Abstract
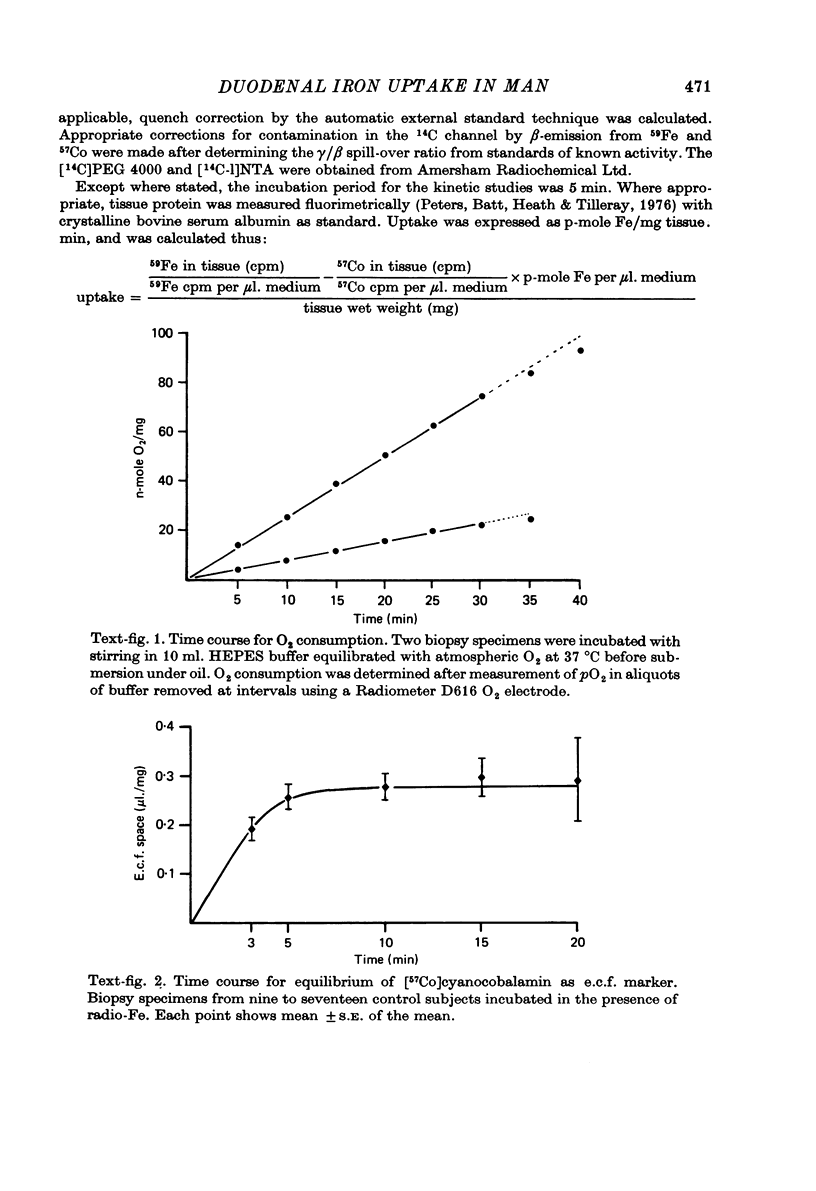
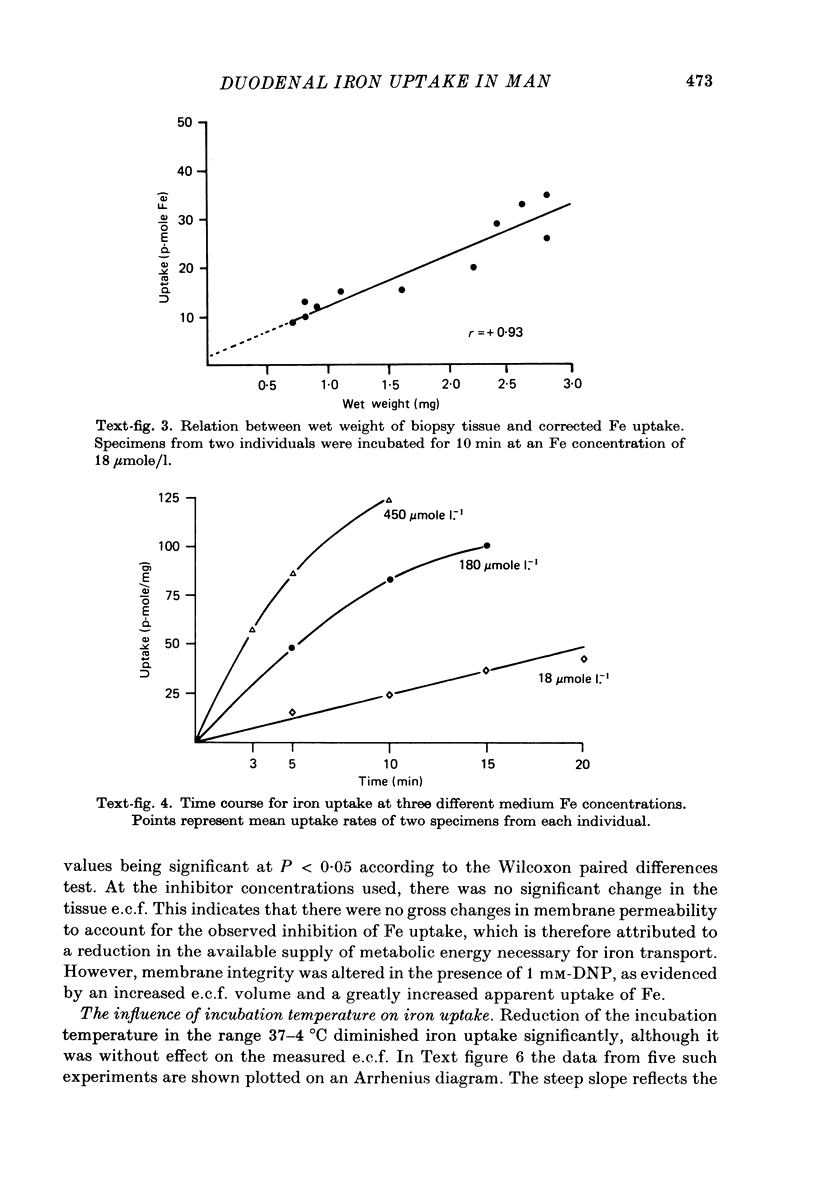
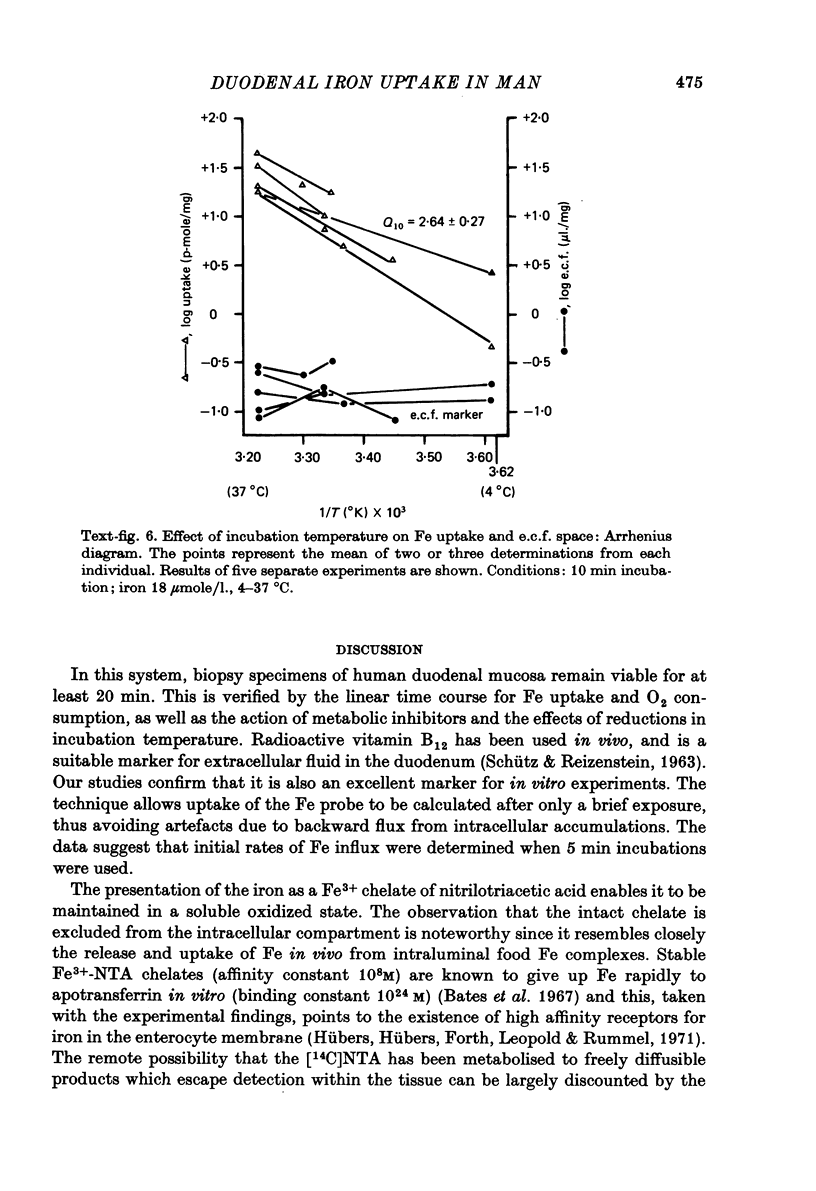
1. A method for determining initial rates of unidirectional radio-Fe uptake from a ferric chelate of nitrilotriacetic acid by human duodenal biopsy specimens in vitro has been devised. [57Co]cyanocobalamin was used as an extracellular fluid marker, and was shown to give results in close agreement with other markers. 2. Uptake was linear for up to 20 min and exhibited saturation kinetics over the concentration range 18--450 mumole/1. 3. In the presence of 2:4 dinitrophenol and fluoride, uptake was reduced by approxi-50%, indicating dependence on metabolic energy. 4. Uptake of Fe was markedly diminished at reduced incubation temperatures, demonstrating a high activation energy for the uptake process. 5. Many of the criteria for the demonstration that the initial uptake of Fe depends on an active transport mechanism have been fulfilled. 6. The apparent distribution volume of 14C-labelled nitrilotriacetate chelate did not exceed the extracellular fluid space, suggesting that Fe is transferred to specific receptors on the enterocyte. The findings are discussed in relation to the possibility that uptake may be a rate-controlling step for the regulation of net intestinal absorption of Fe in man.
Full text
PDF
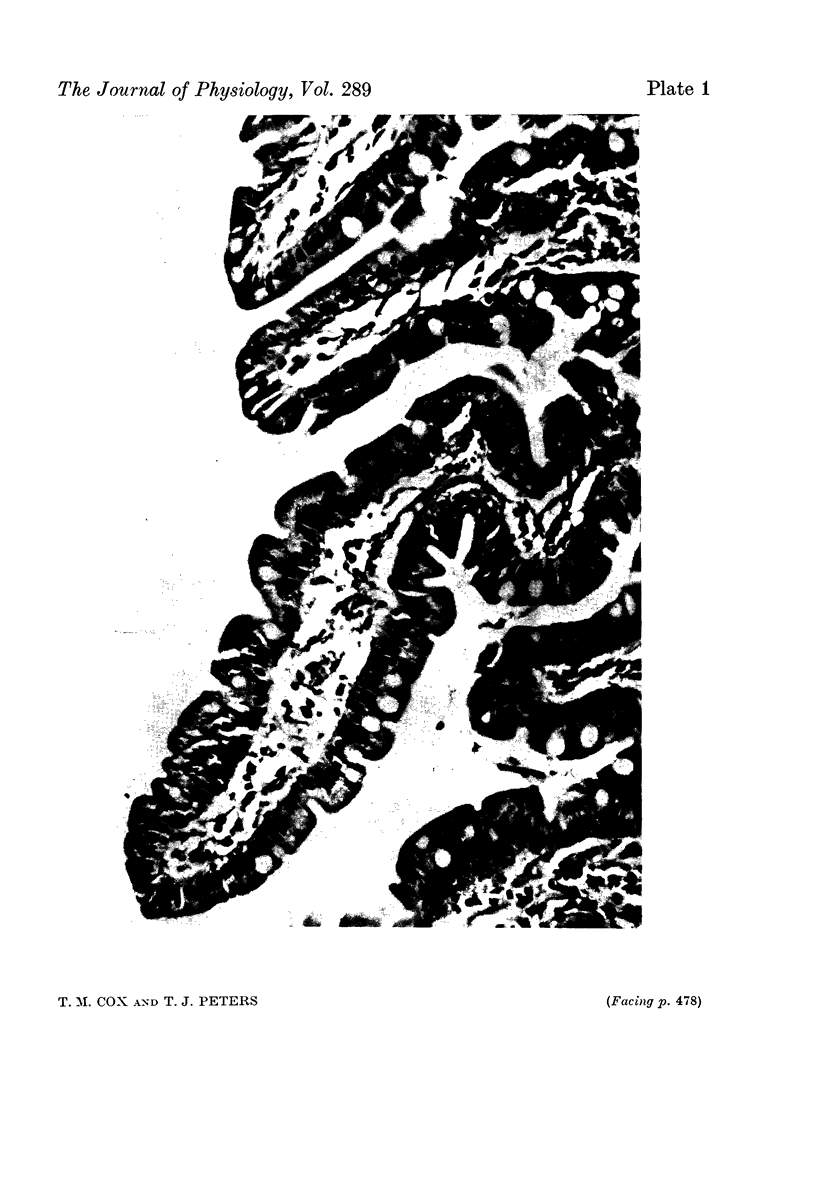







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acheson L. S., Schultz S. G. Iron influx across the brush border of rabbit duodenum: effects of anemia and iron loading. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Feb 11;255(2):479–483. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(72)90151-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bates G. W., Billups C., Saltman P. The kinetics and mechanism of iron (3) exchange between chelates and transferrin. I. The complexes of citrate and nitrilotriacetic acid. J Biol Chem. 1967 Jun 25;242(12):2810–2815. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CONRAD M. E., Jr, CROSBY W. H. INTESTINAL MUCOSAL MECHANISMS CONTROLLING IRON ABSORPTION. Blood. 1963 Oct;22:406–415. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRANE R. K., MANDELSTAM P. The active transport of sugars by various preparations of hamster intestine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 Dec 18;45:460–476. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)91482-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox T. M., Peters T. J. Uptake of iron by duodenal biopsy specimens from patients with iron-deficiency anaemia and primary haemochromatosis. Lancet. 1978 Jan 21;1(8056):123–124. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)90420-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOWDLE E. B., SCHACHTER D., SCHENKER H. Active transport of Fe59 by everted segments of rat duodenum. Am J Physiol. 1960 Mar;198:609–613. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1960.198.3.609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Good N. E., Winget G. D., Winter W., Connolly T. N., Izawa S., Singh R. M. Hydrogen ion buffers for biological research. Biochemistry. 1966 Feb;5(2):467–477. doi: 10.1021/bi00866a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOFSTEE B. H. J. On the evaluation of the constants Vm and KM in enzyme reactions. Science. 1952 Sep 26;116(3013):329–331. doi: 10.1126/science.116.3013.329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JACOBI H., PFLEGER K., RUMMEL W. Komplexbildner und aktiver Eisentransport durch die Darmwand. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Exp Pathol Pharmakol. 1956;229(2):198–206. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs A., Miles P. M. Intraluminal transport of iron from stomach to small-intestinal mucosa. Br Med J. 1969 Dec 27;4(5686):778–781. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5686.778. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs P., Bothwell T. H., Charlton R. W. Intestinal iron transport: studies using a loop of gut with an artificial circulation. Am J Physiol. 1966 Apr;210(4):694–700. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1966.210.4.694. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michael W. R., Wakim J. M. Metabolism of nitrilotriacetic acid (NTA). Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1971 Feb;18(2):407–416. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(71)90133-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orlic D. The use of 55Fe in high-resolution radioautography of developing red cells. J Cell Biol. 1968 Oct;39(1):201–208. doi: 10.1083/jcb.39.1.201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters T. J., Batt R. M., Heath J. R., Tilleray J. The micro-assay of intestinal disaccharidases. Biochem Med. 1976 Apr;15(2):145–148. doi: 10.1016/0006-2944(76)90041-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHUETZ H. B., REIZENSTEIN P. RADIOVITAMIN B12 AS A DILUTION INDICATOR IN GASTROINTESTINAL RESEARCH. Am J Dig Dis. 1963 Nov;8:904–907. doi: 10.1007/BF02232085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sallee V. L., Wilson F. A., Dietschy J. M. Determination of unidirectional uptake rates for lipids across the intestinal brush border. J Lipid Res. 1972 Mar;13(2):184–192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheehan R. G. Unidirectional uptake of iron across intestinal brush border. Am J Physiol. 1976 Nov;231(5 Pt 1):1438–1444. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1976.231.5.1438. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THIER S. O., SEGAL S., FOX M., BLAIR A., ROSENBERG L. E. CYSTINURIA: DEFECTIVE INTESTINAL TRANSPORT OF DIBASIC AMINO ACIDS AND CYSTINE. J Clin Invest. 1965 Mar;44:442–448. doi: 10.1172/JCI105157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]