Abstract
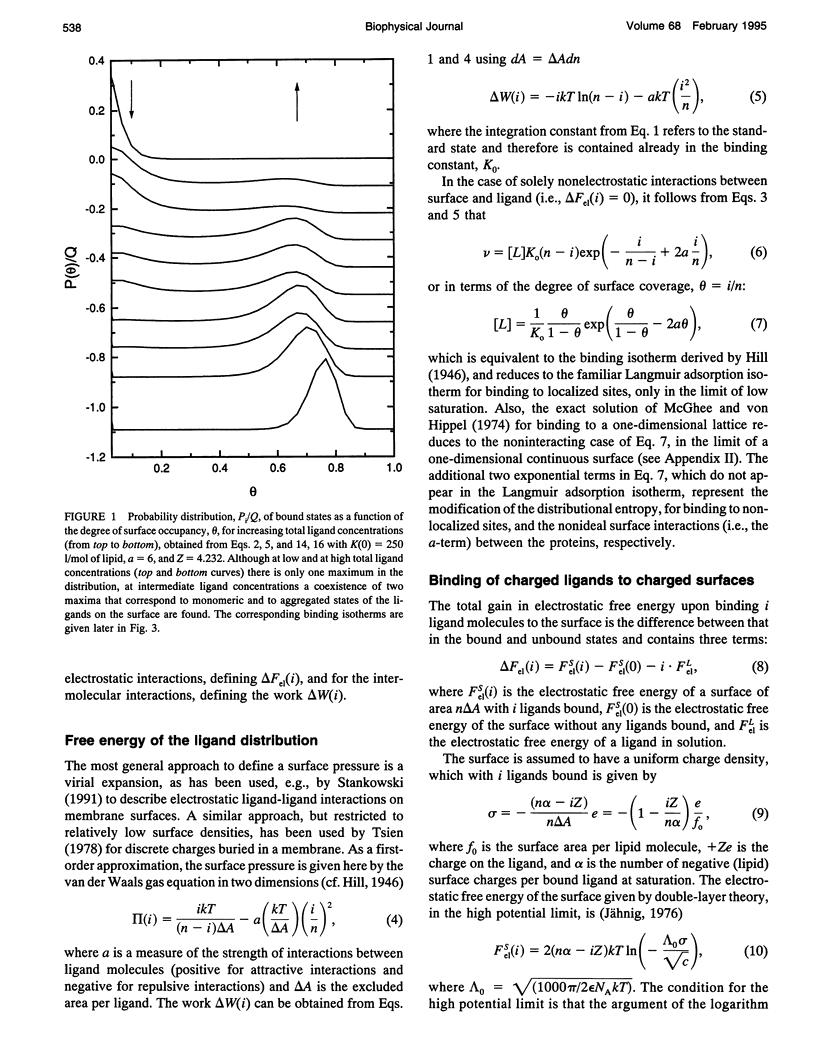
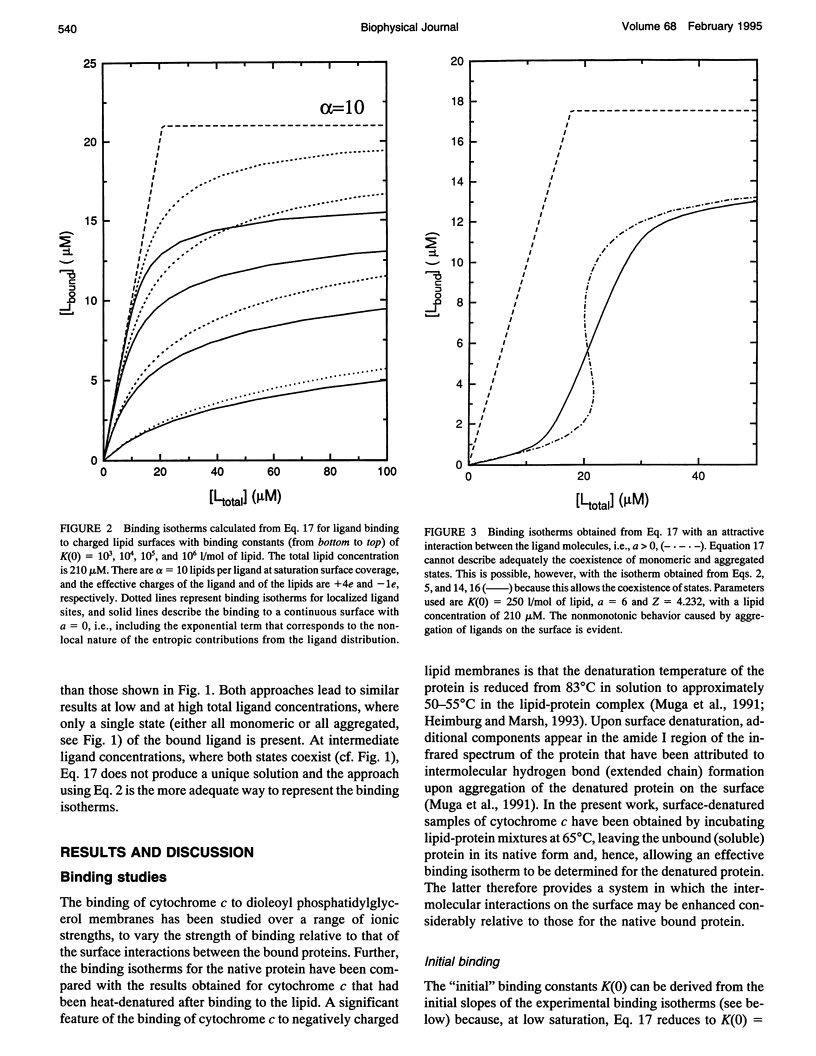
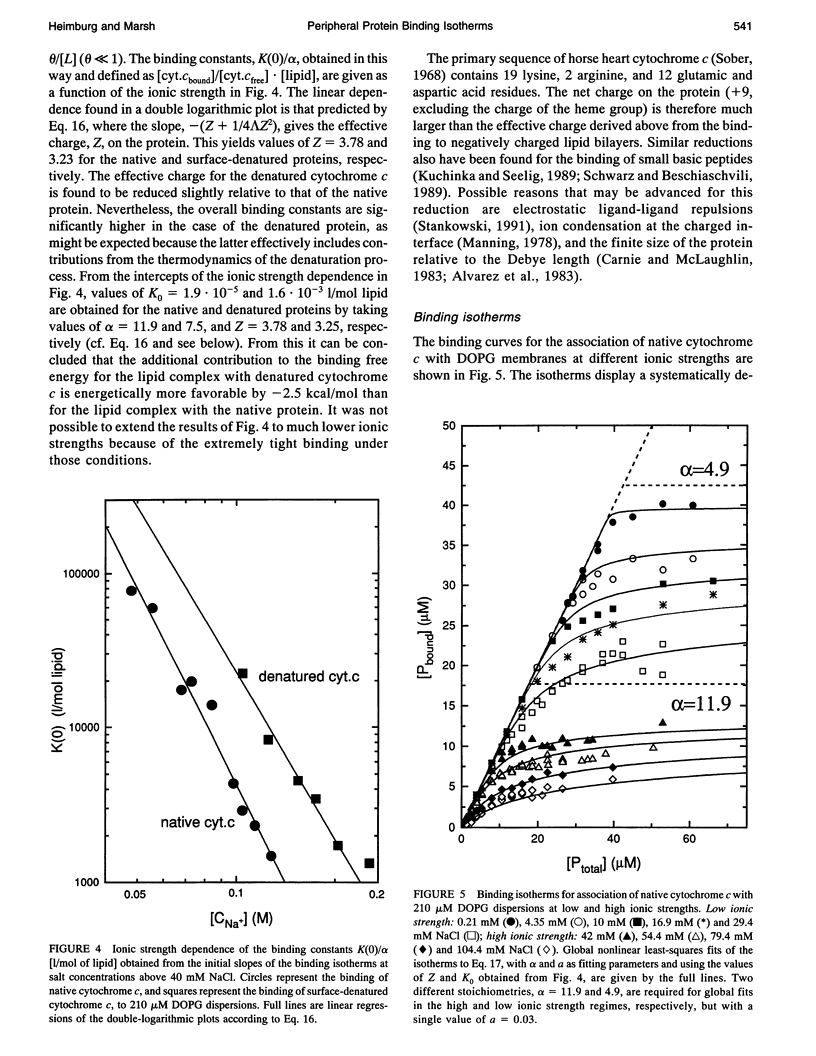
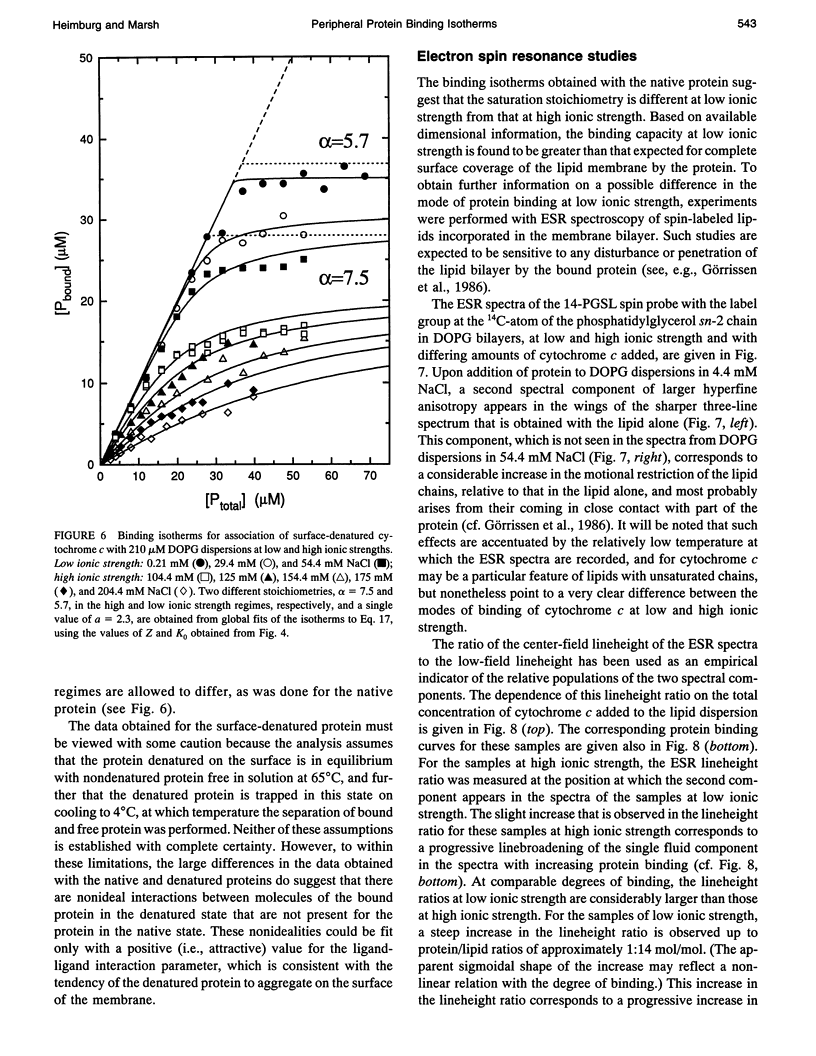
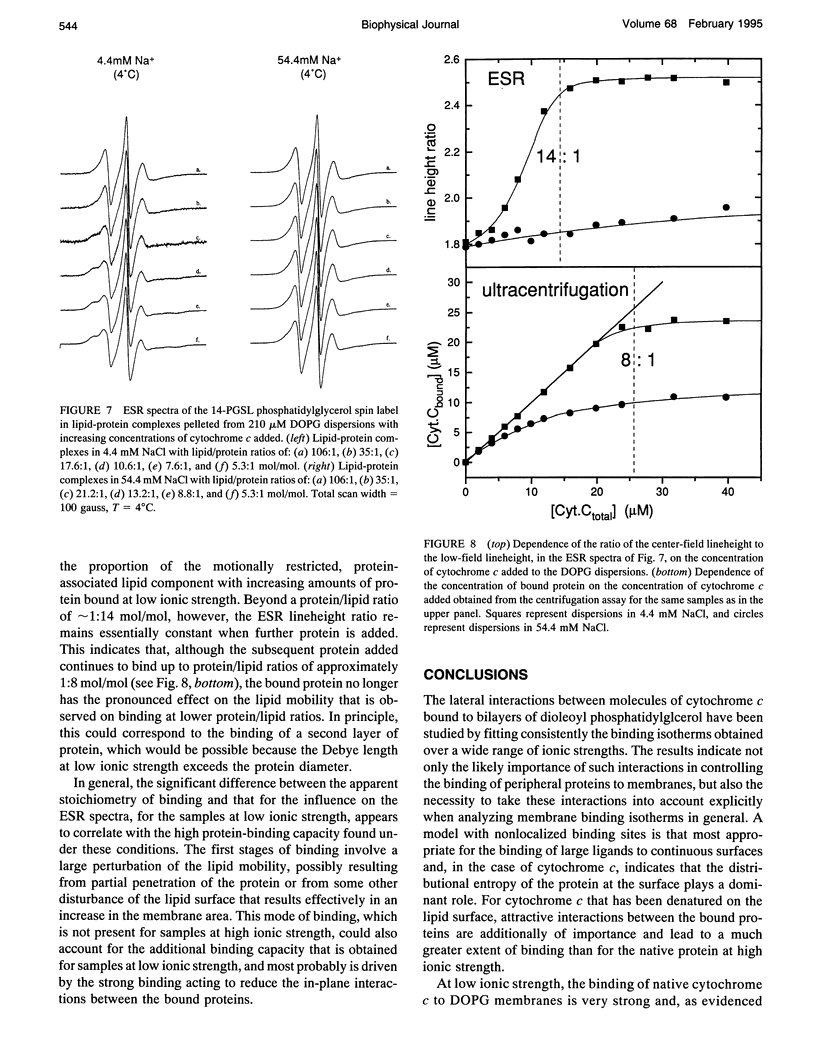
The binding of native cytochrome c to negatively charged lipid dispersions of dioleoyl phosphatidylglycerol has been studied over a wide range of ionic strengths. Not only is the strength of protein binding found to decrease rapidly with increasing ionic strength, but also the binding curves reach an apparent saturation level that decreases rapidly with increasing ionic strength. Analysis of the binding isotherms with a general statistical thermodynamic model that takes into account not only the free energy of the electrostatic double layer, but also the free energy of the surface distribution of the protein, demonstrates that the apparent saturation effects could arise from a competition between the out-of-plane binding reaction and the lateral in-plane interactions between proteins at the surface. It is found that association with nonlocalized sites results in binding isotherms that display the apparent saturation effect to a much more pronounced extent than does the Langmuir adsorption isotherm for binding to localized sites. With the model for nonlocalized sites, the binding isotherms of native cytochrome c can be described adequately by taking into account only the entropy of the surface distribution of the protein, without appreciable enthalpic interactions between the bound proteins. The binding of cytochrome c to dioleoyl phosphatidylglycerol dispersions at a temperature at which the bound protein is denatured on the lipid surface, but is nondenatured when free in solution, has also been studied. The binding curves for the surface-denatured protein differ from those for the native protein in that the apparent saturation at high ionic strength is less pronounced. This indicates the tendency of the denatured protein to aggregate on the lipid surface, and can be described by the binding isotherms for nonlocalized sites only if attractive interactions between the surface-bound proteins are included in addition to the distributional entropic terms. Additionally, it is found that the binding capacity for the native protein is increased at low ionic strength to a value that is greater than that for complete surface coverage, and that corresponds more closely to neutralization of the effective charge (determined from the ionic strength dependence), rather than of the total net charge, on the protein. Electron spin resonance experiments with spin-labeled lipids indicate that this different mode of binding arises from a penetration or disturbance of the bilayer surface by the protein that may alleviate the effects of in-plane interactions under conditions of strong binding.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alvarez O., Brodwick M., Latorre R., McLaughlin A., McLaughlin S., Szabo G. Large divalent cations and electrostatic potentials adjacent to membranes. Experimental results with hexamethonium. Biophys J. 1983 Dec;44(3):333–342. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(83)84307-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carnie S., McLaughlin S. Large divalent cations and electrostatic potentials adjacent to membranes. A theoretical calculation. Biophys J. 1983 Dec;44(3):325–332. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(83)84306-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comfurius P., Zwaal R. F. The enzymatic synthesis of phosphatidylserine and purification by CM-cellulose column chromatography. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Jul 20;488(1):36–42. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(77)90120-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickerson R. E., Takano T., Eisenberg D., Kallai O. B., Samson L., Cooper A., Margoliash E. Ferricytochrome c. I. General features of the horse and bonito proteins at 2.8 A resolution. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 10;246(5):1511–1535. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruner S. M., Tate M. W., Kirk G. L., So P. T., Turner D. C., Keane D. T., Tilcock C. P., Cullis P. R. X-ray diffraction study of the polymorphic behavior of N-methylated dioleoylphosphatidylethanolamine. Biochemistry. 1988 Apr 19;27(8):2853–2866. doi: 10.1021/bi00408a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Görrissen H., Marsh D., Rietveld A., de Kruijff B. Apocytochrome c binding to negatively charged lipid dispersions studied by spin-label electron spin resonance. Biochemistry. 1986 May 20;25(10):2904–2910. doi: 10.1021/bi00358a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heimburg T., Biltonen R. L. Thermotropic behavior of dimyristoylphosphatidylglycerol and its interaction with cytochrome c. Biochemistry. 1994 Aug 16;33(32):9477–9488. doi: 10.1021/bi00198a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heimburg T., Hildebrandt P., Marsh D. Cytochrome c-lipid interactions studied by resonance Raman and 31P NMR spectroscopy. Correlation between the conformational changes of the protein and the lipid bilayer. Biochemistry. 1991 Sep 17;30(37):9084–9089. doi: 10.1021/bi00101a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heimburg T., Marsh D. Investigation of secondary and tertiary structural changes of cytochrome c in complexes with anionic lipids using amide hydrogen exchange measurements: an FTIR study. Biophys J. 1993 Dec;65(6):2408–2417. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81299-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jähnig F. Electrostatic free energy and shift of the phase transition for charged lipid membranes. Biophys Chem. 1976 Jul;4(4):309–318. doi: 10.1016/0301-4622(76)80012-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuchinka E., Seelig J. Interaction of melittin with phosphatidylcholine membranes. Binding isotherm and lipid head-group conformation. Biochemistry. 1989 May 16;28(10):4216–4221. doi: 10.1021/bi00436a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lis L. J., McAlister M., Fuller N., Rand R. P., Parsegian V. A. Interactions between neutral phospholipid bilayer membranes. Biophys J. 1982 Mar;37(3):657–665. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manning G. S. The molecular theory of polyelectrolyte solutions with applications to the electrostatic properties of polynucleotides. Q Rev Biophys. 1978 May;11(2):179–246. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500002031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGhee J. D., von Hippel P. H. Theoretical aspects of DNA-protein interactions: co-operative and non-co-operative binding of large ligands to a one-dimensional homogeneous lattice. J Mol Biol. 1974 Jun 25;86(2):469–489. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90031-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaughlin S. The electrostatic properties of membranes. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1989;18:113–136. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.18.060189.000553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muga A., Mantsch H. H., Surewicz W. K. Membrane binding induces destabilization of cytochrome c structure. Biochemistry. 1991 Jul 23;30(29):7219–7224. doi: 10.1021/bi00243a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson A. P., McQuarrie D. A. The effect of discrete charges on the electrical properties of a membrane. I. J Theor Biol. 1975 Nov;55(1):13–27. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5193(75)80106-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sankaram M. B., Brophy P. J., Marsh D. Spin-label ESR studies on the interaction of bovine spinal cord myelin basic protein with dimyristoylphosphatidylglycerol dispersions. Biochemistry. 1989 Dec 12;28(25):9685–9691. doi: 10.1021/bi00451a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz G., Beschiaschvili G. Thermodynamic and kinetic studies on the association of melittin with a phospholipid bilayer. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Feb 13;979(1):82–90. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(89)90526-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spooner P. J., Watts A. Reversible unfolding of cytochrome c upon interaction with cardiolipin bilayers. 1. Evidence from deuterium NMR measurements. Biochemistry. 1991 Apr 23;30(16):3871–3879. doi: 10.1021/bi00230a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stankowski S. Surface charging by large multivalent molecules. Extending the standard Gouy-Chapman treatment. Biophys J. 1991 Aug;60(2):341–351. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(91)82059-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. Y. A virial expansion for discrete charges buried in a membrane. Biophys J. 1978 Nov;24(2):561–567. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(78)85402-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winiski A. P., McLaughlin A. C., McDaniel R. V., Eisenberg M., McLaughlin S. An experimental test of the discreteness-of-charge effect in positive and negative lipid bilayers. Biochemistry. 1986 Dec 16;25(25):8206–8214. doi: 10.1021/bi00373a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Jongh H. H., Killian J. A., de Kruijff B. A water-lipid interface induces a highly dynamic folded state in apocytochrome c and cytochrome c, which may represent a common folding intermediate. Biochemistry. 1992 Feb 18;31(6):1636–1643. doi: 10.1021/bi00121a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Kruijff B., Cullis P. R. Cytochrome c specifically induces non-bilayer structures in cardiolipin-containing model membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Nov 18;602(3):477–490. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90327-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


