Abstract
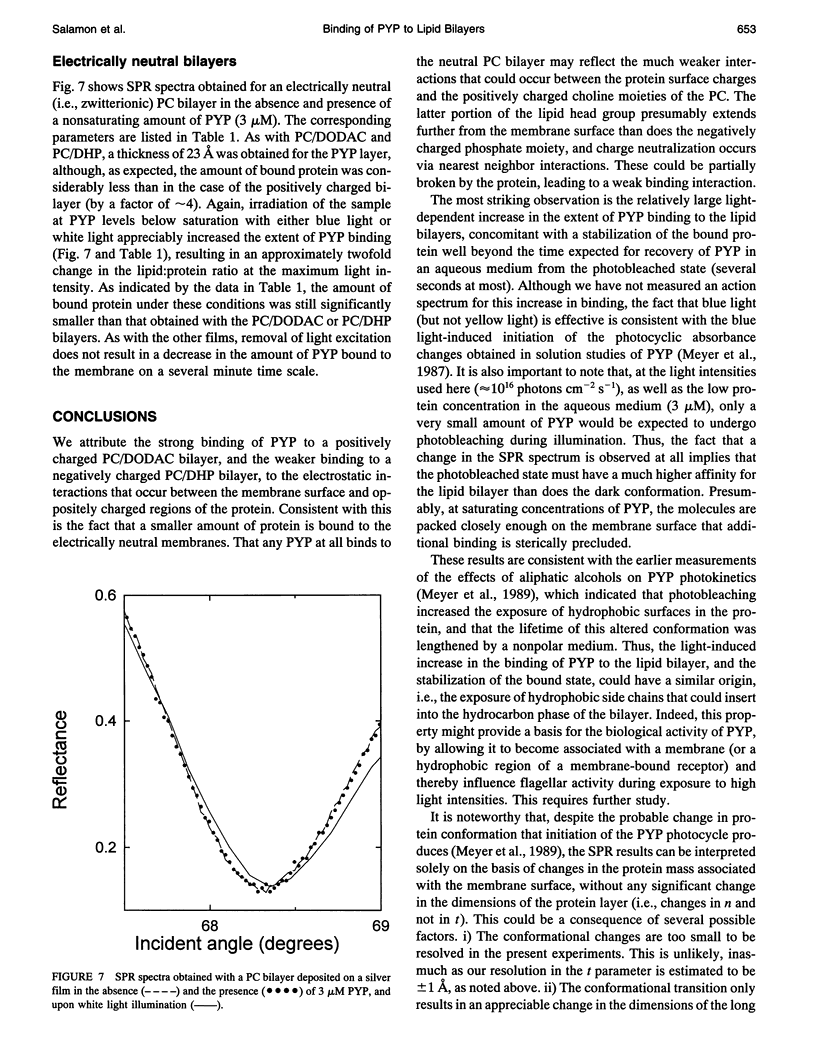
The photoactive yellow protein (PYP) from the phototrophic bacterium Ectothiorhodospira halophila is a small, soluble protein that undergoes reversible photobleaching upon blue light irradiation and may function to mediate the negative phototactic response. Based on previous studies of the effects of solvent viscosity and of aliphatic alcohols on PYP photokinetics, we proposed that photobleaching is concomitant with a protein conformational change that exposes a hydrophobic region on the protein surface. In the present investigation, we have used surface plasmon resonance (SPR) spectroscopy to characterize the binding of PYP to lipid bilayers deposited on a thin silver film. SPR spectra demonstrate that the net negatively charged PYP molecule can bind in a saturable manner to electrically neutral, net positively, and net negatively charged bilayers. Illumination with either blue or white light of a PYP solution, which is in contact with the bilayer, at concentrations below saturation results in an increase in the extent of binding, consistent with exposure of a high affinity hydrophobic surface in the photobleached state, a property that may contribute to its biological function. A value for the thickness of the bound PYP layer (23 A), obtained from theoretical fits to the SPR spectra, is consistent with the structure of the protein determined by x-ray crystallography and indicates that the molecule binds with its long axis parallel to the membrane surface.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bondeson K., Frostell-Karlsson A., Fägerstam L., Magnusson G. Lactose repressor-operator DNA interactions: kinetic analysis by a surface plasmon resonance biosensor. Anal Biochem. 1993 Oct;214(1):245–251. doi: 10.1006/abio.1993.1484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eads J., Sacchettini J. C., Kromminga A., Gordon J. I. Escherichia coli-derived rat intestinal fatty acid binding protein with bound myristate at 1.5 A resolution and I-FABPArg106-->Gln with bound oleate at 1.74 A resolution. J Biol Chem. 1993 Dec 15;268(35):26375–26385. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta S., Morgan T. R., Gordan G. S. Calcitonin gene-related peptide in hepatorenal syndrome. A possible mediator of peripheral vasodilation? J Clin Gastroenterol. 1992 Mar;14(2):122–126. doi: 10.1097/00004836-199203000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoff W. D., Sprenger W. W., Postma P. W., Meyer T. E., Veenhuis M., Leguijt T., Hellingwerf K. J. The photoactive yellow protein from Ectothiorhodospira halophila as studied with a highly specific polyclonal antiserum: (intra)cellular localization, regulation of expression, and taxonomic distribution of cross-reacting proteins. J Bacteriol. 1994 Jul;176(13):3920–3927. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.13.3920-3927.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holden H. M., Rypniewski W. R., Law J. H., Rayment I. The molecular structure of insecticyanin from the tobacco hornworm Manduca sexta L. at 2.6 A resolution. EMBO J. 1987 Jun;6(6):1565–1570. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02401.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McRee D. E., Tainer J. A., Meyer T. E., Van Beeumen J., Cusanovich M. A., Getzoff E. D. Crystallographic structure of a photoreceptor protein at 2.4 A resolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(17):6533–6537. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.17.6533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer T. E., Cusanovich M. A., Tollin G. Transient proton uptake and release is associated with the photocycle of the photoactive yellow protein from the purple phototrophic bacterium Ectothiorhodospira halophila. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1993 Nov 1;306(2):515–517. doi: 10.1006/abbi.1993.1545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer T. E., Fitch J. C., Bartsch R. G., Tollin G., Cusanovich M. A. Soluble cytochromes and a photoactive yellow protein isolated from the moderately halophilic purple phototrophic bacterium, Rhodospirillum salexigens. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Apr 26;1016(3):364–370. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(90)90170-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer T. E. Isolation and characterization of soluble cytochromes, ferredoxins and other chromophoric proteins from the halophilic phototrophic bacterium Ectothiorhodospira halophila. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Jan 23;806(1):175–183. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(85)90094-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer T. E., Tollin G., Causgrove T. P., Cheng P., Blankenship R. E. Picosecond decay kinetics and quantum yield of fluorescence of the photoactive yellow protein from the halophilic purple phototrophic bacterium, Ectothiorhodospira halophila. Biophys J. 1991 May;59(5):988–991. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(91)82313-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer T. E., Tollin G., Hazzard J. H., Cusanovich M. A. Photoactive yellow protein from the purple phototrophic bacterium, Ectothiorhodospira halophila. Quantum yield of photobleaching and effects of temperature, alcohols, glycerol, and sucrose on kinetics of photobleaching and recovery. Biophys J. 1989 Sep;56(3):559–564. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(89)82703-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer T. E., Yakali E., Cusanovich M. A., Tollin G. Properties of a water-soluble, yellow protein isolated from a halophilic phototrophic bacterium that has photochemical activity analogous to sensory rhodopsin. Biochemistry. 1987 Jan 27;26(2):418–423. doi: 10.1021/bi00376a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newcomer M. E., Jones T. A., Aqvist J., Sundelin J., Eriksson U., Rask L., Peterson P. A. The three-dimensional structure of retinol-binding protein. EMBO J. 1984 Jul;3(7):1451–1454. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01995.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salamon Z., Gleason F. K., Tollin G. Direct electrochemistry of thioredoxins and glutathione at a lipid bilayer-modified electrode. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1992 Nov 15;299(1):193–198. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(92)90262-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salamon Z., Hazzard J. T., Tollin G. Direct measurement of cyclic current-voltage responses of integral membrane proteins at a self-assembled lipid-bilayer-modified electrode: cytochrome f and cytochrome c oxidase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 15;90(14):6420–6423. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.14.6420. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salamon Z., Tollin G. Direct electrochemistry of spinach plastocyanin at a lipid bilayer-modified electrode: cyclic voltammetry as a probe of membrane-protein interactions. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1992 May 1;294(2):382–387. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(92)90699-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salamon Z., Wang Y., Brown M. F., Macleod H. A., Tollin G. Conformational changes in rhodopsin probed by surface plasmon resonance spectroscopy. Biochemistry. 1994 Nov 22;33(46):13706–13711. doi: 10.1021/bi00250a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salamon Z., Wang Y., Tollin G., Macleod H. A. Assembly and molecular organization of self-assembled lipid bilayers on solid substrates monitored by surface plasmon resonance spectroscopy. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1994 Nov 2;1195(2):267–275. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(94)90266-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuster S. C., Swanson R. V., Alex L. A., Bourret R. B., Simon M. I. Assembly and function of a quaternary signal transduction complex monitored by surface plasmon resonance. Nature. 1993 Sep 23;365(6444):343–347. doi: 10.1038/365343a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprenger W. W., Hoff W. D., Armitage J. P., Hellingwerf K. J. The eubacterium Ectothiorhodospira halophila is negatively phototactic, with a wavelength dependence that fits the absorption spectrum of the photoactive yellow protein. J Bacteriol. 1993 May;175(10):3096–3104. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.10.3096-3104.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson R. V., Schuster S. C., Simon M. I. Expression of CheA fragments which define domains encoding kinase, phosphotransfer, and CheY binding activities. Biochemistry. 1993 Aug 3;32(30):7623–7629. doi: 10.1021/bi00081a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tien H. T., Salamon Z., Ottova A. Lipid bilayer-based sensors and biomolecular electronics. Crit Rev Biomed Eng. 1991;18(5):323–340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Beeumen J. J., Devreese B. V., Van Bun S. M., Hoff W. D., Hellingwerf K. J., Meyer T. E., McRee D. E., Cusanovich M. A. Primary structure of a photoactive yellow protein from the phototrophic bacterium Ectothiorhodospira halophila, with evidence for the mass and the binding site of the chromophore. Protein Sci. 1993 Jul;2(7):1114–1125. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560020706. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]