Abstract
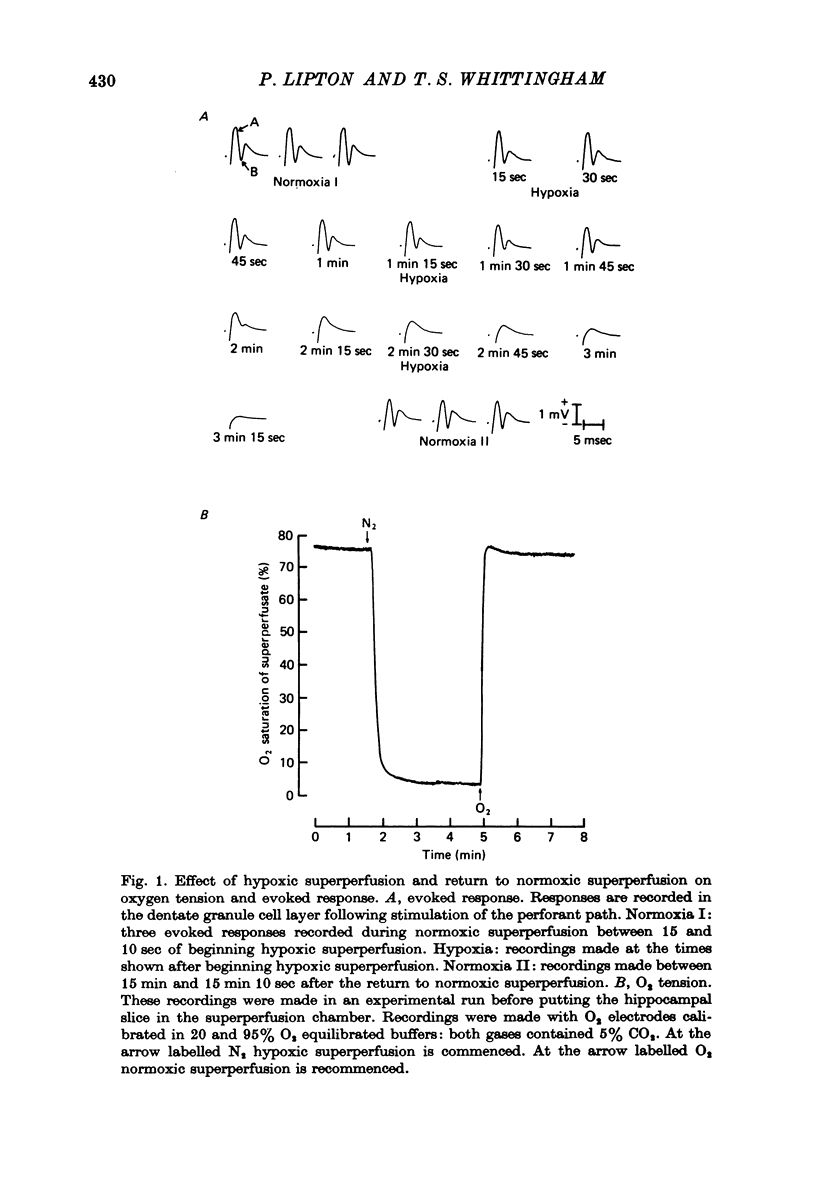
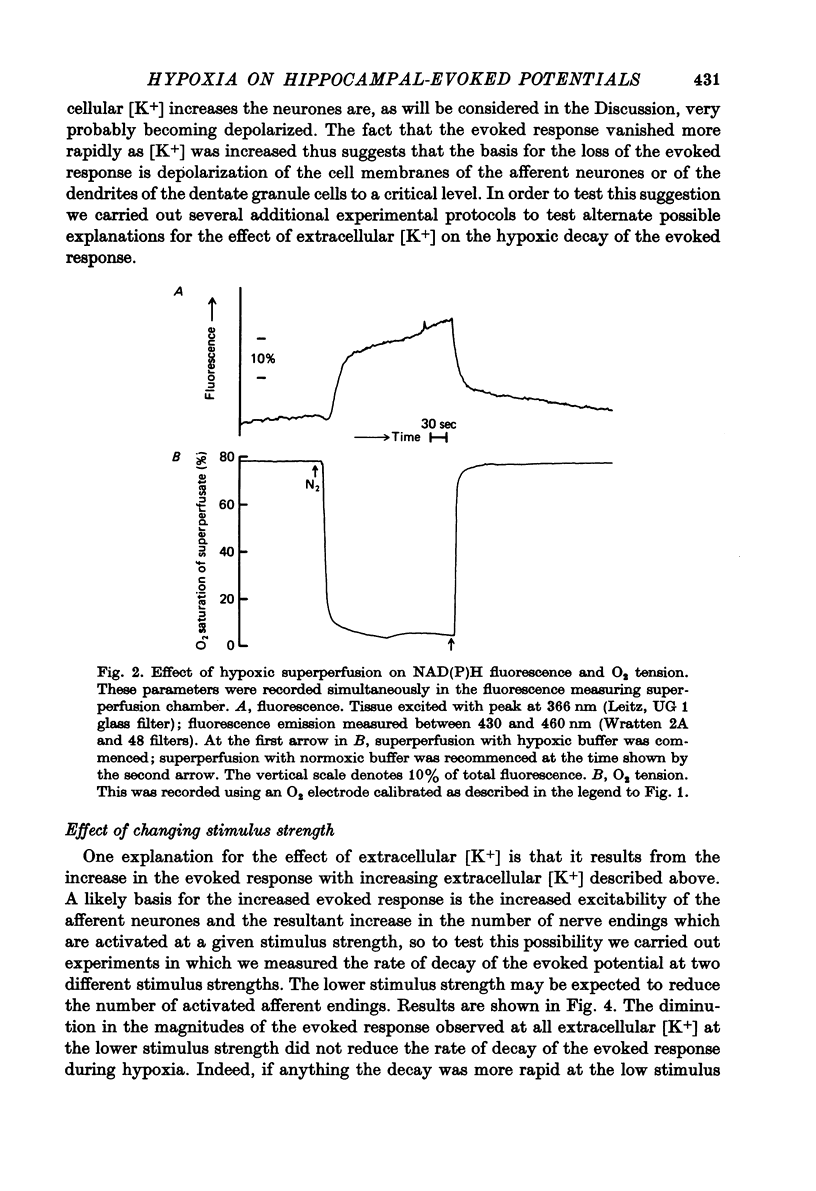
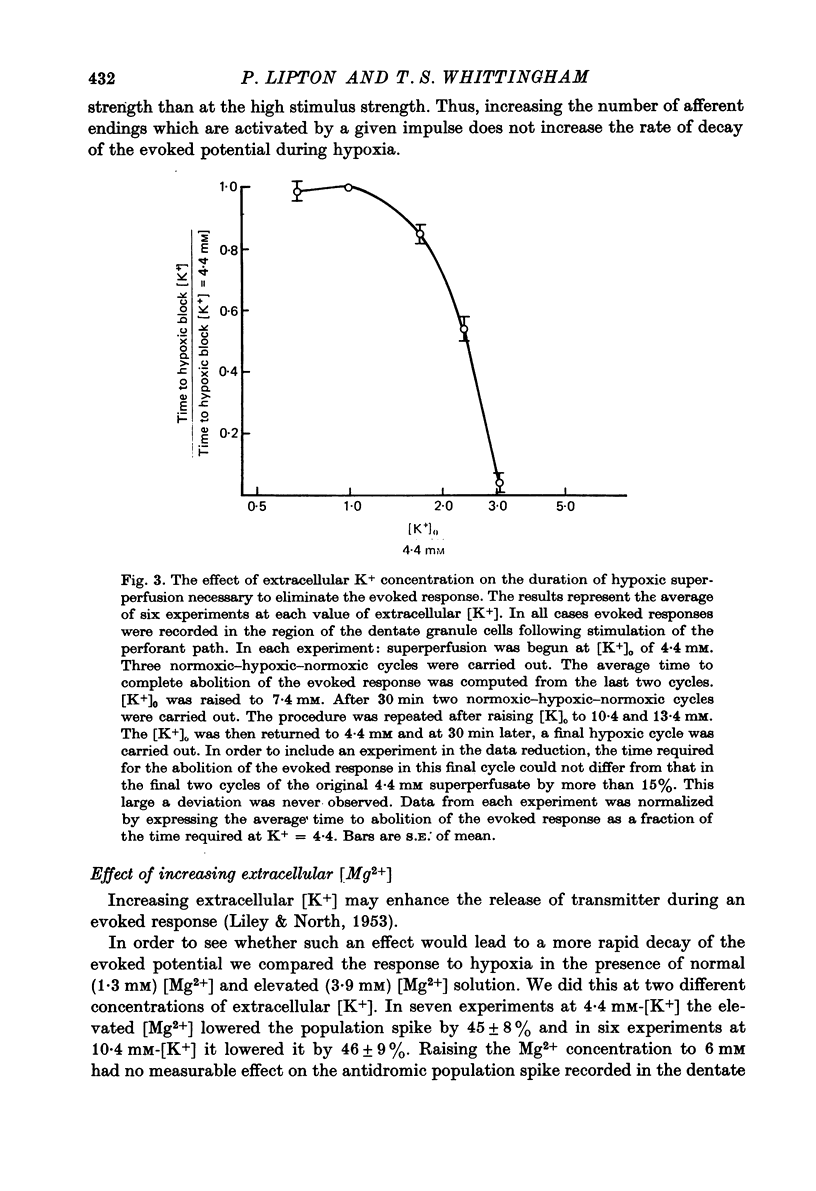
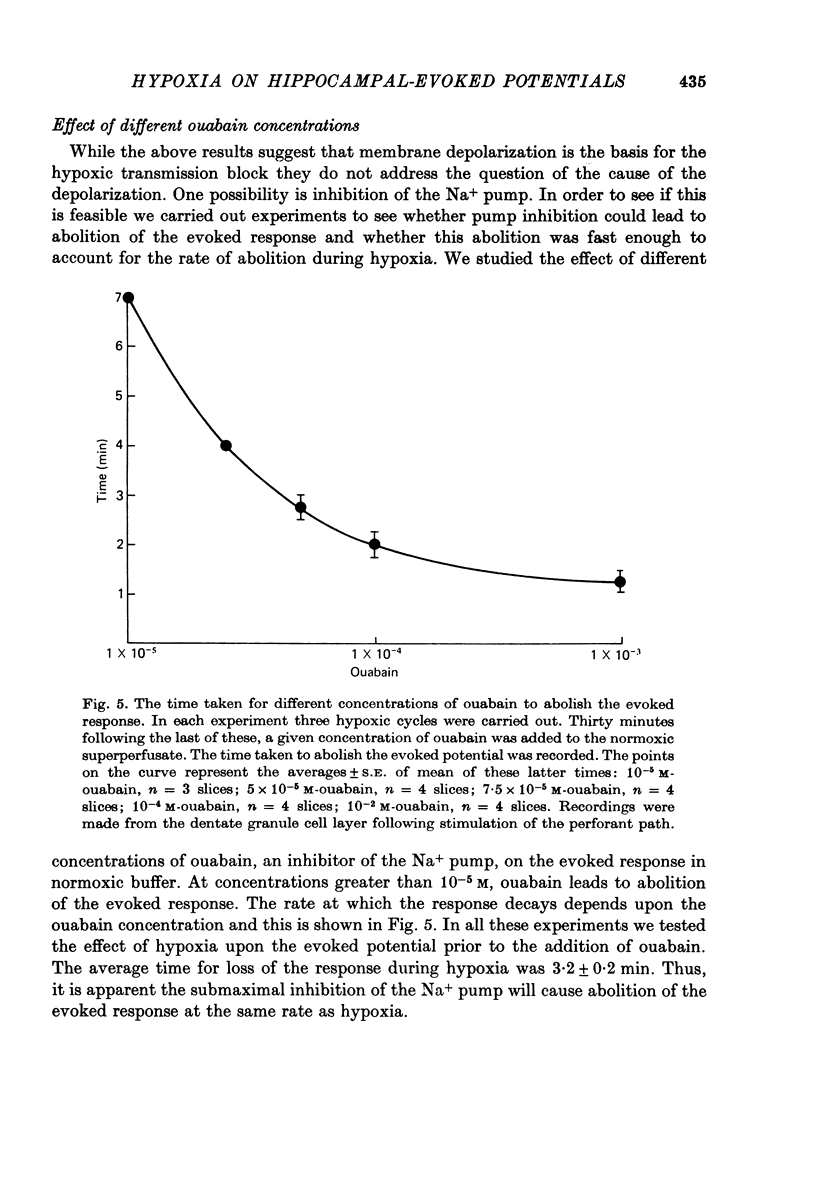
1. We have studied the effect of hypoxia on transmission of electrical activity between the perforant path and the dentate granule cells in the in vitro guinea-pig hippocampus. 2. Hypoxia abolishes the evoked field potential within about 3 min, a time similar to that occurring in vivo (Andersen, 1960). 3. The evoked potential is very rapidly abolished by extracellular K+ concentrations greater than 13.4 mM; it is abolished by ouabain concentrations greater than 10(-5) M. The rate at which it is abolished increases with increasing ouabain concentrations: concentrations of about 8 x 10(-5) M abolish the evoked potential at the same rate as does hypoxia. 4. The time required to abolish the evoked potential during hypoxia decreases markedly as the extracellular K+ concentration is elevated from 4.4 to 13.4 mM. The time to abolish the potential during hypoxia is also decreased by partial replacement of the Cl- in the bathing medium by less permeant anions and by the presence of a low (10(-7) M) concentration of ouabain. All these are conditions which are expected to depolarize neuronal cell membranes. None of these alterations in the perfusing medium affect the concentrations of ATP or creatine phosphate in the hippocampal slice. Increasing extracellular Mg2+/Ca2+ to levels which reduce the evoked response by about 50% has no effect upon the time required to abolish the evoked potential during hypoxia at any concentration of extracellular [K+]. 5. These results provide evidence that the basis for the hypoxic block of the evoked potential is a depolarization of neuronal processes. They are consistent with the hypothesis that this depolarization is a result of inhibition of the Na+/K+ pump.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANDERSEN P. Interhippocampal impulses. II. Apical dendritic activation of CAI neurons. Acta Physiol Scand. 1960 Mar 18;48:178–208. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1960.tb01858.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. A., Scholfield C. N. Movements of labelled sodium ions in isolated rat superior cervical ganglia. J Physiol. 1974 Oct;242(2):321–351. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010710. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carregal E. J. The site of anoxic block in the spinal monosynaptic pathway. J Neurobiol. 1975 Jan;6(1):103–113. doi: 10.1002/neu.480060113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collewijn H., Van Harreveld A. Intracellular recording from cat spinal motoneurones during acute asphyxia. J Physiol. 1966 Jul;185(1):1–14. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp007968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIBSON I. M., MCILWAIN H. CONTINUOUS RECORDINGS OF CHANGES IN MEMBRANE POTENTIAL IN MAMMALIAN CEREBRAL TISSUES IN VITRO; RECOVERY AFTER DEPOLARIZATION BY ADDED SUBSTANCES. J Physiol. 1965 Jan;176:261–283. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HUXLEY A. F. The dual effect of membrane potential on sodium conductance in the giant axon of Loligo. J Physiol. 1952 Apr;116(4):497–506. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., KEYNES R. D. The potassium permeability of a giant nerve fibre. J Physiol. 1955 Apr 28;128(1):61–88. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1955.sp005291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUXLEY A. F., STAMPFLI R. Effect of potassium and sodium on resting and action potentials of single myelinated nerve fibers. J Physiol. 1951 Feb;112(3-4):496–508. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1951.sp004546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henn F. A., Haljamäe H., Hamberger A. Glial cell function: active control of extracellular K + concentration. Brain Res. 1972 Aug 25;43(2):437–443. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(72)90399-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRNJEVIC K., MILEDI R. Presynaptic failure of neuromuscular propagation in rats. J Physiol. 1959 Dec;149:1–22. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuffler S. W., Nicholls J. G., Orkand R. K. Physiological properties of glial cells in the central nervous system of amphibia. J Neurophysiol. 1966 Jul;29(4):768–787. doi: 10.1152/jn.1966.29.4.768. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LILEY A. W., NORTH K. A. An electrical investigation of effects of repetitive stimulation on mammalian neuromuscular junction. J Neurophysiol. 1953 Sep;16(5):509–527. doi: 10.1152/jn.1953.16.5.509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., PASSONNEAU J. V., HASSELBERGER F. X., SCHULZ D. W. EFFECT OF ISCHEMIA ON KNOWN SUBSTRATES AND COFACTORS OF THE GLYCOLYTIC PATHWAY IN BRAIN. J Biol Chem. 1964 Jan;239:18–30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipton P. Effects of membrane depolarization on nicotinamide nucleotide fluorescence in brain slices. Biochem J. 1973 Dec;136(4):999–1009. doi: 10.1042/bj1360999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayevsky A., Chance B. Metabolic responses of the awake cerebral cortex to anoxia hypoxia spreading depression and epileptiform activity. Brain Res. 1975 Nov 7;98(1):149–165. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(75)90515-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nair P., Whalen W. J., Buerk D. PO2 of cat cerebral cortex: response to breathing N2 and 100 per cent O21. Microvasc Res. 1975 Mar;9(2):158–165. doi: 10.1016/0026-2862(75)90077-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor M. J., Herman C. J., Rosenthal M., Jöbsis F. F. Intracellular redox changes preceding onset of epileptiform activity in intact cat hippocampus. J Neurophysiol. 1972 Jul;35(4):471–483. doi: 10.1152/jn.1972.35.4.471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholfield C. N. Electrical properties of neurones in the olfactory cortex slice in vitro. J Physiol. 1978 Feb;275:535–546. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer W., Lux H. D. Presynaptic depolarization and extracellular potassium in the cat lateral geniculate nucleus. Brain Res. 1973 Dec 21;64:17–33. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(73)90168-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skrede K. K., Westgaard R. H. The transverse hippocampal slice: a well-defined cortical structure maintained in vitro. Brain Res. 1971 Dec 24;35(2):589–593. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(71)90508-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams V., Grossman R. G. Ultrastructure of cortical synapses after failure of presynaptic activity in ischemia. Anat Rec. 1970 Feb;166(2):131–141. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091660202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


