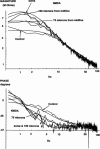
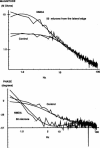
Abstract
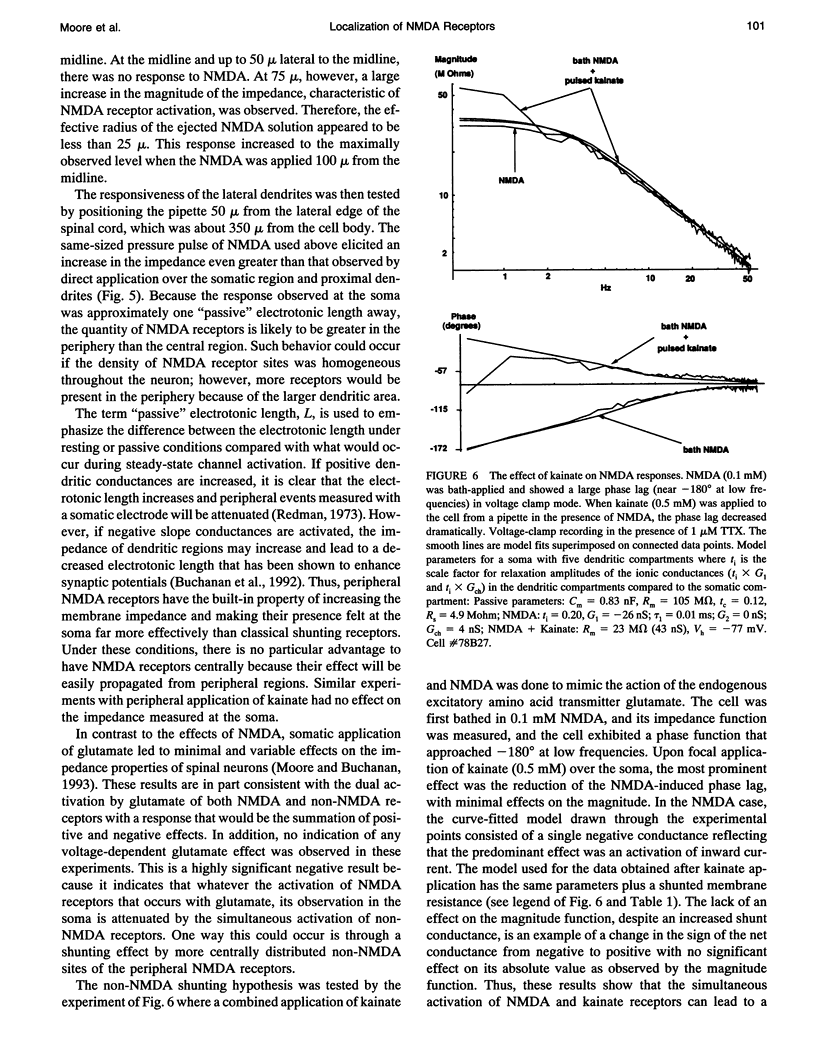
Small volumes of N-Methyl-D-Aspartate (NMDA) and non-NMDA excitatory amino acid receptor agonists were applied to localized regions of the dendritic trees of lamprey spinal neurons along their medial-lateral axis to obtain a spatial map of glutamate receptor distribution. Voltage clamp and frequency domain methods were used to obtain quantitative kinetic data of the voltage dependent ionic channels located both on the soma and on highly branched dendritic membranes. Pressure pulses of NMDA applied to the most peripheral regions of the dendritic tree elicited large somatic impedance increases, indicating that the most peripheral dendrites are well supplied with NMDA receptors. Experiments done with kainate did not elicit somatic responses to agonist applications on peripheral dendrites. The data obtained are consistent with the hypothesis that the activation of NMDA receptors by exogenous glutamate is significantly modified by the simultaneous activation of non-NMDA receptors, which shunts the NMDA response. The non-NMDA shunting hypothesis was tested by a combined application of kainate and NMDA to mimic the action of glutamate showing that the shunting effect of non-NMDA receptor activation virtually abolished the marked voltage dependency typical of NMDA receptor activation. These data were interpreted with a compartmental neuronal model having both NMDA and non-NMDA receptors.
Full text
PDF
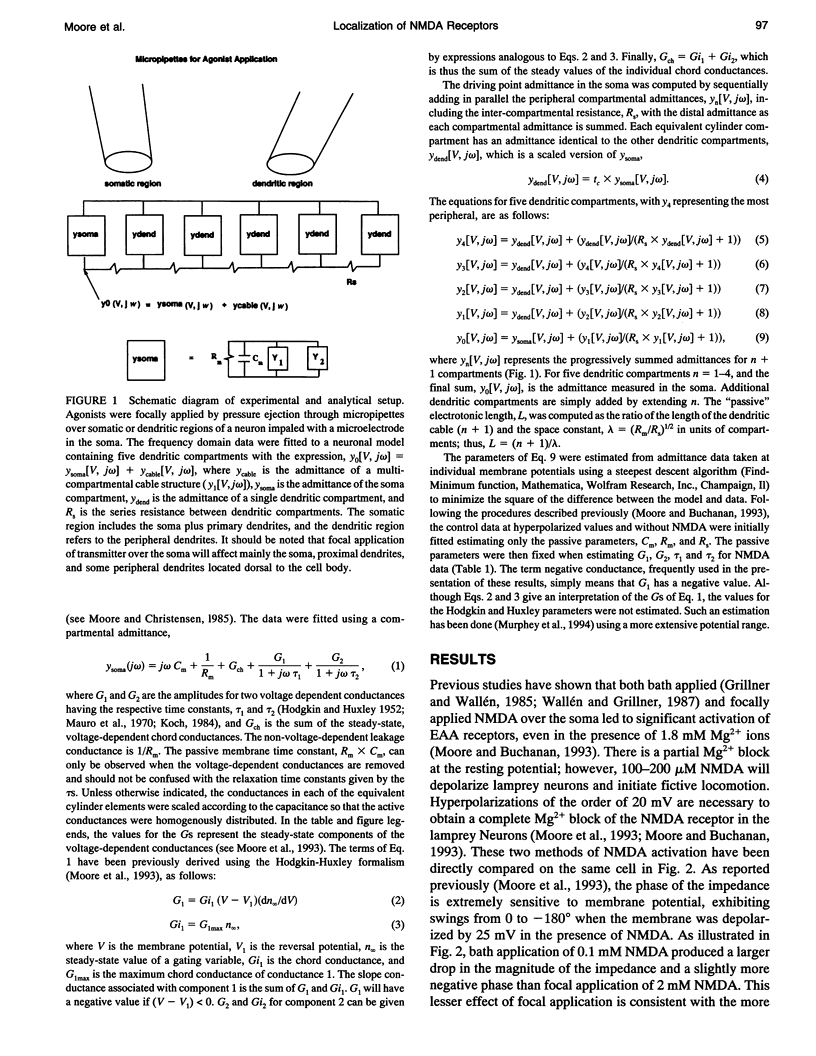


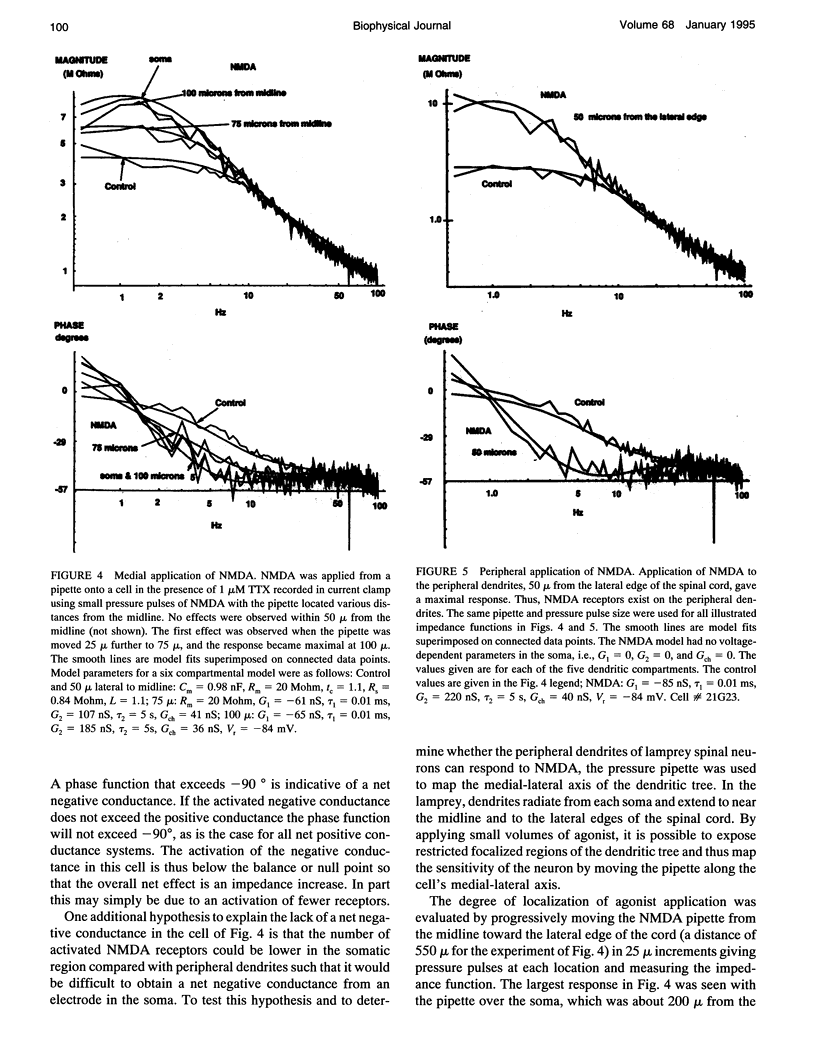


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bekkers J. M., Stevens C. F. NMDA and non-NMDA receptors are co-localized at individual excitatory synapses in cultured rat hippocampus. Nature. 1989 Sep 21;341(6239):230–233. doi: 10.1038/341230a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchanan J. T., Moore L. E., Hill R., Wallén P., Grillner S. Synaptic potentials and transfer functions of lamprey spinal neurons. Biol Cybern. 1992;67(2):123–131. doi: 10.1007/BF00201019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen B. N. Distribution of electrotonic synapses on identified lamprey neurons: a comparison of a model prediction with an electron microscopic analysis. J Neurophysiol. 1983 Mar;49(3):705–716. doi: 10.1152/jn.1983.49.3.705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen B. N., Teubl W. P. Localization of synaptic input on dendrites of a lamprey spinal cord neurone from physiological measurements of membrane properties. J Physiol. 1979 Dec;297(0):319–333. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp013042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements J. D., Redman S. J. Cable properties of cat spinal motoneurones measured by combining voltage clamp, current clamp and intracellular staining. J Physiol. 1989 Feb;409:63–87. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fishman H. M., Leuchtag H. R., Moore L. E. Fluctuation and linear analysis of Na-current kinetics in squid axon. Biophys J. 1983 Sep;43(3):293–307. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(83)84353-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fishman H. M., Poussart D., Moore L. E. Complex admittance of Na+ conduction in squid axon. J Membr Biol. 1979 Oct 5;50(1):43–63. doi: 10.1007/BF01868787. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsythe I. D., Westbrook G. L. Slow excitatory postsynaptic currents mediated by N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors on cultured mouse central neurones. J Physiol. 1988 Feb;396:515–533. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp016975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grillner S., Wallén P. The ionic mechanisms underlying N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor-induced, tetrodotoxin-resistant membrane potential oscillations in lamprey neurons active during locomotion. Neurosci Lett. 1985 Oct 10;60(3):289–294. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(85)90592-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HUXLEY A. F. A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. J Physiol. 1952 Aug;117(4):500–544. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hestrin S., Nicoll R. A., Perkel D. J., Sah P. Analysis of excitatory synaptic action in pyramidal cells using whole-cell recording from rat hippocampal slices. J Physiol. 1990 Mar;422:203–225. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp017980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hestrin S., Sah P., Nicoll R. A. Mechanisms generating the time course of dual component excitatory synaptic currents recorded in hippocampal slices. Neuron. 1990 Sep;5(3):247–253. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90162-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. A., Baughman R. W. Both NMDA and non-NMDA subtypes of glutamate receptors are concentrated at synapses on cerebral cortical neurons in culture. Neuron. 1991 Oct;7(4):593–603. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90372-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch C. Cable theory in neurons with active, linearized membranes. Biol Cybern. 1984;50(1):15–33. doi: 10.1007/BF00317936. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lester R. A., Clements J. D., Westbrook G. L., Jahr C. E. Channel kinetics determine the time course of NMDA receptor-mediated synaptic currents. Nature. 1990 Aug 9;346(6284):565–567. doi: 10.1038/346565a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mauro A., Conti F., Dodge F., Schor R. Subthreshold behavior and phenomenological impedance of the squid giant axon. J Gen Physiol. 1970 Apr;55(4):497–523. doi: 10.1085/jgp.55.4.497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore L. E., Buchanan J. T. The effects of neurotransmitters on the integrative properties of spinal neurons in the lamprey. J Exp Biol. 1993 Feb;175:89–114. doi: 10.1242/jeb.175.1.89. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore L. E., Christensen B. N. White noise analysis of cable properties of neuroblastoma cells and lamprey central neurons. J Neurophysiol. 1985 Mar;53(3):636–651. doi: 10.1152/jn.1985.53.3.636. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore L. E., Hill R. H., Grillner S. Voltage clamp analysis of lamprey neurons--role of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors in fictive locomotion. Brain Res. 1987 Sep 1;419(1-2):397–402. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(87)90616-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore L. E., Hill R. H., Grillner S. Voltage-clamp frequency domain analysis of NMDA-activated neurons. J Exp Biol. 1993 Feb;175:59–87. doi: 10.1242/jeb.175.1.59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore L. E., Tsai T. D. Ion conductances of the surface and transverse tubular membranes of skeletal muscle. J Membr Biol. 1983;73(3):217–226. doi: 10.1007/BF01870536. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore L. E., Yoshii K., Christensen B. N. Transfer impedances between different regions of branched excitable cells. J Neurophysiol. 1988 Mar;59(3):689–705. doi: 10.1152/jn.1988.59.3.689. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perouansky M., Yaari Y. Kinetic properties of NMDA receptor-mediated synaptic currents in rat hippocampal pyramidal cells versus interneurones. J Physiol. 1993 Jun;465:223–244. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1993.sp019674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RALL W. Branching dendritic trees and motoneuron membrane resistivity. Exp Neurol. 1959 Nov;1:491–527. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(59)90046-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rall W. Time constants and electrotonic length of membrane cylinders and neurons. Biophys J. 1969 Dec;9(12):1483–1508. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(69)86467-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redman S. J. The attenuation of passively propagating dendritic potentials in a motoneurone cable model. J Physiol. 1973 Nov;234(3):637–664. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rovainen C. M. Neurobiology of lampreys. Physiol Rev. 1979 Oct;59(4):1007–1077. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1979.59.4.1007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rovainen C. M. Synaptic interactions of identified nerve cells in the spinal cord of the sea lamprey. J Comp Neurol. 1974 Mar 15;154(2):189–206. doi: 10.1002/cne.901540206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallén P., Grillner S. N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor-induced, inherent oscillatory activity in neurons active during fictive locomotion in the lamprey. J Neurosci. 1987 Sep;7(9):2745–2755. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-09-02745.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshii K., Moore L. E., Christensen B. N. Effect of subthreshold voltage-dependent conductances on the transfer function of branched excitable cells and the conduction of synaptic potentials. J Neurophysiol. 1988 Mar;59(3):706–716. doi: 10.1152/jn.1988.59.3.706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]