Abstract
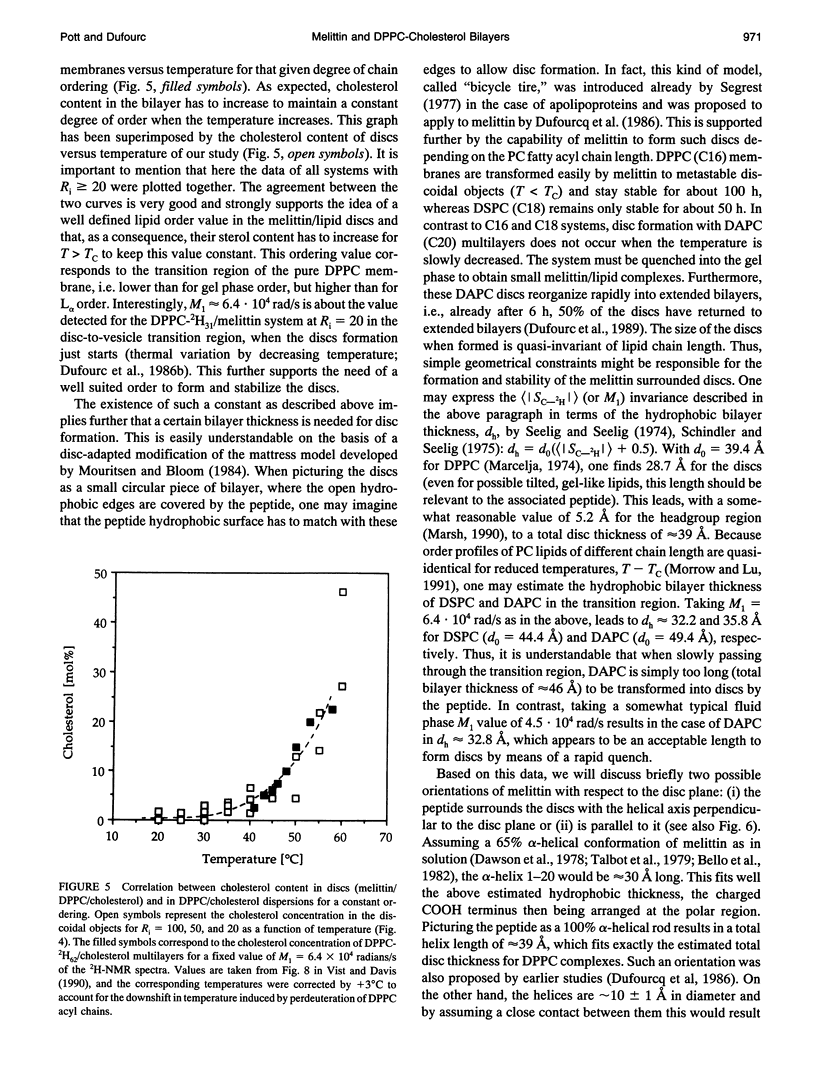
Solid-state deuterium and phosphorus-31 nuclear magnetic resonance studies of deuterium-labeled beta--[2,2',3,4,4',6-2H6]-cholesterol and 1,2-dipalmitoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphatidylcholine have been undertaken to monitor the action of melittin on model membranes containing 30 mol% cholesterol, both at the molecular and macroscopic level. Cholesterol totally inhibits the toxin-triggered formation of large unilamellar vesicles and strongly restricts the appearance of small discs. The latter remain stable over a wide temperature range (20-60 degrees C) because of an increase in their cholesterol content as the temperature increases. This process is related to a constant disc hydrophobic thickness of approximately 29 A. The system, when not in the form of discs, appears to be composed of very large vesicles on which melittin promotes magnetically induced ellipsoidal deformation. This deformation is the greatest when the maximum of discs is observed. A model to describe both the disc formation and stability is proposed.
Full text
PDF








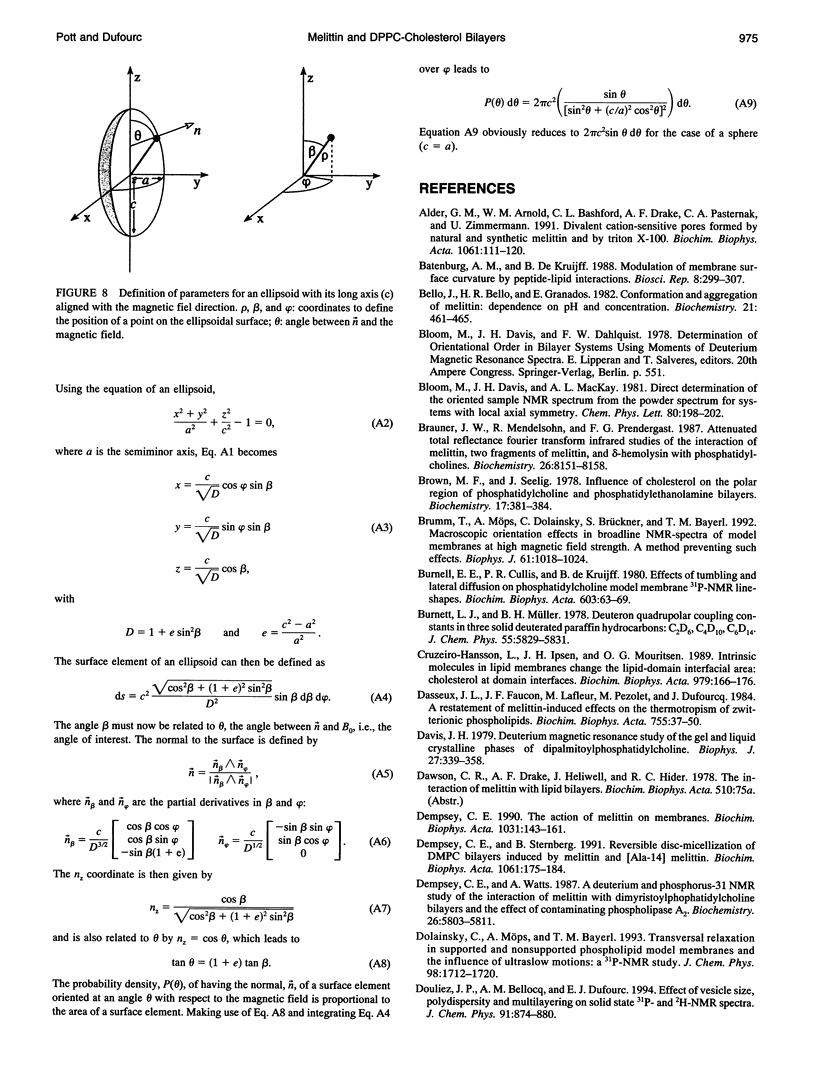


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alder G. M., Arnold W. M., Bashford C. L., Drake A. F., Pasternak C. A., Zimmermann U. Divalent cation-sensitive pores formed by natural and synthetic melittin and by Triton X-100. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Jan 9;1061(1):111–120. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(91)90275-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batenburg A. M., de Kruijff B. Modulation of membrane surface curvature by peptide-lipid interactions. Biosci Rep. 1988 Aug;8(4):299–307. doi: 10.1007/BF01115220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bello J., Bello H. R., Granados E. Conformation and aggregation of melittin: dependence on pH and concentration. Biochemistry. 1982 Feb 2;21(3):461–465. doi: 10.1021/bi00532a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brauner J. W., Mendelsohn R., Prendergast F. G. Attenuated total reflectance Fourier transform infrared studies of the interaction of melittin, two fragments of melittin, and delta-hemolysin with phosphatidylcholines. Biochemistry. 1987 Dec 15;26(25):8151–8158. doi: 10.1021/bi00399a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. F., Seelig J. Influence of cholesterol on the polar region of phosphatidylcholine and phosphatidylethanolamine bilayers. Biochemistry. 1978 Jan 24;17(2):381–384. doi: 10.1021/bi00595a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brumm T., Möps A., Dolainsky C., Brückner S., Bayerl T. M. Macroscopic orientation effects in broadline NMR-spectra of model membranes at high magnetic field strength: A method preventing such effects. Biophys J. 1992 Apr;61(4):1018–1024. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81909-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnell E. E., Cullis P. R., de Kruijff B. Effects of tumbling and lateral diffusion on phosphatidylcholine model membrane 31P-NMR lineshapes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Dec 2;603(1):63–69. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90391-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cruzeiro-Hansson L., Ipsen J. H., Mouritsen O. G. Intrinsic molecules in lipid membranes change the lipid-domain interfacial area: cholesterol at domain interfaces. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Feb 27;979(2):166–176. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(89)90432-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dasseux J. L., Faucon J. F., Lafleur M., Pezolet M., Dufourcq J. A restatement of melittin-induced effects on the thermotropism of zwitterionic phospholipids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Aug 8;775(1):37–50. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(84)90232-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis J. H. Deuterium magnetic resonance study of the gel and liquid crystalline phases of dipalmitoyl phosphatidylcholine. Biophys J. 1979 Sep;27(3):339–358. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(79)85222-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dempsey C. E., Sternberg B. Reversible disc-micellization of dimyristoylphosphatidylcholine bilayers induced by melittin and [Ala-14]melittin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Jan 30;1061(2):175–184. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(91)90283-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dempsey C. E. The actions of melittin on membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 May 7;1031(2):143–161. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(90)90006-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dempsey C. E., Watts A. A deuterium and phosphorus-31 nuclear magnetic resonance study of the interaction of melittin with dimyristoylphosphatidylcholine bilayers and the effects of contaminating phospholipase A2. Biochemistry. 1987 Sep 8;26(18):5803–5811. doi: 10.1021/bi00392a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drake A. F., Hider R. C. The structure of melittin in lipid bilayer membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Aug 7;555(2):371–373. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(79)90178-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dufourc E. J., Bonmatin J. M., Dufourcq J. Membrane structure and dynamics by 2H- and 31P-NMR. Effects of amphipatic peptidic toxins on phospholipid and biological membranes. Biochimie. 1989 Jan;71(1):117–123. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(89)90141-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dufourc E. J., Smith I. C., Dufourcq J. Molecular details of melittin-induced lysis of phospholipid membranes as revealed by deuterium and phosphorus NMR. Biochemistry. 1986 Oct 21;25(21):6448–6455. doi: 10.1021/bi00369a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dufourcq J., Faucon J. F., Fourche G., Dasseux J. L., Le Maire M., Gulik-Krzywicki T. Morphological changes of phosphatidylcholine bilayers induced by melittin: vesicularization, fusion, discoidal particles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Jul 10;859(1):33–48. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(86)90315-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dufourcq J., Faucon J. F. Intrinsic fluorescence study of lipid-protein interactions in membrane models. Binding of melittin, an amphipathic peptide, to phospholipid vesicles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 May 16;467(1):1–11. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90236-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faucon J. F., Dufourcq J., Lussan C. The self-association of melittin and its binding to lipids: an intrinsic fluorescence polarization study. FEBS Lett. 1979 Jun 1;102(1):187–190. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80956-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habermann E. Bee and wasp venoms. Science. 1972 Jul 28;177(4046):314–322. doi: 10.1126/science.177.4046.314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habermann E., Jentsch J. Sequenzanalyse des Melittins aus den tryptischen und peptischen Spaltstücken. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1967 Jan;348(1):37–50. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hong F. T., Mauzerall D., Mauro A. Magnetic anisotropy and the orientation of retinal rods in a homogeneous magnetic field. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jun;68(6):1283–1285. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.6.1283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ipsen J. H., Karlström G., Mouritsen O. G., Wennerström H., Zuckermann M. J. Phase equilibria in the phosphatidylcholine-cholesterol system. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Nov 27;905(1):162–172. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(87)90020-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ipsen J. H., Mouritsen O. G., Zuckermann M. J. Theory of thermal anomalies in the specific heat of lipid bilayers containing cholesterol. Biophys J. 1989 Oct;56(4):661–667. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(89)82713-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansson M., Thurmond R. L., Trouard T. P., Brown M. F. Magnetic alignment and orientational order of dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine bilayers containing palmitoyllysophosphatidylcholine. Chem Phys Lipids. 1990 Jun;54(3-4):157–170. doi: 10.1016/0009-3084(90)90009-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuchinka E., Seelig J. Interaction of melittin with phosphatidylcholine membranes. Binding isotherm and lipid head-group conformation. Biochemistry. 1989 May 16;28(10):4216–4221. doi: 10.1021/bi00436a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lauterwein J., Bösch C., Brown L. R., Wüthrich K. Physicochemical studies of the protein-lipid interactions in melittin-containing micelles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Sep 21;556(2):244–264. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(79)90046-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Léonard A., Dufourc E. J. Interactions of cholesterol with the membrane lipid matrix. A solid state NMR approach. Biochimie. 1991 Oct;73(10):1295–1302. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(91)90092-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mabrey S., Mateo P. L., Sturtevant J. M. High-sensitivity scanning calorimetric study of mixtures of cholesterol with dimyristoyl- and dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholines. Biochemistry. 1978 Jun 13;17(12):2464–2468. doi: 10.1021/bi00605a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcelja S. Chain ordering in liquid crystals. II. Structure of bilayer membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Oct 29;367(2):165–176. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(74)90040-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurer T., Lücke C., Rüterjans H. Investigation of the membrane-active peptides melittin and glucagon by photochemically induced dynamic-nuclear-polarization (photo-CIDNP) NMR. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Feb 26;196(1):135–141. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb15796.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMullen T. P., Lewis R. N., McElhaney R. N. Differential scanning calorimetric study of the effect of cholesterol on the thermotropic phase behavior of a homologous series of linear saturated phosphatidylcholines. Biochemistry. 1993 Jan 19;32(2):516–522. doi: 10.1021/bi00053a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monette M., Van Calsteren M. R., Lafleur M. Effect of cholesterol on the polymorphism of dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine/melittin complexes: an NMR study. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Jul 4;1149(2):319–328. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(93)90217-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mouritsen O. G., Bloom M. Mattress model of lipid-protein interactions in membranes. Biophys J. 1984 Aug;46(2):141–153. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84007-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Needham D., McIntosh T. J., Evans E. Thermomechanical and transition properties of dimyristoylphosphatidylcholine/cholesterol bilayers. Biochemistry. 1988 Jun 28;27(13):4668–4673. doi: 10.1021/bi00413a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neugebauer D. C., Blaurock A. E. Magnetic orientation of purple membranes demonstrated by optical measurements and neutron scattering. FEBS Lett. 1977;78(1):31–35. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80266-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parasassi T., Di Stefano M., Loiero M., Ravagnan G., Gratton E. Influence of cholesterol on phospholipid bilayers phase domains as detected by Laurdan fluorescence. Biophys J. 1994 Jan;66(1):120–132. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80763-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podo F., Strom R., Crifò C., Zulauf M. Dependence of melittin structure on its interaction with multivalent anions and with model membrane systems. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1982 May;19(5):514–527. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1982.tb02637.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qiu X., Mirau P. A., Pidgeon C. Magnetically induced orientation of phosphatidylcholine membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Apr 8;1147(1):59–72. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(93)90316-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinl H., Brumm T., Bayerl T. M. Changes of the physical properties of the liquid-ordered phase with temperature in binary mixtures of DPPC with cholesterol: A H-NMR, FT-IR, DSC, and neutron scattering study. Biophys J. 1992 Apr;61(4):1025–1035. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81910-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sankaram M. B., Thompson T. E. Interaction of cholesterol with various glycerophospholipids and sphingomyelin. Biochemistry. 1990 Nov 27;29(47):10670–10675. doi: 10.1021/bi00499a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schindler H., Seelig J. Deuterium order parameters in relation to thermodynamic properties of a phospholiped bilayer. A statistical mechanical interpretation. Biochemistry. 1975 Jun 3;14(11):2283–2287. doi: 10.1021/bi00682a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott H. L. Lipid-cholesterol interactions. Monte Carlo simulations and theory. Biophys J. 1991 Feb;59(2):445–455. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(91)82238-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seelig A., Seelig J. The dynamic structure of fatty acyl chains in a phospholipid bilayer measured by deuterium magnetic resonance. Biochemistry. 1974 Nov 5;13(23):4839–4845. doi: 10.1021/bi00720a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seelig J., Seelig A. Lipid conformation in model membranes and biological membranes. Q Rev Biophys. 1980 Feb;13(1):19–61. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500000305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segrest J. P. Amphipathic helixes and plasma lipoproteins: thermodynamic and geometric considerations. Chem Phys Lipids. 1977 Jan;18(1):7–22. doi: 10.1016/0009-3084(77)90023-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sessa G., Freer J. H., Colacicco G., Weissmann G. Interaction of alytic polypeptide, melittin, with lipid membrane systems. J Biol Chem. 1969 Jul 10;244(13):3575–3582. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talbot J. C., Dufourcq J., de Bony J., Faucon J. F., Lussan C. Conformational change and self association of monomeric melittin. FEBS Lett. 1979 Jun 1;102(1):191–193. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80957-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terwilliger T. C., Eisenberg D. The structure of melittin. II. Interpretation of the structure. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 10;257(11):6016–6022. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tosteson M. T., Tosteson D. C. Activation and inactivation of melittin channels. Biophys J. 1984 Jan;45(1):112–114. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84130-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vist M. R., Davis J. H. Phase equilibria of cholesterol/dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine mixtures: 2H nuclear magnetic resonance and differential scanning calorimetry. Biochemistry. 1990 Jan 16;29(2):451–464. doi: 10.1021/bi00454a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel H. Comparison of the conformation and orientation of alamethicin and melittin in lipid membranes. Biochemistry. 1987 Jul 14;26(14):4562–4572. doi: 10.1021/bi00388a060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver A. J., Kemple M. D., Brauner J. W., Mendelsohn R., Prendergast F. G. Fluorescence, CD, attenuated total reflectance (ATR) FTIR, and 13C NMR characterization of the structure and dynamics of synthetic melittin and melittin analogues in lipid environments. Biochemistry. 1992 Feb 11;31(5):1301–1313. doi: 10.1021/bi00120a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worcester D. L. Structural origins of diamagnetic anisotropy in proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5475–5477. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeagle P. L. Cholesterol and the cell membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Dec 9;822(3-4):267–287. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(85)90011-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


