Abstract
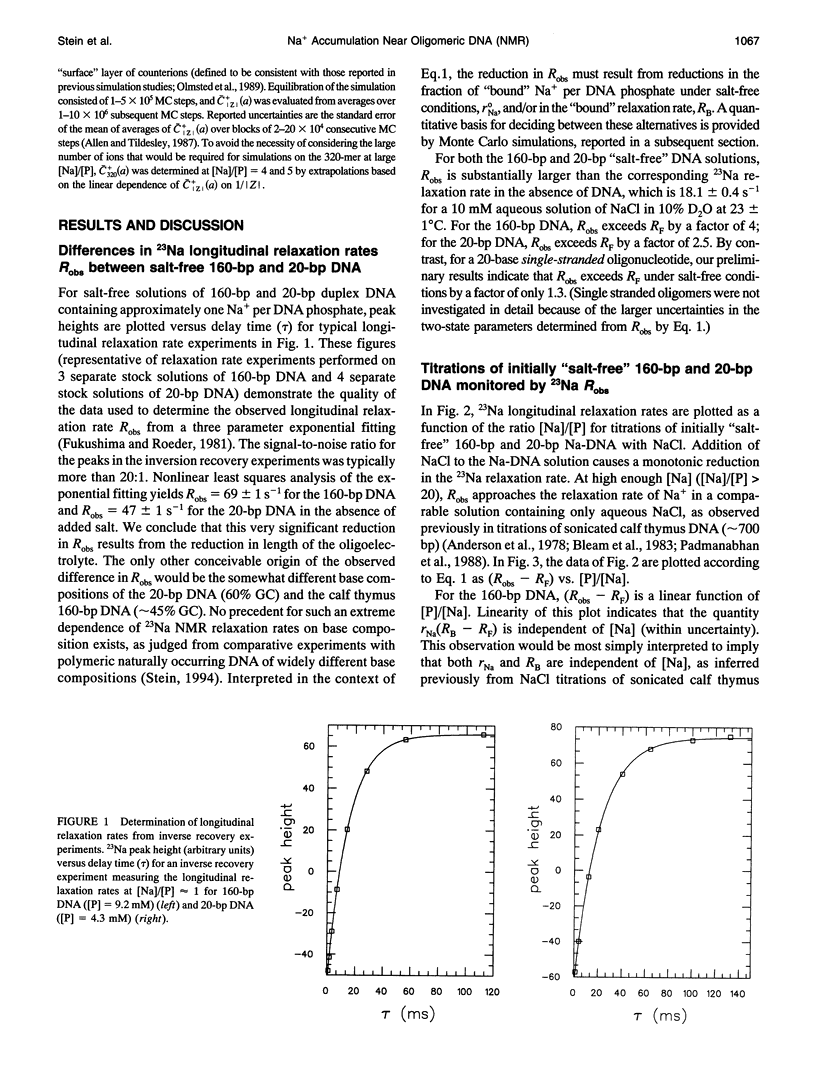
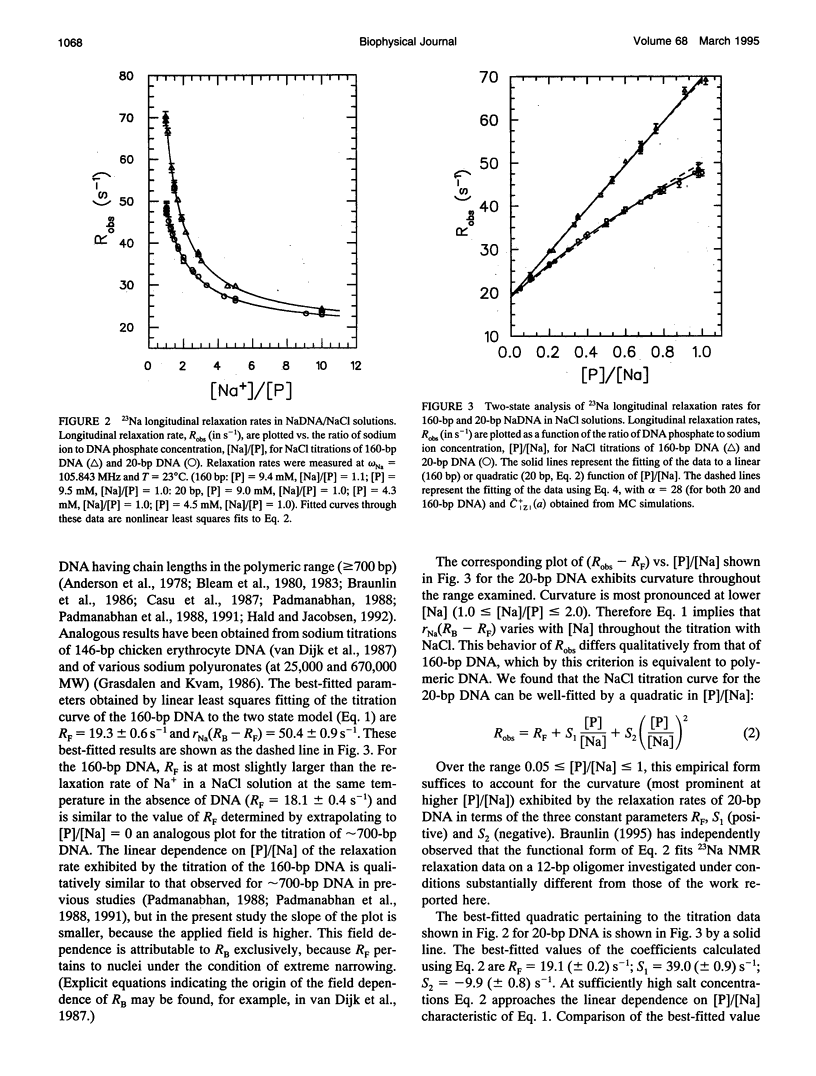
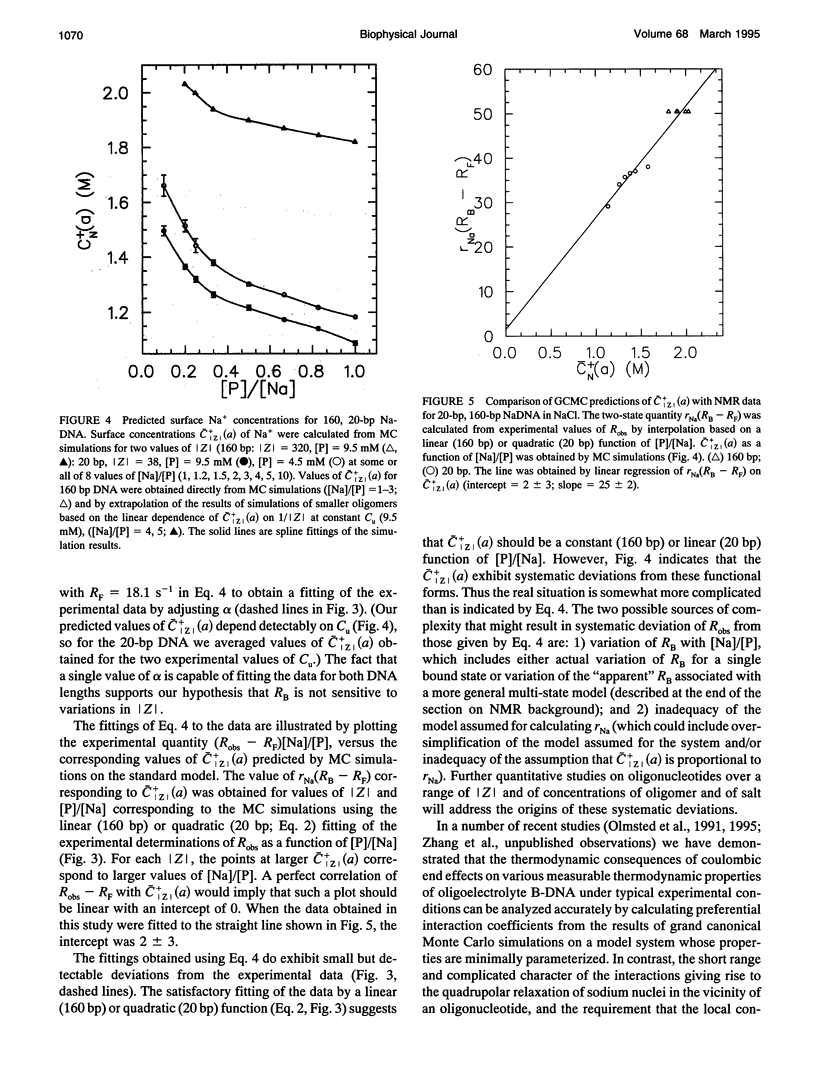
The local cation concentration at the surface of oligomeric or polymeric B-DNA is expected, on the basis of MC simulations (Olmsted, M. C., C. F. Anderson, and M. T. Record, Jr. 1989. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 86:7766-7770), to decrease sharply as either end of the molecule is approached. In this paper we report 23Na NMR measurements indicating the importance of this "coulombic" end effect on the average extent of association of Na+ with oligomeric duplex DNA. In solutions containing either 20-bp synthetic DNA or 160-bp mononucleosomal calf thymus DNA at phosphate monomer concentrations [P] of 4-10 mM, measurements were made over the range of ratios 1 < or = [Na]/[LP] < or = 20, corresponding to Na+ concentrations of 4-200 nM. The longitudinal 23Na NMR relaxation rates measured in these NaDNA solutions, Robs, are interpreted as population-weighted averages of contributions from "bound" (RB) and "free" (RF) 23Na relaxation rates. The observed enhancements of Robs indicate that RB significantly exceeds RF, which is approximately equal to the 23Na relaxation rate in an aqueous solution containing only NaCl. Under salt-fre-tconditions ([Na]/[P] = 1), where the enhancement in Robs is maximal, we find that Robs--RF in the solution containing 160-bp DNA is approximately 1.8 times that observed for the 20-bp DNA. For the 160-bp oligomer (which theoretical calculations predict to be effectively polyion-like), we find that a plot of Robs v. [P]/[Na] is linear, as observed previously for sonicated (approximately 700 bp) DNA samples. For the 20-bp oligonucleotide this plot exhibits a marked departure from linearity that can be fitted to a quadratic function of [P]/[Na]. Monte Carlo simulations based on a simplified model are capable of reproducing the qualitative trends in the 23Na NMR measurements analyzed here. In particular, the dependences of Robs--RF on DNA charge magnitude of Z(320 vs. 38 phosphates) and (for the 20-bp oligomer) on [Na]/[P] are well correlated with the calculated average surface concentration of Na+. Thus, effects of sodium concentration on RB appear to be of secondary importance. We conclude that 23Na NMR relaxation measurements are a sensitive probe of the effects of oligomer charge on the extent of ion accumulation near B-DNA oligonucleotides, as a function of [Na] and [P].
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen F. S., Gray D. M., Roberts G. P., Tinoco I., Jr The ultraviolet circular dichroism of some natural DNAs and an analysis of the spectra for sequence information. Biopolymers. 1972;11(4):853–879. doi: 10.1002/bip.1972.360110410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson C. F., Record M. T., Jr, Hart P. A. Sodium-23 NMR studies of cation-DNA interactions. Biophys Chem. 1978 Jan;7(4):301–316. doi: 10.1016/0301-4622(78)85007-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bleam M. L., Anderson C. F., Record M. T. Relative binding affinities of monovalent cations for double-stranded DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3085–3089. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braunlin W. H., Anderson C. F., Record M. T. 23Na-NMR investigations of counterion exchange reactions of helical DNA. Biopolymers. 1986 Jan;25(1):205–214. doi: 10.1002/bip.360250114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braunlin W. H., Anderson C. F., Record M. T., Jr Competitive interactions of Co(NH3)6(3+) and Na+ with helical B-DNA probed by 59Co and 23Na NMR. Biochemistry. 1987 Dec 1;26(24):7724–7731. doi: 10.1021/bi00398a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braunlin W. H., Xu Q. Hexaamminecobalt(III) binding environments on double-helical DNA. Biopolymers. 1992 Dec;32(12):1703–1711. doi: 10.1002/bip.360321212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delville A., Laszlo P., Schyns R. Displacement of sodium ions by surfactant ions from DNA. A 23Na-NMR investigation. Biophys Chem. 1986 Jul;24(2):121–133. doi: 10.1016/0301-4622(86)80005-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jayaram B., Sharp K. A., Honig B. The electrostatic potential of B-DNA. Biopolymers. 1989 May;28(5):975–993. doi: 10.1002/bip.360280506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manning G. S. The molecular theory of polyelectrolyte solutions with applications to the electrostatic properties of polynucleotides. Q Rev Biophys. 1978 May;11(2):179–246. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500002031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordenskiöld L., Chang D. K., Anderson C. F., Record M. T., Jr 23Na NMR relaxation study of the effects of conformation and base composition on the interactions of counterions with double-helical DNA. Biochemistry. 1984 Sep 11;23(19):4309–4317. doi: 10.1021/bi00314a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olmsted M. C., Anderson C. F., Record M. T., Jr Importance of oligoelectrolyte end effects for the thermodynamics of conformational transitions of nucleic acid oligomers: a grand canonical Monte Carlo analysis. Biopolymers. 1991 Nov;31(13):1593–1604. doi: 10.1002/bip.360311314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olmsted M. C., Anderson C. F., Record M. T., Jr Monte Carlo description of oligoelectrolyte properties of DNA oligomers: range of the end effect and the approach of molecular and thermodynamic properties to the polyelectrolyte limits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):7766–7770. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.7766. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padmanabhan S., Brushaber V. M., Anderson C. F., Record M. T., Jr Relative affinities of divalent polyamines and of their N-methylated analogues for helical DNA determined by 23Na NMR. Biochemistry. 1991 Jul 30;30(30):7550–7559. doi: 10.1021/bi00244a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padmanabhan S., Richey B., Anderson C. F., Record M. T., Jr Interaction of an N-methylated polyamine analogue, hexamethonium(2+), with NaDNA: quantitative 14N and 23Na NMR relaxation rate studies of the cation-exchange process. Biochemistry. 1988 Jun 14;27(12):4367–4376. doi: 10.1021/bi00412a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reuben J., Shporer M., Gabbay E. J. The Alkali Ion-DNA Interaction as Reflected in the Nuclear Relaxation Rates of Na and Rb. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jan;72(1):245–247. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.1.245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheffler I. E., Elson E. L., Baldwin R. L. Helix formation by d(TA) oligomers. II. Analysis of the helix-coli transitions of linear and circular oligomers. J Mol Biol. 1970 Feb 28;48(1):145–171. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90225-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strzelecka T. E., Rill R. L. A 23Na-NMR study of sodium-DNA interactions in concentrated DNA solutions at low-supporting electrolyte concentration. Biopolymers. 1990;30(7-8):803–814. doi: 10.1002/bip.360300715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang L., Ferrari M., Bloomfield V. A. Large-scale preparation of mononucleosomal DNA from calf thymus for biophysical studies. Biotechniques. 1990 Jul;9(1):24, 26-7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Dijk L., Gruwel M. L., Jesse W., de Bleijser J., Leyte J. C. Sodium ion and solvent nuclear relaxation results in aqueous solutions of DNA. Biopolymers. 1987 Feb;26(2):261–284. doi: 10.1002/bip.360260208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


