Abstract
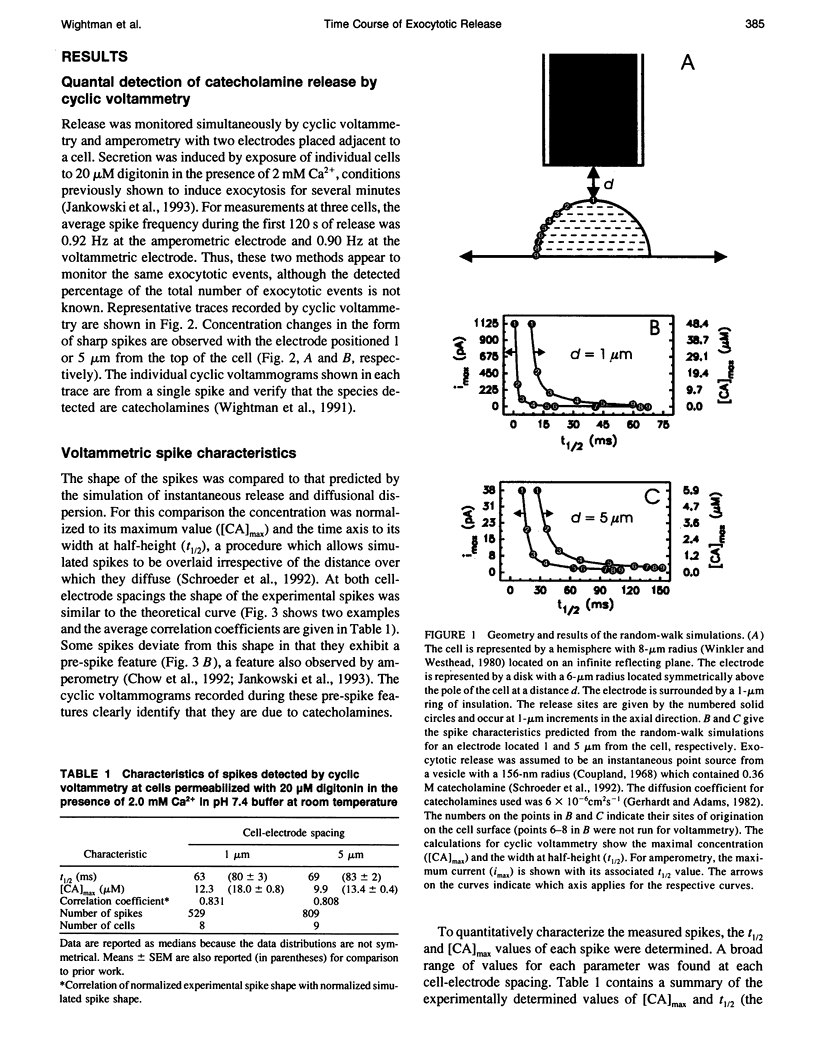
The time course of extrusion of the vesicular contents during exocytosis has been examined at adrenal medullary cells with carbon-fiber microelectrodes. Two electrochemical techniques were used: cyclic voltammetry and amperometry. Spikes obtained by amperometry had a faster time course than those measured by cyclic voltammetry, consistent with the different concentration profiles established by each technique. However, the experimental data obtained with both techniques were temporally broadened with respect to dispersion of an instantaneous point source by diffusion. Measurements with the electrode firmly pressed against the cell surface established that the temporal broadening is a result of a rate-limiting kinetic step associated with extrusion of the vesicular contents at the cell surface. The data do not support a rate-limiting process due to restricted efflux from a small pore. When combined with previous results, the data suggest that the rate-limiting step for chemical secretion from adrenal medullary cells during exocytosis is the dissociation of catecholamines from the vesicular matrix at the surface of the cell.
Full text
PDF

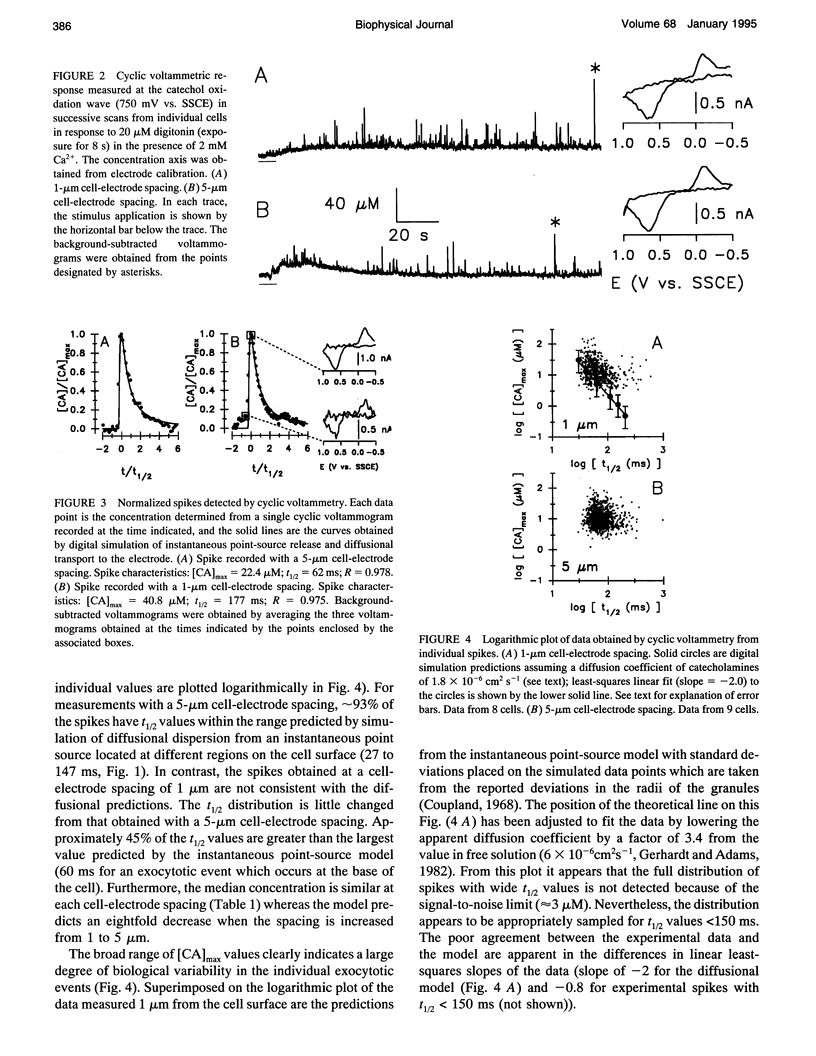




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alvarez de Toledo G., Fernández-Chacón R., Fernández J. M. Release of secretory products during transient vesicle fusion. Nature. 1993 Jun 10;363(6429):554–558. doi: 10.1038/363554a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgoyne R. D. Control of exocytosis in adrenal chromaffin cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Jul 22;1071(2):174–202. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(91)90024-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow R. H., von Rüden L., Neher E. Delay in vesicle fusion revealed by electrochemical monitoring of single secretory events in adrenal chromaffin cells. Nature. 1992 Mar 5;356(6364):60–63. doi: 10.1038/356060a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coupland R. E. Determining sizes and distribution of sizes of spherical bodies such as chromaffin granules in tissue sections. Nature. 1968 Jan 27;217(5126):384–388. doi: 10.1038/217384a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jankowski J. A., Finnegan J. M., Wightman R. M. Extracellular ionic composition alters kinetics of vesicular release of catecholamines and quantal size during exocytosis at adrenal medullary cells. J Neurochem. 1994 Nov;63(5):1739–1747. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.1994.63051739.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jankowski J. A., Schroeder T. J., Ciolkowski E. L., Wightman R. M. Temporal characteristics of quantal secretion of catecholamines from adrenal medullary cells. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jul 15;268(20):14694–14700. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jankowski J. A., Schroeder T. J., Holz R. W., Wightman R. M. Quantal secretion of catecholamines measured from individual bovine adrenal medullary cells permeabilized with digitonin. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 15;267(26):18329–18335. doi: 10.21236/ada251716. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawagoe K. T., Jankowski J. A., Wightman R. M. Etched carbon-fiber electrodes as amperometric detectors of catecholamine secretion from isolated biological cells. Anal Chem. 1991 Aug 1;63(15):1589–1594. doi: 10.1021/ac00015a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawagoe K. T., Zimmerman J. B., Wightman R. M. Principles of voltammetry and microelectrode surface states. J Neurosci Methods. 1993 Jul;48(3):225–240. doi: 10.1016/0165-0270(93)90094-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leszczyszyn D. J., Jankowski J. A., Viveros O. H., Diliberto E. J., Jr, Near J. A., Wightman R. M. Nicotinic receptor-mediated catecholamine secretion from individual chromaffin cells. Chemical evidence for exocytosis. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 5;265(25):14736–14737. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leszczyszyn D. J., Jankowski J. A., Viveros O. H., Diliberto E. J., Jr, Near J. A., Wightman R. M. Secretion of catecholamines from individual adrenal medullary chromaffin cells. J Neurochem. 1991 Jun;56(6):1855–1863. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1991.tb03441.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livett B. G. Adrenal medullary chromaffin cells in vitro. Physiol Rev. 1984 Oct;64(4):1103–1161. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1984.64.4.1103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monck J. R., Fernandez J. M. The exocytotic fusion pore and neurotransmitter release. Neuron. 1994 Apr;12(4):707–716. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90325-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nanavati C., Fernandez J. M. The secretory granule matrix: a fast-acting smart polymer. Science. 1993 Feb 12;259(5097):963–965. doi: 10.1126/science.8438154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor D. T., Frigon R. P. Chromogranin A, the major catecholamine storage vesicle soluble protein. Multiple size forms, subcellular storage, and regional distribution in chromaffin and nervous tissue elucidated by radioimmunoassay. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 10;259(5):3237–3247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder T. J., Jankowski J. A., Kawagoe K. T., Wightman R. M., Lefrou C., Amatore C. Analysis of diffusional broadening of vesicular packets of catecholamines released from biological cells during exocytosis. Anal Chem. 1992 Dec 15;64(24):3077–3083. doi: 10.1021/ac00048a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder T. J., Jankowski J. A., Senyshyn J., Holz R. W., Wightman R. M. Zones of exocytotic release on bovine adrenal medullary cells in culture. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jun 24;269(25):17215–17220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verdugo P. Goblet cells secretion and mucogenesis. Annu Rev Physiol. 1990;52:157–176. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.52.030190.001105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wightman R. M., Jankowski J. A., Kennedy R. T., Kawagoe K. T., Schroeder T. J., Leszczyszyn D. J., Near J. A., Diliberto E. J., Jr, Viveros O. H. Temporally resolved catecholamine spikes correspond to single vesicle release from individual chromaffin cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 1;88(23):10754–10758. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.23.10754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler H., Westhead E. The molecular organization of adrenal chromaffin granules. Neuroscience. 1980;5(11):1803–1823. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(80)90031-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoo S. H., Lewis M. S. Effects of pH and Ca2+ on monomer-dimer and monomer-tetramer equilibria of chromogranin A. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 5;267(16):11236–11241. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]








