Abstract
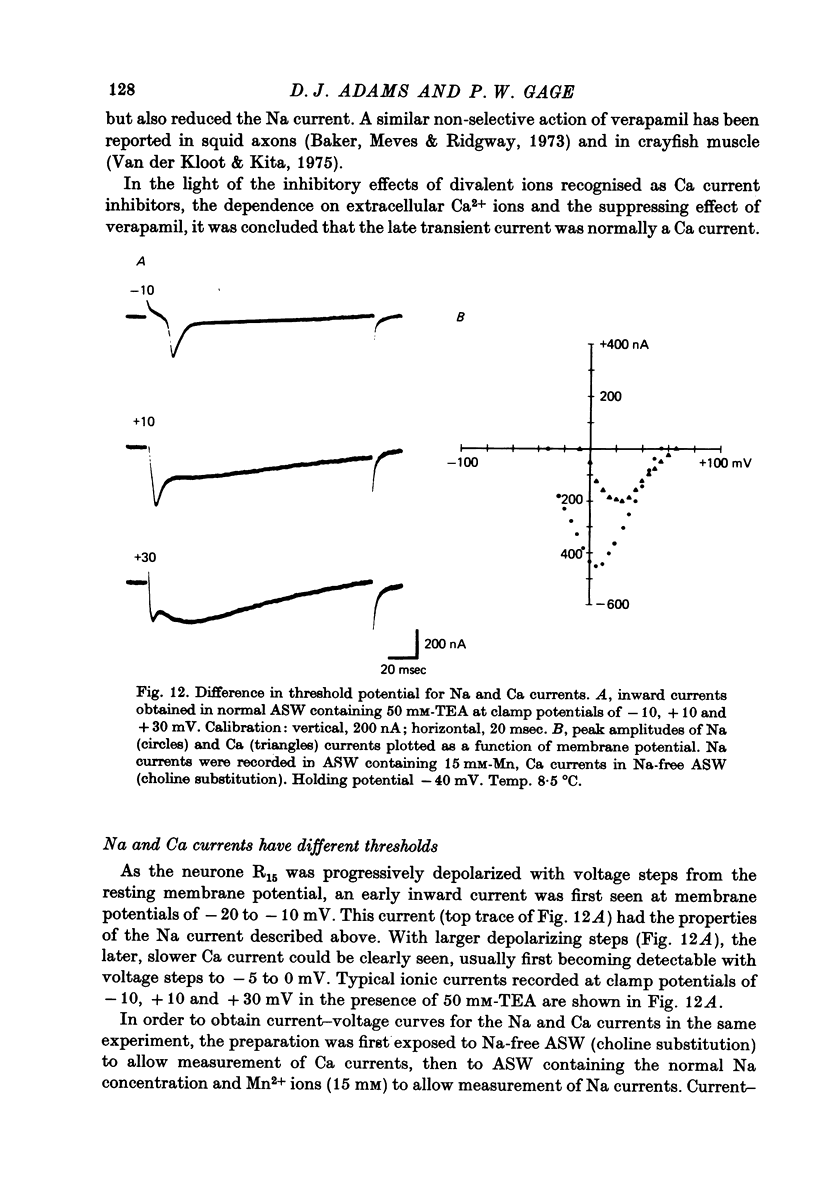
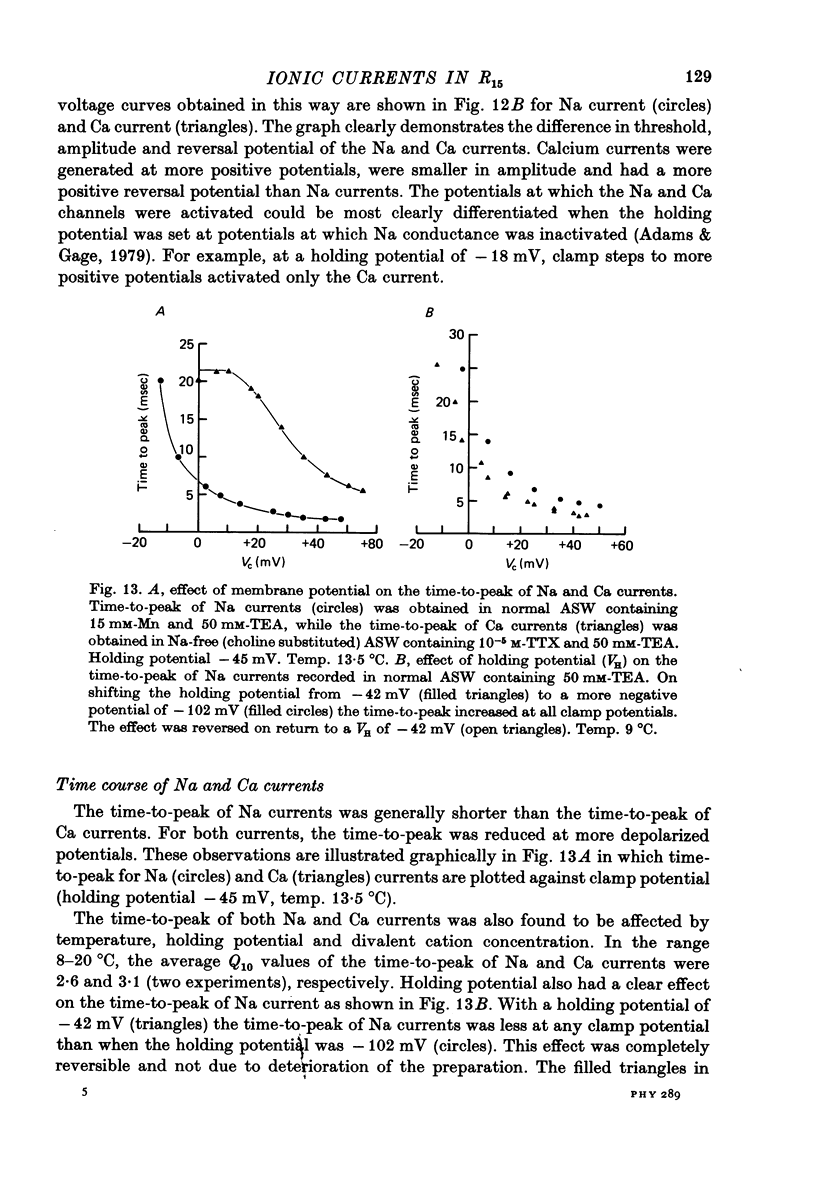
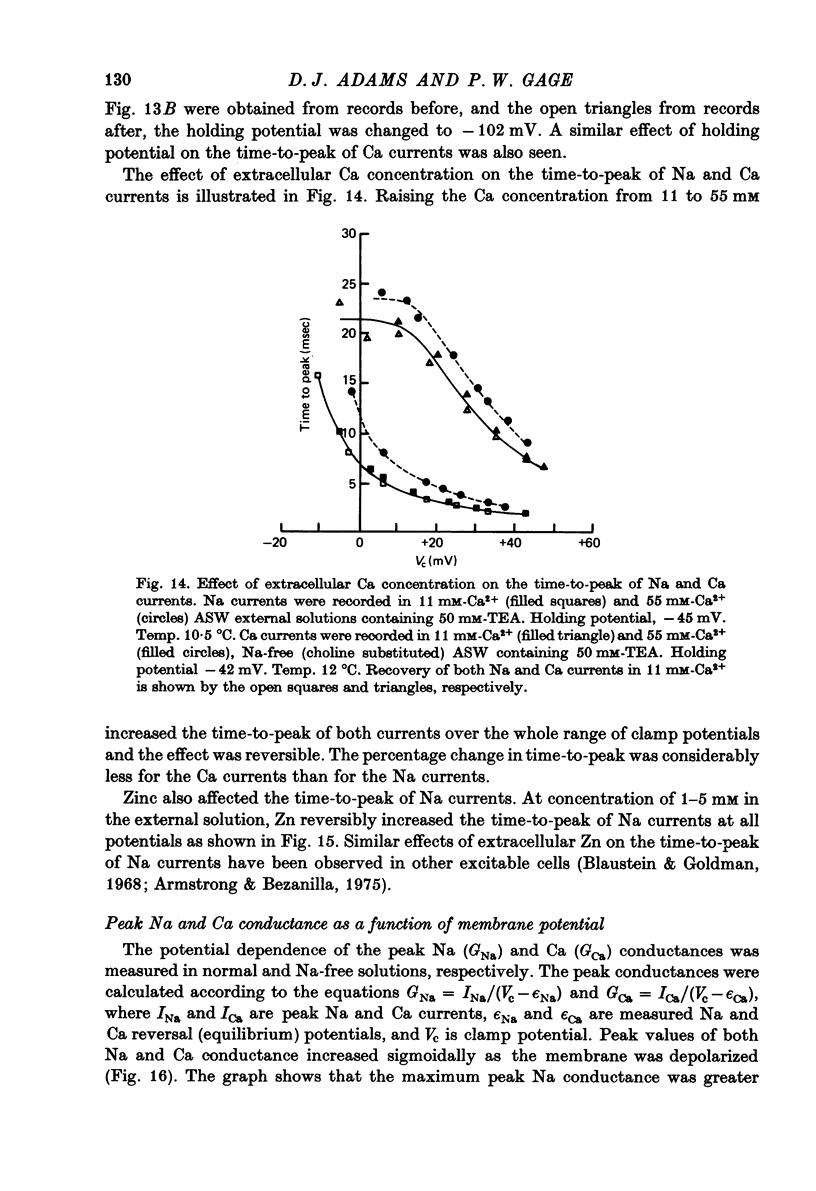
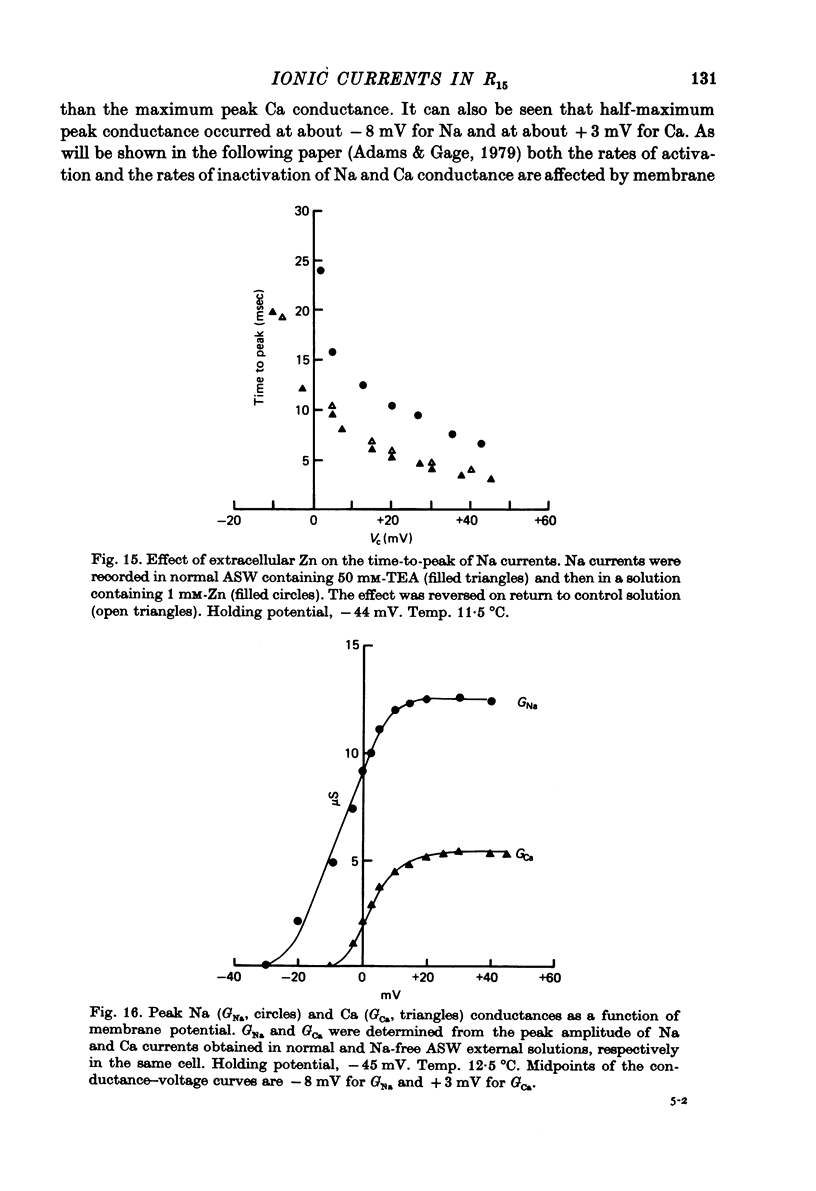
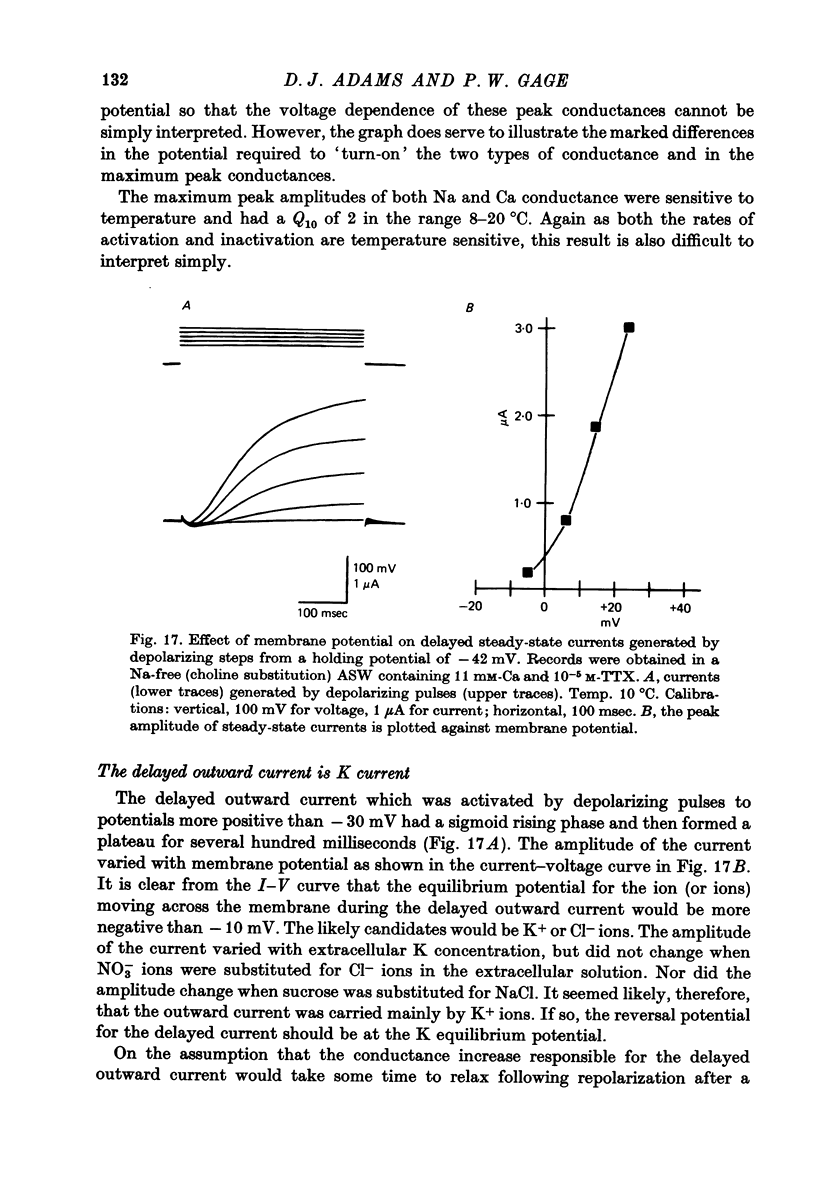
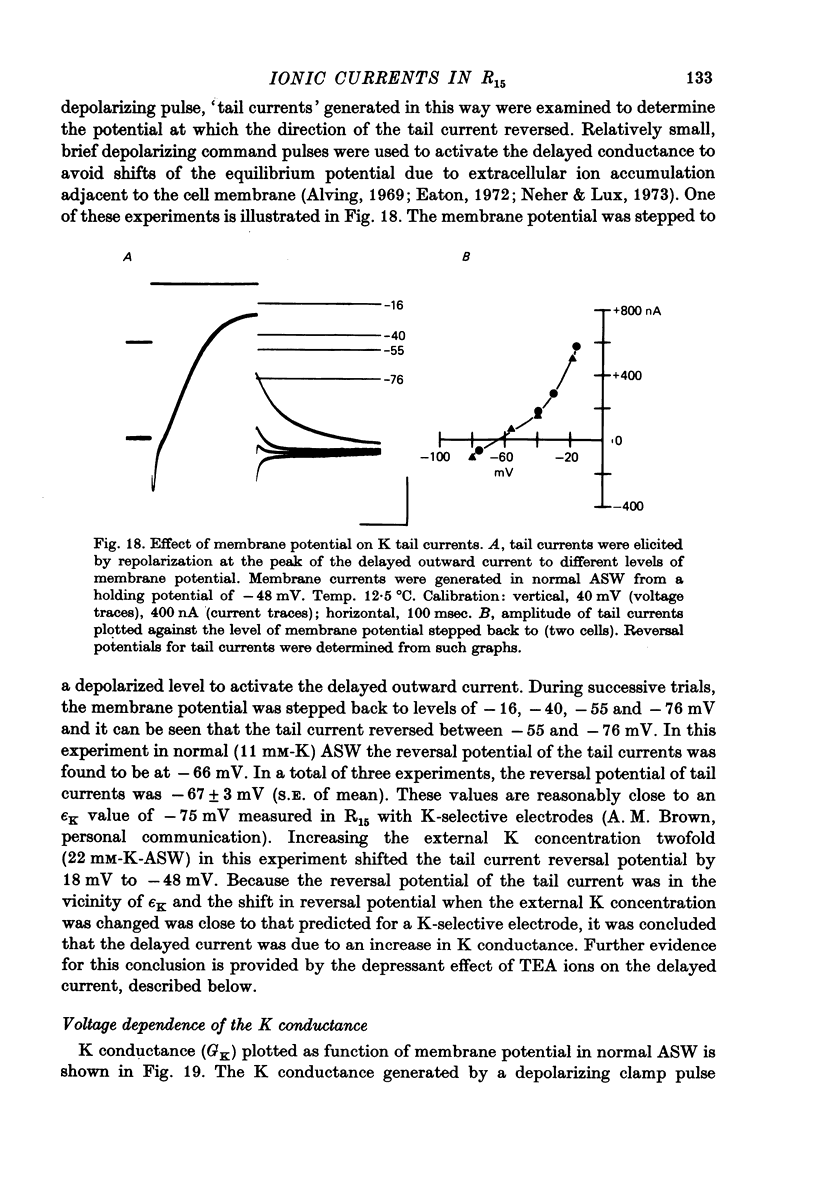
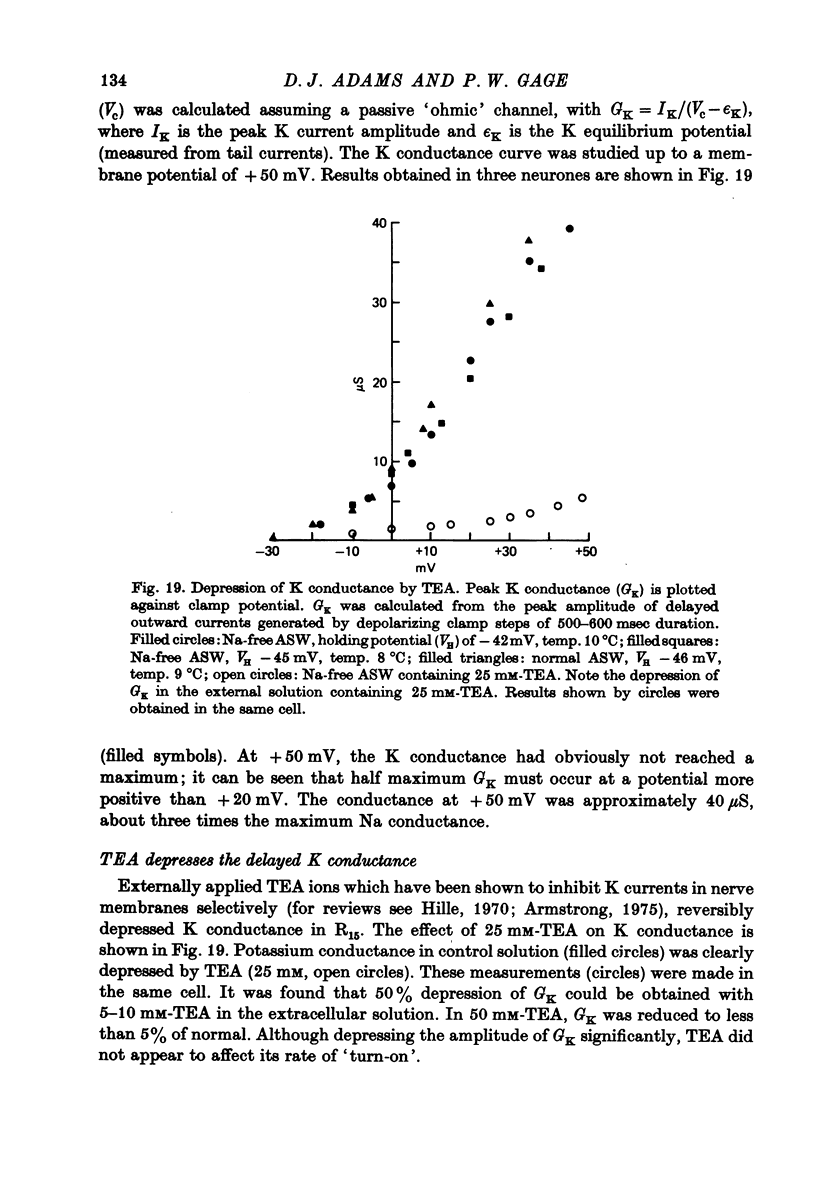
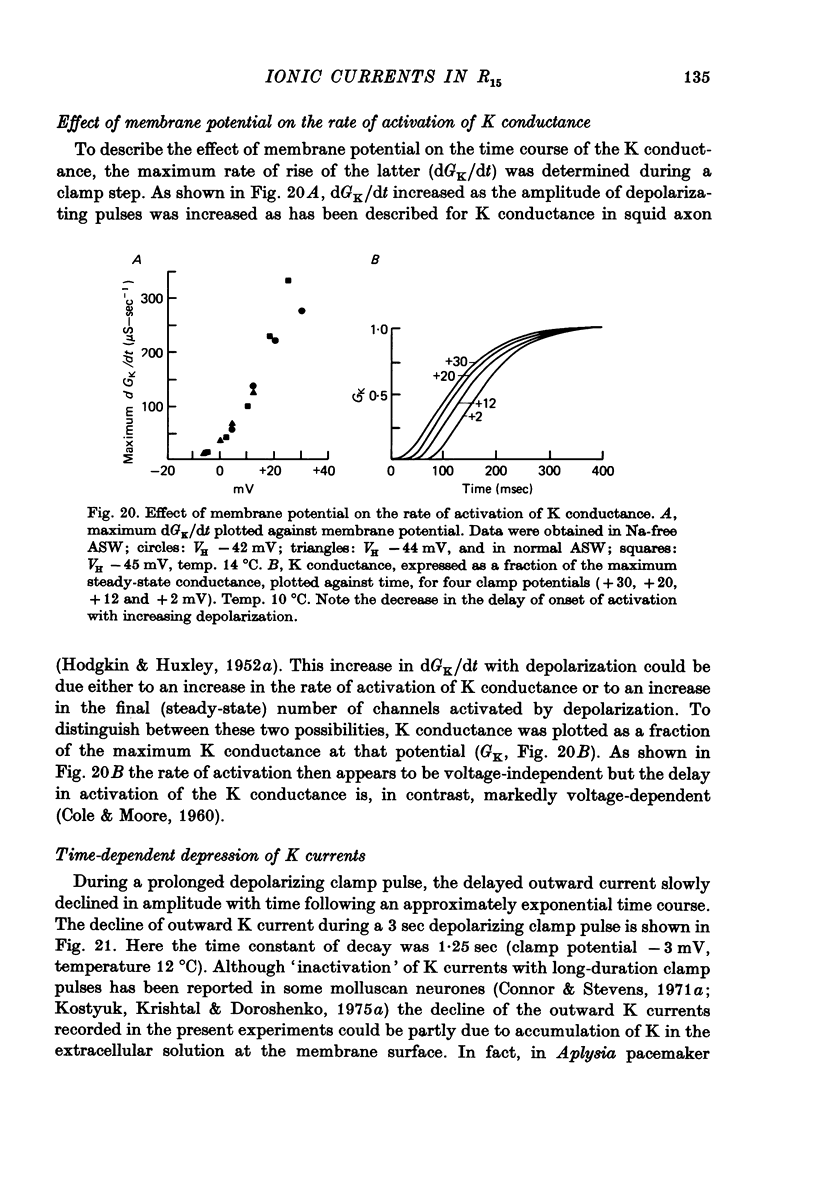
1. Action potentials recorded in the soma of R15 neurones in the abdominal ganglia of Aplysia juliana were not suppressed by selective inhibition of either Na or Ca conductance alone. It was necessary to block both conductances to suppress action potentials. 2. Membrane currents generated by step depolarizations of the soma consisted of early transient and delayed steady-state currents. The early transient current could have one or two components depending on the activating depolarization. 3. The early more rapid component had a reversal potential at +54 mV and the reversal potential changed with extracellular Na concentration in accord with the Nernst equation. It was blocked by substitution of impermeant cations for Na, by TTX and by internal injections of Zn. It was concluded that this component was normally a Na current. 4. The later slower component of the transient current had a reversal potential at about +65 mV and the reversal potential changed with extracellular Ca concentration is accord with the Nernst equation. It was blocked by substitution of Mg for Ca or addition of Mn, Co, Ni or verapamil to the extracellular solution. It was concluded that this component was normally a Ca current. 5. Na and Ca currents were generated at different threshold potentials, Na currents first appearing at about -20 mV and Ca currents at -5 to 0 mV. 6. The time-to-peak of both Na and Ca currents was affected by the holding potential, by the amplitude of the activating depolarization, by temperature and by divalent ion concentration. 7. The peak Na and Ca conductances both increased sigmoidally with increasing depolarization, the maximum Na conductance of 10--15 microS being approximately twice the maximum Ca conductance. Peak conductances for Na and Ca reached half-maximum at -8 and +3 mV, respectively. 8. The amplitude of the delayed steady-state current could be varied by changing the extracellular K+ ion concentration or by adding tetraethylammonium to the extracellular solution. The reversal potential for 'tail currents' was -67 mV and shifted 18 mV when the extracellular K concentration was doubled. It was concluded that the delayed steady-state current was K current. 9. With prolonged depolarizations, K current decayed with a time constant of the order of 1 sec. Peak K conductance increased with increasing depolarization with the half-maximum occurring at a potential more positive than +20 mV. The maximum rate of fractional activation of K conductance was independent of the amplitude of the clamp step.
Full text
PDF

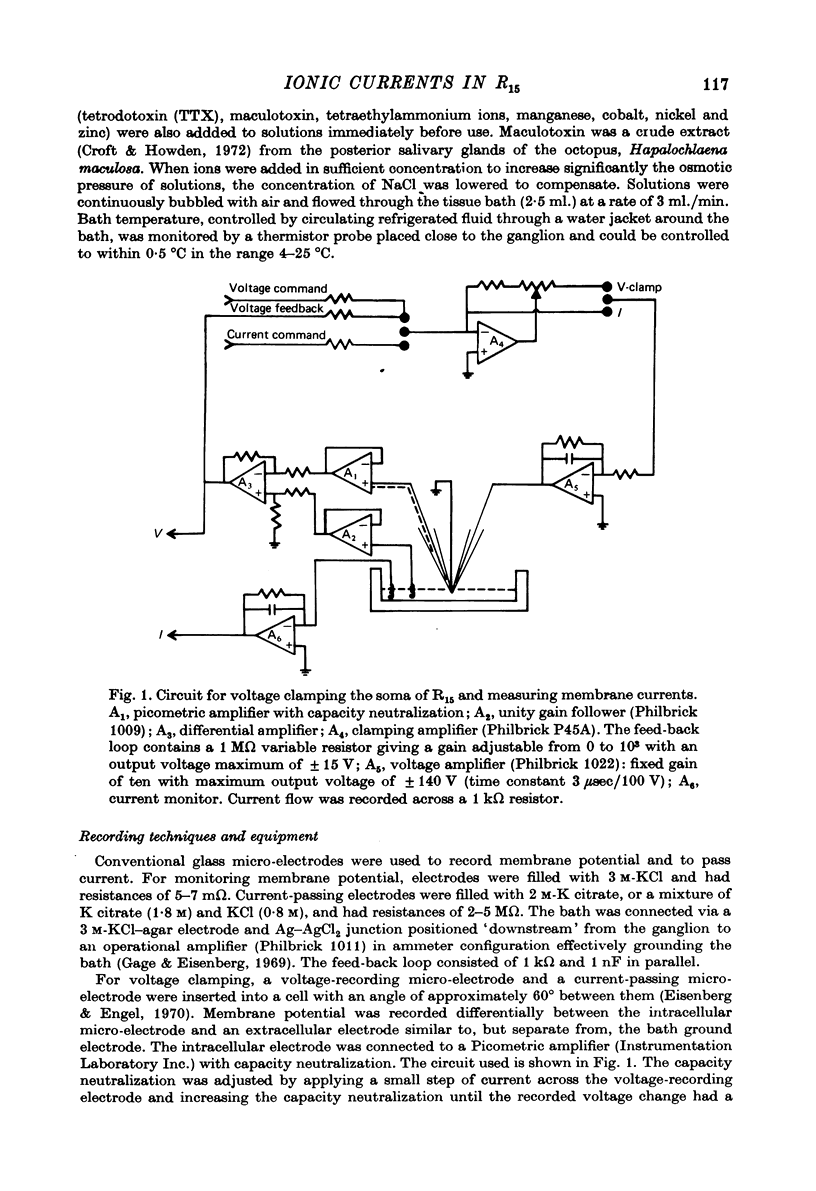
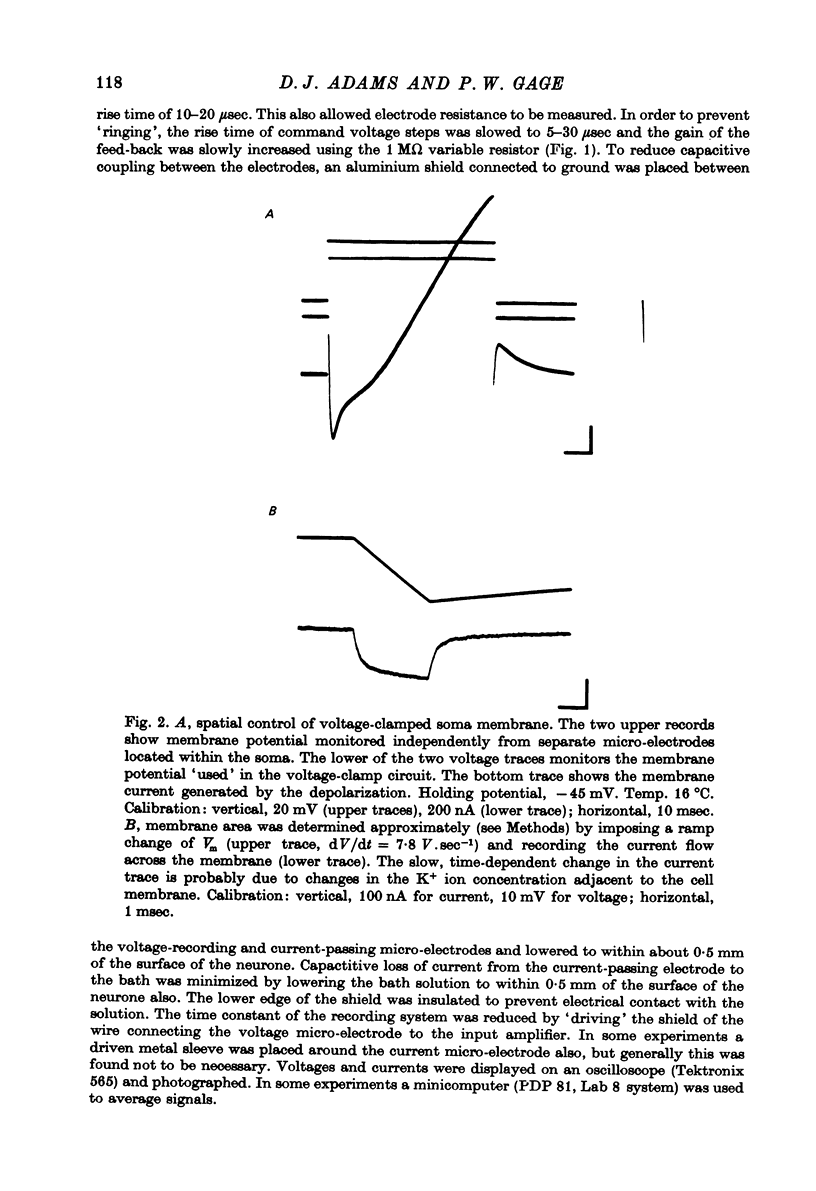

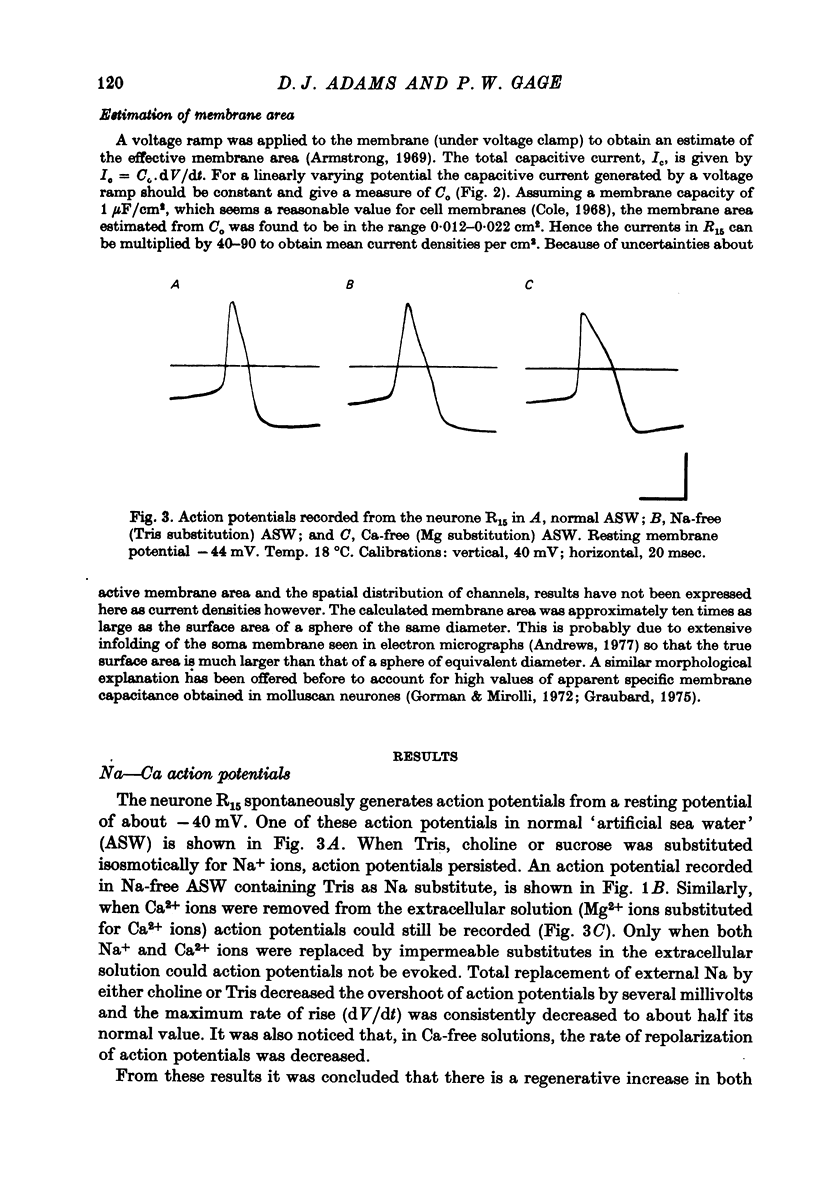

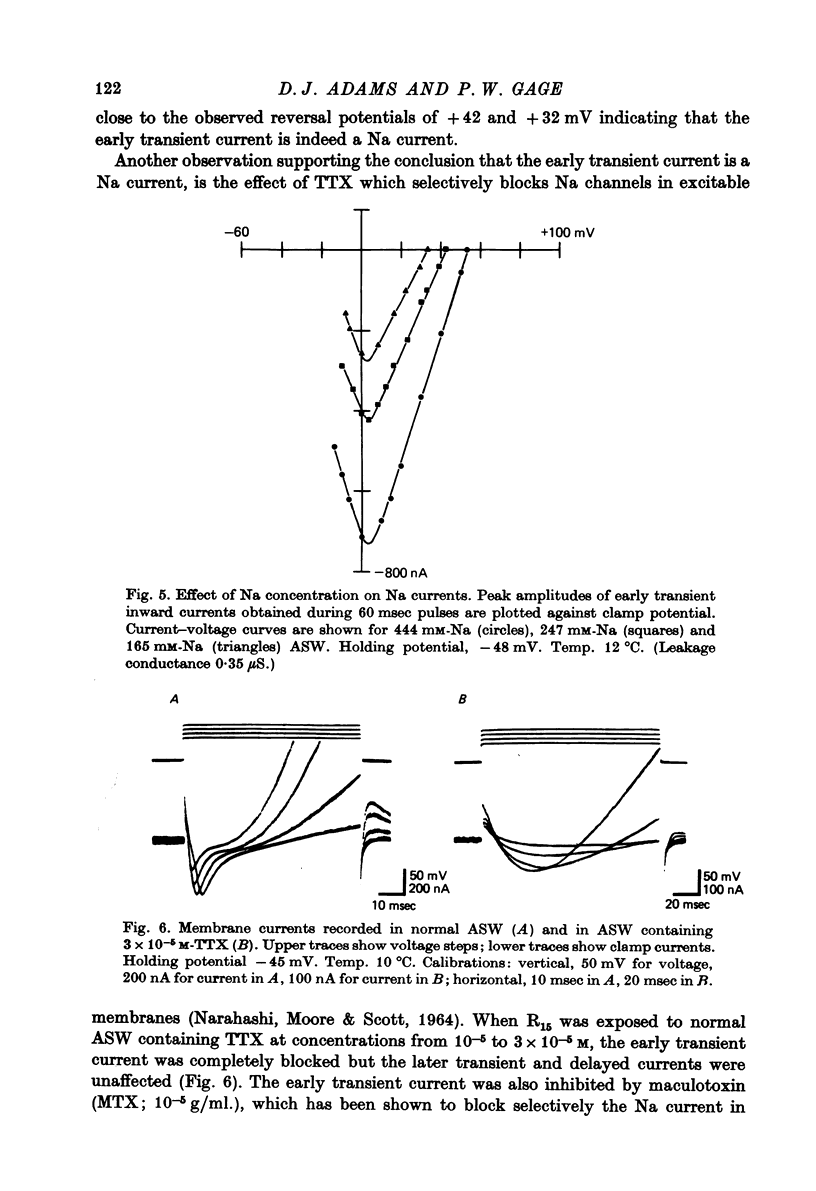
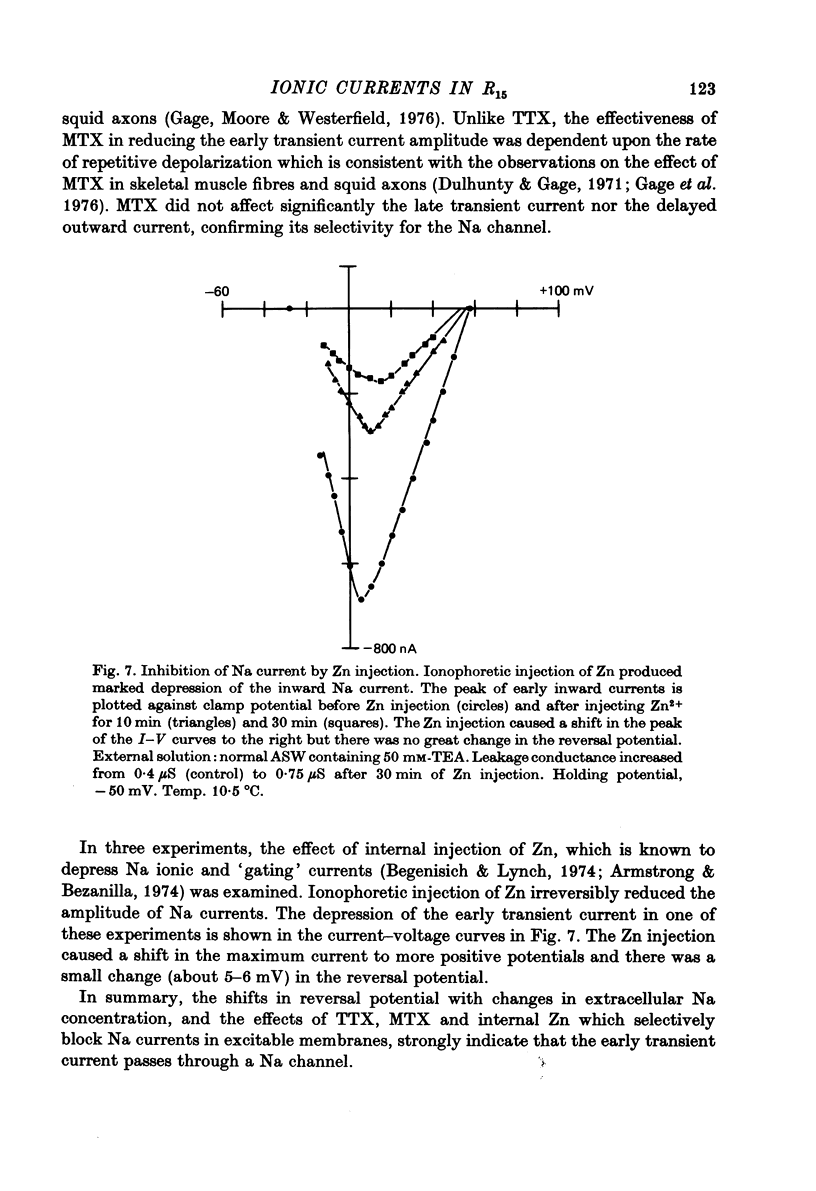
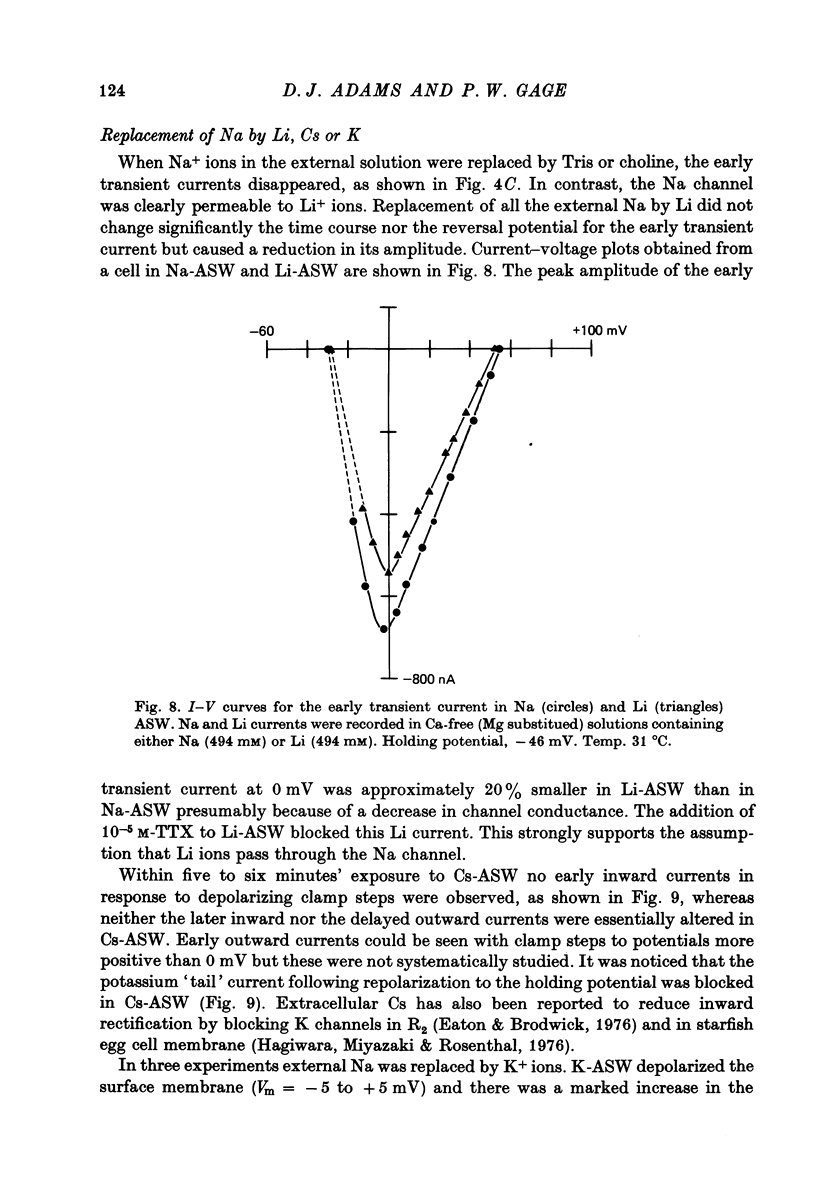

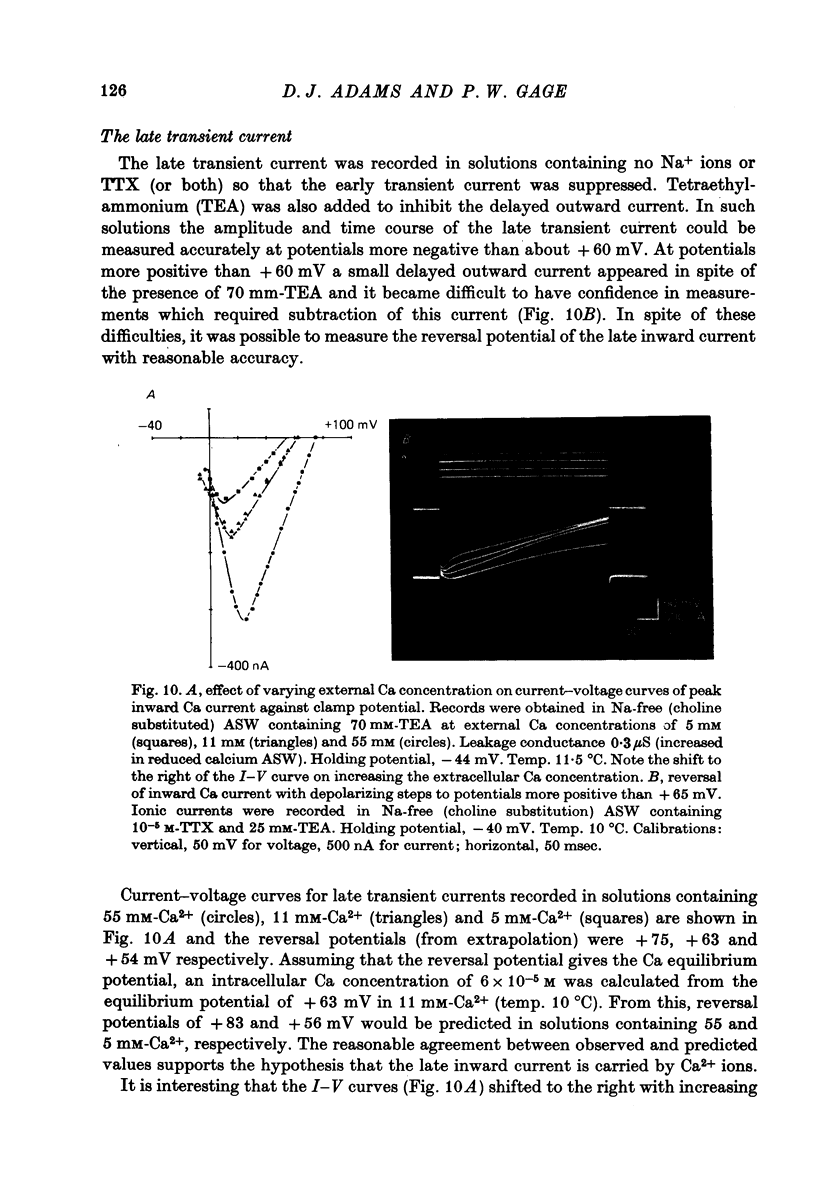
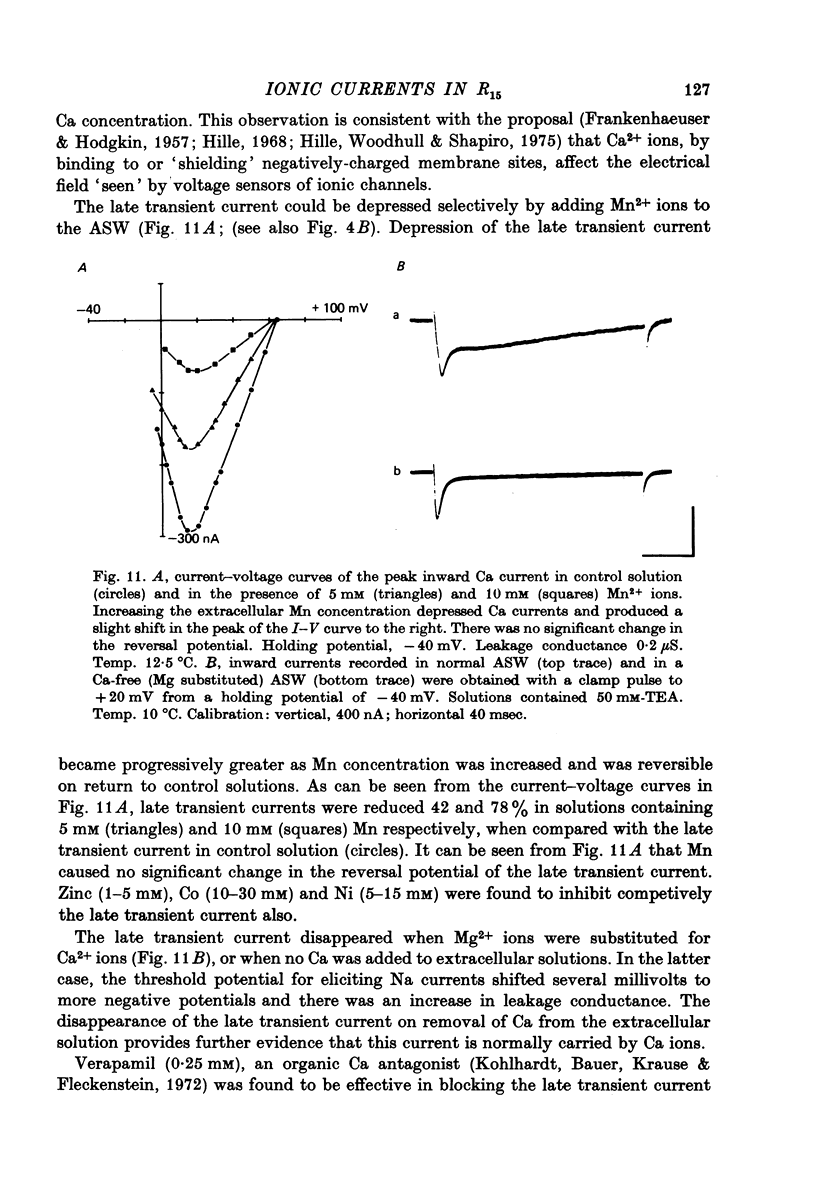





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ADELMAN W. J., TAYLOR R. E. Leakage current rectification in the squid giant axon. Nature. 1961 Jun 3;190:883–885. doi: 10.1038/190883a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams D. J., Gage P. W. Gating currents associated with sodium and calcium currents in an Aplysia neuron. Science. 1976 May 21;192(4241):783–784. doi: 10.1126/science.1265479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alving B. O. Differences between pacemaker and nonpacemaker neurons of Aplysia on voltage clamping. J Gen Physiol. 1969 Oct;54(4):512–531. doi: 10.1085/jgp.54.4.512. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong C. M., Bezanilla F. Charge movement associated with the opening and closing of the activation gates of the Na channels. J Gen Physiol. 1974 May;63(5):533–552. doi: 10.1085/jgp.63.5.533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong C. M. Currents associated with the ionic gating structures in nerve membrane. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1975 Dec 30;264:265–277. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1975.tb31488.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong C. M. Inactivation of the potassium conductance and related phenomena caused by quaternary ammonium ion injection in squid axons. J Gen Physiol. 1969 Nov;54(5):553–575. doi: 10.1085/jgp.54.5.553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong C. M. Ionic pores, gates, and gating currents. Q Rev Biophys. 1974 May;7(2):179–210. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500001402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. F., Meves H., Ridgway E. B. Effects of manganese and other agents on the calcium uptake that follows depolarization of squid axons. J Physiol. 1973 Jun;231(3):511–526. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010246. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Begenisich T., Lynch C. Effects of internal divalent cations on voltage-clamped squid axons. J Gen Physiol. 1974 Jun;63(6):675–689. doi: 10.1085/jgp.63.6.675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaustein M. P., Goldman D. E. The action of certain polyvalent cations on the voltage-clamped lobster axon. J Gen Physiol. 1968 Mar;51(3):279–291. doi: 10.1085/jgp.51.3.279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COLE K. S., MOORE J. W. Potassium ion current in the squid giant axon: dynamic characteristic. Biophys J. 1960 Sep;1:1–14. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3495(60)86871-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler W. K., Meves H. Voltage clamp experiments on internally perfused giant axons. J Physiol. 1965 Oct;180(4):788–820. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007732. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connor J. A., Stevens C. F. Inward and delayed outward membrane currents in isolated neural somata under voltage clamp. J Physiol. 1971 Feb;213(1):1–19. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connor J. A. Time course separation of two inward currents in molluscan neurons. Brain Res. 1977 Jan 7;119(2):487–492. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90330-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Croft J. A., Howden M. E. Chemistry of maculotoxin: a potent neurotoxin isolated from Hapalochlaena maculosa. Toxicon. 1972 Oct;10(6):645–651. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(72)90127-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dulhunty A., Gage P. W. Selective effects of an octopus toxin on action potentials. J Physiol. 1971 Oct;218(2):433–445. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eaton D. C. Potassium ion accumulation near a pace-making cell of Aplysia. J Physiol. 1972 Jul;224(2):421–440. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg R. S., Engel E. The spatial variation of membrane potential near a small source of current in a spherical cell. J Gen Physiol. 1970 Jun;55(6):736–757. doi: 10.1085/jgp.55.6.736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANKENHAEUSER B., HODGKIN A. L. The action of calcium on the electrical properties of squid axons. J Physiol. 1957 Jul 11;137(2):218–244. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005808. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farber D. S., Klee M. R. Membrane characteristics of bursting pacemaker neurones in Aplysia. Nat New Biol. 1972 Nov 1;240(96):29–31. doi: 10.1038/newbio240029a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gage P. W., Eisenberg R. S. Capacitance of the surface and transverse tubular membrane of frog sartorius muscle fibers. J Gen Physiol. 1969 Mar;53(3):265–278. doi: 10.1085/jgp.53.3.265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gage P. W., Moore J. W., Westerfield M. An octopus toxin, maculotoxin, selectively blocks sodium current in squid axons. J Physiol. 1976 Jul;259(2):427–443. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geduldig D., Gruener R. Voltage clamp of the Aplysia giant neurone: early sodium and calcium currents. J Physiol. 1970 Nov;211(1):217–244. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geduldig D., Junge D. Sodium and calcium components of action potentials in the Aplysia giant neurone. J Physiol. 1968 Dec;199(2):347–365. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graubard K. Voltage attenuation within Aplysia neurons: the effect of branching pattern. Brain Res. 1975 May 2;88(2):325–332. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(75)90394-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAGIWARA S., KUSANO K., SAITO N. Membrane changes of Onchidium nerve cell in potassium-rich media. J Physiol. 1961 Mar;155:470–489. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1961.sp006640. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HUXLEY A. F. A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. J Physiol. 1952 Aug;117(4):500–544. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HUXLEY A. F. Currents carried by sodium and potassium ions through the membrane of the giant axon of Loligo. J Physiol. 1952 Apr;116(4):449–472. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HUXLEY A. F., KATZ B. Measurement of current-voltage relations in the membrane of the giant axon of Loligo. J Physiol. 1952 Apr;116(4):424–448. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., KATZ B. The effect of sodium ions on the electrical activity of giant axon of the squid. J Physiol. 1949 Mar 1;108(1):37–77. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1949.sp004310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara S. Ca spike. Adv Biophys. 1973;4:71–102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara S., Miyazaki S., Rosenthal N. P. Potassium current and the effect of cesium on this current during anomalous rectification of the egg cell membrane of a starfish. J Gen Physiol. 1976 Jun;67(6):621–638. doi: 10.1085/jgp.67.6.621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hencek M., Zachar J. Calcium currents and conductances in the msucle membrane of the crayfish. J Physiol. 1977 Jun;268(1):51–71. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011846. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hille B. Charges and potentials at the nerve surface. Divalent ions and pH. J Gen Physiol. 1968 Feb;51(2):221–236. doi: 10.1085/jgp.51.2.221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hille B. The permeability of the sodium channel to metal cations in myelinated nerve. J Gen Physiol. 1972 Jun;59(6):637–658. doi: 10.1085/jgp.59.6.637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hille B., Woodhull A. M., Shapiro B. I. Negative surface charge near sodium channels of nerve: divalent ions, monovalent ions, and pH. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1975 Jun 10;270(908):301–318. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1975.0011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horn R., Miller J. J. A prolonged, voltage-dependent calcium permeability revealed by tetraethylammonium in the soma and axon of Aplysia giant neuron. J Neurobiol. 1977 Sep;8(5):399–415. doi: 10.1002/neu.480080502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Junge D., Miller J. Different spike mechanisms in axon and soma of molluscan neurone. Nature. 1974 Nov 8;252(5479):155–156. doi: 10.1038/252155a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Junge D. Multi-ionic action potentials in molluscan giant neurones. Nature. 1967 Jul 29;215(5100):546–548. doi: 10.1038/215546a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz G. M., Schwartz T. L. Temporal control of voltage-clamped membranes: an examination of principles. J Membr Biol. 1974 Jul 12;17(3):275–291. doi: 10.1007/BF01870188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keynes R. D., Rojas E., Taylor R. E., Vergara J. Calcium and potassium systems of a giant barnacle muscle fibre under membrane potential control. J Physiol. 1973 Mar;229(2):409–455. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohlhardt M., Bauer B., Krause H., Fleckenstein A. Differentiation of the transmembrane Na and Ca channels in mammalian cardiac fibres by the use of specific inhibitors. Pflugers Arch. 1972;335(4):309–322. doi: 10.1007/BF00586221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostyuk P. G., Krishtal O. A., Shakhovalov Y. A. Separation of sodium and calcium currents in the somatic membrane of mollusc neurones. J Physiol. 1977 Sep;270(3):545–568. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. S., Akaike N., Brown A. M. Trypsin inhibits the action of tetrodotoxin on neurones. Nature. 1977 Feb 24;265(5596):751–753. doi: 10.1038/265751a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meech R. W., Standen N. B. Potassium activation in Helix aspersa neurones under voltage clamp: a component mediated by calcium influx. J Physiol. 1975 Jul;249(2):211–239. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NARAHASHI T., MOORE J. W., SCOTT W. R. TETRODOTOXIN BLOCKAGE OF SODIUM CONDUCTANCE INCREASE IN LOBSTER GIANT AXONS. J Gen Physiol. 1964 May;47:965–974. doi: 10.1085/jgp.47.5.965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neher E., Lux H. D. Rapid changes of potassium concentration at the outer surface of exposed single neurons during membrane current flow. J Gen Physiol. 1973 Mar;61(3):385–399. doi: 10.1085/jgp.61.3.385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neher E. Two fast transient current components during voltage clamp on snail neurons. J Gen Physiol. 1971 Jul;58(1):36–53. doi: 10.1085/jgp.58.1.36. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto H., Takahashi K., Yoshii M. Membrane currents of the tunicate egg under the voltage-clamp condition. J Physiol. 1976 Jan;254(3):607–638. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto H., Takahashi K., Yoshii M. Two components of the calcium current in the egg cell membrane of the tunicate. J Physiol. 1976 Feb;255(2):527–561. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reuter H. Divalent cations as charge carriers in excitable membranes. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1973;26:1–43. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(73)90016-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberge F. A., Jacob R., Gulrajani R. M., Mathieu P. A. A study of soma isopotentiality in Aplysia neurons. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1977 Oct;55(5):1162–1169. doi: 10.1139/y77-159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Standen N. B. Voltage-clamp studies of the calcium inward current in an identified snail neurone: comparison with the sodium inward current. J Physiol. 1975 Jul;249(2):253–268. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson S. H. Three pharmacologically distinct potassium channels in molluscan neurones. J Physiol. 1977 Feb;265(2):465–488. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Der Kloot W., Kita H. The effects of the "calcium-antagonist" verapamil on muscle action potentials in the frog and crayfish and on neuromuscular transmission in the crayfish. Comp Biochem Physiol C. 1975 Jan 1;50(1):121–125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wald F. Ionic differences between somatic and axonal action potentials in snail giant neurones. J Physiol. 1972 Jan;220(2):267–281. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009706. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



