Abstract
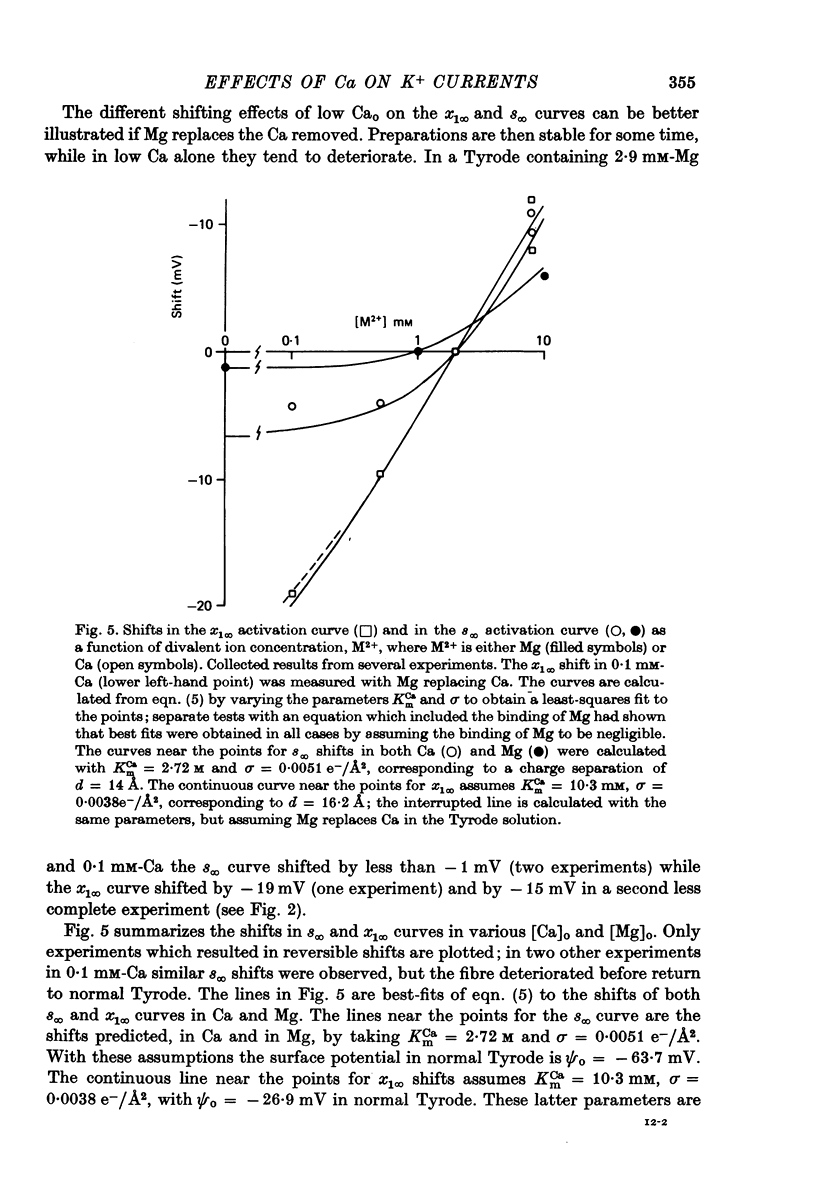
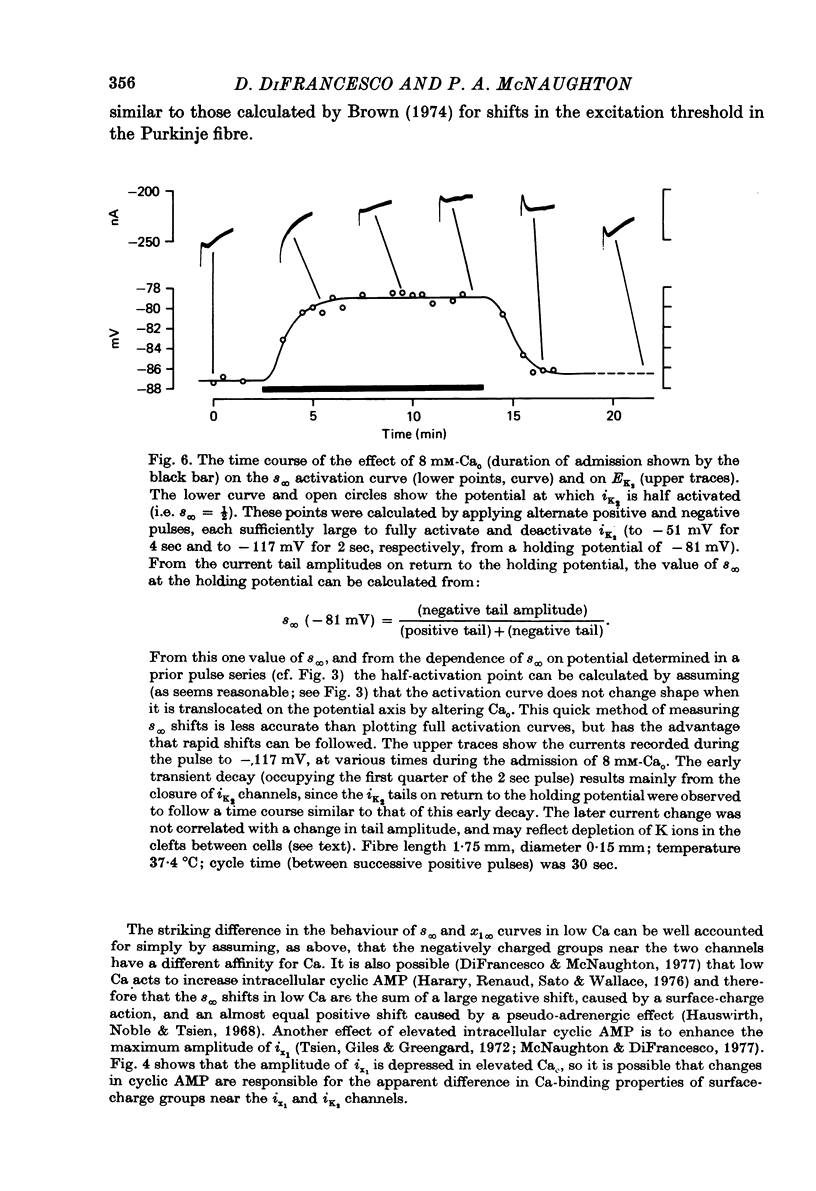
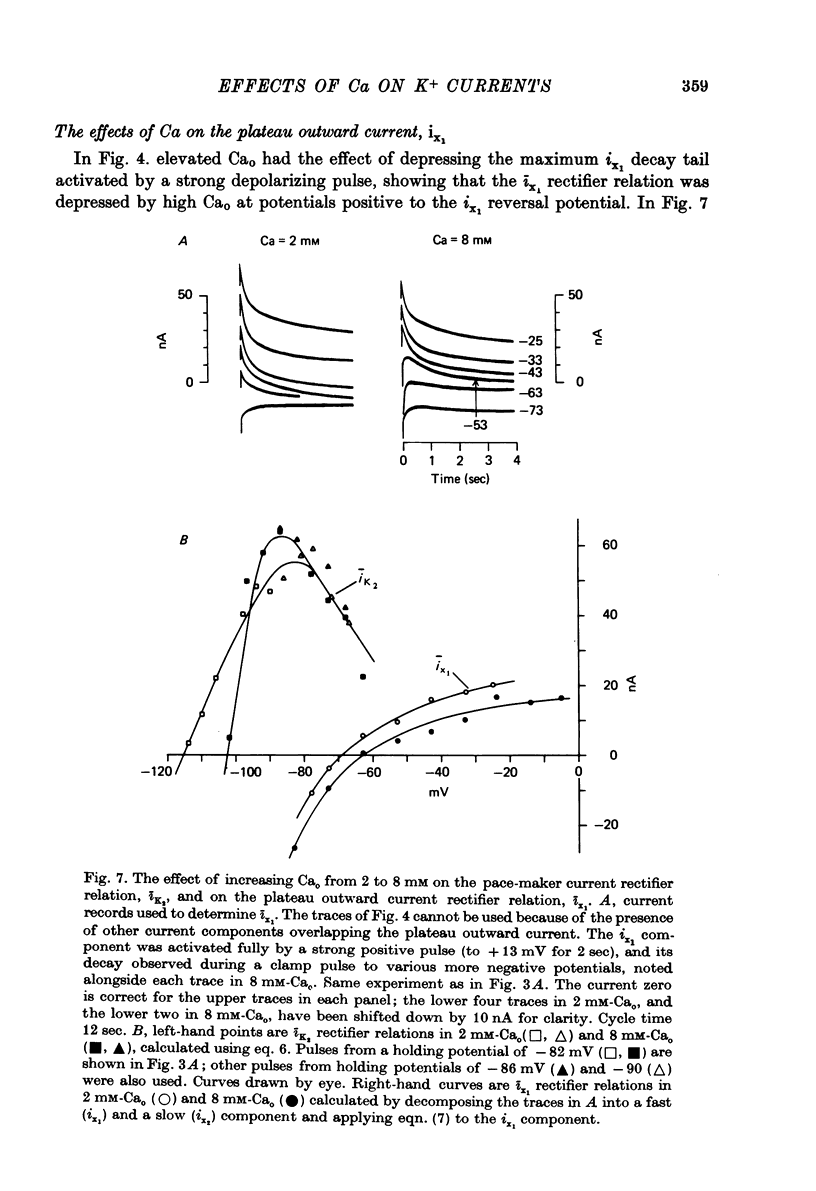
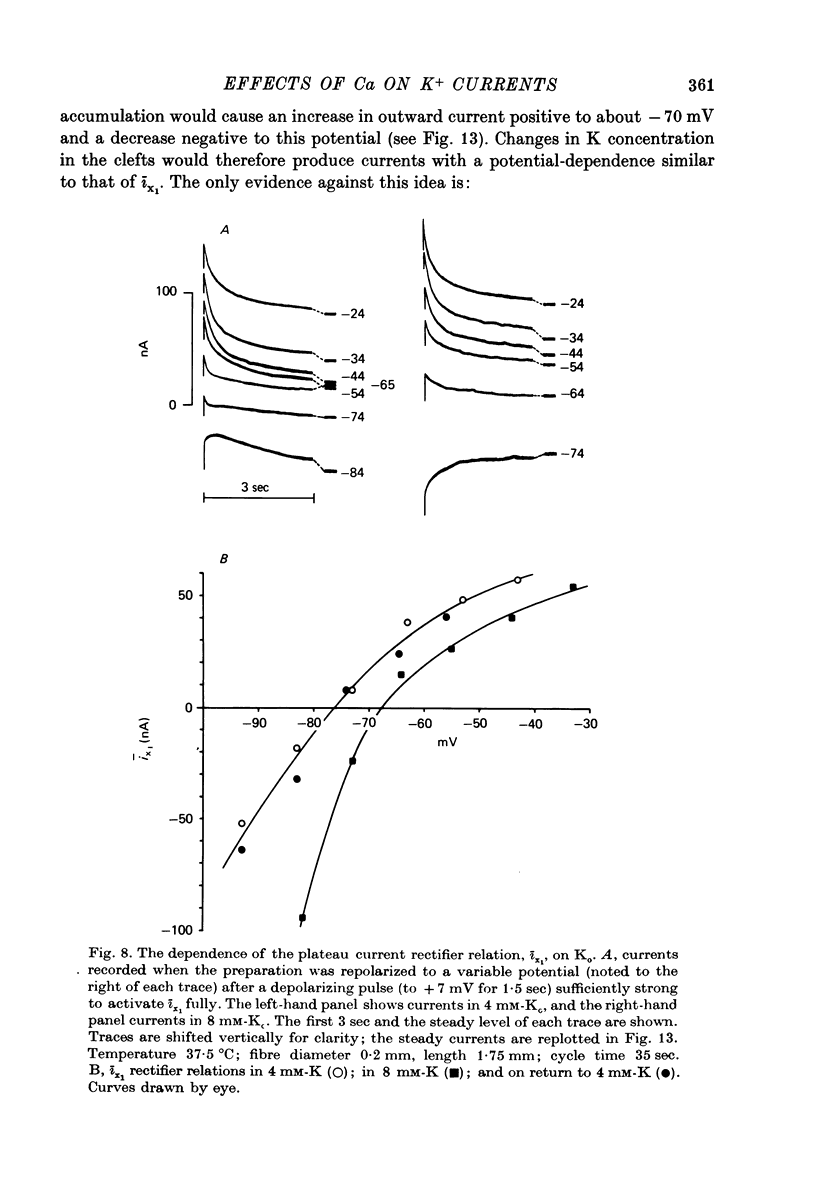
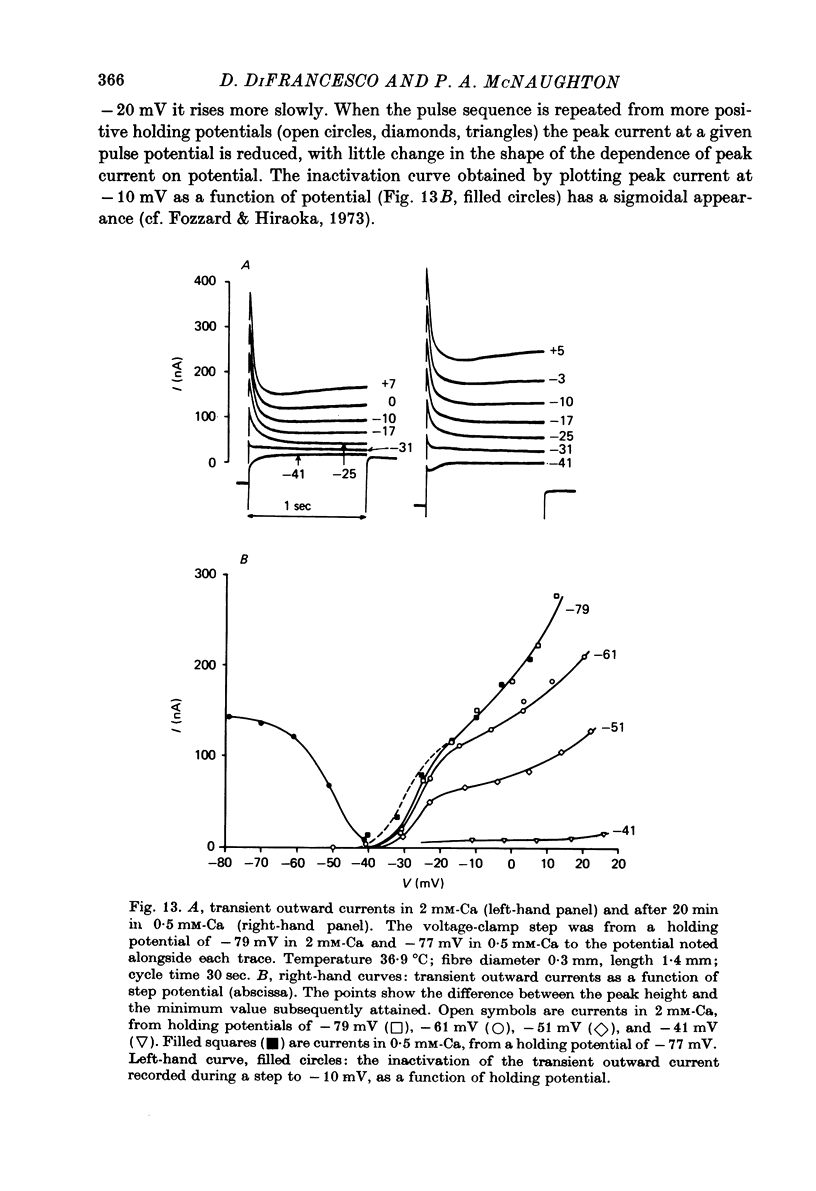
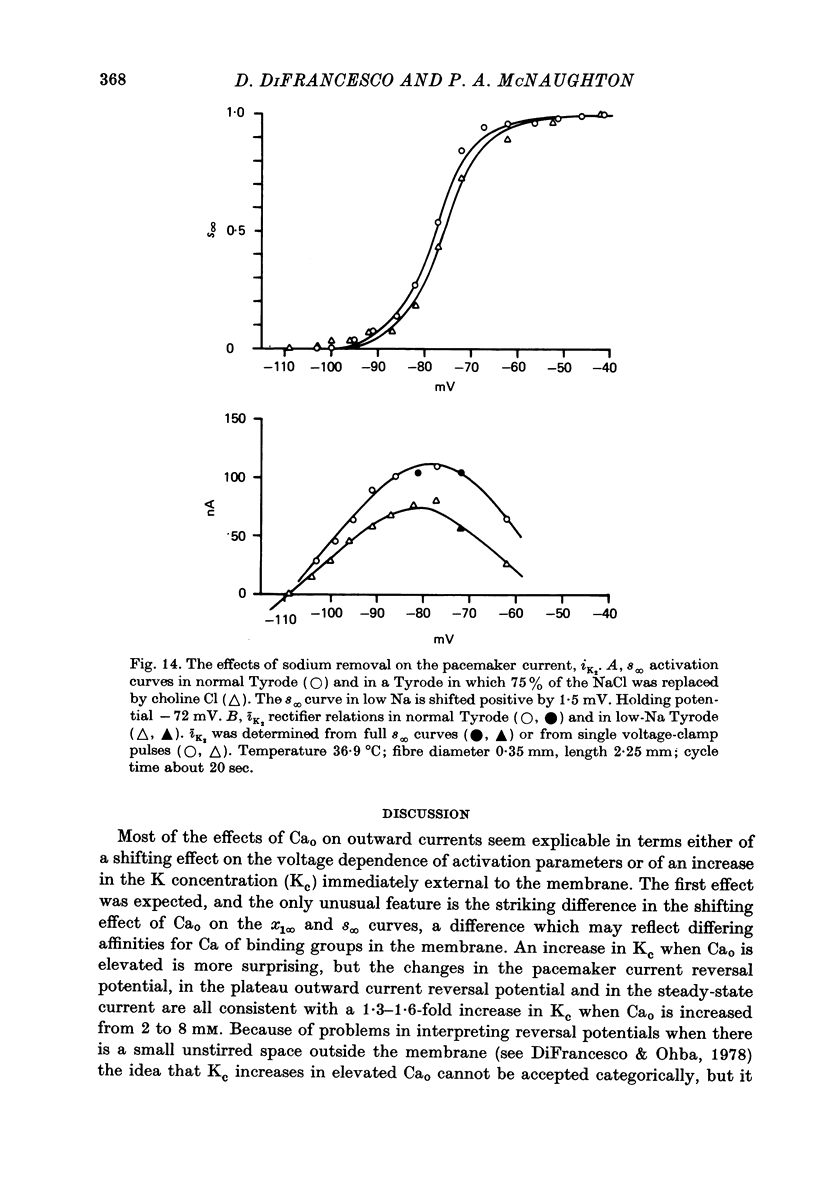
1. Properties of outward membrane currents in Purkinje fibres from sheep's hearts have been studied with particular reference to the effects of external Ca. 2. Altering Cao is found to shift the potential-dependence of channel neutralize negative charges at the external face of the membrane, but the different magnitudes of the effects of low Cao on the pace-maker and plateau currents suggest that the affinities of Ca-binding sites adjacent to each channel type are widely different. 3. Raising Cao causes a positive shift in the pace-maker current reversal potential, EK2, which may reflect a small elevation in the K concentration (Kc) in the restricted cleft space immediately outside the membrane. Other possible causes of the shift in EK2 are also discussed. 4. Raising Cao has effects on the plateau and pace-maker current rectifier relations, and on the time-independent membrane current, which resemble those of a small increase in extracellular K concentration. 5. Possible mechanisms for an increase in Kc in elevated Cao are discussed. Positive shifts in EK2 can be observed even when the membrane current becomes more inward, so it seems unlikely that the increase in Kc results from an activation of K channels by Ca ions. It is possible that increases in Ca partially inhibit the Na:K exchange pump. 6. The maximum transient outward current elicited by strong depolarizing steps is not affected by moderate reductions in Cao. 7. Reducing Nao depresses the pace-maker current rectifier relation with little shift in the activation curve. 8. We conclude that some of the effects of Cao on outward currents are due to shifts in the potential-dependence of channel activation, while others result from a small increase in Kc. No evidence for a direct effect of Ca on K channels has been found in the present study.
Full text
PDF












Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen D. G., Blinks J. R. Calcium transients in aequorin-injected frog cardiac muscle. Nature. 1978 Jun 15;273(5663):509–513. doi: 10.1038/273509a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. F., McNaughton P. A. The influence of extracellular calcium binding on the calcium efflux from squid axons. J Physiol. 1978 Mar;276:127–150. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bassingthwaighte J. B., Fry C. H., McGuigan J. A. Relationship between internal calcium and outward current in mammalian ventricular muscle; a mechanism for the control of the action potential duration? J Physiol. 1976 Oct;262(1):15–37. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumgarten C. M., Isenberg G. Depletion and accumulation of potassium in the extracellular clefts of cardiac Purkinje fibers during voltage clamp hyperpolarization and depolarization. Pflugers Arch. 1977 Mar 11;368(1-2):19–31. doi: 10.1007/BF01063450. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown R. H., Jr Membrane surface charge: discrete and uniform modelling. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1974;28:341–370. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(74)90021-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carmeliet E., Verdonck F. Reduction of potassium permeability by chloride substitution in cardiac cells. J Physiol. 1977 Feb;265(1):193–206. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011712. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler W. K., Hodgkin A. L., Meves H. The effect of changing the internal solution on sodium inactivation and related phenomena in giant axons. J Physiol. 1965 Oct;180(4):821–836. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clusin W., Spray D. C., Bennett M. V. Activation of a voltage-insensitive conductance by inward calcium current. Nature. 1975 Jul 31;256(5516):425–427. doi: 10.1038/256425a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiFrancesco D., Ohba M. Dependence of the apparent reversal potential for the pace-maker current iK2 on its degree of activation in cardiac Purkinje fibres [proceedings]. J Physiol. 1978 Jul;280:73P–74P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudel J., Peper K., Rüdel R., Trautwein W. The dynamic chloride component of membrane current in Purkinje fibers. Pflugers Arch Gesamte Physiol Menschen Tiere. 1967;295(3):197–212. doi: 10.1007/BF01844100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis D. The effects of external cations and ouabain on the intracellular sodium activity of sheep heart Purkinje fibres. J Physiol. 1977 Dec;273(1):211–240. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp012090. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANKENHAEUSER B., HODGKIN A. L. The action of calcium on the electrical properties of squid axons. J Physiol. 1957 Jul 11;137(2):218–244. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005808. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons W. R., Fozzard H. A. Slow inward current and contraction of sheep cardiac Purkinje fibers. J Gen Physiol. 1975 Mar;65(3):367–384. doi: 10.1085/jgp.65.3.367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert D. L., Ehrenstein G. Effect of divalent cations on potassium conductance of squid axons: determination of surface charge. Biophys J. 1969 Mar;9(3):447–463. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(69)86396-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALL A. E., HUTTER O. F., NOBLE D. Current-voltage relations of Purkinje fibres in sodium-deficient solutions. J Physiol. 1963 Apr;166:225–240. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HUXLEY A. F. A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. J Physiol. 1952 Aug;117(4):500–544. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harary I., Renaud J. F., Sato E., Wallace G. A. Calcium ions regulate cyclic AMP and beating in cultured heart cells. Nature. 1976 May 6;261(5555):60–61. doi: 10.1038/261060a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauswirth O., Noble D., Tsien R. W. Adrenaline: mechanism of action on the pacemaker potential in cardiac Purkinje fibers. Science. 1968 Nov 22;162(3856):916–917. doi: 10.1126/science.162.3856.916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isenberg G. Cardiac Purkinje fibres: [Ca2+]i controls steady state potassium conductance. Pflugers Arch. 1977 Oct 19;371(1-2):71–76. doi: 10.1007/BF00580774. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isenberg G. Cardiac Purkinje fibres: [Ca2+]i controls the potassium permeability via the conductance components gK1 and gK2. Pflugers Arch. 1977 Oct 19;371(1-2):77–85. doi: 10.1007/BF00580775. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isenberg G. Cardiac Purkinje fibres: resting, action, and pacemaker potential under the influence of [Ca2+]i as modified by intracellular injection techniques. Pflugers Arch. 1977 Oct 19;371(1-2):51–59. doi: 10.1007/BF00580772. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isnberg G. Is potassium conductance of cardiac Purkinje fibres controlled by (Ca2+)? Nature. 1975 Jan 24;253(5489):273–274. doi: 10.1038/253273a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kass R. S., Tsien R. W. Control of action potential duration by calcium ions in cardiac Purkinje fibers. J Gen Physiol. 1976 May;67(5):599–617. doi: 10.1085/jgp.67.5.599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kass R. S., Tsien R. W. Multiple effects of calcium antagonists on plateau currents in cardiac Purkinje fibers. J Gen Physiol. 1975 Aug;66(2):169–192. doi: 10.1085/jgp.66.2.169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenyon J. L., Gibbons W. R. Effects of low-chloride solutions on action potentials of sheep cardiac Purkinje fibers. J Gen Physiol. 1977 Nov;70(5):635–660. doi: 10.1085/jgp.70.5.635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krnjević K., Lisiewicz A. Injections of calcium ions into spinal motoneurones. J Physiol. 1972 Sep;225(2):363–390. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAllister R. E., Noble D. The time and voltage dependence of the slow outward current in cardiac Purkinje fibres. J Physiol. 1966 Oct;186(3):632–662. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp008060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald T. F., Trautwein W. The potassium current underlying delayed rectification in cat ventricular muscle. J Physiol. 1978 Jan;274:217–246. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meech R. W., Standen N. B. Potassium activation in Helix aspersa neurones under voltage clamp: a component mediated by calcium influx. J Physiol. 1975 Jul;249(2):211–239. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meech R. W. The sensitivity of Helix aspersa neurones to injected calcium ions. J Physiol. 1974 Mar;237(2):259–277. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mobley B. A., Page E. The surface area of sheep cardiac Purkinje fibres. J Physiol. 1972 Feb;220(3):547–563. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009722. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NIEDERGERKE R. The staircase phenomenon and the action of calcium on the heart. J Physiol. 1956 Dec 28;134(3):569–583. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noble D., Tsien R. W. Outward membrane currents activated in the plateau range of potentials in cardiac Purkinje fibres. J Physiol. 1969 Jan;200(1):205–231. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noble D., Tsien R. W. The kinetics and rectifier properties of the slow potassium current in cardiac Purkinje fibres. J Physiol. 1968 Mar;195(1):185–214. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008454. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OTSUKA M. Die Wirkung von Adrenalin auf Purkinje-Fasern von Säugetierherzen. Pflugers Arch. 1958;266(5):512–517. doi: 10.1007/BF00362255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peper K., Trautwein W. A note on the pacemaker current in Purkinje fibers. Pflugers Arch. 1969 Jun 19;309(4):356–361. doi: 10.1007/BF00587758. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiter M., Stickel F. J. Der Einfluss der Kontraktionsfrequenz auf das Aktionspotential des Meerschweinchem-Papillarmuskels. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Exp Pathol Pharmakol. 1968;260(4):342–365. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reuter H. Slow inactivation of currents in cardiac Purkinje fibres. J Physiol. 1968 Jul;197(1):233–253. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegelbaum S. A., Tsien R. W., Kass R. S. Role of intracellular calcium in the transient outward current of calf Purkinje fibres. Nature. 1977 Oct 13;269(5629):611–613. doi: 10.1038/269611a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. W., Giles W., Greengard P. Cyclic AMP mediates the effects of adrenaline on cardiac purkinje fibres. Nat New Biol. 1972 Dec 6;240(101):181–183. doi: 10.1038/newbio240181a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vitek M., Trautwein W. Slow inward current and action potential in cardiac Purkinje fibres. The effect of Mn plus,plus-ions. Pflugers Arch. 1971;323(3):204–218. doi: 10.1007/BF00586384. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEIDMANN S. The electrical constants of Purkinje fibres. J Physiol. 1952 Nov;118(3):348–360. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


