Abstract
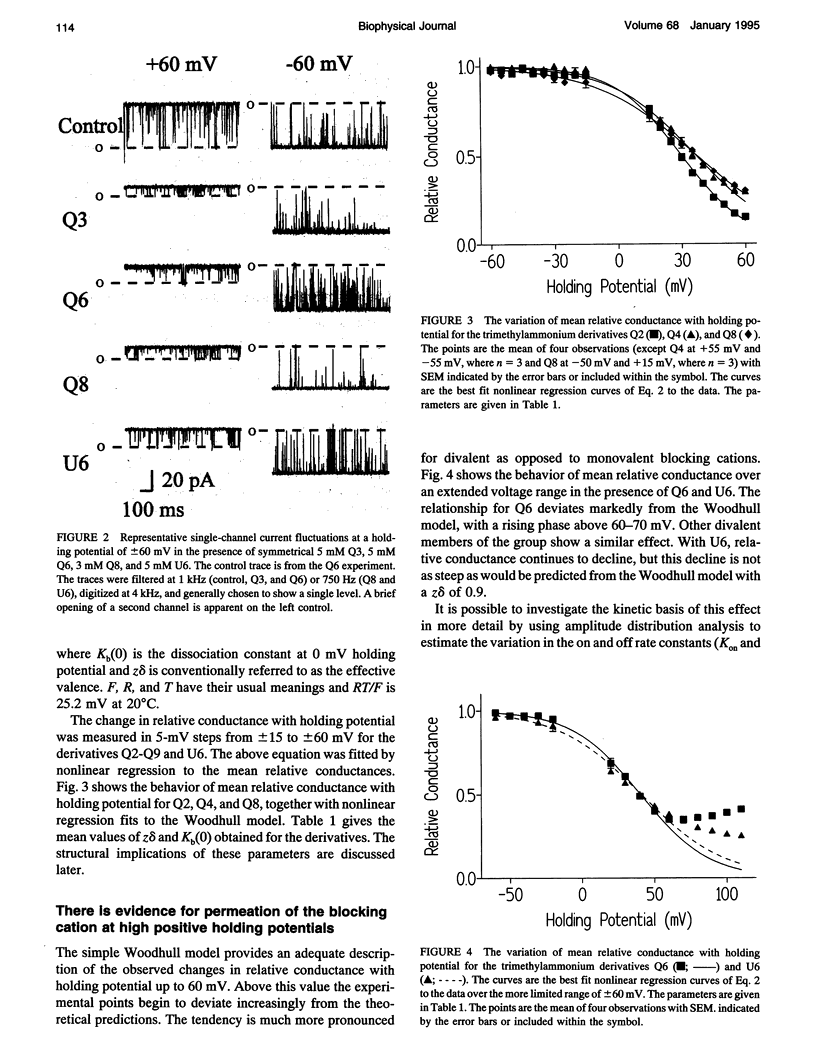
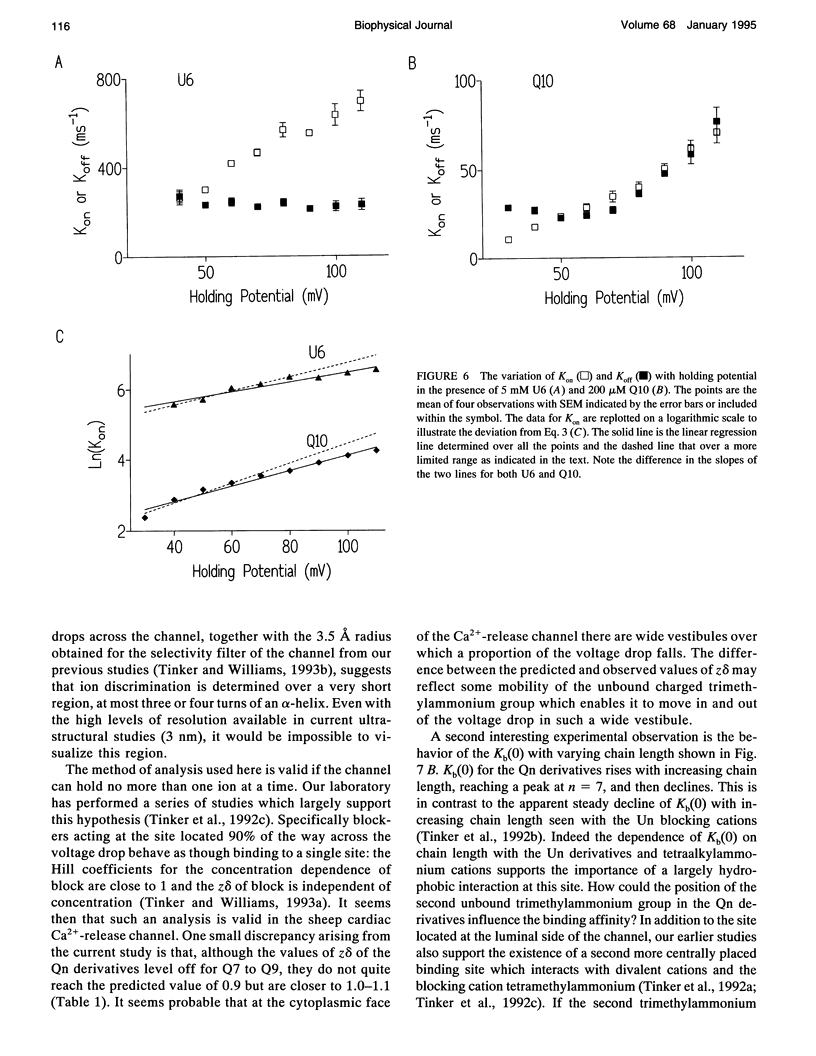
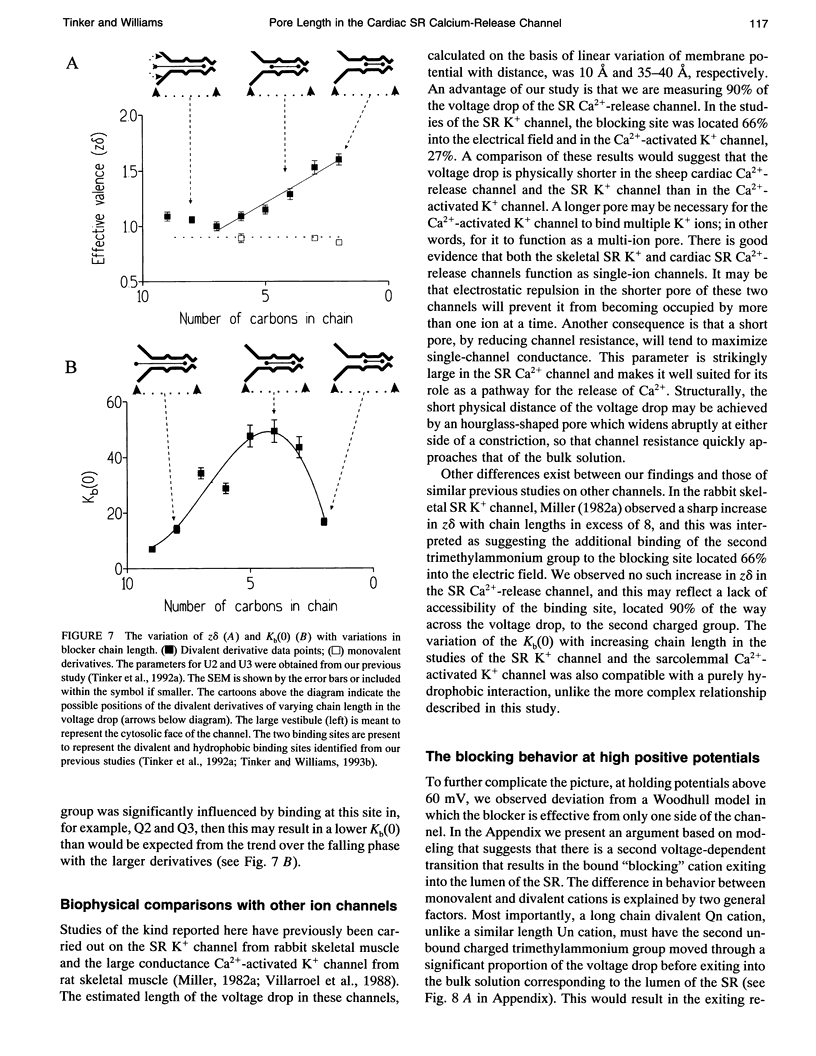
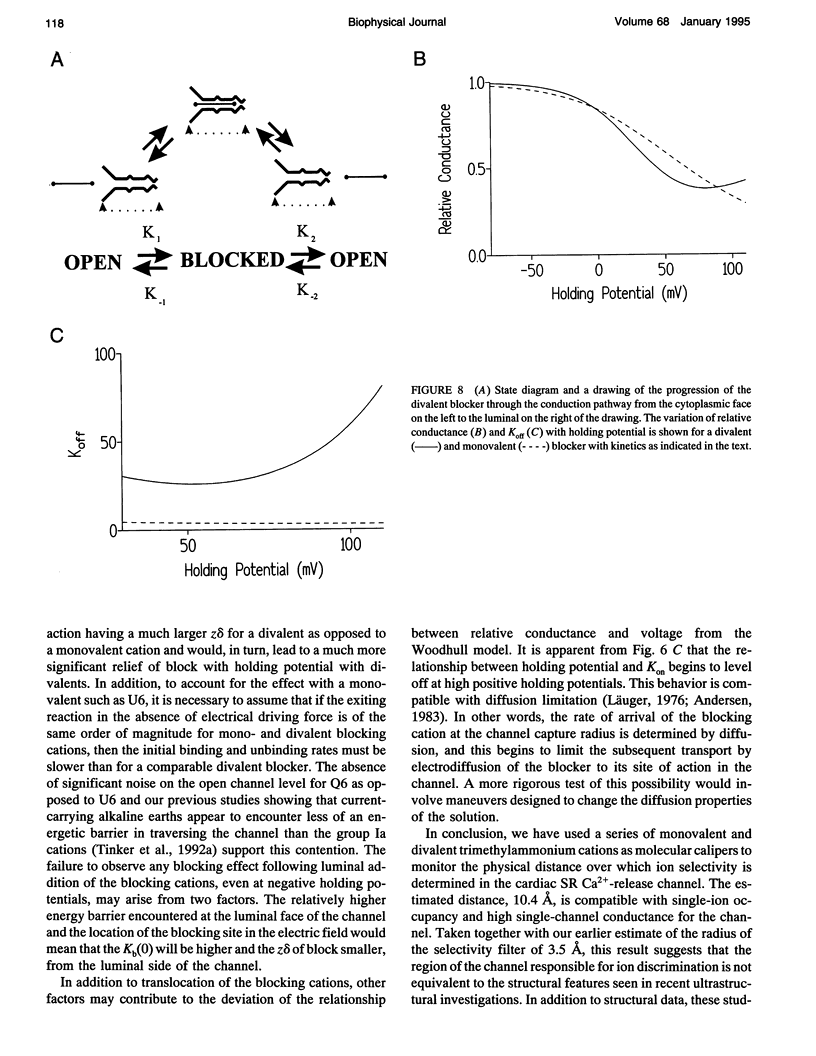
After incorporation of purified sheep cardiac Ca(2+)-release channels into planar phospholipid bilayers, we have investigated the blocking effects of a series of monovalent (CH3-(CH2)n-1-N+(CH3)3) and divalent ((CH3)3N(+)-(CH2)n-N+(CH3)3) trimethylammonium derivatives under voltage clamp conditions. All the compounds tested produce voltage-dependent block from the cytoplasmic face of the channel. With divalent (Qn) derivatives the effective valence of block decreases with increasing chain length, reaching a plateau with a chain length of n > or = 7. No decline in effective valence is observed with the monovalent (Un) derivatives. A plausible interpretation of this phenomena suggests that for the 90% of the voltage drop measured, the increase in length following the addition of a CH2 in the chain spans 12.7% of the electrical field. Extrapolating this distance to include the remaining 10% suggests that the applied holding potential falls over a total distance of 10.4 A. In addition, at high positive holding potentials there is evidence for permeation of the trimethylammonium ions and a valency specific relief of block.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersen O. S. Ion movement through gramicidin A channels. Studies on the diffusion-controlled association step. Biophys J. 1983 Feb;41(2):147–165. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(83)84416-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashley R. H., Williams A. J. Divalent cation activation and inhibition of single calcium release channels from sheep cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Gen Physiol. 1990 May;95(5):981–1005. doi: 10.1085/jgp.95.5.981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inui M., Saito A., Fleischer S. Isolation of the ryanodine receptor from cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum and identity with the feet structures. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 15;262(32):15637–15642. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai F. A., Erickson H. P., Rousseau E., Liu Q. Y., Meissner G. Purification and reconstitution of the calcium release channel from skeletal muscle. Nature. 1988 Jan 28;331(6154):315–319. doi: 10.1038/331315a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindsay A. R., Manning S. D., Williams A. J. Monovalent cation conductance in the ryanodine receptor-channel of sheep cardiac muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Physiol. 1991 Aug;439:463–480. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindsay A. R., Williams A. J. Functional characterisation of the ryanodine receptor purified from sheep cardiac muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Apr 26;1064(1):89–102. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(91)90415-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Läuger P. Diffusion-limited ion flow through pores. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Dec 2;455(2):493–509. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90320-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meissner G. Ryanodine receptor/Ca2+ release channels and their regulation by endogenous effectors. Annu Rev Physiol. 1994;56:485–508. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.56.030194.002413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller C. Bis-quaternary ammonium blockers as structural probes of the sarcoplasmic reticulum K+ channel. J Gen Physiol. 1982 May;79(5):869–891. doi: 10.1085/jgp.79.5.869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller C. Open-state substructure of single chloride channels from Torpedo electroplax. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1982 Dec 1;299(1097):401–411. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1982.0140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quayle J. M., Standen N. B., Stanfield P. R. The voltage-dependent block of ATP-sensitive potassium channels of frog skeletal muscle by caesium and barium ions. J Physiol. 1988 Nov;405:677–697. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radermacher M., Wagenknecht T., Grassucci R., Frank J., Inui M., Chadwick C., Fleischer S. Cryo-EM of the native structure of the calcium release channel/ryanodine receptor from sarcoplasmic reticulum. Biophys J. 1992 Apr;61(4):936–940. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81900-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sitsapesan R., Williams A. J. Mechanisms of caffeine activation of single calcium-release channels of sheep cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Physiol. 1990 Apr;423:425–439. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. S., Coronado R., Meissner G. Sarcoplasmic reticulum contains adenine nucleotide-activated calcium channels. Nature. 1985 Aug 1;316(6027):446–449. doi: 10.1038/316446a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tinker A., Lindsay A. R., Williams A. J. A model for ionic conduction in the ryanodine receptor channel of sheep cardiac muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Gen Physiol. 1992 Sep;100(3):495–517. doi: 10.1085/jgp.100.3.495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tinker A., Lindsay A. R., Williams A. J. Block of the sheep cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca(2+)-release channel by tetra-alkyl ammonium cations. J Membr Biol. 1992 Apr;127(2):149–159. doi: 10.1007/BF00233287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tinker A., Lindsay A. R., Williams A. J. Large tetraalkyl ammonium cations produce a reduced conductance state in the sheep cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca(2+)-release channel. Biophys J. 1992 May;61(5):1122–1132. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81922-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tinker A., Williams A. J. Charged local anesthetics block ionic conduction in the sheep cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium release channel. Biophys J. 1993 Aug;65(2):852–864. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81104-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tinker A., Williams A. J. Probing the structure of the conduction pathway of the sheep cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium-release channel with permeant and impermeant organic cations. J Gen Physiol. 1993 Dec;102(6):1107–1129. doi: 10.1085/jgp.102.6.1107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomlins B., Harding S. E., Kirby M. S., Poole-Wilson P. A., Williams A. J. Contamination of a cardiac sarcolemmal preparation with endothelial plasma membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Mar 27;856(1):137–143. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(86)90020-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villarroel A., Alvarez O., Oberhauser A., Latorre R. Probing a Ca2+-activated K+ channel with quaternary ammonium ions. Pflugers Arch. 1988 Dec;413(2):118–126. doi: 10.1007/BF00582521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagenknecht T., Grassucci R., Frank J., Saito A., Inui M., Fleischer S. Three-dimensional architecture of the calcium channel/foot structure of sarcoplasmic reticulum. Nature. 1989 Mar 9;338(6211):167–170. doi: 10.1038/338167a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams A. J. Ion conduction and discrimination in the sarcoplasmic reticulum ryanodine receptor/calcium-release channel. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1992 Feb;13(1):7–26. doi: 10.1007/BF01738423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodhull A. M. Ionic blockage of sodium channels in nerve. J Gen Physiol. 1973 Jun;61(6):687–708. doi: 10.1085/jgp.61.6.687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu L., Jones R., Meissner G. Effects of local anesthetics on single channel behavior of skeletal muscle calcium release channel. J Gen Physiol. 1993 Feb;101(2):207–233. doi: 10.1085/jgp.101.2.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yellen G. Ionic permeation and blockade in Ca2+-activated K+ channels of bovine chromaffin cells. J Gen Physiol. 1984 Aug;84(2):157–186. doi: 10.1085/jgp.84.2.157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zahradníková A., Palade P. Procaine effects on single sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ release channels. Biophys J. 1993 Apr;64(4):991–1003. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81465-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]