Abstract
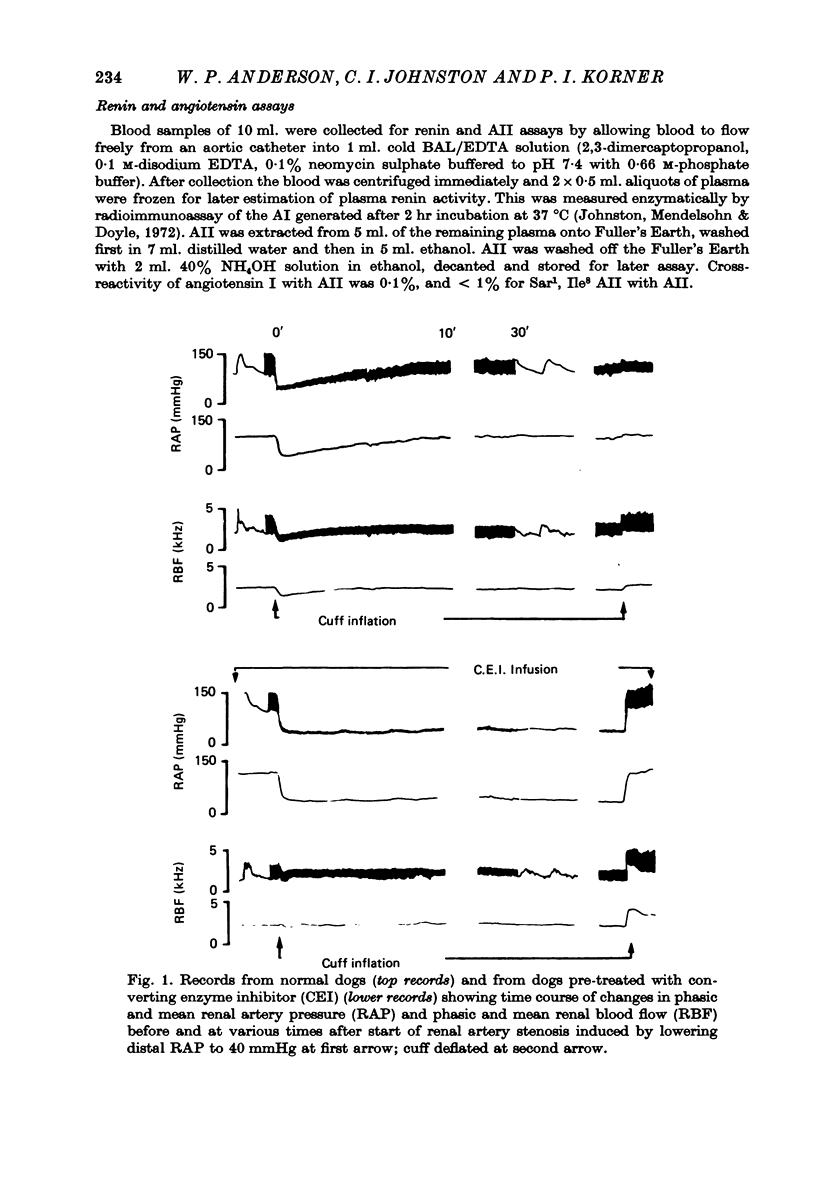
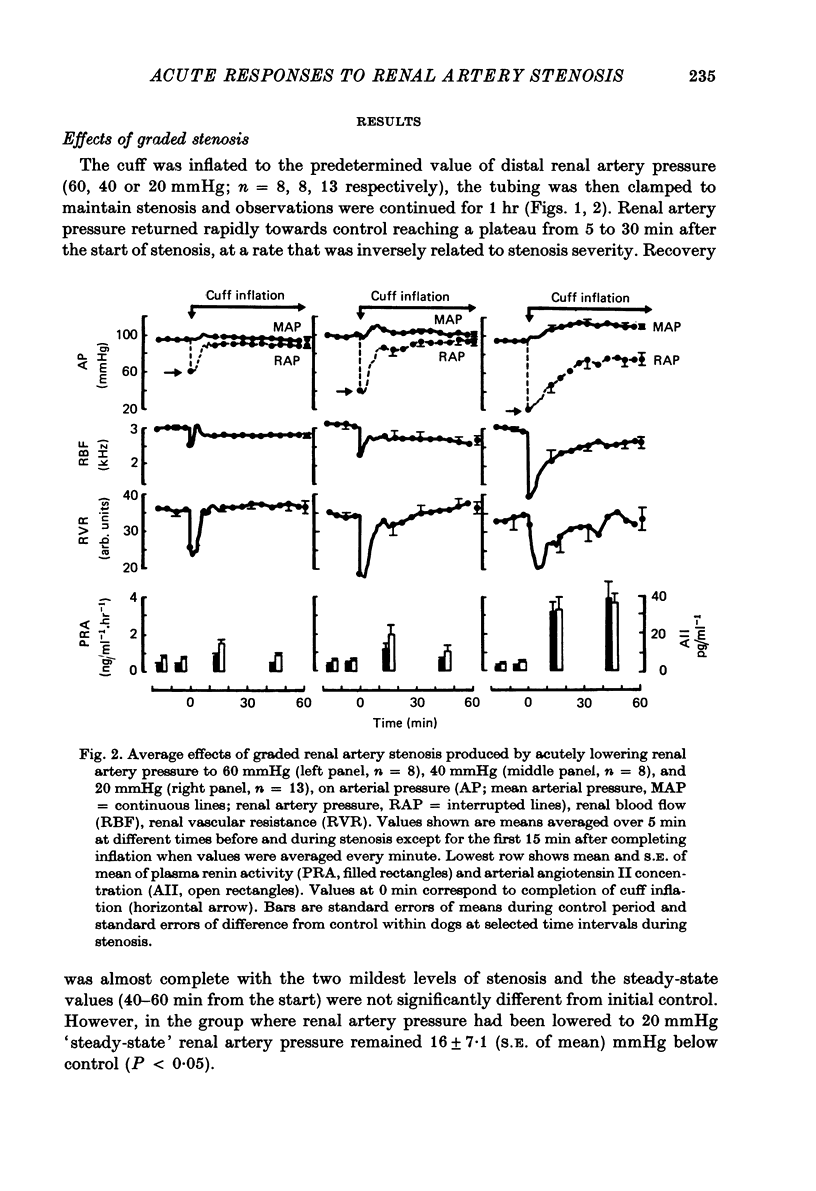
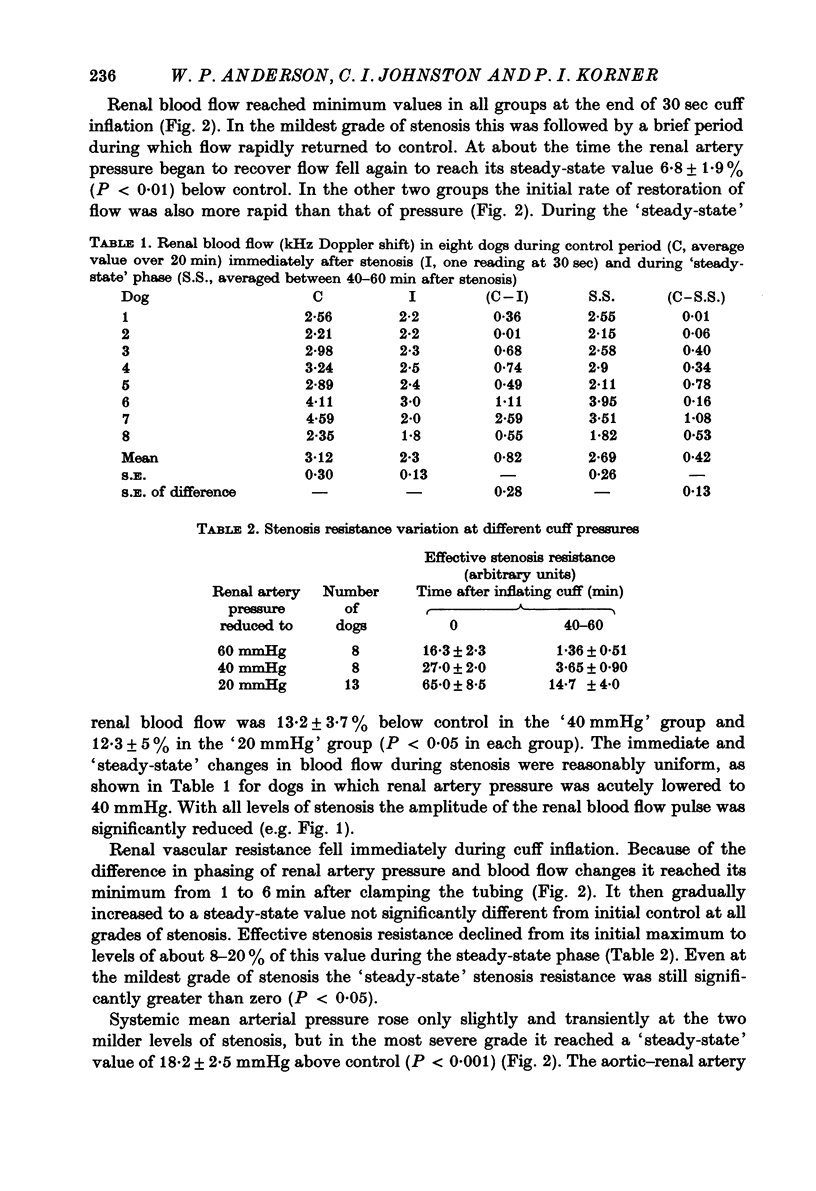
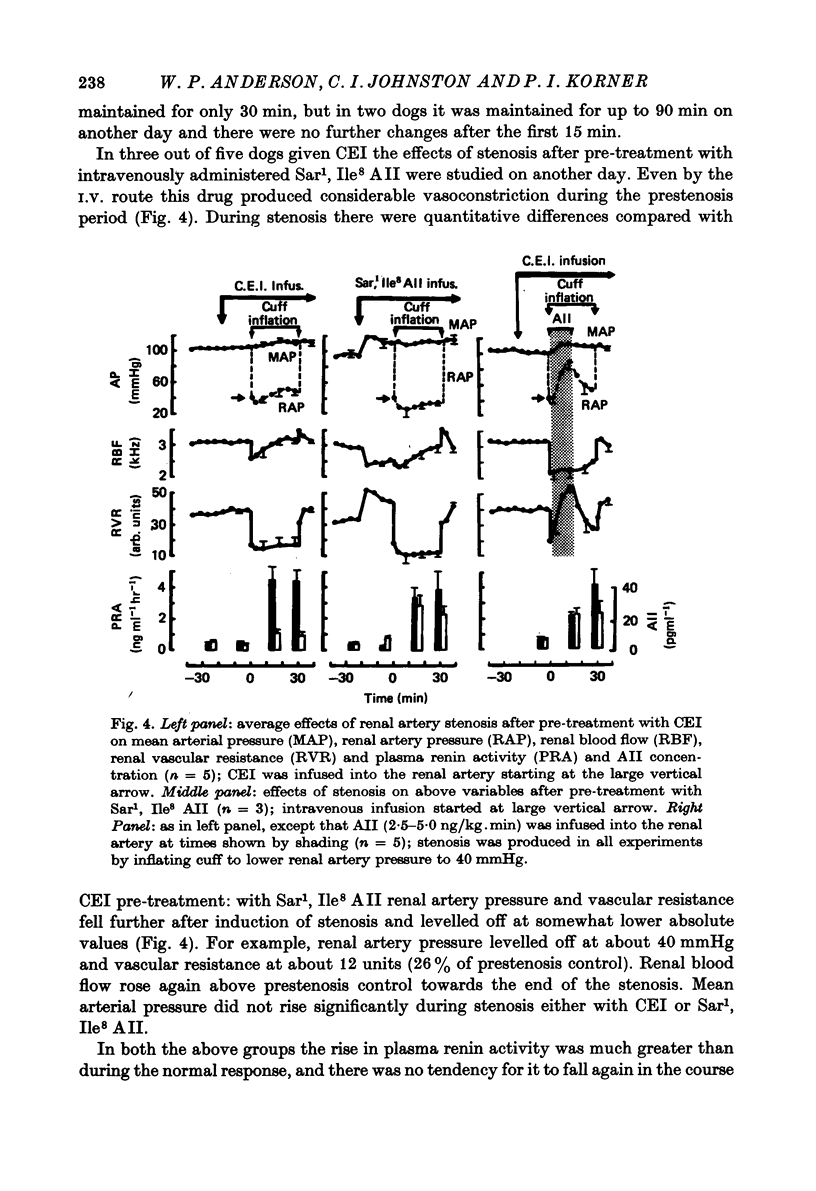
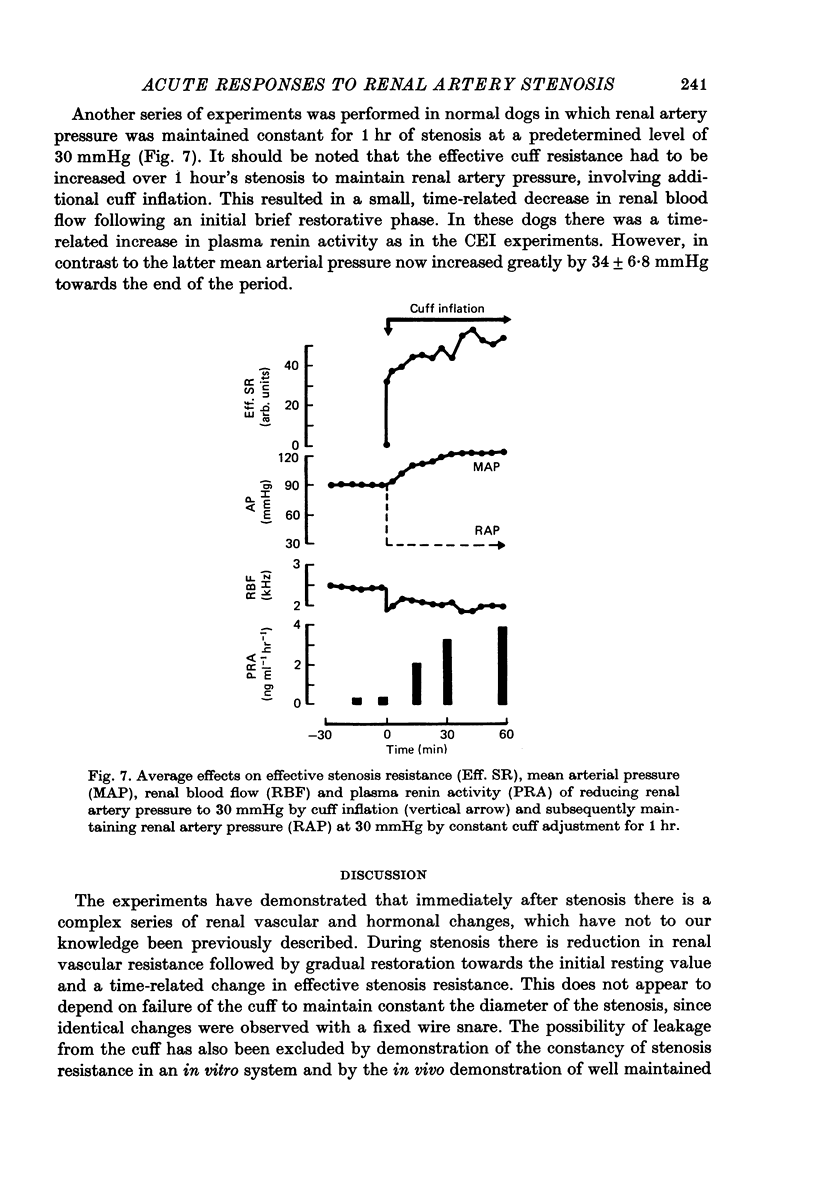
1. The acute renal haemodynamic and renin-angiotensin system responses to graded renal artery stenosis were studied in chronically instrumented, unanaesthetized dogs. 2. Stenosis was induced over 30 sec by inflation of a cuff around the renal artery to lower distal pressure to 60, 40 or 20 mmHg, with stenosis maintained for 1 hr. This resulted in an immediate fall in renal vascular resistance, but over the next 5--30 min both resistance and renal artery pressure were restored back towards prestenosis values. Only transient increases in systemic arterial blood pressure and plasma renin and angiotensin levels were seen with the two milder stenoses. Despite restoration of renal artery pressure, renal blood flow remained reduced at all grades of stenosis. 3. Pre-treatment with angiotensin I converting enzyme inhibitor or sarosine1, isoleucone8 angiotensin II greatly attenuated or abolished the restoration of renal artery pressure and renal vascular resistance after stenosis, and plasma renin and angiotensin II levels remained high. Renal dilatation was indefinitely maintained, but the normal restoration of resistance and pressure could be simulated by infusing angiotensin II into the renal artery. 4. The effective resistance to blood flow by the stenosis did not remain constant but varied with changes in the renal vascular resistance.
Full text
PDF









Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson W. P., Korner P. I., Johnston C. I., Angus J. A., Casley D. J. Intrarenal action of angiotensin II in restoring renal artery pressure after acute renal artery stenosis. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 1978 Sep-Oct;5(5):529–533. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1681.1978.tb00706.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ayers C. R., Katholi R. E., Vaughan E. D., Jr, Carey R. M., Kimbrough H. M., Jr, Yancey M. R., Morton C. L. Intrarenal renin-angiotensin-sodium interdependent mechanism controlling postclamp renal artery pressure and renin release in the conscious dog with chronic one-kidney Goldblatt hypertension. Circ Res. 1977 Mar;40(3):238–242. doi: 10.1161/01.res.40.3.238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berguer R., Hwang N. H. Critical arterial stenosis: a theoretical and experimental solution. Ann Surg. 1974 Jul;180(1):39–50. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197407000-00007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis J. O., Freeman R. H. Mechanisms regulating renin release. Physiol Rev. 1976 Jan;56(1):1–56. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1976.56.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fekete A. Functions of the kidney after ligation of the renal artery. Acta Med Acad Sci Hung. 1967;23(4):353–363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrario C. M., McCubbin J. W. Renal blood flow and perfusion pressure before and after development of renal hypertension. Am J Physiol. 1973 Jan;224(1):102–109. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1973.224.1.102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fletcher P. J., Korner P. I., Angus J. A., Oliver J. R. Changes in cardiac output and total peripheral resistance during development of renal hypertension in the rabbit: lack of confomity with the autoregulation theory. Circ Res. 1976 Nov;39(5):633–639. doi: 10.1161/01.res.39.5.633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fray J. C., Siwek L. G., Strull W. M., Steller R. N., Wilson J. M. Influence of dietary sodium on renin activity and arterial pressure during anesthesia. Am J Physiol. 1976 Oct;231(4):1185–1190. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1976.231.4.1185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould K. L., Lipscomb K., Hamilton G. W. Physiologic basis for assessing critical coronary stenosis. Instantaneous flow response and regional distribution during coronary hyperemia as measures of coronary flow reserve. Am J Cardiol. 1974 Jan;33(1):87–94. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(74)90743-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granger P., Dahlheim H., Thurau K. Enzyme activities of the single juxtaglomerular apparatus in the rat kidney. Kidney Int. 1972 Feb;1(2):78–88. doi: 10.1038/ki.1972.11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERD J. A., BARGER A. C. SIMPLIFIED TECHNIQUE FOR CHRONIC CATHETERIZATION OF BLOOD VESSELS. J Appl Physiol. 1964 Jul;19:791–792. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1964.19.4.791. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall J. E., Guyton A. C., Jackson T. E., Coleman T. G., Lohmeier T. E., Trippodo N. C. Control of glomerular filtration rate by renin-angiotensin system. Am J Physiol. 1977 Nov;233(5):F366–F372. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1977.233.5.F366. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris R. C., Ayers C. R. Renal hemodynamics and plasma renin activity after renal artery constriction in conscious dogs. Circ Res. 1972 Oct;31(4):520–530. doi: 10.1161/01.res.31.4.520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofbauer K. G., Zschiedrich H., Gross F. Regulation of renin release and intrarenal formation of angiotensin. Studies in the isolated perfused rat kidney. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 1976 Jan-Feb;3(1):73–93. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1681.1976.tb00593.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson T. E., Guyton A. C., Hall J. E. Transient response of glomerular filtration rate and renal blood flow to step changes in arterial pressure. Am J Physiol. 1977 Nov;233(5):F396–F402. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1977.233.5.F396. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston C. I., Mendelsohn F. A., Doyle A. E. Metabolism of angiotensin II in sodium depletion and hypertension in humans. Circ Res. 1972 Sep;31(9 Suppl):203–213. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korner P. I., Stokes G. S., White S. W., Chalmers J. P. Role of the autonomic nervous system in the renal vasoconstriction response to hemorrhage in the rabbit. Circ Res. 1967 Jun;20(6):676–685. doi: 10.1161/01.res.20.6.676. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krahé P., Hofbauer K. G., Gross F. Effects of endogenous renin on the function of the isolated kidney. Life Sci I. 1970 Nov 15;9(22):1317–1320. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(70)90272-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liard J. F., Cowley A. W., Jr, McCaa R. E., McCaa C. S., Guyton A. C. Renin, aldosterone, body fluid volumes, and the baroreceptor reflex in the development and reversal of Goldblatt hypertension in conscious dogs. Circ Res. 1974 Apr;34(4):549–560. doi: 10.1161/01.res.34.4.549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lupu A. N., Maxwell M. H., Kaufman J. J., White F. N. Experimental unilateral renal artery constriction in the dog. Circ Res. 1972 May;30(5):567–574. doi: 10.1161/01.res.30.5.567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAY A. G., VAN DE BERG L., DEWEESE J. A., ROB C. G. Critical arterial stenosis. Surgery. 1963 Jul;54:250–259. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor W. J. Normal sodium balance in dogs and in man. Cardiovasc Res. 1977 Sep;11(5):375–408. doi: 10.1093/cvr/11.5.375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel M. B., Levinsky N. G. Collateral circulation after renal artery occlusion in the rat. Circ Res. 1977 Aug;41(2):227–231. doi: 10.1161/01.res.41.2.227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tagawa H., Gutmann F. D., Haber E., Miller E. D., Jr, Samuels A. I., Barger A. C. Reversible renovascular hypertension and renal arterial pressure. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1974 Sep;146(4):975–982. doi: 10.3181/00379727-146-38231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins B. E., Davis J. O., Hanson R. C., Lohmeier T. E., Freeman R. H. Incidence and pathophysiological changes in chronic two-kidney hypertension in the dog. Am J Physiol. 1976 Sep;231(3):954–960. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1976.231.3.954. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West M. J., Angus J. A., Korner P. I. Estimation of non-autonomic and autonomic components of iliac bed vascular resistance in renal hypertensive rabbits. Cardiovasc Res. 1975 Sep;9(5):697–706. doi: 10.1093/cvr/9.5.697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young D. F., Cholvin N. R., Kirkeeide R. L., Roth A. C. Hemodynamics of arterial stenoses at elevated flow rates. Circ Res. 1977 Jul;41(1):99–107. doi: 10.1161/01.res.41.1.99. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


