Abstract
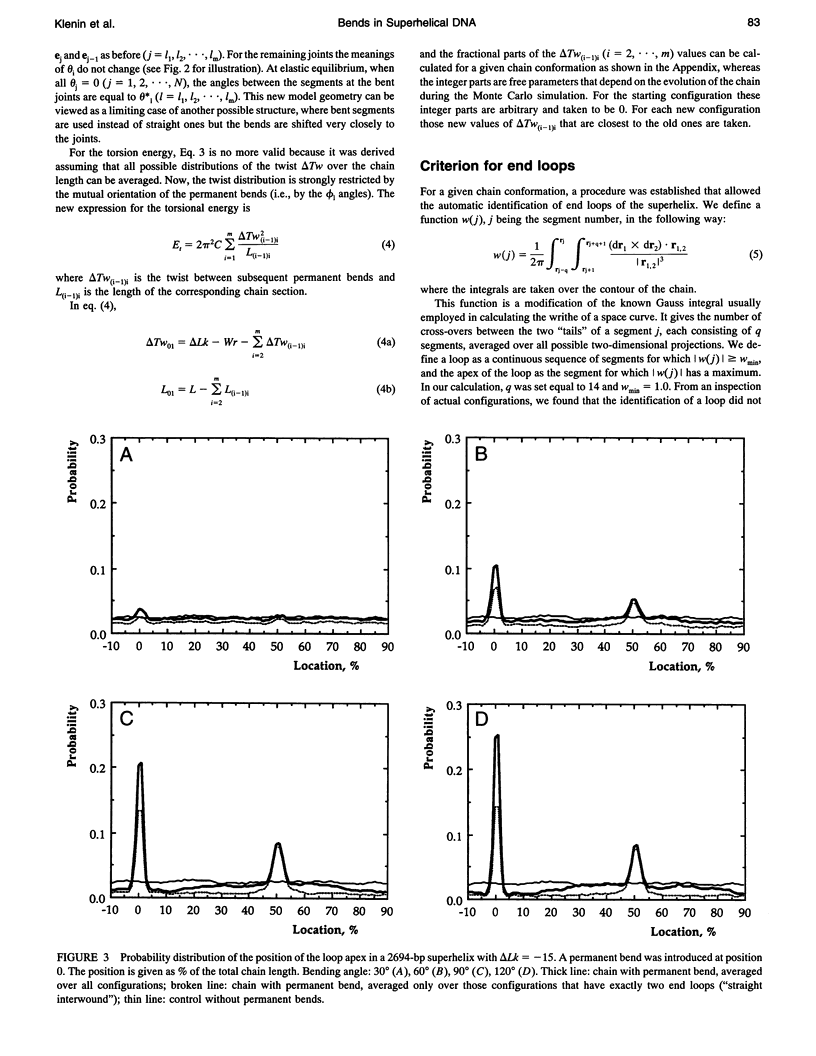
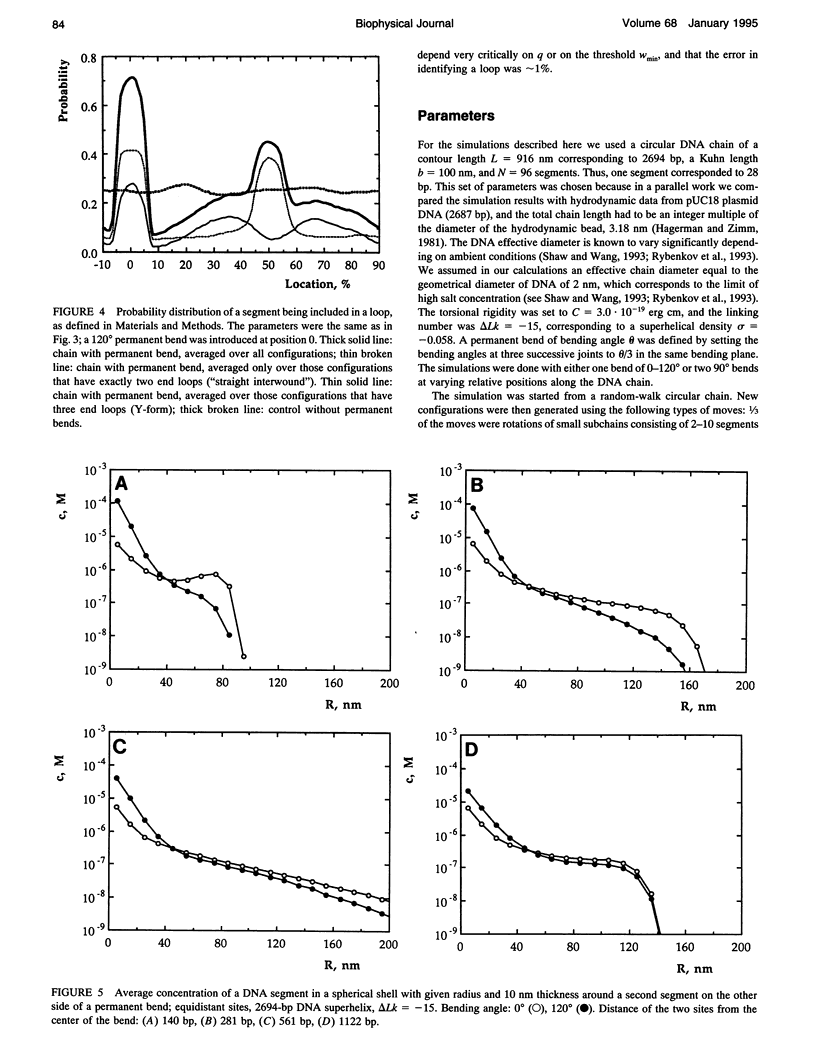
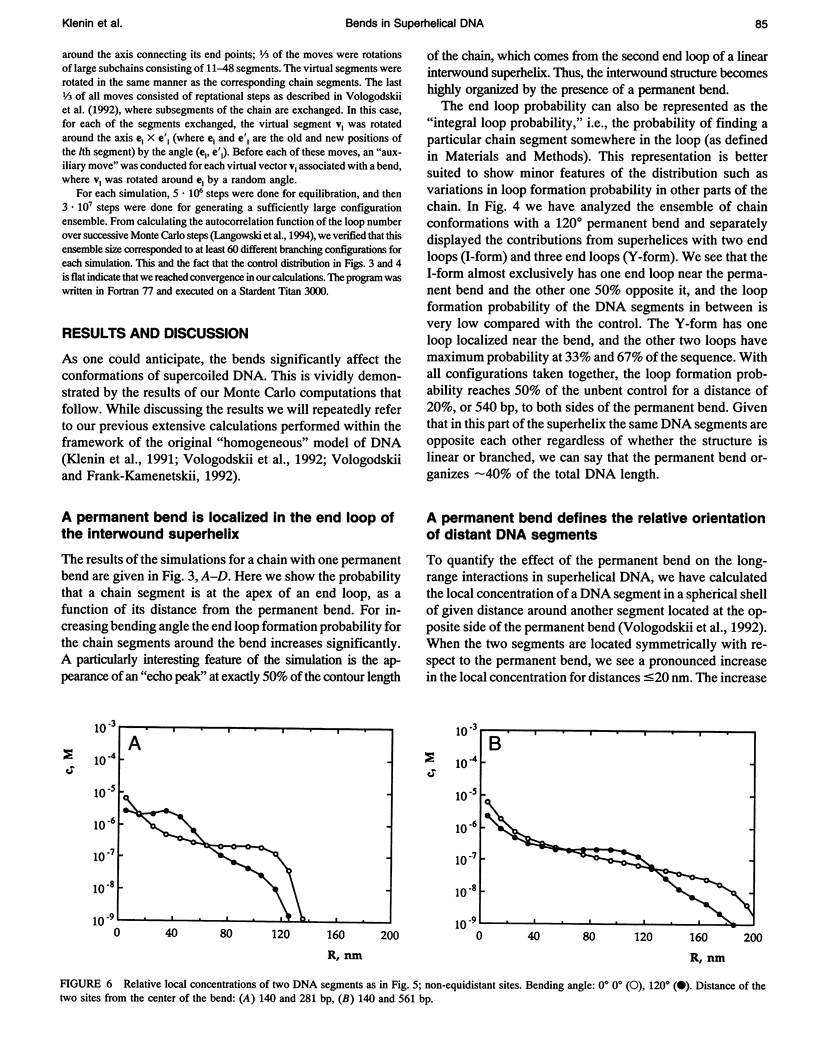
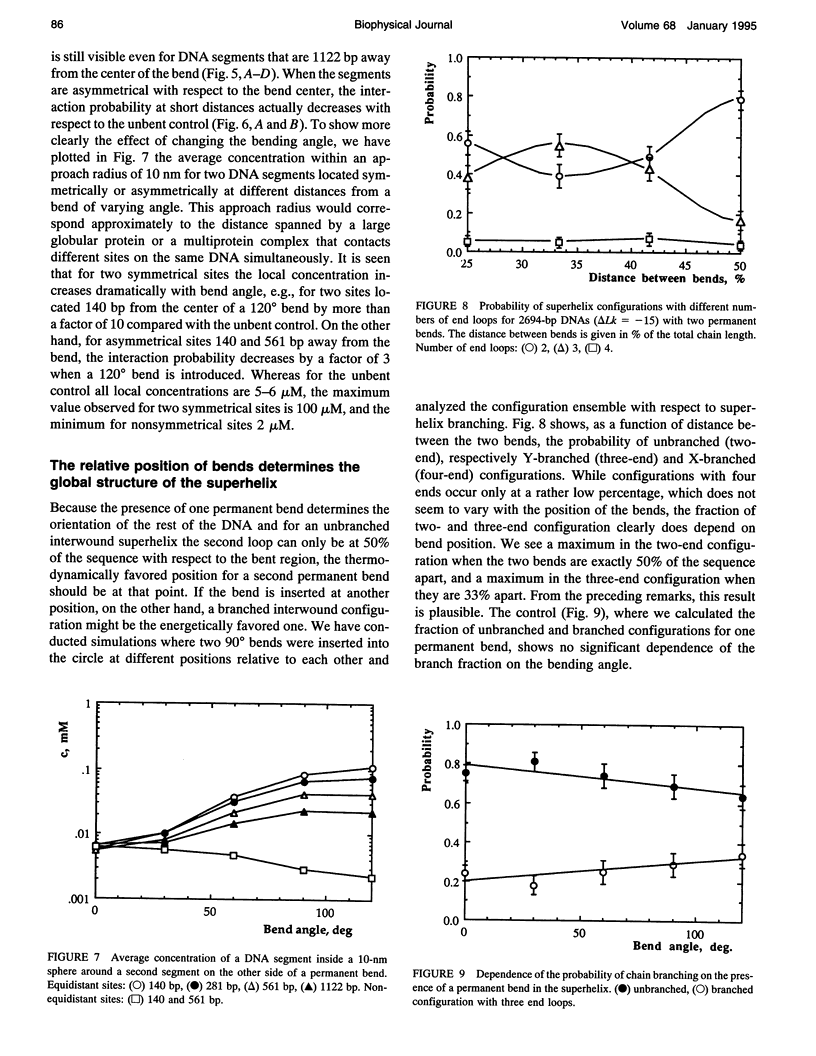
A Monte Carlo model for the generation of superhelical DNA structures at thermodynamic equilibrium (Klenin et al., 1991; Vologodskii et al., 1992) was modified to account for the presence of local curvature. Equilibrium ensembles of a 2700-bp DNA chain at linking number difference delta Lk = -15 were generated, with one or two permanent bends up to 120 degrees inserted at different positions. The computed structures were then analyzed with respect to the number and positions of the end loops of the interwound superhelix, and the intramolecular interaction probability of different segments of the DNA. We find that the superhelix structure is strongly organized by permanent bends. A DNA segment with a 30 degrees bend already has a significantly higher probability of being at the apex of a superhelix than the control, and for a 120 degrees bend the majority of DNAs have one end loop at the position of the bend. The entropy change due to the localization of a 120 permanent bend in the end loop is estimated to be -17 kJ mol-1 K-1. When two bends are inserted, the conformation of the superhelix is found to be strongly dependent on their relative positions: the straight interwound form dominates when the two bends are separated by 50% of the total DNA length, whereas the majority of the superhelices are in a branched conformation when the bends are separated by 33%. DNA segments in the vicinity of the permanent bend are strongly oriented with respect to each other.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bauer W. R., Lund R. A., White J. H. Twist and writhe of a DNA loop containing intrinsic bends. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Feb 1;90(3):833–837. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.3.833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bednar J., Furrer P., Stasiak A., Dubochet J., Egelman E. H., Bates A. D. The twist, writhe and overall shape of supercoiled DNA change during counterion-induced transition from a loosely to a tightly interwound superhelix. Possible implications for DNA structure in vivo. J Mol Biol. 1994 Jan 21;235(3):825–847. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borowiec J. A., Zhang L., Sasse-Dwight S., Gralla J. D. DNA supercoiling promotes formation of a bent repression loop in lac DNA. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jul 5;196(1):101–111. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90513-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bracco L., Kotlarz D., Kolb A., Diekmann S., Buc H. Synthetic curved DNA sequences can act as transcriptional activators in Escherichia coli. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 20;8(13):4289–4296. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08615.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crothers D. M. Architectural elements in nucleoprotein complexes. Curr Biol. 1993 Oct 1;3(10):675–676. doi: 10.1016/0960-9822(93)90065-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diekmann S. Sequence specificity of curved DNA. FEBS Lett. 1986 Jan 20;195(1-2):53–56. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80128-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank-Kamenetskii M. D., Lukashin A. V., Anshelevich V. V., Vologodskii A. V. Torsional and bending rigidity of the double helix from data on small DNA rings. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1985 Feb;2(5):1005–1012. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1985.10507616. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gartenberg M. R., Crothers D. M. Synthetic DNA bending sequences increase the rate of in vitro transcription initiation at the Escherichia coli lac promoter. J Mol Biol. 1991 May 20;219(2):217–230. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90563-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman S. D., Nash H. A. Functional replacement of a protein-induced bend in a DNA recombination site. Nature. 1989 Sep 21;341(6239):251–254. doi: 10.1038/341251a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hao M. H., Olson W. K. Modeling DNA supercoils and knots with B-spline functions. Biopolymers. 1989 Apr;28(4):873–900. doi: 10.1002/bip.360280407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klenin K. V., Vologodskii A. V., Anshelevich V. V., Dykhne A. M., Frank-Kamenetskii M. D. Computer simulation of DNA supercoiling. J Mol Biol. 1991 Feb 5;217(3):413–419. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90745-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klenin K. V., Vologodskii A. V., Anshelevich V. V., Dykhne A. M., Frank-Kamenetskii M. D. Effect of excluded volume on topological properties of circular DNA. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1988 Jun;5(6):1173–1185. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1988.10506462. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klenin K. V., Vologodskii A. V., Anshelevich V. V., Klishko VYu, Dykhne A. M., Frank-Kamenetskii M. D. Variance of writhe for wormlike DNA rings with excluded volume. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1989 Feb;6(4):707–714. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1989.10507731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koo H. S., Wu H. M., Crothers D. M. DNA bending at adenine . thymine tracts. Nature. 1986 Apr 10;320(6062):501–506. doi: 10.1038/320501a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kremer W., Klenin K., Diekmann S., Langowski J. DNA curvature influences the internal motions of supercoiled DNA. EMBO J. 1993 Nov;12(11):4407–4412. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06125.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laundon C. H., Griffith J. D. Curved helix segments can uniquely orient the topology of supertwisted DNA. Cell. 1988 Feb 26;52(4):545–549. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90467-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law S. M., Bellomy G. R., Schlax P. J., Record M. T., Jr In vivo thermodynamic analysis of repression with and without looping in lac constructs. Estimates of free and local lac repressor concentrations and of physical properties of a region of supercoiled plasmid DNA in vivo. J Mol Biol. 1993 Mar 5;230(1):161–173. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Bret M. Monte Carlo computation of the supercoiling energy, the sedimentation constant, and the radius of gyration of unknotted and knotted circular DNA. Biopolymers. 1980 Mar;19(3):619–637. doi: 10.1002/bip.1980.360190312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-Martín J., Espinosa M. The RepA repressor can act as a transcriptional activator by inducing DNA bends. EMBO J. 1991 Jun;10(6):1375–1382. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07657.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rybenkov V. V., Cozzarelli N. R., Vologodskii A. V. Probability of DNA knotting and the effective diameter of the DNA double helix. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jun 1;90(11):5307–5311. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.11.5307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlick T., Olson W. K. Supercoiled DNA energetics and dynamics by computer simulation. J Mol Biol. 1992 Feb 20;223(4):1089–1119. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90263-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz S. C., Shields G. C., Steitz T. A. Crystal structure of a CAP-DNA complex: the DNA is bent by 90 degrees. Science. 1991 Aug 30;253(5023):1001–1007. doi: 10.1126/science.1653449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw S. Y., Wang J. C. Knotting of a DNA chain during ring closure. Science. 1993 Apr 23;260(5107):533–536. doi: 10.1126/science.8475384. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan R. K., Harvey S. C. Molecular mechanics model of supercoiled DNA. J Mol Biol. 1989 Feb 5;205(3):573–591. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90227-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobias I., Olson W. K. The effect of intrinsic curvature on supercoiling: predictions of elasticity theory. Biopolymers. 1993 Apr;33(4):639–646. doi: 10.1002/bip.360330413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vologodskii A. V., Frank-Kamenetskii M. D. Modeling supercoiled DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1992;211:467–480. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(92)11025-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vologodskii A. V., Levene S. D., Klenin K. V., Frank-Kamenetskii M., Cozzarelli N. R. Conformational and thermodynamic properties of supercoiled DNA. J Mol Biol. 1992 Oct 20;227(4):1224–1243. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90533-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



