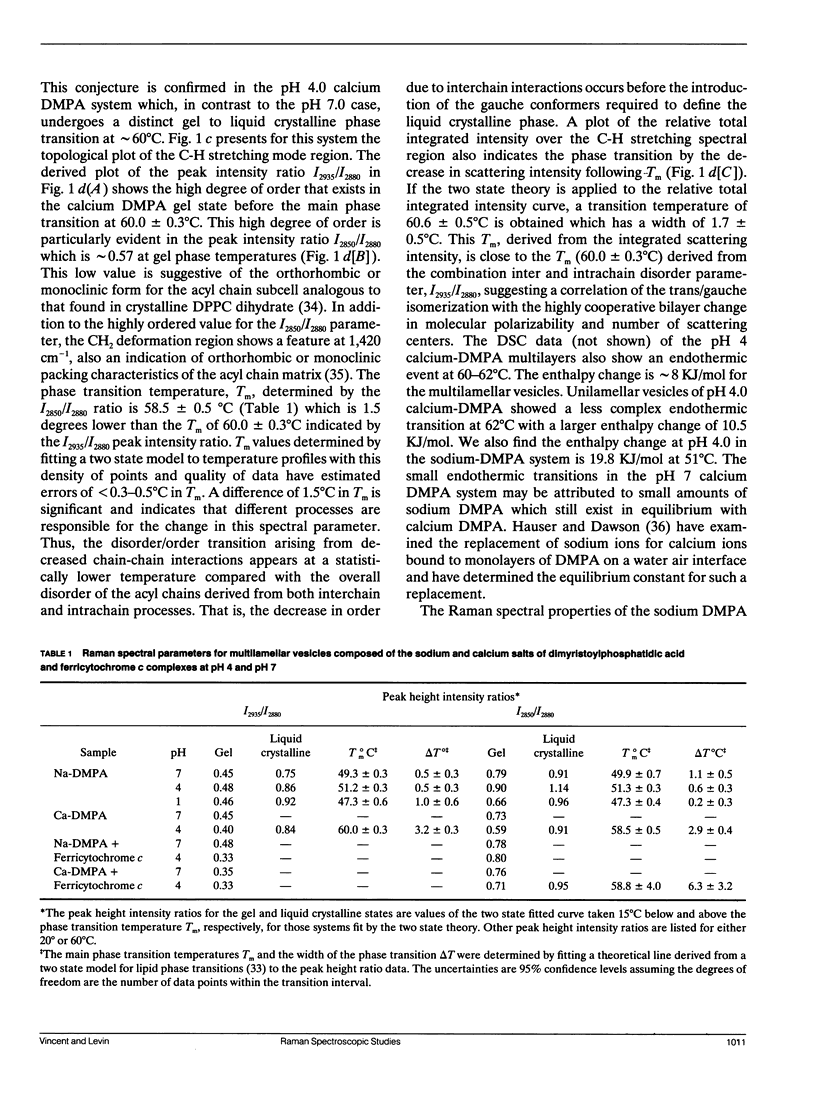
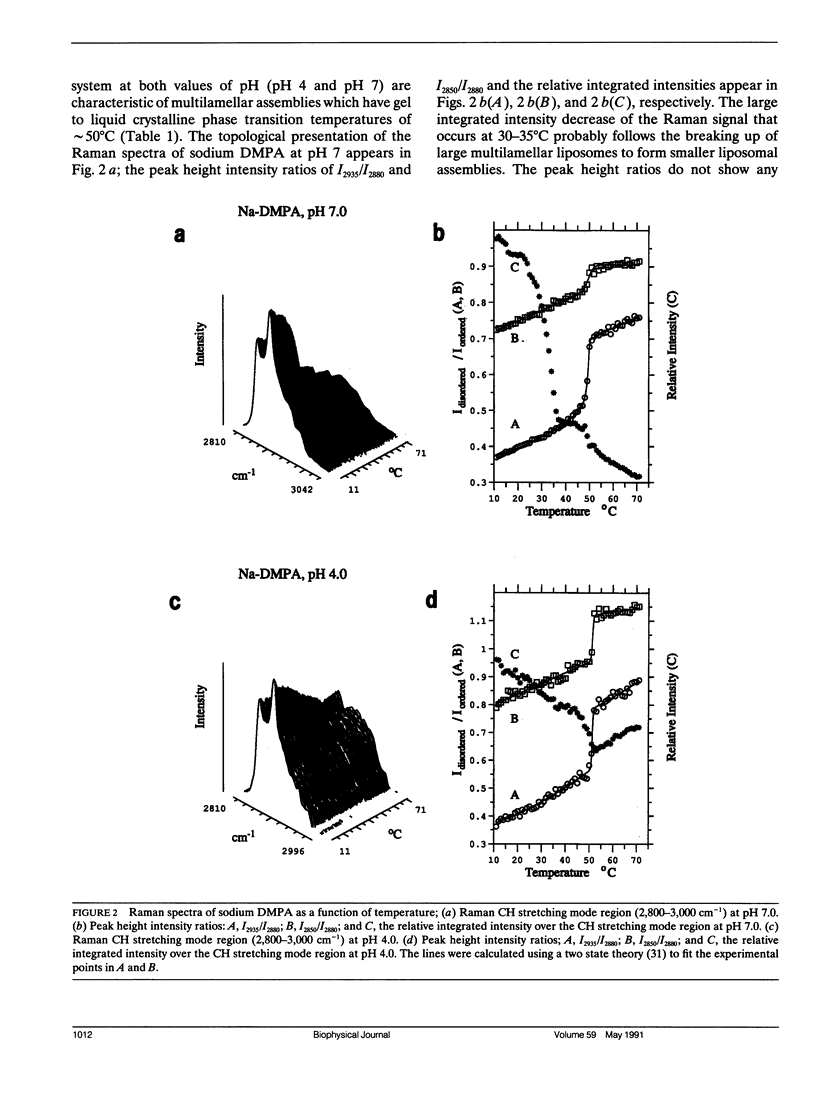
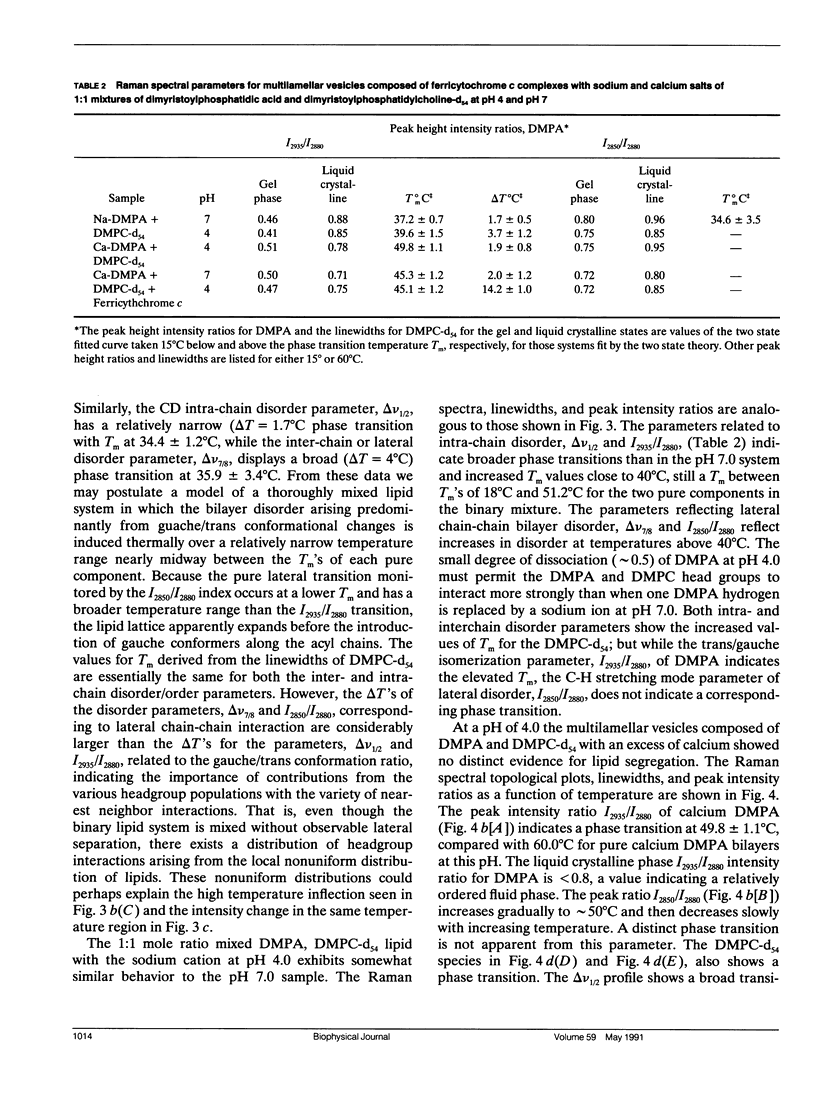
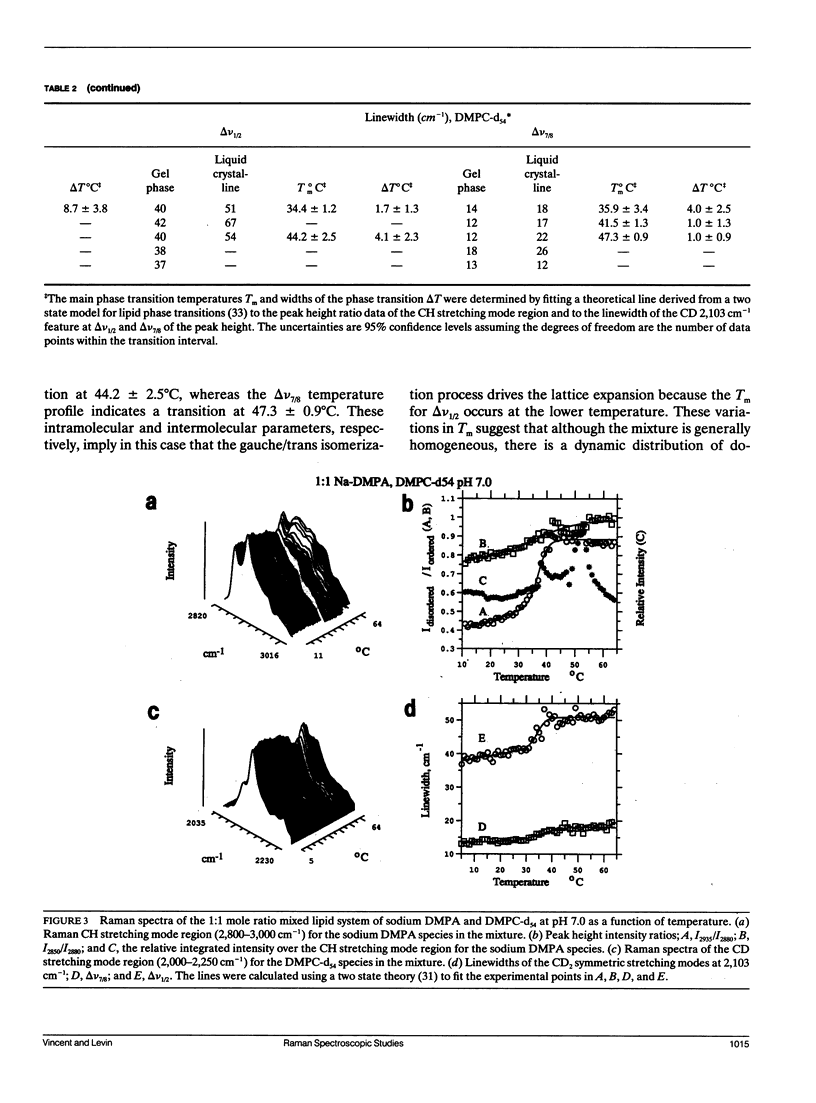
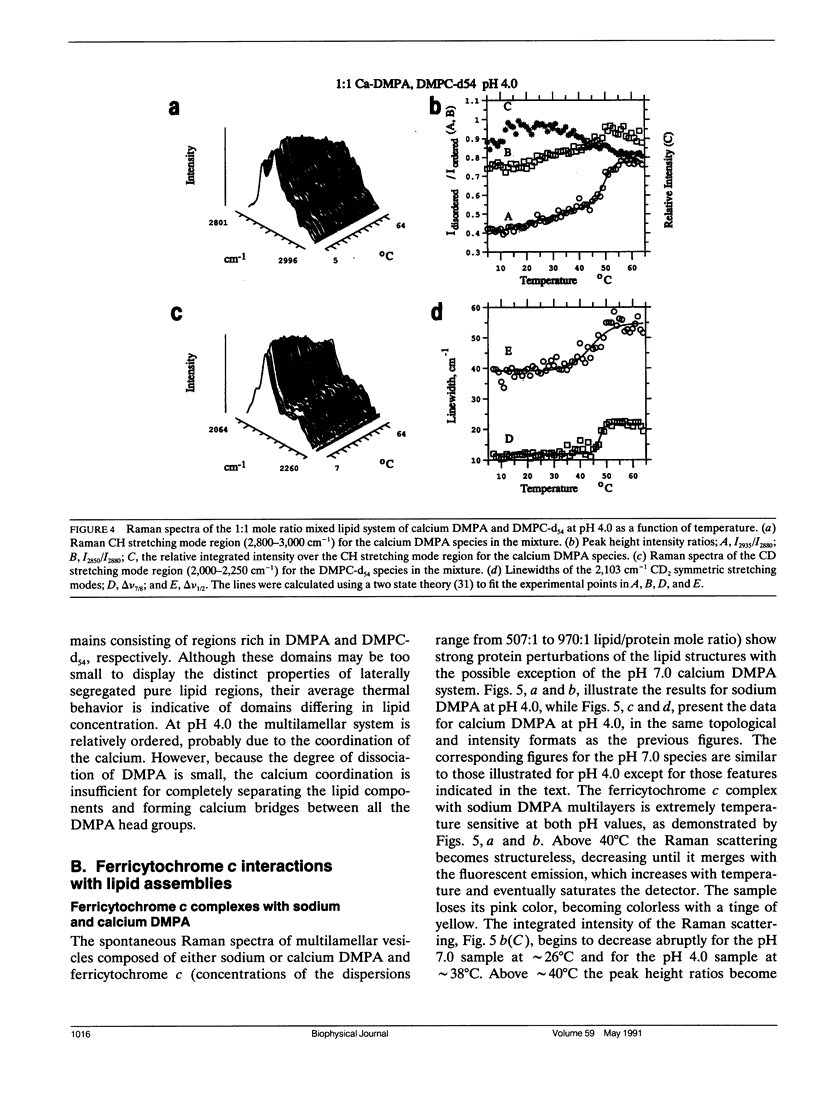
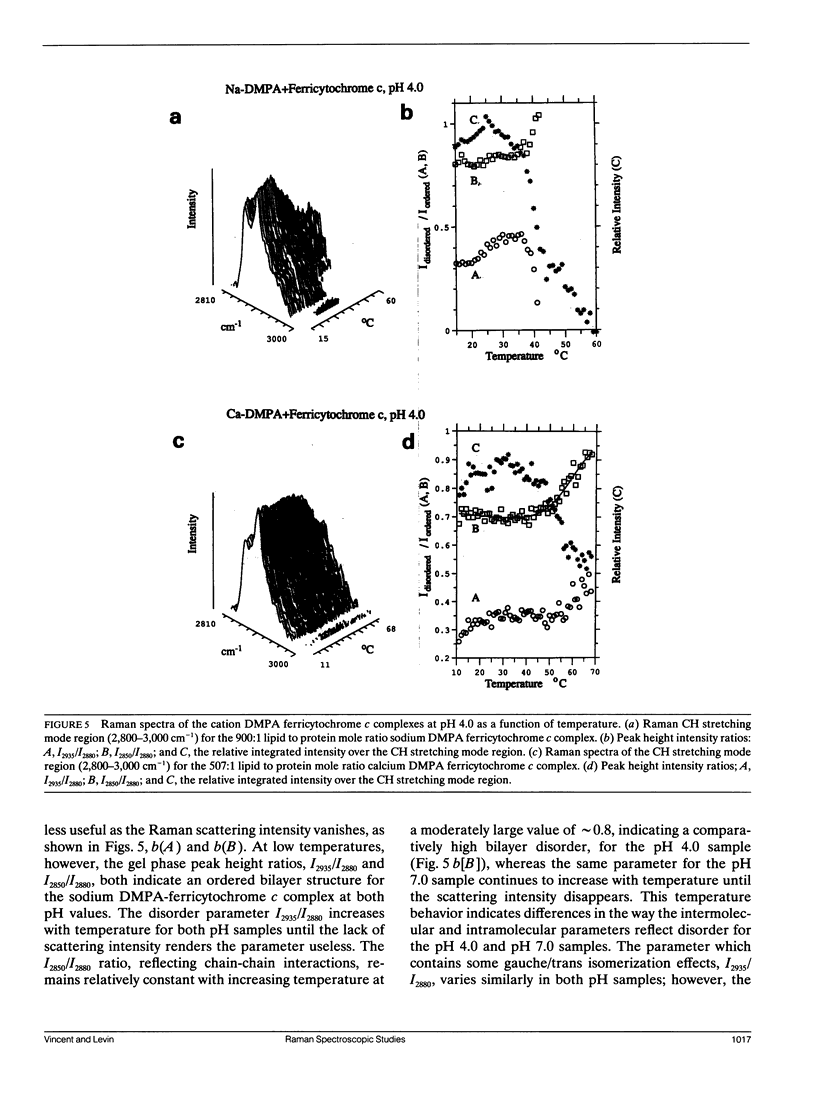
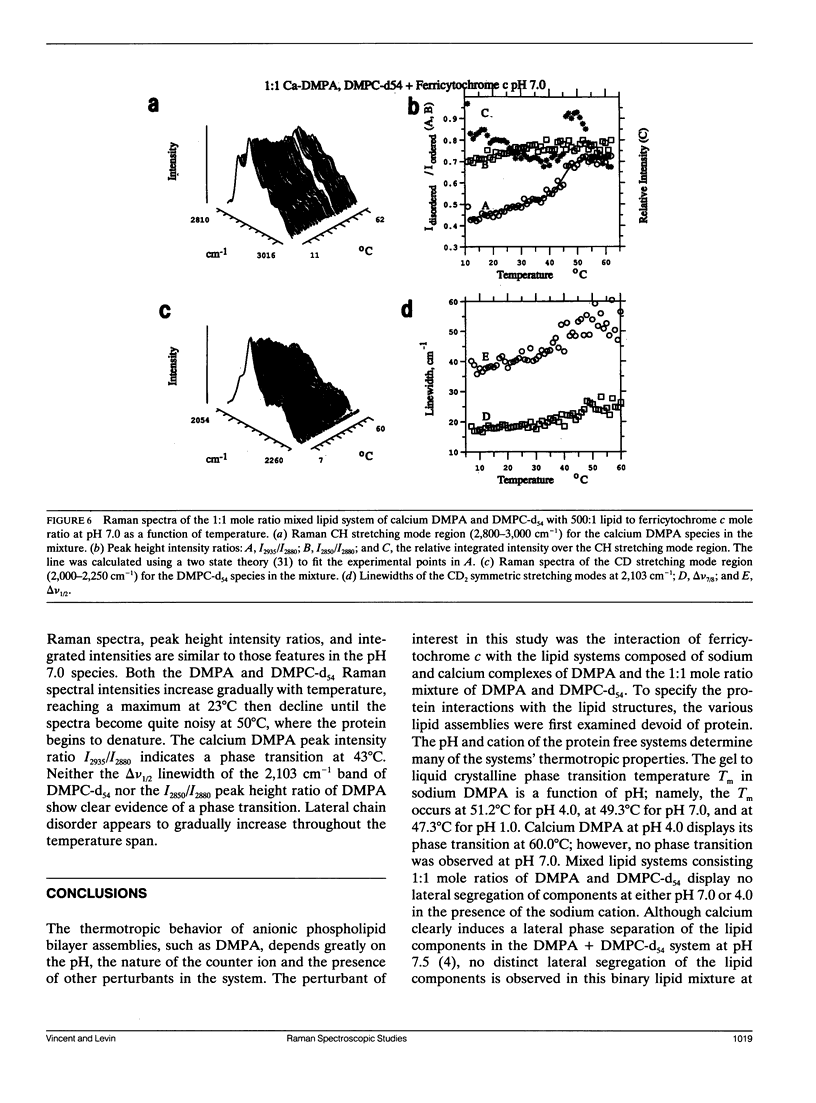
The vibrational Raman spectra of both pure 1-alpha-dimyristoylphosphatidic acid (DMPA) liposomes and DMPA multilayers reconstituted with ferricytochrome c at pH 7 and pH 4, with either sodium or calcium as the cation, are reported as a function of temperature. Multilayers composed of a 1:1 mol ratio DMPA and dimyristoylphosphatidylcholine with perdeuterated acyl chains (DMPC-d54) have also been reconstituted with approximately 10(-4) M ferricytochrome c for Raman spectroscopic observation. Total integrated band intensities and relative peak height intensity ratios, two spectral Raman scattering parameters used to characterize bilayer properties, are sensitive to the presence of both ferricytochrome c and the cation in the reconstituted liposomes. Temperature profiles, derived from the various Raman intensity parameters for the 3,100-2,800 cm-1 lipid acyl chain C-H stretching mode region specifically reflect bilayer perturbations due to the interactions of ferricytochrome c. At pH 4 the calcium DMPA multilamellar gel to liquid crystalline phase transition temperatures Tm, defined by either the C-H stretching mode I2850/I2880 and I2935/I2880 peak height intensity ratios, are 58.5 +/- 0.5 degrees C and 60.0 +/- 0.3 degrees C, respectively. This difference in Tm's resolves the phase transition process into first an expansion of the lipid lattice and then a melting of the lipid acyl chains. At pH 7 the calcium DMPA liposomes show no distinct phase transition characteristics below 75 degrees C. For sodium DMPA liposomes reconstituted with ferricytochrome c at either pH 4.0 or pH 7.0, spontaneous Raman spectra show altered lipid structures at temperatures above 40 degrees C. Resonance Raman spectra indicate that ferricytochrome c reconstituted in either calcium or sodium DMPA liposomes changes irreversibly above Tm. For either the binary lipid or ternary lipid-protein systems reconstituted with DMPC-d54, linewidth parameters of the DMPC-d54 acyl chain CD2 symmetric stretching modes at 2,103 cm-1 provide a sensitive measure of the conformational and dynamic properties of the perdeuterated lipid component, while the 3,000 cm-1 C-H spectral region reflects the bilayer characteristics of the DMPA species in the complex. Although calcium clearly induces a lateral phase separation in the DMPA/DMPC-d54 system at pH 7.5 (Kouaouci, R., J.R. Silvius, I. Grah, and M. Pezolet. 1985. Biochemistry. 24:7132-7140), no distinct lateral segregation of the lipid components is observed in the mixed DMPA/DMPC-d54 lipid system in the presence of either ferricytochrome c or the sodium and calcium cations at pH 4.0. However, domain formation, consisting of regions rich in DMPA and DMPC-d54, respectively, is suggested for the calcium binary lipid mixture at pH 4.0 by the different values for Tm and AT characterizing the DMPA and DMPC-d54 species.Spectral evidence strongly suggests that ferricytochrome c also induces domain formation in the ternary lipid-protein mixtures at pH 7.0, but only for the sodium cation.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berridge M. J. Inositol trisphosphate and diacylglycerol as second messengers. Biochem J. 1984 Jun 1;220(2):345–360. doi: 10.1042/bj2200345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birrell G. B., Griffith O. H. Cytochrome c induced lateral phase separation in a diphosphatidylglycerol-steroid spin-label model membrane. Biochemistry. 1976 Jun 29;15(13):2925–2929. doi: 10.1021/bi00658a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blume A., Eibl H. The influence of charge on bilayer membranes. Calorimetric investigations of phosphatidic acid bilayers. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Nov 16;558(1):13–21. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(79)90311-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brautigan D. L., Ferguson-Miller S., Margoliash E. Mitochondrial cytochrome c: preparation and activity of native and chemically modified cytochromes c. Methods Enzymol. 1978;53:128–164. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(78)53021-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown L. R., Wüthrich K. NMR and ESR studies of the interactions of cytochrome c with mixed cardiolipin-phosphatidylcholine vesicles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Aug 1;468(3):389–410. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90290-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bush S. F., Adams R. G., Levin I. W. Structural reorganizations in lipid bilayer systems: effect of hydration and sterol addition on Raman spectra of dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine multilayers. Biochemistry. 1980 Sep 16;19(19):4429–4436. doi: 10.1021/bi00560a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickerson R. E., Takano T., Eisenberg D., Kallai O. B., Samson L., Cooper A., Margoliash E. Ferricytochrome c. I. General features of the horse and bonito proteins at 2.8 A resolution. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 10;246(5):1511–1535. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eibl H., Blume A. The influence of charge on phosphatidic acid bilayer membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Jun 2;553(3):476–488. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(79)90303-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eibl H., Woolley P. Electrostatic interactions at charged lipid membranes. Hydrogen bonds in lipid membrane surfaces. Biophys Chem. 1979 Nov;10(3-4):261–271. doi: 10.1016/0301-4622(79)85015-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaber B. P., Peticolas W. L. On the quantitative interpretation of biomembrane structure by Raman spectroscopy. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Mar 1;465(2):260–274. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90078-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauser H., Dawson R. M. The binding of calcium at lipid-water interfaces. Eur J Biochem. 1967 Mar;1(1):61–69. doi: 10.1007/978-3-662-25813-2_11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koppenol W. H., Margoliash E. The asymmetric distribution of charges on the surface of horse cytochrome c. Functional implications. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 25;257(8):4426–4437. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kouaouci R., Silvius J. R., Graham I., Pézolet M. Calcium-induced lateral phase separations in phosphatidylcholine-phosphatidic acid mixtures. A Raman spectroscopic study. Biochemistry. 1985 Dec 3;24(25):7132–7140. doi: 10.1021/bi00346a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liao M. J., Prestegard J. H. Structural properties of a Ca2+-phosphatidic acid complex: small angle X-ray scattering and calorimetric results. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Jul 6;645(1):149–156. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(81)90523-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendelsohn R., Koch C. C. Deuterated phospholipids as Raman spectroscopic probes of membrane structure. Phase diagrams for the dipalmitoyl phosphatidylcholine(and its d62 derivative)-dipalmitoyl phosphatidylethanolamine system. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 May 23;598(2):260–271. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90004-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendelsohn R., Maisano J. Use of deuterated phospholipids in Raman spectroscopic studies of membrane structure. I. Multilayers of dimyristoyl phosphatidylcholine (and its -d54 derivative) with distearoyl phosphatidylcholine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Jan 19;506(2):192–201. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(78)90390-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendelsohn R., Taraschi T. Deuterated phospholipids as Raman spectroscopic probes of membrane structure: dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine-dipalmitoylphosphatidylethanolamine multilayers. Biochemistry. 1978 Sep 19;17(19):3944–3949. doi: 10.1021/bi00612a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mushayakarara E., Albon N., Levin I. W. Effect of water on the molecular structure of a phosphatidylcholine hydrate. Raman spectroscopic analysis of the phosphate, carbonyl and carbon-hydrogen stretching mode regions of 1,2-dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine dihydrate. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Apr 7;686(2):153–159. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(82)90107-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholls P. Cytochrome c binding to enzymes and membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Dec 30;346(3-4):261–310. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(74)90003-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papahadjopoulos D., Vail W. J., Pangborn W. A., Poste G. Studies on membrane fusion. II. Induction of fusion in pure phospholipid membranes by calcium ions and other divalent metals. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Oct 5;448(2):265–283. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90241-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinn P. J., Dawson R. M. Interactions of cytochrome c and [14C]. Biochem J. 1969 Oct;115(1):65–75. doi: 10.1042/bj1150065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smaal E. B., Mandersloot J. G., Demel R. A., de Kruijff B., de Gier J. Consequences of the interaction of calcium with dioleoylphosphatidate-containing model membranes: calcium-membrane and membrane-membrane interactions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Feb 12;897(1):180–190. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(87)90326-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiker R. C., Levin I. W. Effect of bilayer curvature on vibrational Raman spectroscopic behavior of phospholipid-water assemblies. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Dec 2;455(2):560–575. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90325-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Träuble H., Eibl H. Electrostatic effects on lipid phase transitions: membrane structure and ionic environment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jan;71(1):214–219. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.1.214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent J. S., Kon H., Levin I. W. Low-temperature electron paramagnetic resonance study of the ferricytochrome c-cardiolipin complex. Biochemistry. 1987 Apr 21;26(8):2312–2314. doi: 10.1021/bi00382a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent J. S., Levin I. W. Interaction of ferricytochrome c with zwitterionic phospholipid bilayers: a Raman spectroscopic study. Biochemistry. 1988 May 3;27(9):3438–3446. doi: 10.1021/bi00409a047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Bosch H. Phosphoglyceride metabolism. Annu Rev Biochem. 1974;43(0):243–277. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.43.070174.001331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


