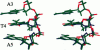Abstract
Conformational flexibility of molecules in solution implies that different conformers contribute to the NMR signal. This may lead to internal inconsistencies in the 2D NOE-derived interproton distance restraints and to conflict with scalar coupling-based torsion angle restraints. Such inconsistencies have been revealed and analyzed for the DNA octamer GTATAATG.CATATTAC, containing the Pribnow box consensus sequence. A number of subsets of distance restraints were constructed and used in the restrained Monte Carlo refinement of different double-helical conformers. The probabilities of conformers were then calculated by a quadratic programming algorithm, minimizing a relaxation rate-base residual index. The calculated distribution of conformers agrees with the experimental NOE data as an ensemble better than any single structure. A comparison with the results of this procedure, which we term PARSE (Probability Assessment via Relaxation rates of a Structural Ensemble), to an alternative method to generate solution ensembles showed, however, that the detailed multi-conformational description of solution DNA structure remains ambiguous at this stage. Nevertheless, some ensemble properties can be deduced with confidence, the most prominent being a distribution of sugar puckers with minor populations in the N-region and major populations in the S-region. Importantly, such a distribution is in accord with the analysis of independent experimental data--deoxyribose proton-proton scalar coupling constants.
Full text
PDF




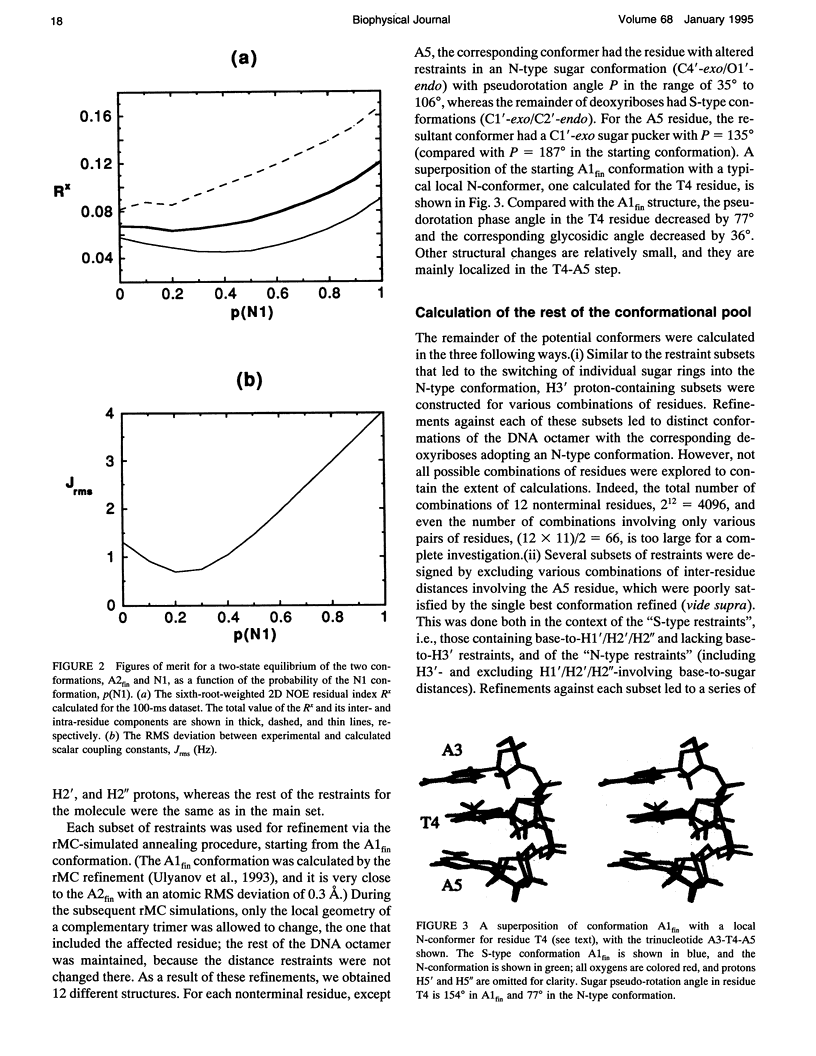

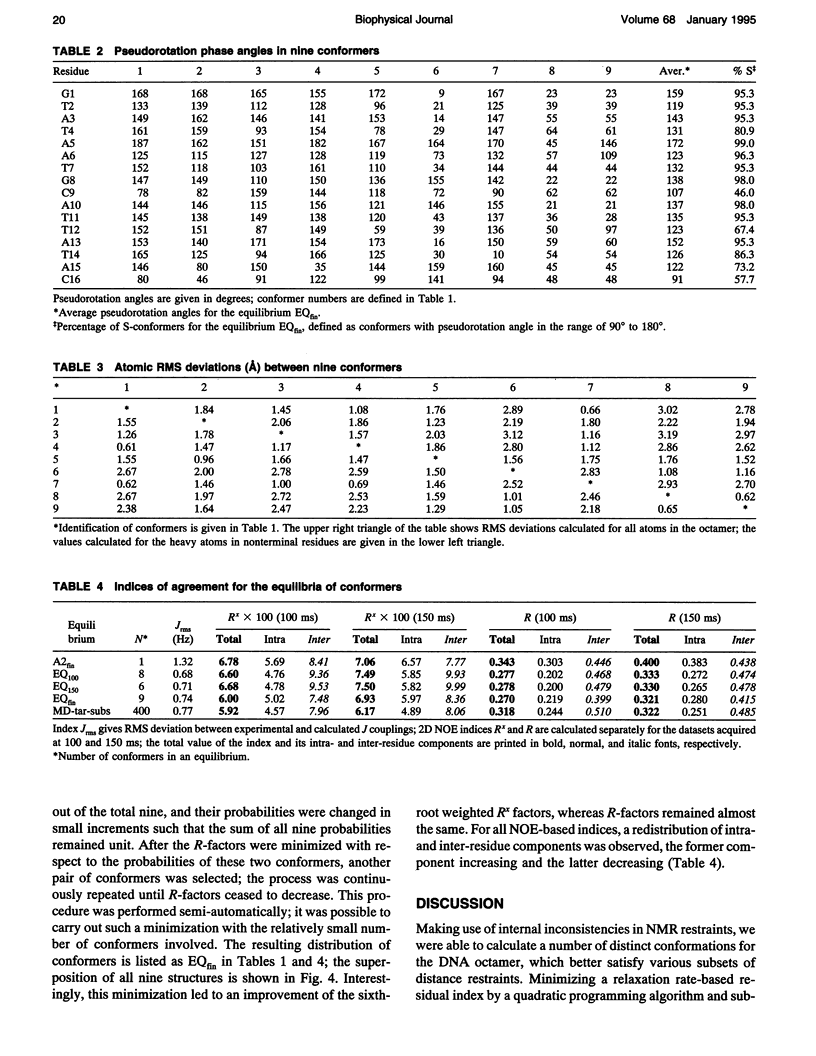




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baikalov I., Grzeskowiak K., Yanagi K., Quintana J., Dickerson R. E. The crystal structure of the trigonal decamer C-G-A-T-C-G-6meA-T-C-G: a B-DNA helix with 10.6 base-pairs per turn. J Mol Biol. 1993 Jun 5;231(3):768–784. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop K. D., Blocker F. J., Egan W., James T. L. Hepatitis B virus direct repeat sequence: imino proton exchange rates and distance and torsion angle restraints from NMR. Biochemistry. 1994 Jan 18;33(2):427–438. doi: 10.1021/bi00168a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackledge M. J., Brüschweiler R., Griesinger C., Schmidt J. M., Xu P., Ernst R. R. Conformational backbone dynamics of the cyclic decapeptide antamanide. Application of a new multiconformational search algorithm based on NMR data. Biochemistry. 1993 Oct 19;32(41):10960–10974. doi: 10.1021/bi00092a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borgias B. A., James T. L. Two-dimensional nuclear Overhauser effect: complete relaxation matrix analysis. Methods Enzymol. 1989;176:169–183. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(89)76011-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brünger A. T., Clore G. M., Gronenborn A. M., Saffrich R., Nilges M. Assessing the quality of solution nuclear magnetic resonance structures by complete cross-validation. Science. 1993 Jul 16;261(5119):328–331. doi: 10.1126/science.8332897. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brüschweiler R., Blackledge M., Ernst R. R. Multi-conformational peptide dynamics derived from NMR data: a new search algorithm and its application to antamanide. J Biomol NMR. 1991 May;1(1):3–11. doi: 10.1007/BF01874565. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celda B., Widmer H., Leupin W., Chazin W. J., Denny W. A., Wüthrich K. Conformational studies of d-(AAAAATTTTT)2 using constraints from nuclear overhauser effects and from quantitative analysis of the cross-peak fine structures in two-dimensional 1H nuclear magnetic resonance spectra. Biochemistry. 1989 Feb 21;28(4):1462–1471. doi: 10.1021/bi00430a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies D. B., Danyluk S. S. Nuclear magnetic resonance studies of 2'- and 3'-ribonucleotide structures in solution. Biochemistry. 1975 Feb 11;14(3):543–554. doi: 10.1021/bi00674a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagerman P. J. Flexibility of DNA. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1988;17:265–286. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.17.060188.001405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagerman P. J. Sequence-directed curvature of DNA. Annu Rev Biochem. 1990;59:755–781. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.59.070190.003543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jardetzky O. On the nature of molecular conformations inferred from high-resolution NMR. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Feb 27;621(2):227–232. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(80)90174-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy M. A., Nuutero S. T., Davis J. T., Drobny G. P., Reid B. R. Mobility at the TpA cleavage site in the T3A3-containing AhaIII and PmeI restriction sequences. Biochemistry. 1993 Aug 10;32(31):8022–8035. doi: 10.1021/bi00082a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim Y., Prestegard J. H. A dynamic model for the structure of acyl carrier protein in solution. Biochemistry. 1989 Oct 31;28(22):8792–8797. doi: 10.1021/bi00448a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macaya R., Wang E., Schultze P., Sklenár V., Feigon J. Proton nuclear magnetic resonance assignments and structural characterization of an intramolecular DNA triplex. J Mol Biol. 1992 Jun 5;225(3):755–773. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90399-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mujeeb A., Kerwin S. M., Egan W., Kenyon G. L., James T. L. A potential gene target in HIV-1: rationale, selection of a conserved sequence, and determination of NMR distance and torsion angle constraints. Biochemistry. 1992 Oct 6;31(39):9325–9338. doi: 10.1021/bi00154a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mujeeb A., Kerwin S. M., Kenyon G. L., James T. L. Solution structure of a conserved DNA sequence from the HIV-1 genome: restrained molecular dynamics simulation with distance and torsion angle restraints derived from two-dimensional NMR spectra. Biochemistry. 1993 Dec 14;32(49):13419–13431. doi: 10.1021/bi00212a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearlman D. A., Kollman P. A. Are time-averaged restraints necessary for nuclear magnetic resonance refinement? A model study for DNA. J Mol Biol. 1991 Jul 20;220(2):457–479. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90024-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poltev V. I., Shulyupina N. V. Simulation of interactions between nucleic acid bases by refined atom-atom potential functions. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1986 Feb;3(4):739–765. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1986.10508459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinkel L. J., Altona C. Conformational analysis of the deoxyribofuranose ring in DNA by means of sums of proton-proton coupling constants: a graphical method. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1987 Feb;4(4):621–649. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1987.10507665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz U., Pearlman D. A., James T. L. Solution structure of [d(GTATATAC)]2 via restrained molecular dynamics simulations with nuclear magnetic resonance constraints derived from relaxation matrix analysis of two-dimensional nuclear Overhauser effect experiments. J Mol Biol. 1991 Sep 5;221(1):271–292. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)80219-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz U., Sethson I., Egan W. M., James T. L. Solution structure of a DNA octamer containing the Pribnow box via restrained molecular dynamics simulation with distance and torsion angle constraints derived from two-dimensional nuclear magnetic resonance spectral fitting. J Mol Biol. 1992 Sep 20;227(2):510–531. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90904-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz U., Ulyanov N. B., Kumar A., James T. L. Molecular dynamics with weighted time-averaged restraints for a DNA octamer. Dynamic interpretation of nuclear magnetic resonance data. J Mol Biol. 1993 Nov 20;234(2):373–389. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz U., Zon G., James T. L. Deoxyribose conformation in [d(GTATATAC)]2: evaluation of sugar pucker by simulation of double-quantum-filtered COSY cross-peaks. Biochemistry. 1990 Mar 6;29(9):2357–2368. doi: 10.1021/bi00461a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steitz T. A. Structural studies of protein-nucleic acid interaction: the sources of sequence-specific binding. Q Rev Biophys. 1990 Aug;23(3):205–280. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500005552. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stolarski R., Egan W., James T. L. Solution structure of the EcoRI DNA octamer containing 5-fluorouracil via restrained molecular dynamics using distance and torsion angle constraints extracted from NMR spectral simulations. Biochemistry. 1992 Aug 11;31(31):7027–7042. doi: 10.1021/bi00146a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torda A. E., Scheek R. M., van Gunsteren W. F. Time-averaged nuclear Overhauser effect distance restraints applied to tendamistat. J Mol Biol. 1990 Jul 5;214(1):223–235. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90157-H. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trifonov E. N. Curved DNA. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1985;19(2):89–106. doi: 10.3109/10409238509082540. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulyanov N. B., Gorin A. A., Zhurkin V. B., Chen B. C., Sarma M. H., Sarma R. H. Systematic study of nuclear Overhauser effects vis-à-vis local helical parameters, sugar puckers, and glycosidic torsions in B DNA: insensitivity of NOE to local transitions in B DNA oligonucleotides due to internal structural compensations. Biochemistry. 1992 Apr 28;31(16):3918–3930. doi: 10.1021/bi00131a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulyanov N. B., Schmitz U., James T. L. Metropolis Monte Carlo calculations of DNA structure using internal coordinates and NMR distance restraints: an alternative method for generating a high-resolution solution structure. J Biomol NMR. 1993 Sep;3(5):547–568. doi: 10.1007/BF00174609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisz K., Shafer R. H., Egan W., James T. L. Solution structure of the octamer motif in immunoglobulin genes via restrained molecular dynamics calculations. Biochemistry. 1994 Jan 11;33(1):354–366. doi: 10.1021/bi00167a046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisz K., Shafer R. H., Egan W., James T. L. The octamer motif in immunoglobulin genes: extraction of structural constraints from two-dimensional NMR studies. Biochemistry. 1992 Aug 25;31(33):7477–7487. doi: 10.1021/bi00148a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhurkin V. B., Lysov Y. P., Florentiev V. L., Ivanov V. I. Torsional flexibility of B-DNA as revealed by conformational analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Mar 11;10(5):1811–1830. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.5.1811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhurkin V. B., Ulyanov N. B., Gorin A. A., Jernigan R. L. Static and statistical bending of DNA evaluated by Monte Carlo simulations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 15;88(16):7046–7050. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.16.7046. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]