Abstract
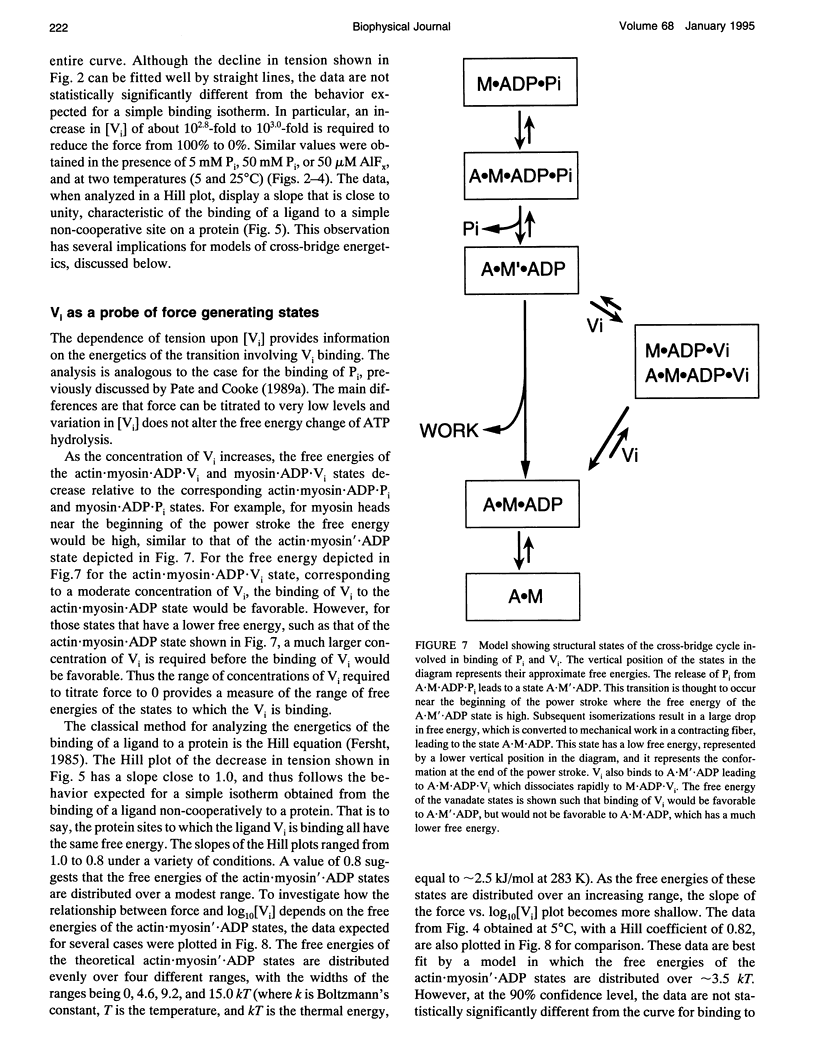
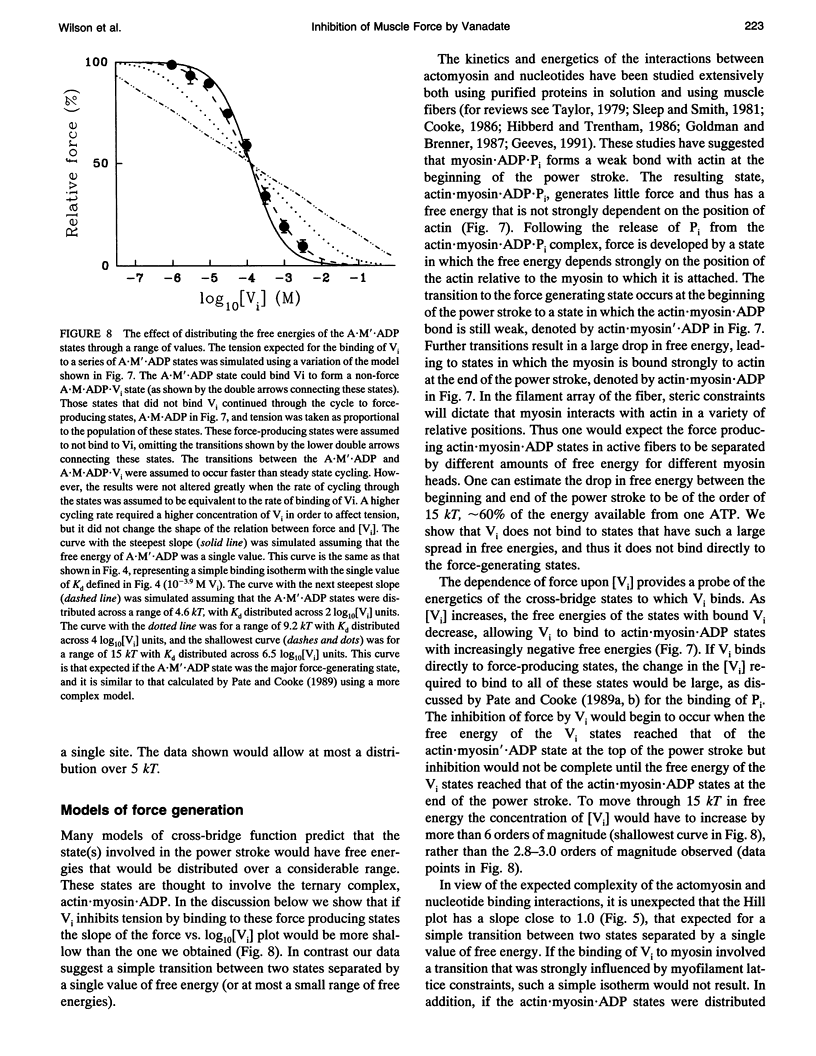
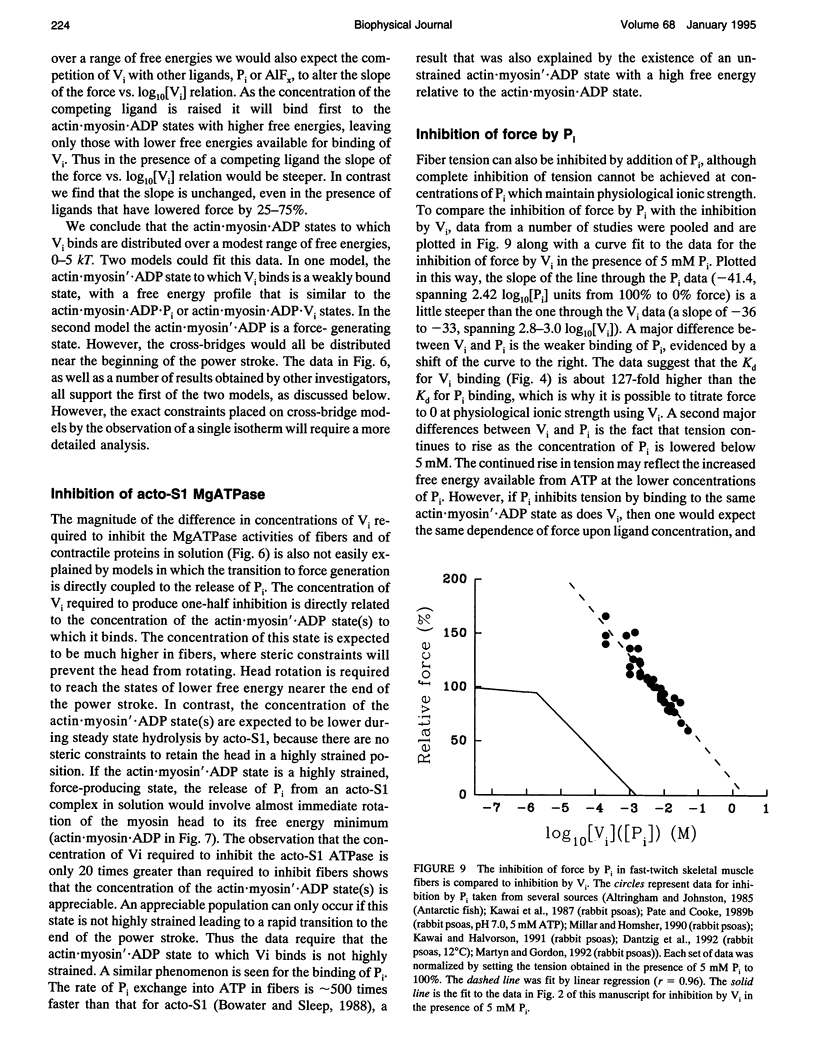
Vanadate (Vi), an analogue of inorganic phosphate (Pi), is known to bind tightly with a long half life to the myosin MgATPase site, producing a complex which inhibits force. Both of these ligands bind to an actin.myosin.ADP state that follows the release of Pi in the enzymatic cycle, and their effects on muscle fibers and proteins in solution provide information on the properties of this state. The inhibition of active force generation began to occur at a [Vi] of 5 microM and was 90% complete at a [Vi] of 1 mM. Hill plots of the inhibition of force by Vi approximated that expected for a simple binding isotherm. Similar plots were obtained at both 25 degrees C and 5 degrees C. A simple binding isotherm is not expected to occur in a muscle fiber where steric constraints imposed by the intact filaments should introduce more complexity into the energetics of ligand binding. The inhibition of MgATPase activity for acto-subfragment-1 to 50% of controls occurred at a [Vi] which was only 20-fold higher than that required to inhibit force generation in fibers to the same level. Some models of actomyosin interactions would predict that the range of [Vi] required for complete force inhibition in fibers and the difference in the [Vi] required for inhibition in fibers and of myosin in solution would both be much larger.
Full text
PDF

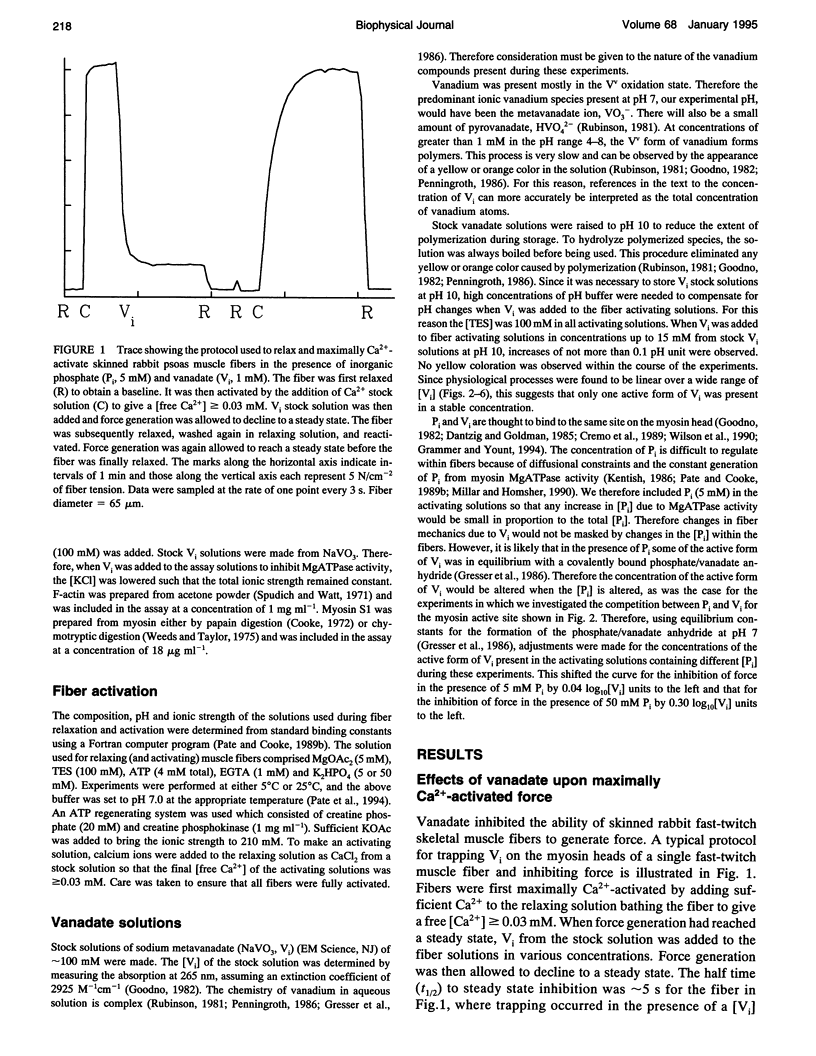
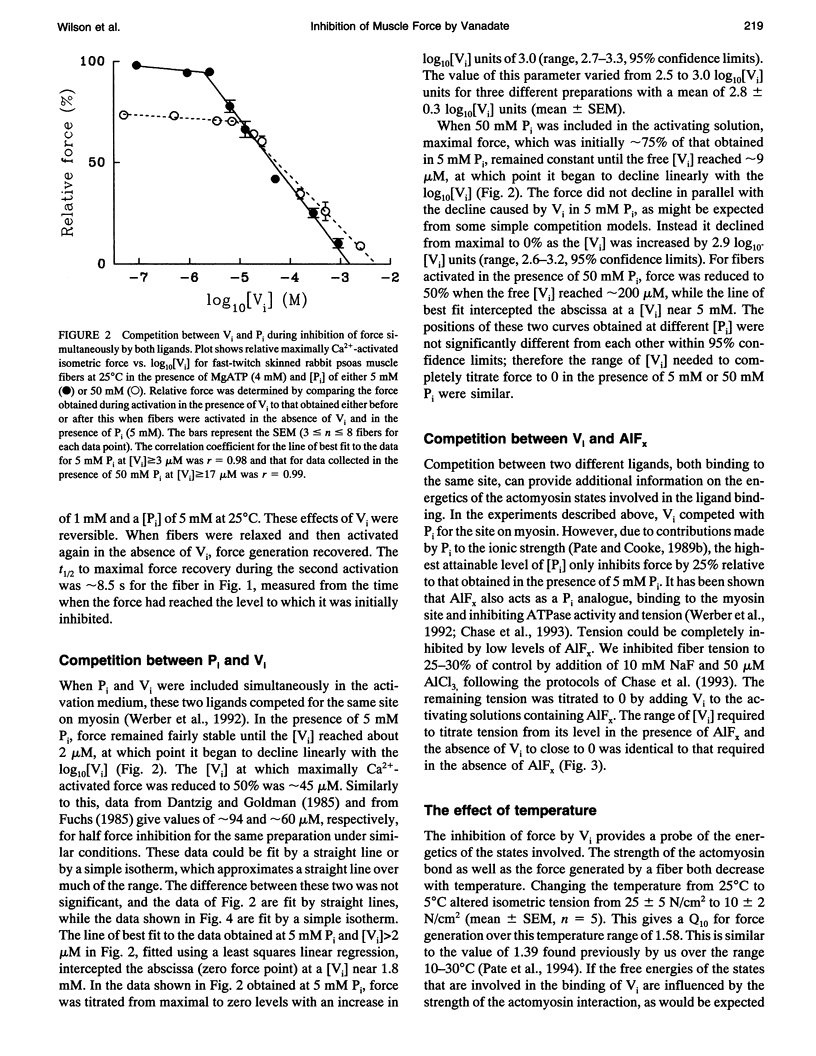
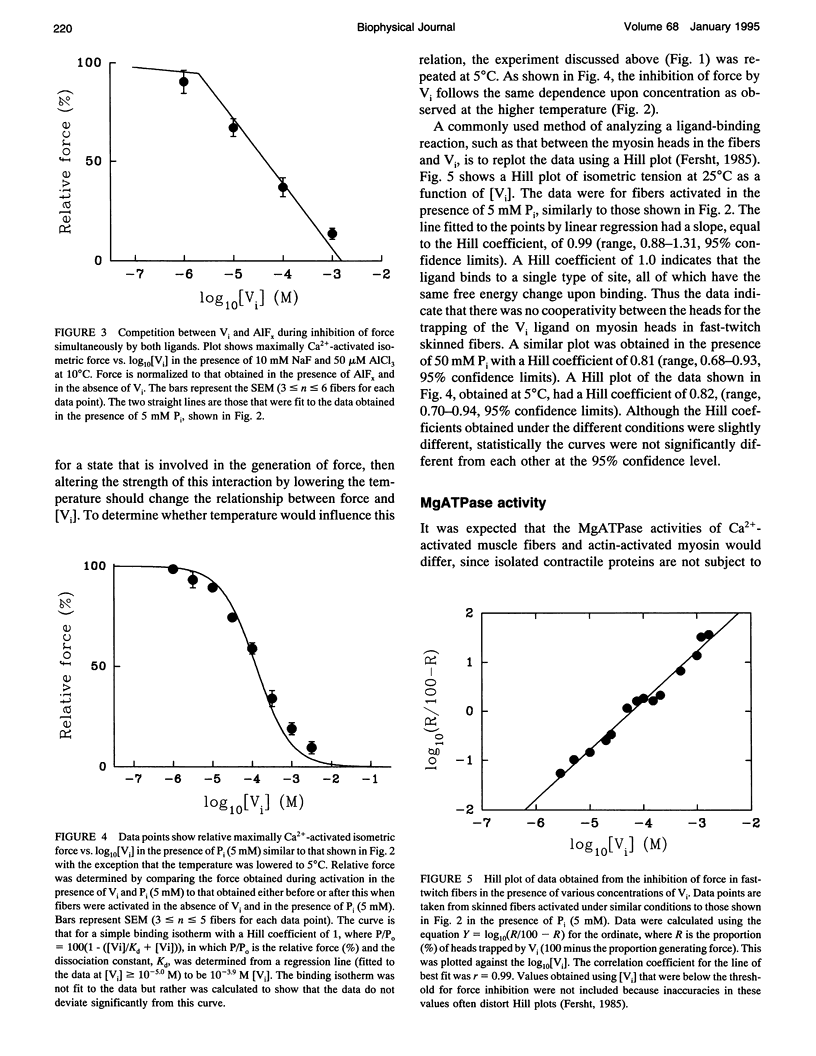
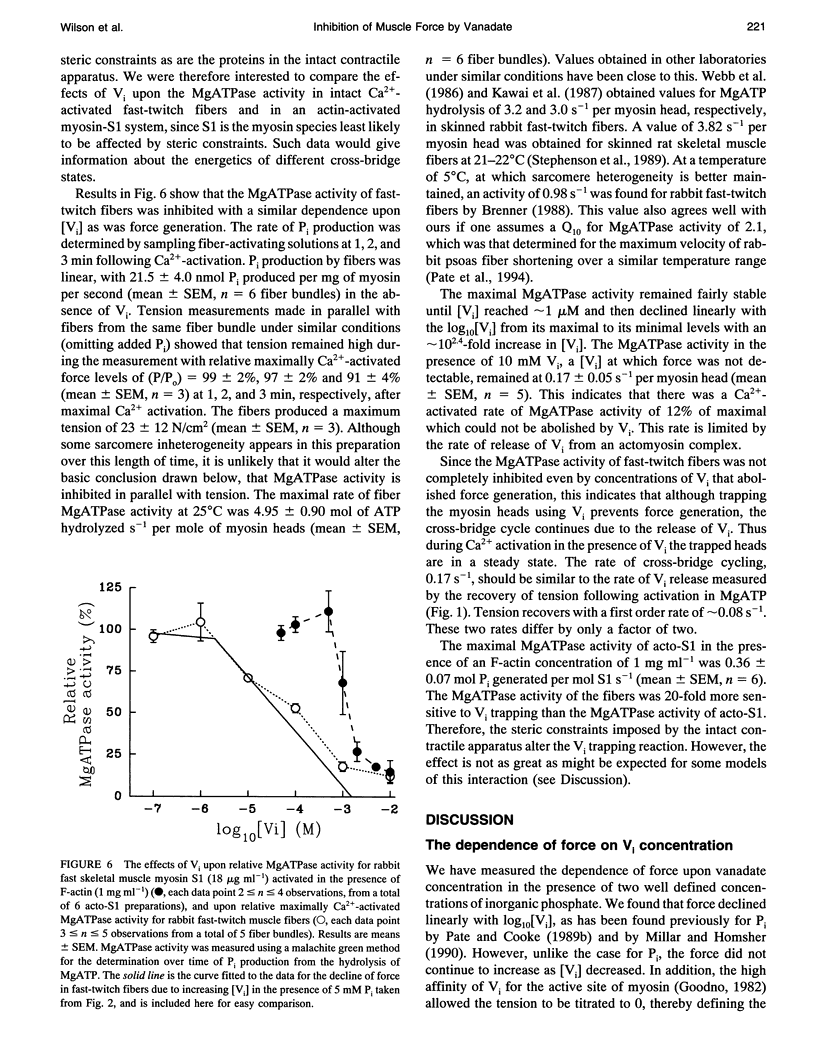


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altringham J. D., Johnston I. A. Effects of phosphate on the contractile properties of fast and slow muscle fibres from an Antarctic fish. J Physiol. 1985 Nov;368:491–500. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowater R., Sleep J. Demembranated muscle fibers catalyze a more rapid exchange between phosphate and adenosine triphosphate than actomyosin subfragment 1. Biochemistry. 1988 Jul 12;27(14):5314–5323. doi: 10.1021/bi00414a055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner B. Effect of Ca2+ on cross-bridge turnover kinetics in skinned single rabbit psoas fibers: implications for regulation of muscle contraction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(9):3265–3269. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.9.3265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chase P. B., Kushmerick M. J. Effects of pH on contraction of rabbit fast and slow skeletal muscle fibers. Biophys J. 1988 Jun;53(6):935–946. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(88)83174-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chase P. B., Martyn D. A., Kushmerick M. J., Gordon A. M. Effects of inorganic phosphate analogues on stiffness and unloaded shortening of skinned muscle fibres from rabbit. J Physiol. 1993 Jan;460:231–246. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1993.sp019469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke R. A new method for producing myosin subfragment-1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Nov 15;49(4):1021–1028. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90314-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke R., Franks K. E. Generation of force by single-headed myosin. J Mol Biol. 1978 Apr 15;120(3):361–373. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90424-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke R., Franks K., Luciani G. B., Pate E. The inhibition of rabbit skeletal muscle contraction by hydrogen ions and phosphate. J Physiol. 1988 Jan;395:77–97. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp016909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke R. The mechanism of muscle contraction. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1986;21(1):53–118. doi: 10.3109/10409238609113609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cremo C. R., Grammer J. C., Yount R. G. Direct chemical evidence that serine 180 in the glycine-rich loop of myosin binds to ATP. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 25;264(12):6608–6611. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dantzig J. A., Goldman Y. E., Millar N. C., Lacktis J., Homsher E. Reversal of the cross-bridge force-generating transition by photogeneration of phosphate in rabbit psoas muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1992;451:247–278. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dantzig J. A., Goldman Y. E. Suppression of muscle contraction by vanadate. Mechanical and ligand binding studies on glycerol-extracted rabbit fibers. J Gen Physiol. 1985 Sep;86(3):305–327. doi: 10.1085/jgp.86.3.305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs F. The binding of calcium to detergent-extracted rabbit psoas muscle fibres during relaxation and force generation. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1985 Aug;6(4):477–486. doi: 10.1007/BF00712584. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geeves M. A. The dynamics of actin and myosin association and the crossbridge model of muscle contraction. Biochem J. 1991 Feb 15;274(Pt 1):1–14. doi: 10.1042/bj2740001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman Y. E., Brenner B. Special topic: molecular mechanism of muscle contraction. General introduction. Annu Rev Physiol. 1987;49:629–636. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.49.030187.003213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodno C. C. Myosin active-site trapping with vanadate ion. Methods Enzymol. 1982;85(Pt B):116–123. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(82)85014-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herzig J. W., Peterson J. W., Rüegg J. C., Solaro R. J. Vanadate and phosphate ions reduce tension and increase cross-bridge kinetics in chemically skinned heart muscle. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Jan 21;672(2):191–196. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(81)90392-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hibberd M. G., Dantzig J. A., Trentham D. R., Goldman Y. E. Phosphate release and force generation in skeletal muscle fibers. Science. 1985 Jun 14;228(4705):1317–1319. doi: 10.1126/science.3159090. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hibberd M. G., Trentham D. R. Relationships between chemical and mechanical events during muscular contraction. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1986;15:119–161. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.15.060186.001003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawai M., Güth K., Winnikes K., Haist C., Rüegg J. C. The effect of inorganic phosphate on the ATP hydrolysis rate and the tension transients in chemically skinned rabbit psoas fibers. Pflugers Arch. 1987 Jan;408(1):1–9. doi: 10.1007/BF00581833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawai M., Halvorson H. R. Two step mechanism of phosphate release and the mechanism of force generation in chemically skinned fibers of rabbit psoas muscle. Biophys J. 1991 Feb;59(2):329–342. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(91)82227-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kentish J. C. The effects of inorganic phosphate and creatine phosphate on force production in skinned muscles from rat ventricle. J Physiol. 1986 Jan;370:585–604. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp015952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kodama T., Fukui K., Kometani K. The initial phosphate burst in ATP hydrolysis by myosin and subfragment-1 as studied by a modified malachite green method for determination of inorganic phosphate. J Biochem. 1986 May;99(5):1465–1472. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a135616. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lymn R. W., Taylor E. W. Mechanism of adenosine triphosphate hydrolysis by actomyosin. Biochemistry. 1971 Dec 7;10(25):4617–4624. doi: 10.1021/bi00801a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margossian S. S., Lowey S. Preparation of myosin and its subfragments from rabbit skeletal muscle. Methods Enzymol. 1982;85(Pt B):55–71. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(82)85009-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martyn D. A., Gordon A. M. Force and stiffness in glycerinated rabbit psoas fibers. Effects of calcium and elevated phosphate. J Gen Physiol. 1992 May;99(5):795–816. doi: 10.1085/jgp.99.5.795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mihashi K., Ooi A., Hiratsuka T. Evidence for the existence of two equilibrium conformations of the ternary complex of myosin subfragment-1, ADP, and orthovanadate. J Biochem. 1990 Mar;107(3):464–469. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a123068. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millar N. C., Homsher E. The effect of phosphate and calcium on force generation in glycerinated rabbit skeletal muscle fibers. A steady-state and transient kinetic study. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 25;265(33):20234–20240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pate E., Cooke R. A model of crossbridge action: the effects of ATP, ADP and Pi. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1989 Jun;10(3):181–196. doi: 10.1007/BF01739809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pate E., Cooke R. Addition of phosphate to active muscle fibers probes actomyosin states within the powerstroke. Pflugers Arch. 1989 May;414(1):73–81. doi: 10.1007/BF00585629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penningroth S. M. Erythro-9-[3-(2-hydroxynonyl)]adenine and vanadate as probes for microtubule-based cytoskeletal mechanochemistry. Methods Enzymol. 1986;134:477–487. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(86)34114-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubinson K. A. Concerning the form of biochemically active vanadium. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1981 May 7;212(1186):65–84. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1981.0025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sleep J. A., Hutton R. L. Exchange between inorganic phosphate and adenosine 5'-triphosphate in the medium by actomyosin subfragment 1. Biochemistry. 1980 Apr 1;19(7):1276–1283. doi: 10.1021/bi00548a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spudich J. A., Watt S. The regulation of rabbit skeletal muscle contraction. I. Biochemical studies of the interaction of the tropomyosin-troponin complex with actin and the proteolytic fragments of myosin. J Biol Chem. 1971 Aug 10;246(15):4866–4871. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson D. G., Stewart A. W., Wilson G. J. Dissociation of force from myofibrillar MgATPase and stiffness at short sarcomere lengths in rat and toad skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1989 Mar;410:351–366. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor E. W. Kinetic studies on the association and dissociation of myosin subfragment 1 and actin. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 5;266(1):294–302. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor E. W. Mechanism of actomyosin ATPase and the problem of muscle contraction. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1979;6(2):103–164. doi: 10.3109/10409237909102562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. W., Lu Z., Moss R. L. Effects of Ca2+ on the kinetics of phosphate release in skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 5;267(4):2459–2466. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb M. R., Hibberd M. G., Goldman Y. E., Trentham D. R. Oxygen exchange between Pi in the medium and water during ATP hydrolysis mediated by skinned fibers from rabbit skeletal muscle. Evidence for Pi binding to a force-generating state. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 25;261(33):15557–15564. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeds A. G., Taylor R. S. Separation of subfragment-1 isoenzymes from rabbit skeletal muscle myosin. Nature. 1975 Sep 4;257(5521):54–56. doi: 10.1038/257054a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werber M. M., Peyser Y. M., Muhlrad A. Characterization of stable beryllium fluoride, aluminum fluoride, and vanadate containing myosin subfragment 1-nucleotide complexes. Biochemistry. 1992 Aug 11;31(31):7190–7197. doi: 10.1021/bi00146a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White D. C., Thorson J. Phosphate starvation and the nonlinear dynamics of insect fibrillar flight muscle. J Gen Physiol. 1972 Sep;60(3):307–336. doi: 10.1085/jgp.60.3.307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


