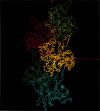Abstract
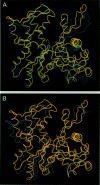
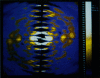
The slow normal modes of G-actin were used as structural parameters to refine the F-actin model against 8-A resolution x-ray fiber diffraction data. The slowest frequency normal modes of G-actin pertain to collective rearrangements of domains, motions that are characterized by correlation lengths on the order of the resolution of the fiber diffraction data. Using a small number of normal mode degrees of freedom (< or = 12) improved the fit to the data significantly. The refined model of F-actin shows that the nucleotide binding cleft has narrowed and that the DNase I binding loop has twisted to a lower radius, consistent with other refinement techniques and electron microscopy data. The methodology of a normal mode refinement is described, and the results, as applied to actin, are detailed.
Full text
PDF



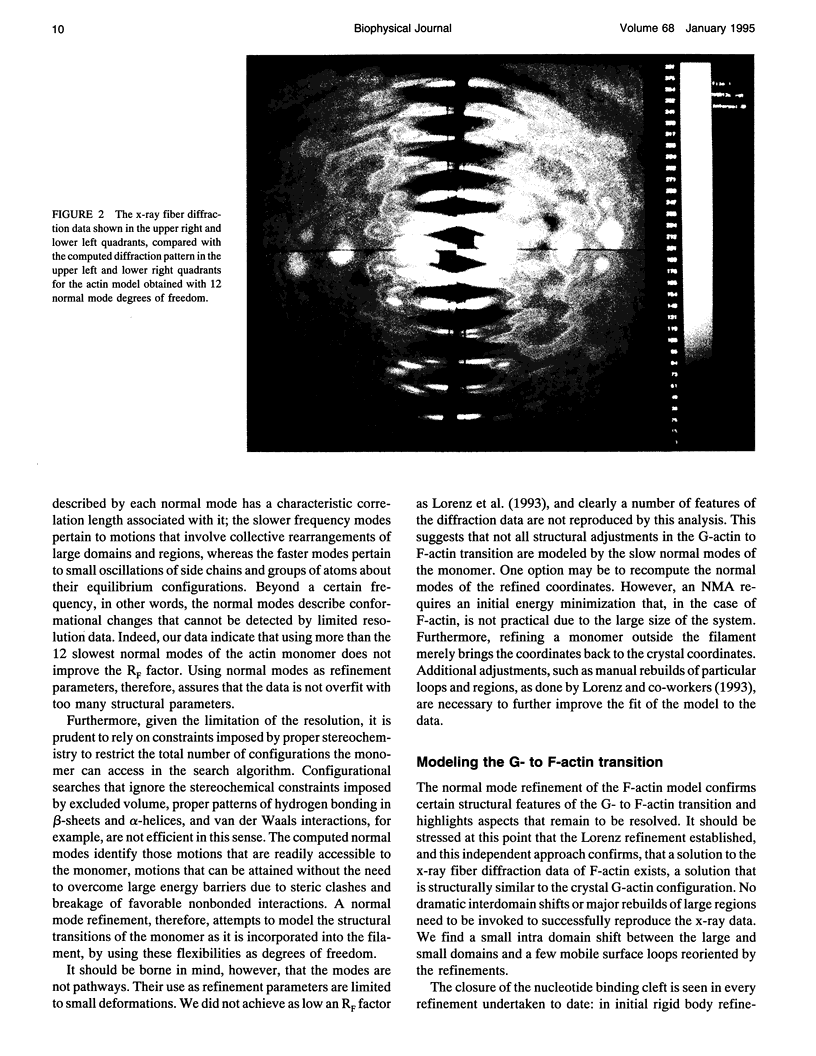
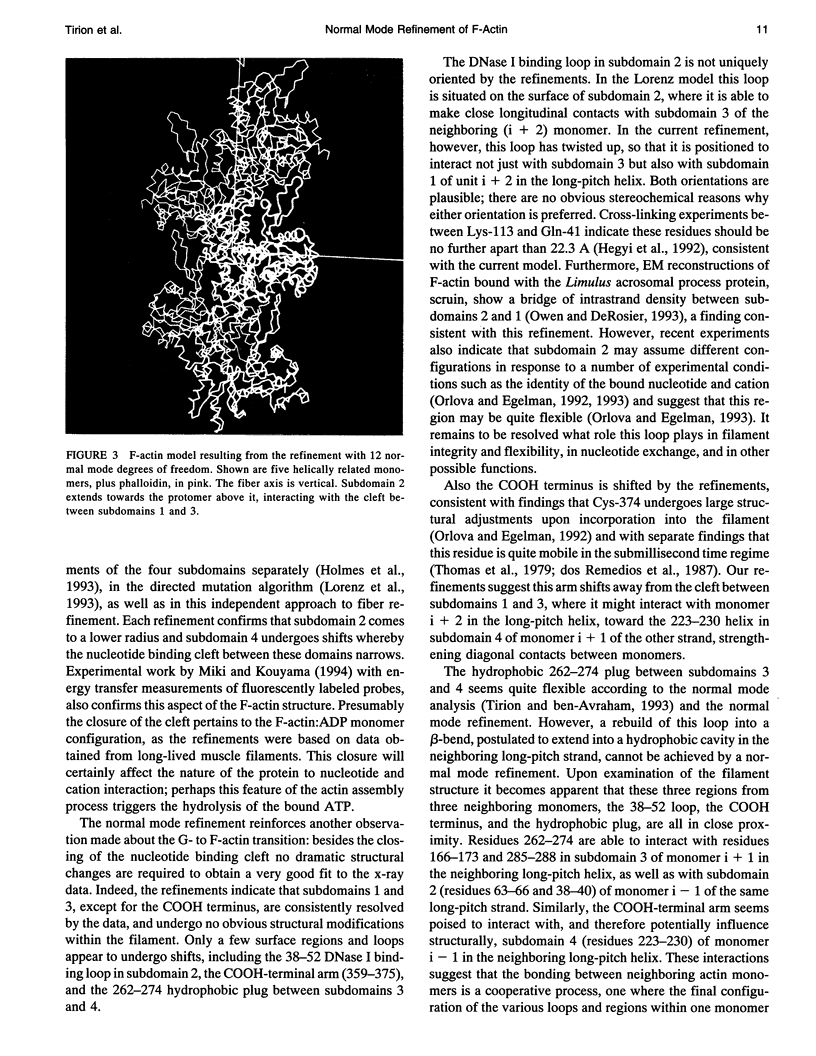

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brooks B., Karplus M. Harmonic dynamics of proteins: normal modes and fluctuations in bovine pancreatic trypsin inhibitor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(21):6571–6575. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.21.6571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen X., Cook R. K., Rubenstein P. A. Yeast actin with a mutation in the "hydrophobic plug" between subdomains 3 and 4 (L266D) displays a cold-sensitive polymerization defect. J Cell Biol. 1993 Dec;123(5):1185–1195. doi: 10.1083/jcb.123.5.1185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elzinga M., Phelan J. J. F-actin is intermolecularly crosslinked by N,N'-p-phenylenedimaleimide through lysine-191 and cysteine-374. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(21):6599–6602. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.21.6599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Go N., Noguti T., Nishikawa T. Dynamics of a small globular protein in terms of low-frequency vibrational modes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3696–3700. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hegyi G., Michel H., Shabanowitz J., Hunt D. F., Chatterjie N., Healy-Louie G., Elzinga M. Gln-41 is intermolecularly cross-linked to Lys-113 in F-actin by N-(4-azidobenzoyl)-putrescine. Protein Sci. 1992 Jan;1(1):132–144. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560010113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes K. C., Tirion M., Popp D., Lorenz M., Kabsch W., Milligan R. A. A comparison of the atomic model of F-actin with cryo-electron micrographs of actin and decorated actin. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1993;332:15–24. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-2872-2_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kabsch W., Mannherz H. G., Suck D., Pai E. F., Holmes K. C. Atomic structure of the actin:DNase I complex. Nature. 1990 Sep 6;347(6288):37–44. doi: 10.1038/347037a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitt M. Molecular dynamics of native protein. I. Computer simulation of trajectories. J Mol Biol. 1983 Aug 15;168(3):595–617. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80304-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitt M., Sander C., Stern P. S. Protein normal-mode dynamics: trypsin inhibitor, crambin, ribonuclease and lysozyme. J Mol Biol. 1985 Feb 5;181(3):423–447. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90230-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorenz M., Popp D., Holmes K. C. Refinement of the F-actin model against X-ray fiber diffraction data by the use of a directed mutation algorithm. J Mol Biol. 1993 Dec 5;234(3):826–836. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1628. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mannherz H. G., Kabsch W., Leverman R. Crystals of skeletal muscle actin: pancreatic DNAase I complex. FEBS Lett. 1977 Feb 1;73(2):141–143. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80966-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miki M., Kouyama T. Domain motion in actin observed by fluorescence resonance energy transfer. Biochemistry. 1994 Aug 23;33(33):10171–10177. doi: 10.1021/bi00199a045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan R. A., Whittaker M., Safer D. Molecular structure of F-actin and location of surface binding sites. Nature. 1990 Nov 15;348(6298):217–221. doi: 10.1038/348217a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orlova A., Egelman E. H. A conformational change in the actin subunit can change the flexibility of the actin filament. J Mol Biol. 1993 Jul 20;232(2):334–341. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orlova A., Egelman E. H. Structural basis for the destabilization of F-actin by phosphate release following ATP hydrolysis. J Mol Biol. 1992 Oct 20;227(4):1043–1053. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90520-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen C., DeRosier D. A 13-A map of the actin-scruin filament from the limulus acrosomal process. J Cell Biol. 1993 Oct;123(2):337–344. doi: 10.1083/jcb.123.2.337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas D. D., Seidel J. C., Gergely J. Rotational dynamics of spin-labeled F-actin in the sub-millisecond time range. J Mol Biol. 1979 Aug 15;132(3):257–273. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90259-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tirion M. M., ben-Avraham D. Normal mode analysis of G-actin. J Mol Biol. 1993 Mar 5;230(1):186–195. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- dos Remedios C. G., Miki M., Barden J. A. Fluorescence resonance energy transfer measurements of distances in actin and myosin. A critical evaluation. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1987 Apr;8(2):97–117. doi: 10.1007/BF01753986. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]