Abstract
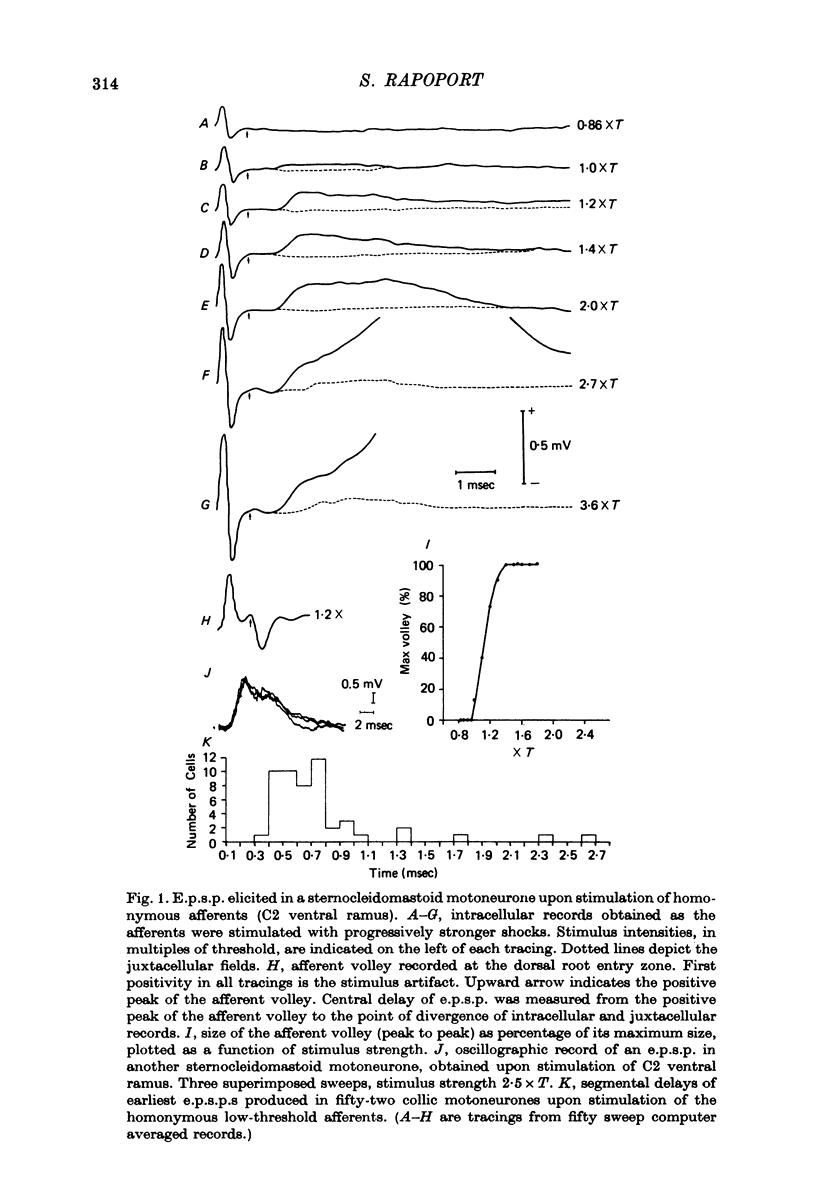
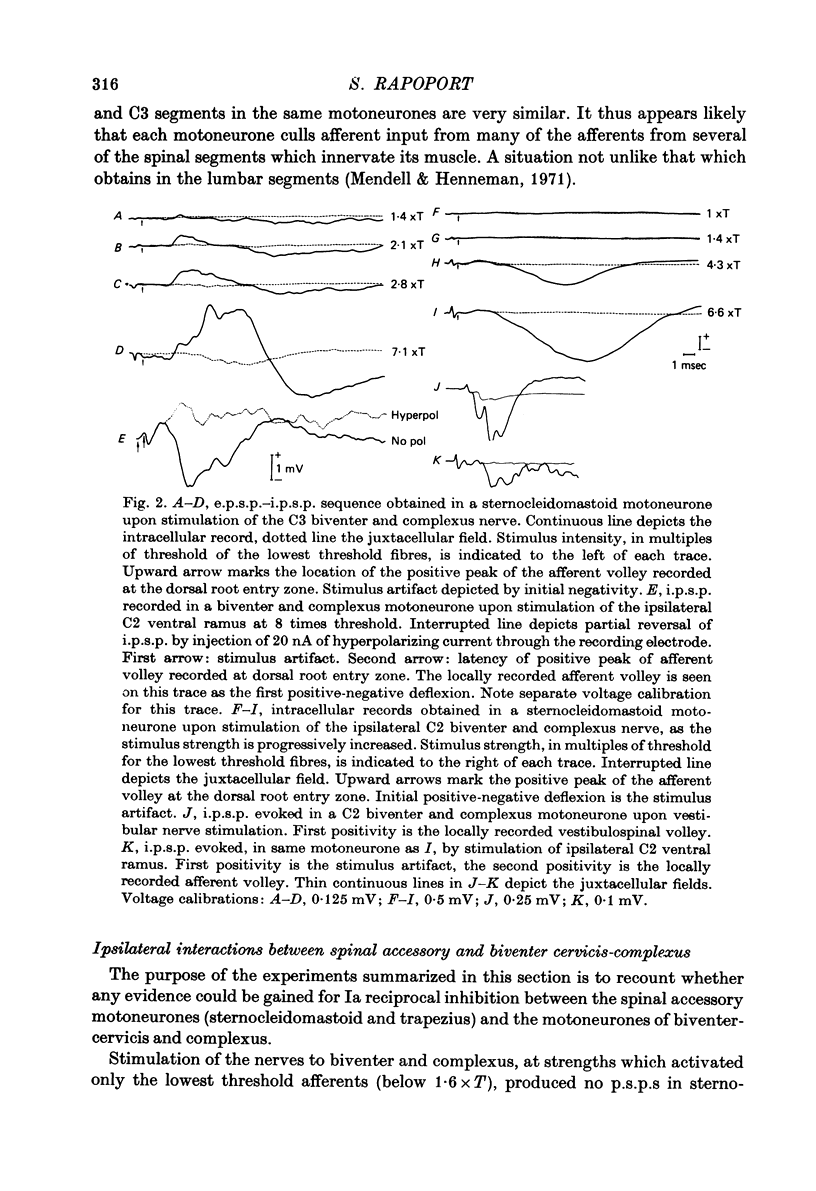
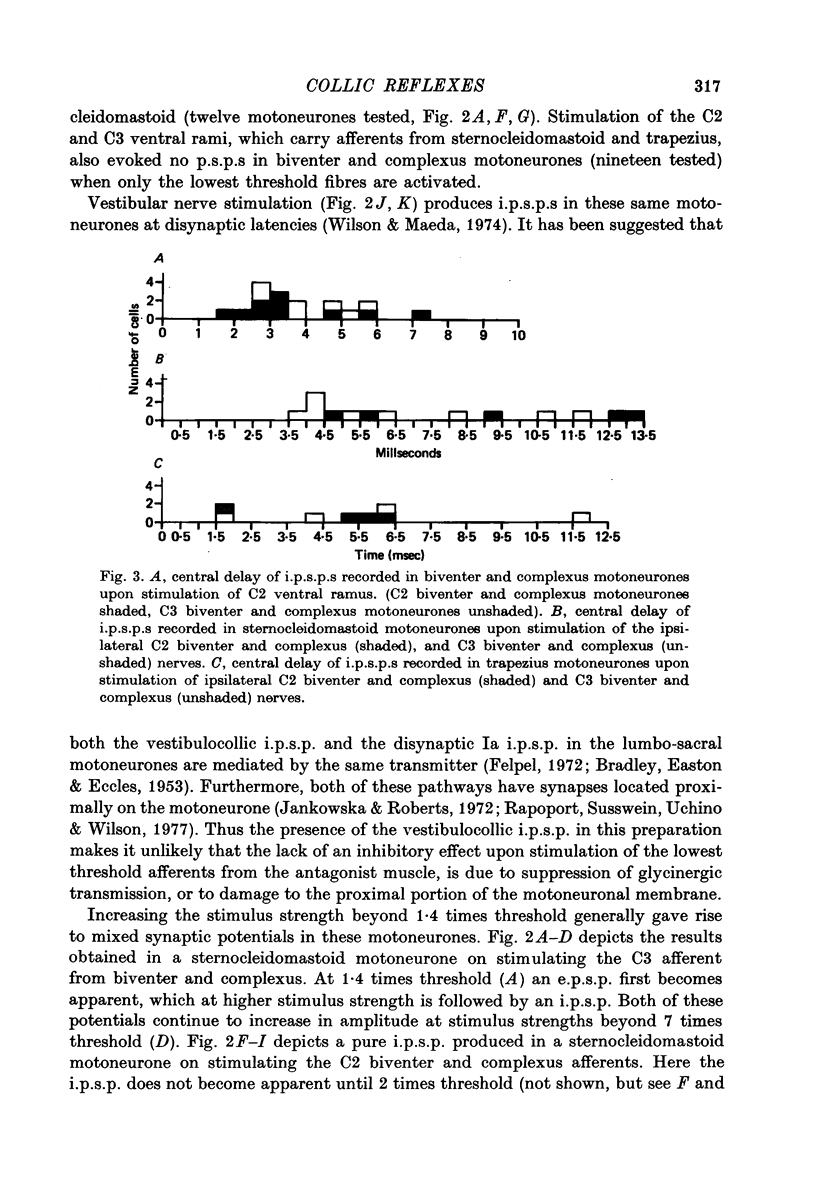
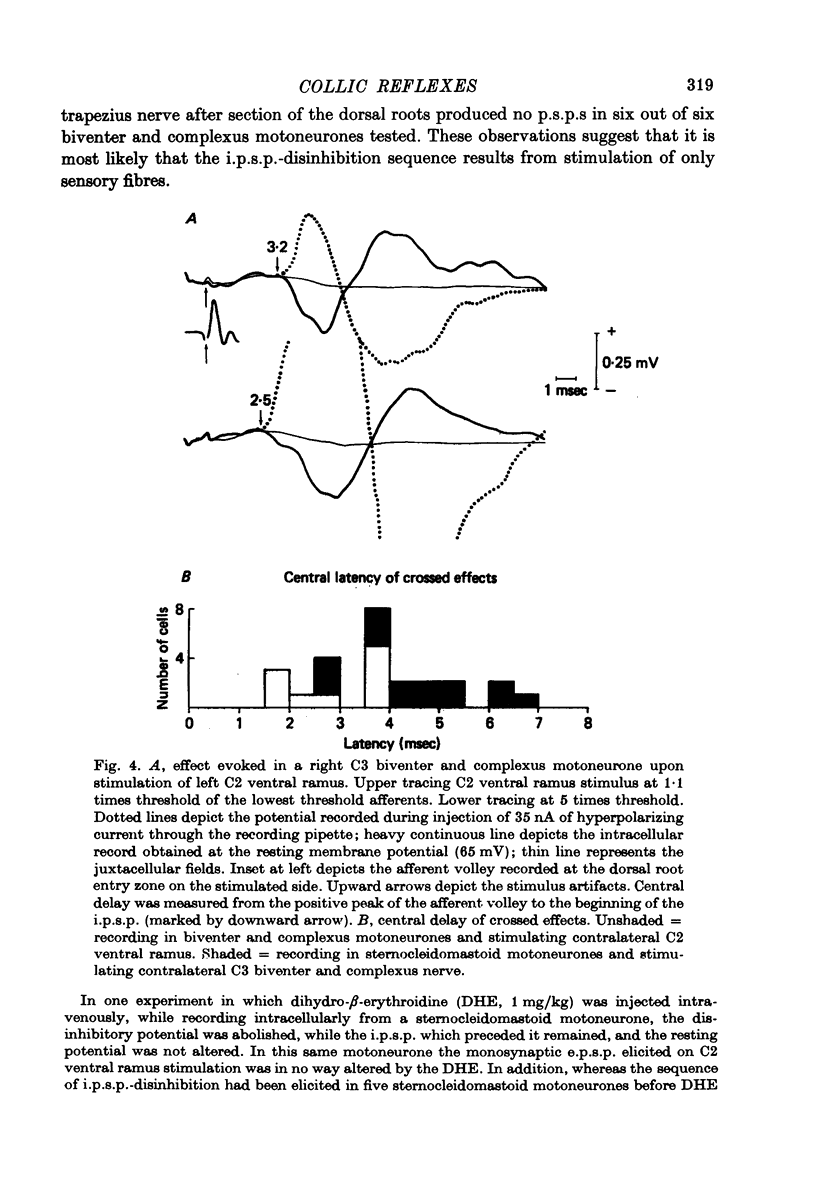
1. The reflex connexions from muscle afferents and ventral root fibres to the motoneurones of the muscles biventer-cervicis, complexus, sternocleidomastoid, trapezius and splenius, the principal muscles involved in head movement in the cat, were studied with the technique of intracellular recording. 2. Electrical stimulation of homonymous muscle afferents of biventer-cervicis and complexus, sternocleidomastoid and trapezius, at strengths below 1.6 times threshold of the dorsal root afferent volley, produced monosynaptic e.p.s.p.s in the corresponding motoneurones. Recruitment of higher threshold muscle afferents produced additional p.s.p.s with longer central delays. 3. Stimulation of low-threshold muscle afferents did not produce any p.s.p.s in the motoneurones of the ipsilateral antagonist. Stimulation of higher threshold afferents evoked i.p.s.p.s with central delays longer than 1.6 msec, or mixed e.p.s.p.-i.p.s.p.s in the ipsilateral antagonist. 4. Mixed e.p.s.p.-i.p.s.p.s or i.p.s.p.s with central delays longer than 1.5 msec were evoked in trapezius motoneurones upon stimulation of high threshold afferents from biventer-cervicis and complexus, while stimulation of low-threshold biventercervicis and complexus afferents evoked no p.s.p.s in trapezius motoneurones. 5. Stimulation of contralateral low-threshold biventer-cervicis and complexus afferents evoked a sequence of i.p.s.p. disinhibition in sternocleidomastoid motoneurones, and vice versa, with central delays longer than 1.7 msec. 6. Stimulation of the deafferented biventer-cervicis, complexus, splenius, sternocleidomastoid and trapezius muscle nerves frequently activated interneurones in the ventral horn at monosynaptic central delays. Activation of homoynmous ventral root fibres rarely evoked p.s.p.s in biventer-cervicis, complexius, splenius or sternocleidomastoid motoneurones, while it produced disynaptic i.p.s.p.s in 80% of trapezius motoneurones. 7. It is concluded that Ia reciprocal inhibition and recurrent inhibition, two reflex circuits which are so prominent in limb segments of the spinal cord, do not play a major role in the generation of head movement. Rather, head movement may be primarily controlled from supraspinal centres.
Full text
PDF











Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson M. E. Segmental reflex inputs to motoneurons innervating dorsal neck musculature in the cat. Exp Brain Res. 1977 May 23;28(1-2):175–187. doi: 10.1007/BF00237095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRADLEY K., EASTON D. M., ECCLES J. C. An investigation of primary or direct inhibition. J Physiol. 1953 Dec 29;122(3):474–488. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1953.sp005015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CURTIS D. R., KRNJEVIC K., MILEDI R. Crossed inhibition of sacral motoneurones. J Neurophysiol. 1958 Jul;21(4):319–326. doi: 10.1152/jn.1958.21.4.319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECCLES J. C., ECCLES R. M., IGGO A., ITO M. Distribution of recurrent inhibition among motoneurones. J Physiol. 1961 Dec;159:479–499. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1961.sp006822. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECCLES J. C., ECCLES R. M., LUNDBERG A. Synaptic actions on motoneurones in relation to the two components of the group I muscle afferent volley. J Physiol. 1957 May 23;136(3):527–546. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005778. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECCLES J. C., FATT P., KOKETSU K. Cholinergic and inhibitory synapses in a pathway from motor-axon collaterals to motoneurones. J Physiol. 1954 Dec 10;126(3):524–562. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005226. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECCLES R. M., LUNDBERG A. Integrative pattern of Ia synaptic actions on motoneurones of hip and knee muscles. J Physiol. 1958 Dec 4;144(2):271–298. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1958.sp006101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felpel L. P. Effects of strychnine, bicuculline and picrotoxin on labyrinthine-evoked inhibition in neck motoneurons of the cat. Exp Brain Res. 1972 Apr 27;14(5):494–502. doi: 10.1007/BF00236591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GILL P. K., KUNO M. PROPERTIES OF PHRENIC MOTONEURONES. J Physiol. 1963 Sep;168:258–273. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRANIT R., PASCOE J. E., STEG G. The behaviour of tonic alpha and gamma motoneurones during stimulation of recurrent collaterals. J Physiol. 1957 Oct 30;138(3):381–400. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLMQVIST B. Crossed spinal reflex actions evoked by volleys in somatic afferents. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl. 1961;52(181):1–66. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hultborn H., Jankowska E., Lindström S., Roberts W. Neuronal pathway of the recurrent facilitation of motoneurones. J Physiol. 1971 Oct;218(2):495–514. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009630. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jankowska E., Roberts W. J. Synaptic actions of single interneurones mediating reciprocal Ia inhibition of motoneurones. J Physiol. 1972 May;222(3):623–642. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009818. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato M., Hirata Y. Sensory neurons in the spinal ventral roots of the cat. Brain Res. 1968 Mar;7(3):479–482. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(68)90018-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato M., Tanji J. Physiological properties of sensory fibers in the spinal ventral roots in the cat. Jpn J Physiol. 1971 Feb;21(1):71–77. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.21.71. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kidokoro Y., Kubota K., Shuto S., Sumino R. Reflex organization of cat masticatory muscles. J Neurophysiol. 1968 Sep;31(5):695–708. doi: 10.1152/jn.1968.31.5.695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendell L. M., Henneman E. Terminals of single Ia fibers: location, density, and distribution within a pool of 300 homonymous motoneurons. J Neurophysiol. 1971 Jan;34(1):171–187. doi: 10.1152/jn.1971.34.1.171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PERL E. R. Crossed reflex effects evoked by activity in myelinated afferent fibers of muscle. J Neurophysiol. 1958 Mar;21(2):101–112. doi: 10.1152/jn.1958.21.2.101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PERL E. R. Effects of muscle stretch on excitability of contralateral motoneurones. J Physiol. 1959 Jan 28;145(1):193–203. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapoport S., Susswein A., Uchino Y., Wilson V. J. Synaptic actions of individual vestibular neurones on cat neck motoneurones. J Physiol. 1977 Nov;272(2):367–382. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp012049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richmond F. J., Abrahams V. C. Morphology and enzyme histochemistry of dorsal muscles of the cat neck. J Neurophysiol. 1975 Nov;38(6):1312–1321. doi: 10.1152/jn.1975.38.6.1312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richmond F. J., Anstee G. C., Sherwin E. A., Abrahams V. C. Motor and sensory fibres of neck muscle nerves in the cat. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1976 Jun;54(3):294–304. doi: 10.1139/y76-043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryall R. W. Renshaw cell mediated inhibition of Renshaw cells: patterns of excitation and inhibition from impulses in motor axon collaterals. J Neurophysiol. 1970 Mar;33(2):257–270. doi: 10.1152/jn.1970.33.2.257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHMIDT R. F., WILLIS W. D. Intracellular recording from motoneurons of the cervical spinal cord of the cat. J Neurophysiol. 1963 Jan;26:28–43. doi: 10.1152/jn.1963.26.1.28. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEARS T. A. SOME PROPERTIES AND REFLEX CONNEXIONS OF RESPIRATORY MOTONEURONES OF THE CAT'S THORACIC SPINAL CORD. J Physiol. 1964 Dec;175:386–403. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1964.sp007523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas R. C., Wilson V. J. Recurrent interactions between motoneurons of known location in the cervical cord of the cat. J Neurophysiol. 1967 Jul;30(4):661–674. doi: 10.1152/jn.1967.30.4.661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILSON V. J., BURGESS P. R. Disinhibition in the cat spinal cord. J Neurophysiol. 1962 May;25:392–404. doi: 10.1152/jn.1962.25.3.392. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson V. J., Maeda M. Connections between semicircular canals and neck motorneurons in the cat. J Neurophysiol. 1974 Mar;37(2):346–357. doi: 10.1152/jn.1974.37.2.346. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson V. J., Yoshida M. Vestibulospinal and reticulospinal effects on hindlimb, forelimb, and neck alpha motoneurons of the cat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Jul;60(3):836–840. doi: 10.1073/pnas.60.3.836. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


